Hyponatremia
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Hyponatremia Serum Sodium
Serum sodium < 135 mEq/L
Severe Hyponatremia
Serum sodium, symptoms
<110 mEq/L
Seizure
Coma
Brain damage
Brain stem herniation
Moderate Hyponatremia
Serum sodium, symptoms
110-125 mEq/L
Headache
Lethargy
Restlessness
disorientation
Mild Hyponatremia
Serum sodium, symptoms
<135 mEq/L
Nausea
Malaise
What total body water imbalance causes HYPOnatremia?
EXCESS free water
Why must sodium level correction rate be monitored?
rapid correction can cause osmotic demyelination
Brain Compensation in Hyponatremia
→ In hypotonic hyponatremia, the brain transports solutes extracellularly to reduce its osmolality and prevent swelling/herniation.
If serum sodium levels are corrected too rapidly, it can cause osmotic demyelination (brain loses water causing permanent brain damage).
Symptoms of Osmotic Demyelination
Dysarthria (difficulty speaking)
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Quadraplegia
Seizure
Coma
Death
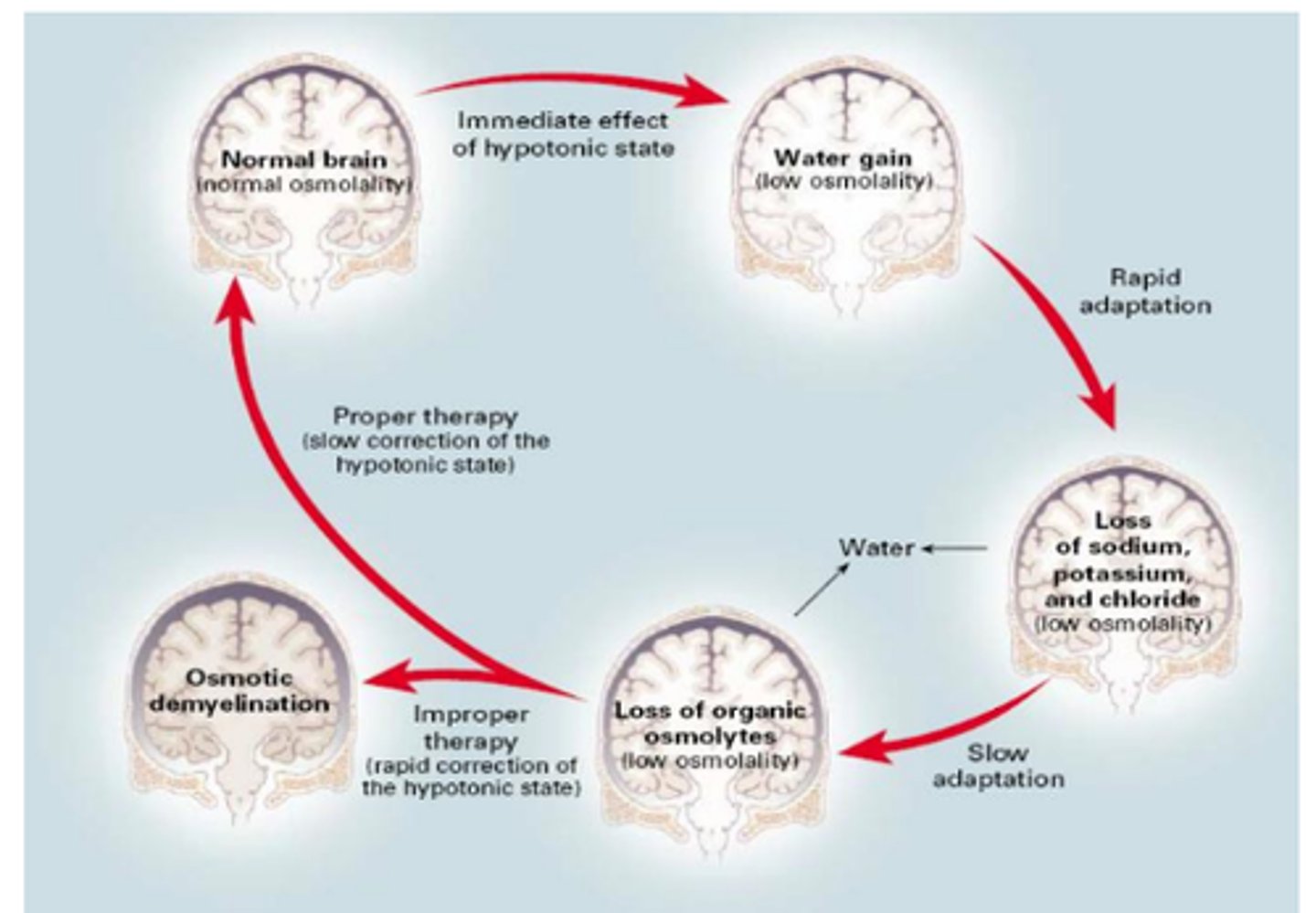
What patients are at high risk for demyelination?
