Linear
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is Ax = 0?
A homogeneous system where the output is zero.
- The set of all solutions forms a subspace.
- There is one solution (x = 0), which is the trivial solution.
= Invertible
- Finds null space
What is Ax = b?
A nonhomogeneous system.
- Might have 0, 1, or infinitely many solutions only if b is in the column space of A.
Rank
# of pivot columns
- Tells you how much indpedence (linearly independent columns) the matrix has
Column Space: Col(A)
The set of all linear combinations of columns of A.
- It is a subspace of R^M (the output space).
- All vectors b for which Ax = b has a solution
Null Space: Nul(A)
It is a subspace of R^n (the input space)
- All vectors that the matrix sends to zero.
dim(Col A)
This is the rank.
- Tells you how many independent columns the matrix has.
dimNul(A)
Tells you how many free variables there are when solving Ax = 0.
Rank-Nullity Theorem
rank(A) + nullity(A) = n
- Rank counts pivot columns
- Nullity counts free columns
Row Space: (Row(A))
The span of the rows of A
- dim(Row(A)) = rank(A)
- Row space tells you linear relationships among columns
- Nonzero rows
m x n matrix
m = rows
n = columns
What is the range of T?
Column space of A
Invertible Matrix Theorem
1. A is invertible
2. A has n pivots
3. Nul(A) = {0}
4. The columns of A are linearly indepdent
5. The columns of A span R^n
6. Ax = b has a unique solution for each b in R^n
7. T is invertible
8. T is one-to-one
9. T is onto
10. det(A) not equal to 0
11. 0 is not an eigenvalue of A.
Diagonalizable
The eigenvalue can show up more than once (AM > 1), but there also has to be more than one eigenvector for the same eigenvalue (GM > 1).
- If GM < AM, then it is not diagonalizable
Basis of a subspace
A set of vectors that satisfies two properties:
1. Linearly independent: none of the vectors are a combination of the other.
2. Spans the subspace: any vector can be written as a combination of the basis vectors.
- Basis in R^m = finding Col(A)
- Basis in R^n = finding Nul(A)
Subspace
1. Zero vector in the subspace
2. Closed under addition
3. Closed under scalar multiplication
Determinant
1. Row replacement does not change det(A)
2. Scaling a row multiplies the det by C.
3. Swapping two rows mutiplies the det by -1.
4. The det of matrix is equal to 1.
Dot Product
The dot product of two vectors is a scalar.
1. Commutative: u*v = v*u
2. Distributive: u*(v+w) = u*v + u*w
3. Scalar multiplication: (cu)*v = c(u*v)
4. Self-dot gives legth squared: u*u = IIuII^2
Orthogonal Complement
The orthogonal complement of V⊥ is the set of all vectors in R^n.
- Orthogonal means perpendicular, so dot product = 0.
Orthogonal Projection
The orthogonal projection of a vector v onto a subspace W is the vector in W that is closest to v.
Least Squares Solution
Solve a system of equations Ax = b that does not have an exact solution (inconsistent system).
A^TAx = A^Tb
Counter-clockwise rotation by 90 degrees
(0 -1)
(1 0)
Reflection over the line y = x
(0 1)
(1 0)
Clockwise rotation by 90 degrees
(0 1)
(-1 0)
Reflection across the x-axis
(1 0)
(0 -1)
negate the y value
Codomain
R^m (output)
- Number of rows of A
Reflection across the y-axis
(-1 0)
(0 1)
negate the x value
One-to-One
For each y in R^n there is at most one x in R^m so that T(x) = y
- Pivot in every column
Onto
For each y in R^n there is at least one x in R^m so that T(x) = y
- Pivot in every row
(ColA)⊥ = Nul(A^T)
col(A) = Nul(A^T)⊥
Col(A^T)⊥ = Nul(A)
Col(A^T) = Nul(A)⊥
Domain
R^n (inputs)
- Number of columns of A
Linearly independent has __ solutions
trivial
A linearly dependent system has __ solutions
nontrivial
A solution set with one free variable is a ___, two free variables is a __
Line, Plane
Span
All the linear combinations of a set of vectors
- Set of solutions to Ax = 0
Linear combination of vectors
Combining vectors into one equation to produce a new vector.
Determinant of a 2x2 formula
ad - bc
Inverse of A formula
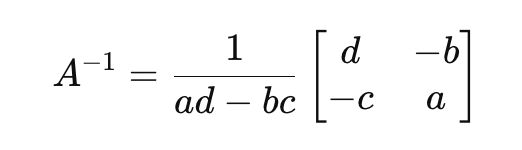
Characteristic Polynomial equation
- Tr(A): (a+d)
- det(A): (ad - bc)
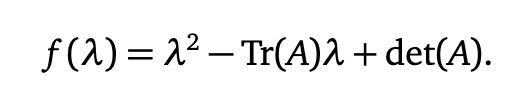
det(3AB^-1) = 1, det(A) = 2
(3^2)*2
EX) Write one vector c so that the orthogonal projection of v onto W is the zero vector
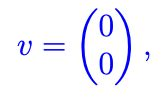
EX) Find the matrix B for orthogonal projection onto W formula.
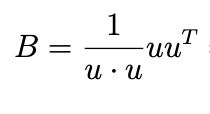
Find Xw formula.
Xw = Bx
Find Xw⊥
X - Xw
To find dimensional subspace...
dim(colA) = pivots
dim(nulA) = free variables
- subspace is the amount of columns
To find W⊥ from Span...
Put in parametric vector form
Subspace
1. Zero vector in the subspace
2. Closed under addition
3. Closed under scalar multiplication
Steady-State Vector formula
What are eigenvalues for 2×2 reflection matrix?
-1 and 1
What are eigenvalues for 2×2 projection matrix?
0 and 1