Human physiology
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
ingestion
eating
digestion
This process of breaking down food into molecular particles of usable size and content.
absorption
taking up monomers, vitamins, minerals, water
egestion
(also called elimination) getting rid of waste products that weren’t absorbable
chemical digestion
breaking down the food by saliva, pancreatic juice (enzymes, NaOH), bile, gastric juice (enzymes, HCl).
mechanical digestion
Breaking down food by teeth and muscle movement (peristalsis)
enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions
amylase
breaks down starch into maltose and later glucose
pepsin (a protease)
breaks down protein into polypeptides and dipeptide
lipase
breaks down triglycerides into glycerol and 3 fatty acids
alimentary canal
esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine
peristalsis
the muscle movement in the esophagus
bolus
a ball-like mixture of food and saliva that forms in the mouth during the process of chewing
salivary glands
produces saliva
Esophagus
transports the food from the mouth to the stomach
Gastric juice (mucus, HCI, pepsin)
break down food and mixes it into chyme.
optimum pH
the pH level that makes the enzymes the most effective
small intestine
break down food, absorb nutrients needed for the body, and transports other components to the large intestine
Doudenum
Chemical digestion with the help of pancreatic juice and bile from the liver.
pancreas
Chemical digestion by pancreatic juice (containing amylase, protease and lipase) Alkaline ions →increase the pH to 7
pancreatic juice
contains amylase, protease and lipase
Sodium, hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate ions)
regulating pH
gall bladder
Chemical digestion by bile, which is stored by the gall bladder.
bile
Bile is emulsifying lipids, meaning that it splits bigger fat drops into smaller ones.
Emulsification
Emulsifying lipids, meaning that it splits bigger fat drops into smaller ones.
villus
Small extension of the wall of the small intestine to increase surface area.
villi function
Increase surface area to increase absorption.
large intestine
Absorption of water (osmosis), minerals and vitamins. Bacteria live their and they help with the production of vitamin K.
Feces
what is eliminated from the body after absorption.
assimilation
the process of absorption of vitamins, minerals, and other chemicals from food as part of the nutrition of an organism.
atrium-atria
Atria are smaller and have thinner walls compared to the ventricles.
ventricle
The left ventricle has the largest muscular wall.
valves
Open and close due to changes in pressure
Opens only in one direction
Make sure that the blood doesnt backflow
atrioventricular valves
Atrioventricular valves (AV valves) - between atria and ventricles
semi lunar valves
Semi lunar valves (SL valves) - between ventricles and the big arteries
aorta
Ventrical systole - ventricles contract (both left and right side), the blood goes from the ventricles to the aorta and the pulmonary artery through the SL-valves. SL-valves close (sounds DUB) due to the pressure being higher in the aorta and pulmonary artery compared to the ventricles.
vena cava (superior/inferior)
Your inferior vena cava, your body's largest vein, carries oxygen-depleted blood back to your heart from the lower part of your body (below your diaphragm). Your superior vena cava, your second biggest vein, brings oxygen-poor blood from your upper body to your heart.
pulmonary artery
ventricles contract (both left and right side), the blood goes from the ventricles to the aorta and the pulmonary artery through the SL-valves. SL-valves close (sounds DUB) due to the pressure being higher in the aorta and pulmonary artery compared to the ventricles.
pulmonary vein
The lung veins sometimes referred to as the pulmonary veins, are blood vessels that transfer freshly oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atria of the heart.
double circulatory system
Two circuits
Pulomonary (lungs) circulation
From the right side of the heart to the lungs and back again. In the lungs, the blood becomes oxygenated. O2 diffuses (by simple diffusion) from a high concentration in the alveoli (lung sacks) to a low concentration in the blood, while CO2 diffuses from a high concentration in the blood to a low concentration in the alveoli.
Systemic circulation
From the left side of the heart to the body and back again on the right side. During the way through the body the blood becomes deoxygenated. O2 diffuses from a high concentration in the blood to a low concentration in the cells O2 is used in cell respiration and the waste product is CO2. CO2 diffuses into the blood with its concentration gradient.
oxygenated blood
carries oxygen, has a larger concentration of O2 than CO2
deoxygenated blood
carries a larger concentration of CO2 than o2
coronary arteries
Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle. Like all other tissues in the body, the heart muscle needs oxygen-rich blood to function. Also, oxygen-depleted blood must be carried away. The coronary arteries wrap around the outside of the heart.
heart beat
Control of a heart beat
The heart muscle is myogenic = the signals for contracting the muscle arise in the heart itself (not needing any impulse from the nervous system).
