Database Design Final (copy)
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
database
organized collection of logically related data
data
stored representations of meaningful objects and events
what are the two types of data
structured and unstructured
structured data
numbers, text, dates
unstructured data
images, video, documents
information
data processed to increase knowledge in the person using the data
metadata
data that describes the properties and context of user data, how to make the database useful through definitions
context
helps users understand data
disadvantages of file processing
program-data dependence
duplication of data
limited data sharing
lengthy developmental times
excessive program maintenance
what is the solution of file processing?
databases
database management system (DBMS)
software system used to create, maintain, and provide controlled access to user databases
advantages of a database
program-data independence
improved data consistency and quality
increased application development productivity
enforcement of standards
elements of the database
data models
entities
relationships
relational databases
what are the types of data model
enterprise data model and project data model
data model
graphical system capturing nature/relationship of data
enterprise data model
high level entities and relationships for an organization
project data model
more detailed, new, matching data structure in database or data warehouse
entities
noun form describing a person, place, object, event or concept that is composed of attributes
relationships
between entities, usually one to many (1:N) or many to many (N:N)
relational databases
database technology involving tables (relations) representing entities and primary/ foreign keys representing relationships
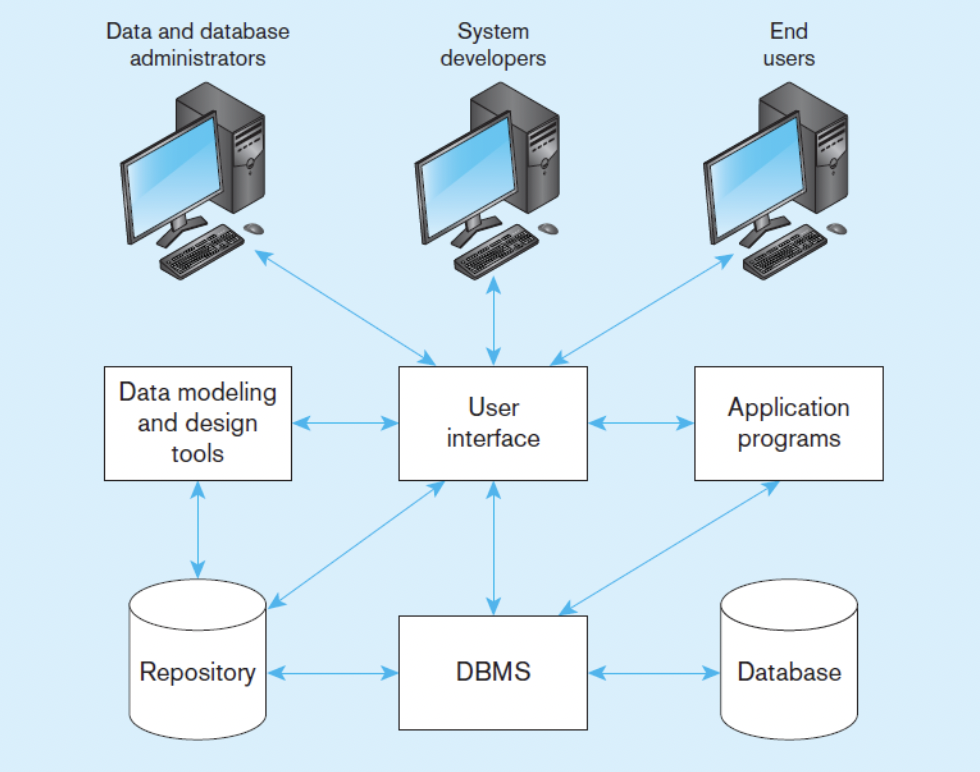
what is this picture showcasing?
the components of the database environment
CASE tools
computer-aided software engineering
repository
centralized storehouse of metadata
application program
software using the data
user interface
text and graphical display to users
database administrators
personnel responsible for maintaining database
system developers
personnel responsible for designing databases and software
end users
people who use applications and databases
what are the approaches to database and IS development?
