Physics - Unit 1: Motion, forces and energy
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
How can length be measured?
Using a ruler
how to measure the volume of a liquid?
using a measuring cylinder
how to measure the volume of a regular solid?
by calculation:
use a ruler to measure dimensions
use an appropriate equation to calculate volume
how to find the volume of an irregular solid?
by submersion:
fill a measuring cylinder with water and read the initial volume
submerge the object and measure the final volume
final volume - initial volume = volume of object
how can time be measured?
using clocks or stopwatches
how can the accuracy of measurements be increased?
by taking multiple measurements and calculating the average
what is a scalar quantity?
a quantity with magnitude (size) only
what is a vector quantity?
a quantity with magnitude and direction
what are examples of vector quantities?
displacement
force
weight
velocity
acceleration
momentum
electric field strength
gravitational field strength
what are examples of scalar quantities?
distance
speed
time
mass
energy
temperature
how can you measure the resultant of two forces at a right angle
graphically (by drawing each to scale) or by calculation (by Pythagoras or trigonometry)
what is speed?
distance travelled per unit time
what is velocity?
change in displacement per unit time
what is the formula for velocity/speed?
v=ˢ⁄ₜ
what is the equation for average speed?
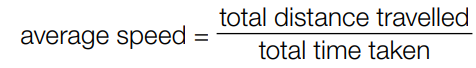
what is acceleration?
change in velocity per unit time
what is the formula for acceleration?
a=-ᵛ⁻ᵘ⁄ₜ
when does uniform acceleration occur?
when velocity changes at a constant rate
when does non-uniform acceleration occur?
when velocity changes at different rates at different times
what is deceleration?
a negative acceleration
what does a horizontal line represent on a displacement-time graph?
that the object is at rest
what does a straight line with a constant slope mean on a displacement-time graph?
that the object is moving with constant speed
what does a curve upwards mean on a displacement-time graph?
that the object is moving with acceleration
what does a curve downward mean on a displacement-time graph?
that the object is decelerating
what state is the object in when the Y axis is at 0 on the velocity-time graph?
The object is at rest
what does a horizontal line represent on a velocity-time graph?
that the object is moving with constant speed
what does a straight line with a constant slope mean on a velocity-time graph?
that the object is moving with constant acceleration
what does a curve represent on a velocity-time graph?
that the object is moving with changing acceleration
what is the acceleration of free fall g for an object near to the surface of the Earth
approximately constant
approximately 9.8 m/s²
how can you calculate the speed of a distance-time graph?
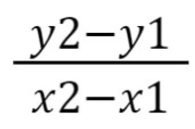
what does the area under the speed-time graph represent?
the displacement
how can you calculate the acceleration of a speed-time graph?
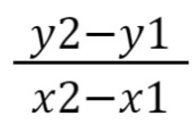
what is mass?
a measure of the quantity of matter in an object at rest relative to the observer
what does the mass of an object resist change from?
its state of rest or motion (inertia)
how can you compare weights and masses?
using a beam balance or equal-arm balance
how can you determine mass?
using an electronic balance
how can you determine weight?
using a forcemeter
what is gravitational field strength?
force per unit mass
what is the formula for gravitational field strength?
g = ʷ⁄ₘ
what is gravitational field strength equivalent to?
the acceleration of free fall
what is gravitational field?
a region in which a mass experiences a force due to gravitational attraction
what is density?
mass per unit volume
what is the formula for density?
ρ=ᵐ⁄ᵥ
how can you measure the density of a regular solid?
take measurements of relevant dimensions using a ruler
calculate the volume using an appropriate equation
measure mass using a balance and calculate density using ρ=ᵐ⁄ᵥ
how can you determine the density of an irregular solid?
measure volume by submersion: read the volume of the liquid, submerge the solid, then read the change in volume
measure mass using a balance
use ρ=ᵐ⁄ᵥ to calculate density
how can you calculate the density of a liquid?
place an empty beaker on top of a balance and zero the device
pour liquid into the beaker to determine the mass
pour the same liquid into a measuring cylinder and read off the volume
use ρ=ᵐ⁄ᵥ to calculate density
what is weight (gravitational force)?
a gravitational force on an object that has mass
what is drag/air resistance?
the friction of the air on a moving object
what is tension?
force in a string or string being stretched
what is electrostatic force?
the force between two charged objects
what is magnetic force?
attraction or repulsion that arises between electrically charged particles because of their motion
what is thrust?
the force causing an object to move
what is contact force?
a force which acts between objects that are physically touching
what is newton’s first law?
an object either remains at rest or continues to move in a straight line at constant speed unless acted on by a resultant force
how can a force change the velocity of an object?
the velocity of an object by changing its direction of motion or its speed
what is the formula for resultant force?