The heart beat is controlled by specialized cells located in the atrial wall (right). These cells are called the SA-node (the hearts natural pacemaker).
The SA-node starts the heart cycle about 60 times per minute. The electrical impulse spread to the atrial walls →contraction of the atria.
The impulse travel further down to the AV-nod where the impulse is delayed →the ventricles are filled with blood.
The impulses are further spread from the AV-node to the bundle of His and the Purkinje fibers in the ventricle walls (contraction of ventricles).
systole - diastole
Systole - the heart muscle contract (working phase)
Push out the blood from the heart
Atrial systole - atria (both left and right side) contract, the blood goes from atria to ventricles. AV-valves close (sounds LUB) due to the pressure being higher in the ventricles than in the atria.
Ventrical systole - ventricles contract (both left and right side), the blood goes from the ventricles to the aorta and the pulmonary artery through the SL-valves. SL-valves close (sounds DUB) due to the pressure being higher in the aorta and pulmonary artery compared to the ventricles.
Pacemaker, SA-node, AV-node
The heart beat is controlled by specialized cells located in the atrial wall (right). These cells are called the SA-node (the hearts natural pacemaker).
The impulse travel further down to the AV-nod where the impulse is delayed →the ventricles are filled with blood.
artificial pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered device that prevents the heart from beating too slowly. You need surgery to get a pacemaker. The device is placed under the skin near the collarbone. A pacemaker also is called a cardiac pacing device.
blood vessels, structure and function
arteries: big, large musculary wall, transport blood from the heart; capillaries: small, here the gas and nutrient exchange takes place; veins: big, thin musculary wall, transport blood to the heart
arteries
arteries: big, large musculary wall, transport blood from the heart
veins
veins: big, thin musculary wall, transport blood to the heart
capillaries
small blood vessels only one cell thick, allows an efficient exchange of molecules. All amino acids and monosaccharides are transported into the capillaries, and then transported through the blood stream to all body cells.
blood
the red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying oxygen to and carbon dioxide from the tissues of the body.
blood composition
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