system development lifecycle (SDLC) and rapid application development (RAD)
system developmental lifecycle
detailed, well planned development process with a long cycle, time consuming but comprehensive
what are the stages of the SDLC?
planning
analysis
logical design
physical design
implementation
maintenance
rapid application development
prototyping: cursory attempt and conceptual data modeling, defines DB during development and repeats implementation and maintenance w new prototype
agile: individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, responding to change
what are the types of database schema?
external, conceptual, and internal
external schema
user reviews, subsets of conceptual schema. Can be determined from business functionality data entity materials
conceptual schema
used for entity relational model
internal schema
logical and physical structures, underlying design and implementation
what are the database architectures?
hierarchical
network
relational
object oriented
star schema
big data/ data lake
what is the range of database applications
personal databases
two tier and N tier client/server databases
enterprise applications
what are the enterprise database applications?
enterprise resource planning
data warehouse
data lake
enterprise resource planning (ERP)
integrate all enterprise functions (manufacturing, finance, sales, etc.)
data warehouse
integrated decision support system derived from various operational databases
data lake
‘collect everything’ integrated repository for internal and external data that is not based on a predefined data model or schema
what are the versions of an ERD?
original ER model
extended ER model
information engineering
IDEF1X
Unified modeling language
what are the types of attributes?
single value, composite, and multi-value
what are the types of identifiers?
unique, non unique, and composite
unique identifier
the value identifies one and only one entity instance
non unique identifier
the value identifies a set of instances
composite identifier
identifiers that consist of 2+ attributes
primary key (PK)
uniquely identifies a record in the table, can be designated as a field or collection of fields
How to make foreign key in 1:N?
take PK from 1 side and put it in N side
How to make foreign key in 1:1?
take PK on one side to the other, either works just explain
FK in N;M?
not possible, because foreign key is not unique in that relationship!
foreign key (FK)
when the primary key of one table is represented in a second table to form a relationship
what are the types of degrees of a relationship?
unary, binary, and ternary
unary relationship
one entity is directly related to another of the same entity type of a single class
binary relationship
entities of 2 types are related to each other (can be 1:1, 1:N, N:M)
ternary relationship
entities of 3 types are related to each other
maximum carnality
indicates the max # of entities that can be involved in a relationship
minimum carnality
indicate that there may or may not be an entity in a relationship, showcased by O or |
weak entities
logically depends on another entity, can be ID-dependent entities, have a minimum carnality of 1
subtype entity
represents a special case of another entity that is specialized
supertype entity
generalization of subtypes
composite key
foreign and primary key to create a relationship and break many to many, used in associative entity
associative entity
a relationship with an attribute, but is also considered to be an entity in its own right. Breaks N:M by creating a ‘checkpoint’ to ensure the ERD is valid
business rules when creating database or ERD
statements define/constrain some aspect of business
asset business structure
control/influence business behavior
expressed in terms familiar to end users
automated through DBMS software
steps on the data modeling process
plan project
determine requirements
specify entities, then relationships
determine identifies (PK and FK)
specify attributes and domains
validate model
attribute inheritance
subtype entities inherit the values of all attributes of the supertype, an instance of a subtype is also an instance of the supertype
what does generalization do?
put common attributes in supertype
determine if supertype could be only one of the subtypes or both
only entities with unique attributes of the supertype get a subtype
completeness constraints
whether an instance of a supertype must also be a member of at lease one subtype
total specialization rule
instance of a supertype is in 1+ subtype, shown as double line
partial specialization rule
instance of supertype is not in subtype or is a ghost subtype, shown as single line
disjointness constraints
whether an instance of a supertype may simultaneously be a member of 2+ subtypes
disjoint rule
an instance of the supertype can only be in ONE of the subtypes, shown as a “d” in a circle
overlap rule
an instance of a supertype can be in more than one of the subtypes, shown as an “o” i a circle
subtype discriminator
an attribute of the supertype whose values determine the target subtype(s)
disjoint discriminator
a simple attribute with alternative values to indicate the possible subtypes (Attribute X leads to subtype A or B)
overlapping discriminator
a composite attribute whose subparts pertain to different subtypes, each support containing a boolean value to indicate whether or not the instance belongs to the associated subtype (Attribute X with A?B?C? to sort into proper subtypes in boolean manner)
relation definition and components
2 dimensional table
rows contain data about an entity
columns contain data about attributes
cels of table hold a single value
all entries in a column are form the same kind, each column has unique name
order or columns and rows is unimportant, but cannot be identical
tuple
record = row
key field have what purpose?