Na < 120 mEq/L
Duration > 48 hours (chronic)
What patients are at severe risk for demyelination?
Na < 105 mEq/L
Hypokalemia, alcoholism, malnutrition, advanced liver disease.
Hyponatremia is associated with what osmolar state(s)?
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
Hypertonic Hypernatremia Causes
Caused by increases in plasma glucose or exogenous administration of mannitol (iatrogenic).
Relationship between blood glucose and serum sodium
For every 100 mg/dL increase in serum glucose, there is a loss of 1.7 mEq/L of serum sodium
Isotonic Hypernatremia Causes
A pseudohyponatremia usually caused by hyperlipidemia or hyperproteinemia.
3 Causes/Types of Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Hypervolemic
Euvolemic
Hypovolemic
Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
TBW, TBNa
TBW↑↑ , TBNa ↑
Water gain > sodium gain
Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Causes
Congestive heart failure
Liver failure
Nephrotic syndrome
Acute or chronic renal failure
Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Treatment
1. Treat the underlying cause.
2. Dietary sodium restriction/fluid restriction.
3. Loop diuretics to remove excess water.
4. Can consider vasopressin receptor antagonists
Why should sodium be restricted in hypervolemic hypotonic hyponatremia?
The hyponatremia is not caused by insufficient sodium intake, rather it is caused by fluid retention. Restrict sodium intake to prevent further fluid retention.
Vasopressor Receptor Antagonists Examples
conivapatan, tolvaptan
Vasopressor Receptor Antagonists MOA
Inhibits the action of AVP to reduce water reabsorption via aquaporins.
Conivaptan
Dose and Route
IV
20 mg bolus over 30min, then 20 mg/24hours
Conivaptan
Receptors, SEs
V1A, V2
Hypotension
Injection site reaction
Hypokalemia
Tolvaptan
Dose and Route
15 mg PO daily
Tolvaptan
Receptors, SEs
V2
Hypotension
Hypovolemia
GI hemorrhage
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
TBW, TBNa
TBW↑ , TBNa no change
Water gain > sodium gain
Associated with mild water retention.
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Causes
Hypothyroidism
Adrenal Insufficiency/Addison's disease (insufficient aldosterone production)
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH)
Why is SIADH associated with euvolemia?
A disorder that leads to inappropriate water reabsorption via aquaporins.
Enough water is retained to dilute serum sodium but not enough to affect overall volume status.
Causes of SIADH
CNS Disorders
Stroke
Trauma
Malignancy (lung tumors particularly)
Medications
Infections, HIV
Severe pain
Severe nausea**
Medications Associated with ADH (AVP) Release
Haloperidol, chlorpropamide, carbamazepine, TCAs, SSRIs, desmopressin
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Mild-Moderate Symptoms Treatment
1. Fluid restriction
2. Furosemide with NaCl tablet or NS supplementation.
3. Demeclocycline if chronic SIADH.
Euvolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Severe Symptoms Treatment
1. Furosemide
2. 3% NaCl infusion
Demeclocycline MOA
Inhibits the renal response to AVP by inhibition of cAMP.