plasma
blood plasma: consists of H2O, nutrients, hormones, antibodies…
Erythrocytes
red blood cells (RBC), are the functional component of blood responsible for the transportation of gases and nutrients throughout the human body.
plateles
platelets: help with blood clotting
leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes, immune cells, or immunocytes,
hemoglobin
a red protein responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates. Its molecule comprises four subunits, each containing an iron atom bound to a haem group.
ECG
(electro cardiogram)
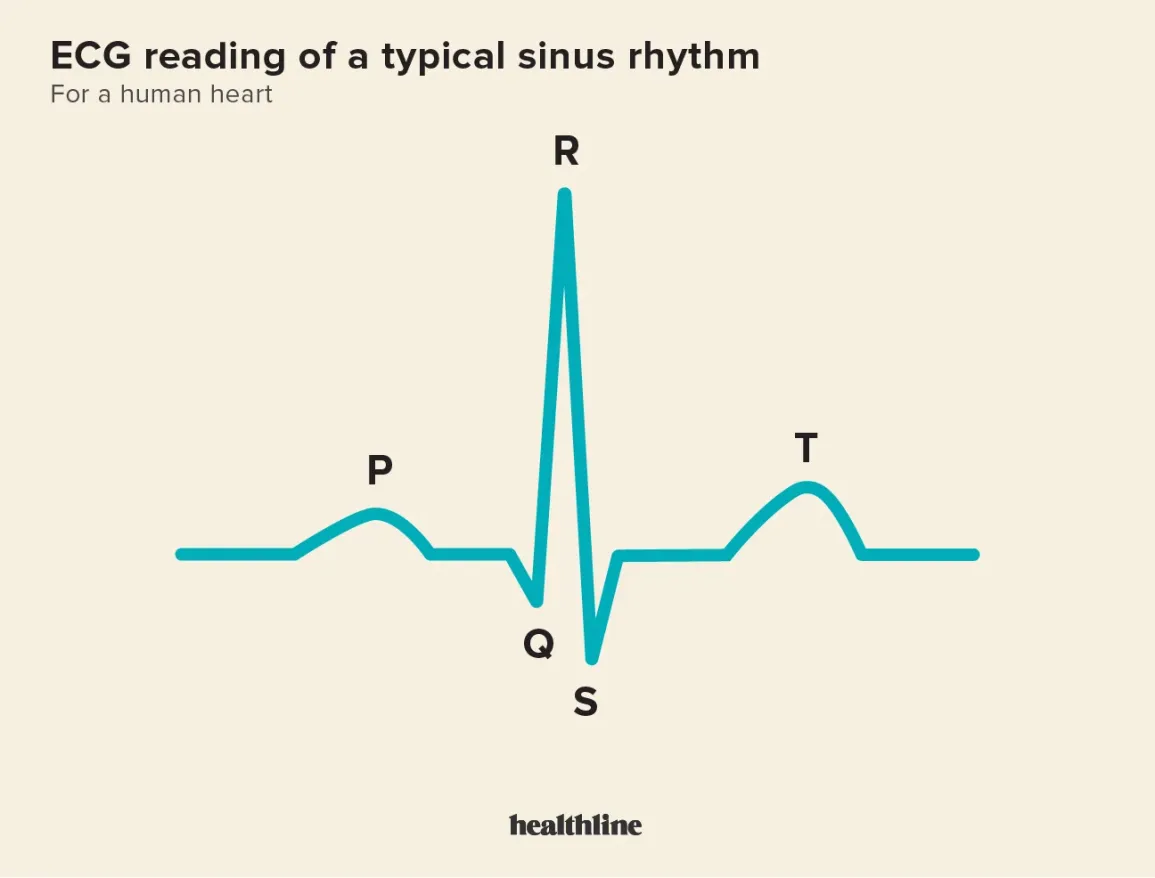 P - atria contract (SA-node/AV-node)
P - atria contract (SA-node/AV-node)
QRS - ventricles contract (AV-node/bundle of His/Purkinjefibers)
T - ventricles reset
ventilation
The process of air entering and exiting the lungs.
Inhalation = air enters
Exhalation = air exits
respiration
Transports O2 to all cells for cell respiration.
Remove CO2, which is a waste product from cell respiration (CO2 forms carbonic acid, which decreses pH, meaning its important to remove).
gas exchange
To take in O2 and take out CO2.
O2 is headed for cellular respiration (all cells)
CO2 is a rest product of cellular respiration
Location: the alveoli
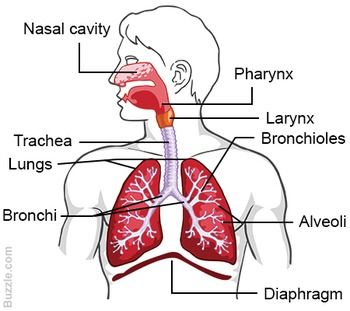
trachea
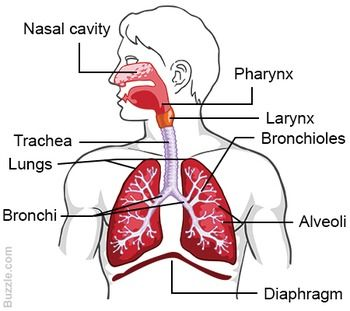
brochus/ bronchi

Bronchioles
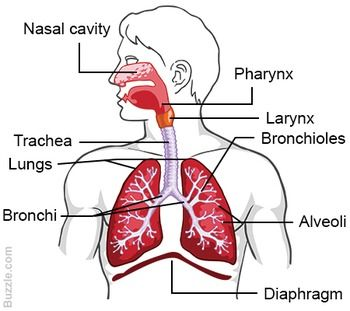

inhalation
Diaphragm contracts and moves the chest cavity downwards → Increase the lung volume.
External intercostal muscles contract and move the chest cavity outwards → increase the lung volume.
The gas pressure inside the lungs decreases and a pressure gradient is formed.
Air will move from a higher pressure in the atmosphere to a lower pressure inside of the lungs.
exhalation
Diaphragm relaxes and the chest cavity move upwards → decrease the lung volume.
Internal intercostal muscles contract and the chest cavity moves inwards → decrease the lung volume.
The gas pressure in the lungs Increases.
Air will move with its pressure gradient from the lungs to the atmosphere.
diaphragm
located between the chest cavity (thorax) and The abdominal cavity.
external intercostal muscles
External intercostal muscles contract and move the chest cavity outwards → increase the lung volume.
internal intercostal muscles
Internal intercostal muscles contract and the chest cavity moves inwards → decrease the lung volume.
thorax
Diaphragm - located between the chest cavity (thorax) and The abdominal cavity.