serve as a unique identifier (PK)
enable a dependent relation to refer to its parent relation (FK)
simple attributes while mapping to relations
ER attributes map directly onto the relation
composite attributes while mapping to relations
use only their simple, component attribute
multi-valued attributes while mapping to relations
becomes a separate relation with a FK taken from the superior entity
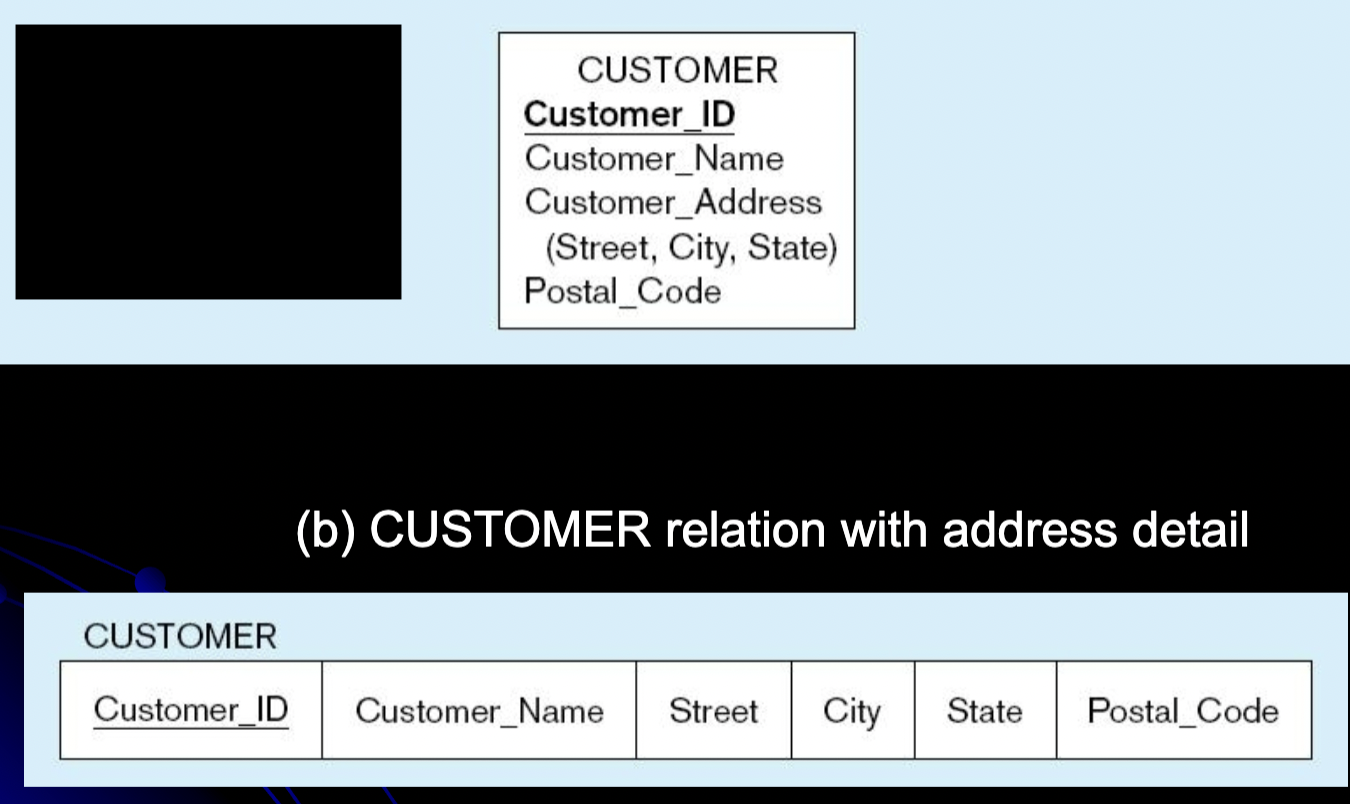
what attribute type is this mapping?