Demeclocycline Dose
300-600 mg PO BID.
Take 1 hour ac or 2 hr pc.
Demeclocycline onset
Onset is 2-5 days.
only used in cases of chronic SIADH
Demeclocycline SEs
Photosensitivity
Nephrotoxicity
Nausea
Is demeclocycline more or less predictable that vasopressin receptor antagonists?
Has more predictable effect and less ADRs than the vasopressin receptor antagonists.
Demeclocycline DDIs
Separate administration from calcium and iron supplements.
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
TBW, TBNa
TBW↓ , TBNa ↓↓
Sodium loss > water loss
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Renal Causes
Cerebral salt wasting (rare endocrine disorder)
Excessive diuresis (iatrogenic)
Adrenal insufficiency (Addison's Disease)
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Non-Renal Causes
Bleeding
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Burns
Sweating
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Mild-Moderate Symptoms Treatment
NaCl tablet
0.9% NaCl
Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia
Severe Symptoms Treatment
3% NaCl
Goal Corrected Serum Sodium Level
goal serum sodium levels of 125-130 mEq/L.
A conservative goal to prevent overcorrection.
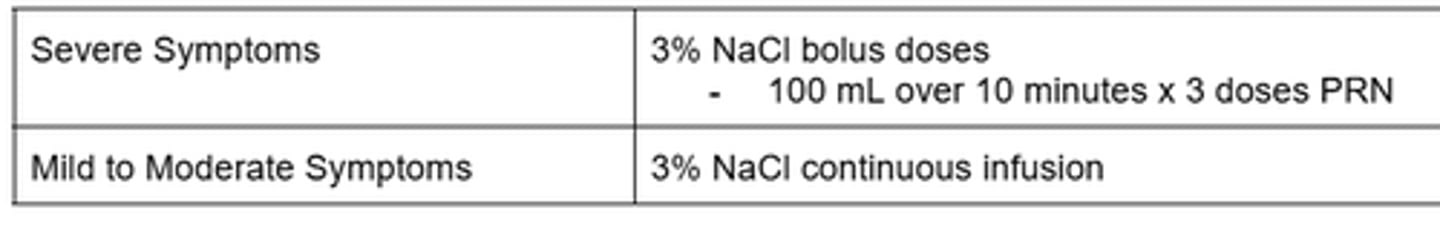
What fluids are used to treat hyponatremia?
(severe vs. mild-moderate symptoms)
Acute Hyponatremia
< 48 hours
Requires rapid intervention to prevent brain herniation
Severe, acute hyponatremia
Goal Na+ Increases
4-6 mEq/L in 1-2 hours
Severe, acute hyponatremia
Treatment
Bolus infusions of 3% NaCl
Severe, acute hyponatremia
Max sodium correction
varies
Mild-moderate, acute hyponatremia
Goal Na+ increases
4-6 mEq/L in 1-2 hours
Mild-moderate, acute hyponatremia
Treatment
Bolus infusions of 3% NaCl
Mild-moderate, acute hyponatremia
Max sodium correction
8 mEq/L per day
Chronic Hyponatremia
> 48 hours
Requires slow, conservative correction of serum sodium levels to prevent osmotic demyelination.
Moderate, chronic hyponatremia
Goal Na+ increases
4-6 mEq/L in 6-12 hours
Moderate, chronic hyponatremia
Treatment
Continuous infusion of 3% NaCl
Moderate, chronic hyponatremia
Max sodium correction
8 mEq/L per day
Mild, chronic hyponatremia
Goal Na+ increases
4-6 mEq/L in 24 hours
Mild, chronic hyponatremia
Treatment
Correct underlying causes
Mild, chronic hyponatremia
Max sodium correction
8 mEq/L per day
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor serum sodium
- After any 3% NaCl bolus
- Every 2-4 hours during continuous infusions
What fluid should be used to fix overcorrection?
D5W
What is the sodium content of 3% NaCl?
513 mEq/L sodium concentration
100% distribution into the ECF