F = ma
what is newton’s third law?
when object A exerts a force on object B, then object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A
what does newton’s third law describe
pairs of forces of the same type acting on different objects
what is friction
a force that may impede motion and produce heating
how does an object reach terminal velocity?
initially, the only force is weight so acceleration is 9.8m/s²
as it accelerates, speed increases, which increases air resistance
this decreases the resultant force, so acceleration decreases
eventually, weight and air resistance are equal and opposite, so there is no resultant force, no acceleration, and terminal velocity is reached
what is thinking distance?
distance travelled during reaction time of driver before the brakes are applied
what is braking distance
distance over which brakes applied before vehicle brought to rest
what is stopping distance
total distance travelled in the time it takes to stop a vehicle
what is the formula for stopping distance?
thinking distance + braking distance
what are the factors that affect thinking distance?
thinking distance is reliant on the driver’s reaction time so factors such as tiredness, alcohol or drug abuse will affect it
what are the factors that affect braking distance
breaking distance becomes longer when the road is wet or icy and there is an increased load carried by the vehicle. however, a deep tyre tread will reduce braking distance
what change may a force produce on an object?
changing the size and shape of an object
what is the spring constant?
force per unit extension
what is the formula for spring constant?
k=F/x
what is the limit of proportionality?
the point where the graph starts to curve away from this straight line
what happens to the motion in a circular path due to a force perpendicular to the motion if the mass and radius are constant?
speed will increase if force increases
what happens to the motion in a circular path due to a force perpendicular to the motion if the mass and speed are constant
if force increases, radius decreases
how do you keep the speed and radius constant during the motion in a circular path due to a force perpendicular to the motion in the case that mass increases?
increase the force
what is the moment of a force?
a measure of its turning effect
what is the equation of the moment of a force?
moment = force × perpendicular distance from the pivot
what is the principle of moments for an object in equilibrium?
when the clockwise moment equals the anticlockwise moment, there is no resultant force. no resultant moment, and the object is in equilibrium.
what is an experiment used to verify the principle of moments?
pivot a uniform ruler at its centre
place different masses at different distances from the centre on either side until it balances
multiply the total mass on either side by 9.81 N/kg to calculate clockwise and anticlockwise moments
the clockwise and anticlockwise moments will be equal
what is the centre of gravity?
the point at which all of its weight can be considered to act
how to determine the position of the centre of gravity of a plane lamina using a plumb line
hang up the lamina and suspend a plumb line (thread) from the same place
mark the position of the plumb line
repeat with the lamina suspended from different places
where these lines intersect is the centre of gravity
what is the effect of the position of the centre of gravity on the stability of simple objects
objects with a lower centre of gravity and wider base are more stable
what is momentum and what is its formula?
momentum is mass x velocity, its formula is p=mv
what is impulse and what is its formula?
impulse is force x time, its formula is F△t
what is the principal of the conservation of momentum?
momentum before = momentum after (provided that there are no external forces)
what is resultant force in terms of momentum and what is its formula?
change in momentum per unit time, its formula is F=△p/△t
what are ways in which energy can be stored?
kinetic
gravitational potential
chemical
elastic (strain)
nuclear
electrostatic
internal/thermal
what is the principle of the conservation of energy?
energy is neither created or destroyed during an energy transfer. it simply changes
what is the formula for kinetic energy?
Ek = (1/2)mv²
what is the formula for the change in gravitational potential energy?
△Ep = mg△h
state 4 ways in which energy could be transferred?
forces
electrical currents
heating
waves (electromagnetic/sound)
what is the formula for work done?
W = Fd
what are examples of renewable energy sources?
biofuels
wind
hydroelectric and tidal energy
geothermal energy
solar power
what are examples of non-renewable energy sources?
fossil fuels
nuclear fuels
how can electrical power be generated from the chemical energy stored in fossil fuels and biofuels?
they are burnt to generate electrical power:
their chemical energy is transferred to heat energy
the heat energy is used to boil water, creating steam
the steam turns the turbine
how can hydroelectric resources be used to generate electrical power?
the water behind the dam is above the ground level, so Ep increases
Ep gets converted into Ek when water is released down a slope
the flowing water turns the turbine
how can solar radiation be used to produce electrical power?
solar energy from sunlight is turned into an electric current by solar cells
how do nuclear fuels generate electrical power?
they undergo nuclear fission to produce electrical power:
thermal energy is released by nuclear fission
thermal energy is used to boil water, creating steam
steam turns a turbine
how do geothermal resources generate electrical power?
as radioactive elements decay, their geothermal energy heats the surrounding rock
water is poured into shafts in the hot rock
thermal energy boils the water, creating steam, which is returned via another shaft
steam turns a turbine
how can wind be used to generate electricity?
as the wind blows, it transfers kinetic energy to the blades of wind turbines
how do the waves and tides in the sea be used to generate electrical power?
the kinetic energy as waves and tides move is used to turn underwater turbines.