composite attribute
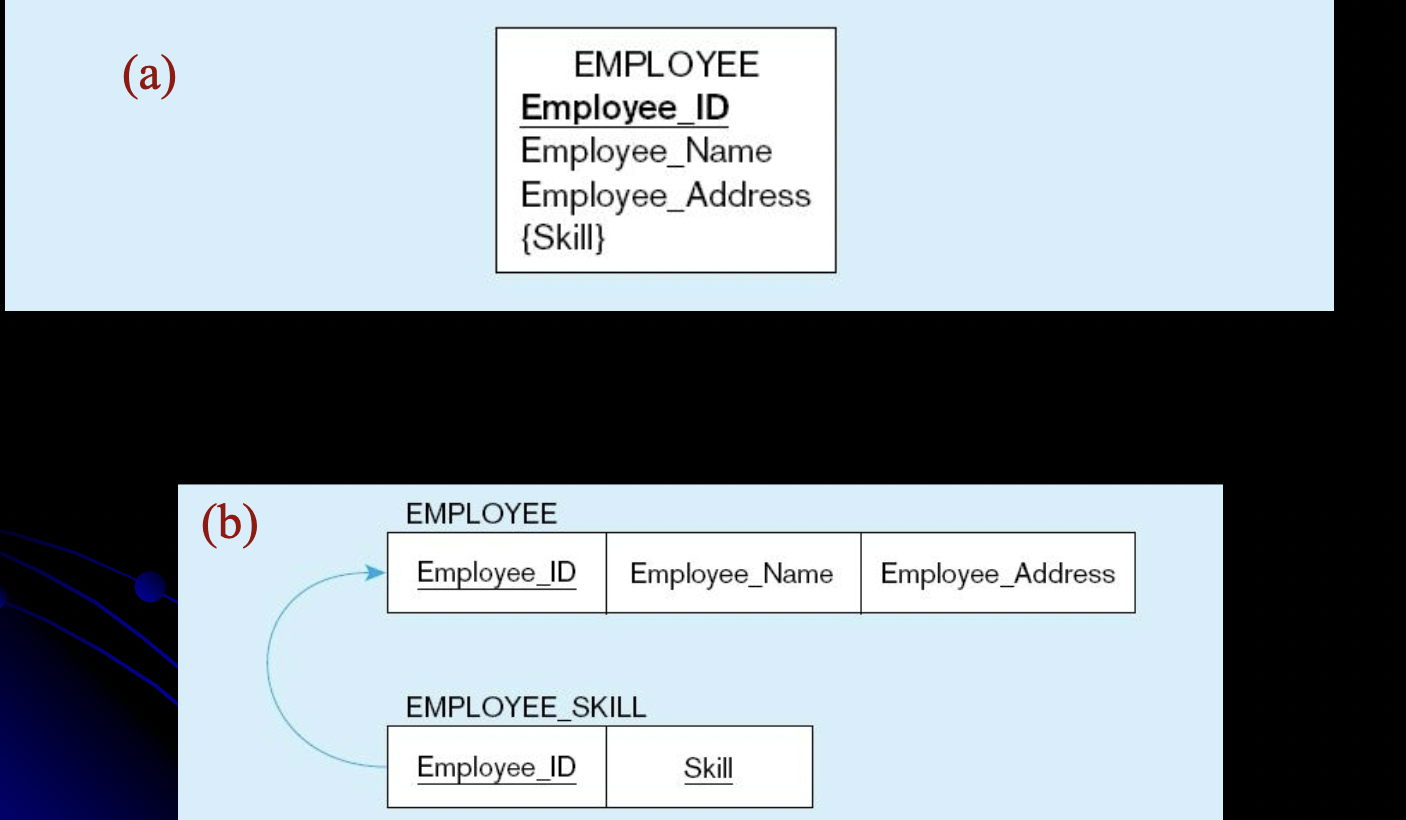
what attribute type is this mapping?