alveolus/ alveoli
Alveoli (lung sacks, where gas exchange happens)
capillary
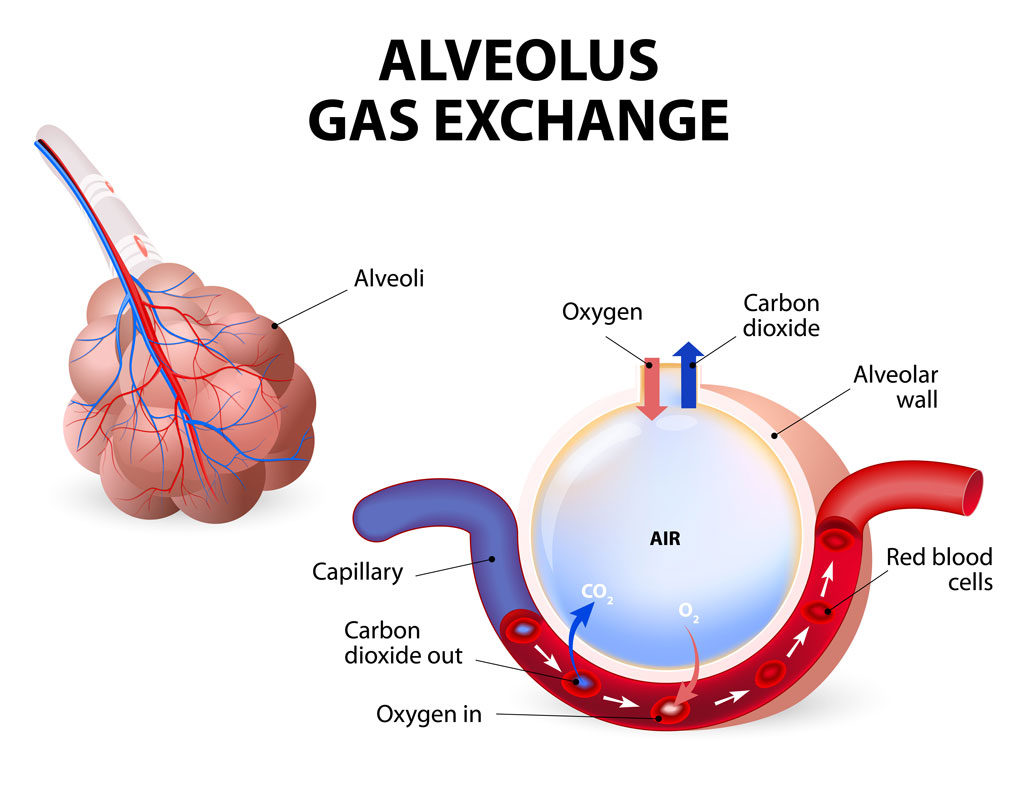 Capillaries are delicate blood vessels that exist throughout your body. They transport blood, nutrients and oxygen to cells in your organs and body systems. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in your vascular system.
Capillaries are delicate blood vessels that exist throughout your body. They transport blood, nutrients and oxygen to cells in your organs and body systems. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in your vascular system.

red blood cell
red blood cells: transport O2
diffusion
From the right side of the heart to the lungs and back again. In the lungs, the blood becomes oxygenated. O2 diffuses (by simple diffusion) from a high concentration in the alveoli (lung sacks) to a low concentration in the blood, while CO2 diffuses from a high concentration in the blood to a low concentration in the alveoli.
tar, carbon monoxide, nicotine
Tar is the name for the resinous, combusted particulate matter made by the burning of tobacco and other plant material in the act of smoking.
In smoking, long term exposure to compounds found in the smoke (e.g., carbon monoxide and cyanide) are believed to be responsible for pulmonary damage and for loss of elasticity in the alveoli, leading to emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Nicotine is a dangerous and highly addictive chemical. It can cause an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, flow of blood to the heart and a narrowing of the arteries (vessels that carry blood). Nicotine may also contribute to the hardening of the arterial walls, which in turn, may lead to a heart attack.
carcinogens
These chemicals damage our DNA, including parts of our DNA that protect us against cancer. Chemicals in cigarette smoke also make it harder for our cells to repair DNA damage. This means DNA damage can build up. It's the build-up of DNA damage in the same cell over time that leads to cancer.
chronic bronchitis
(cilia, epithelium, mucus, smokers cough, obstructed airways)
Emphysema
(Infection, phagocytes, elastin, elastase, decreased recoiling, brusted alveoli)
Lung cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called lung cancer. Lung cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body, such as the brain. Cancer from other organs also may spread to the lungs.
diastole
Diastole - the heart muscle relax (resting phase)
Fill up the heart with blood
Av- valve opens, so both the atria and ventricles can be filled with blood.