multivalued attribute
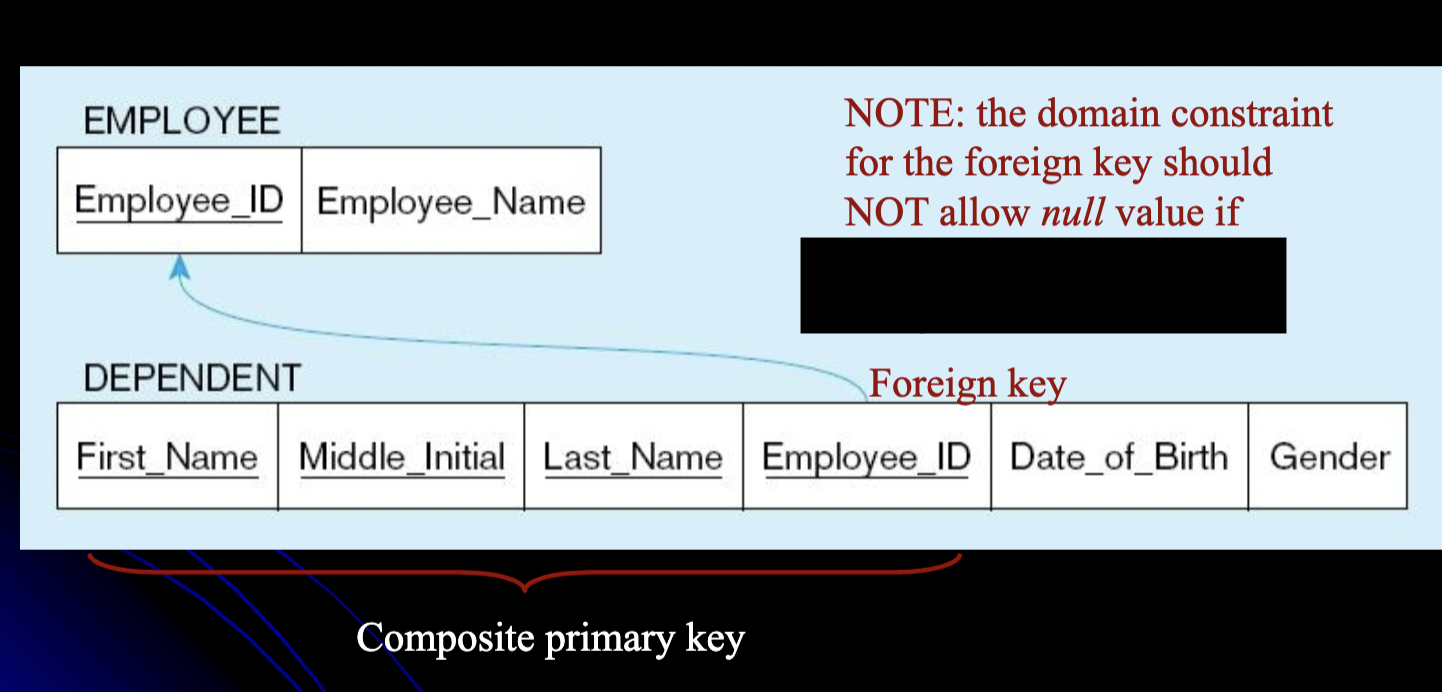
what entity is being mapped?
weak entity
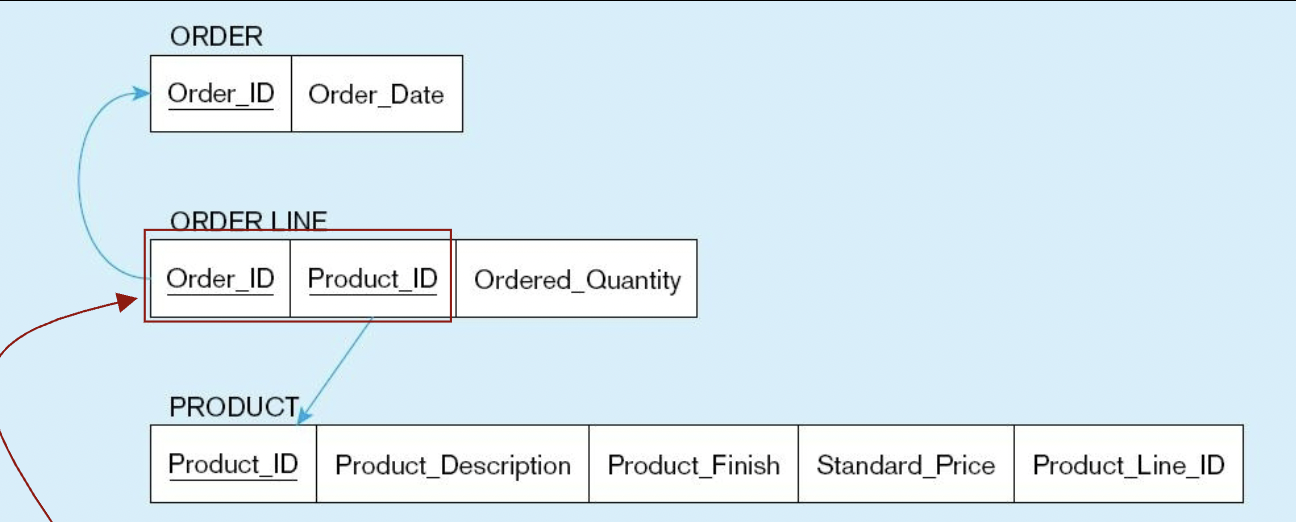
what entity is being mapped?
associative entity
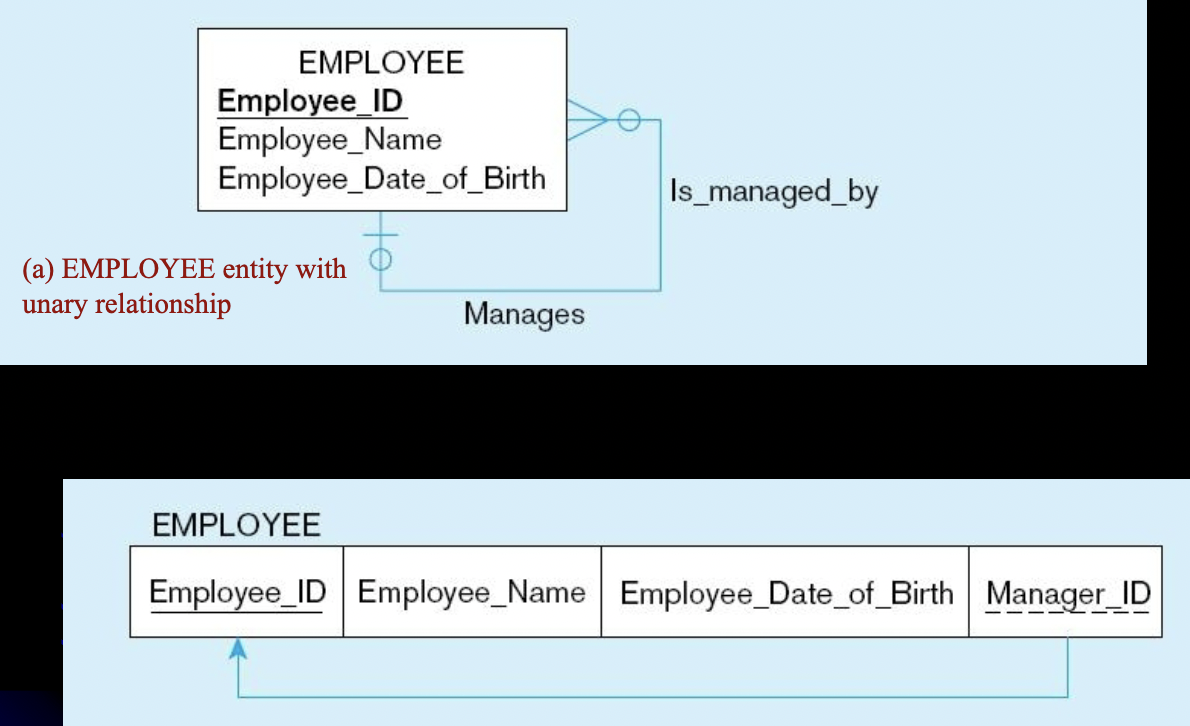
what entity is being mapped?
an entity with a unary 1:N relationship
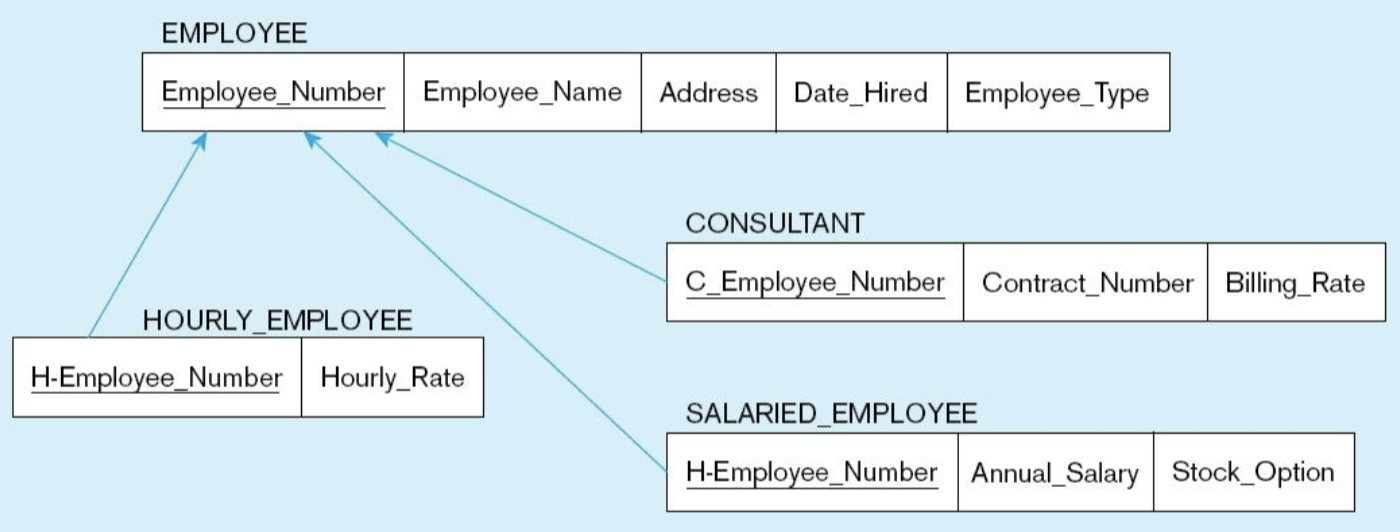
what entity is being mapped?
an entity with a supertype and subtype relationship
what are the types of modification anomalies?
deletion and insertion
deletion anomaly
facts about 2 entities are lost with one deletion
insertion anomaly
cannot insert an entity until information about a second entity is known
functional dependency
the value of one (set of) attribute(s) determines the value of a second (set of) attribute(s)
determinant
attributes on the left side of a functional dependency
what is always a determinant?
a primary key!
normalization
eliminated modification anomalies by breaking a relation into 2+ relations with a different,
1NF
any table of data if it meets the definition of a relation
2NF
if all non-key attributes are dependent on all of the key (no partial dependencies)
how does a relation automatically become 2NF?
if it has a single attribute key
3NF
if a relation is in 2NF and has no transitive dependencies