AP Econ
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Labor Participation Rate =
#working/#working age population x 100
Unemployment rate =
#unemployed/work force # x 100
% change in GDP =
new GDP - old GDP/old GDP x 100
Consumer Price Index=
new market basket/base market basket x 100
GDP Deflator=
nominal GDP/Real GDP x 100
GDP (Expenditure approach)
C+I+G+Xn
GDP (Income approach)=
Wages + rent + interest + profit
MPS= (Marginal propensity to save)
1-MPC (Marginal propensity to consume)
spending multiplier=
1/MPS
Tax multiplier
1/MPS - 1 or MPC/MPS
Money Multiplier
1/reserve ratio
Real Interest Rate =
nominal interest - expected inflation
Quantity Theory of Money
M(quantity of money) x V(velocity of circulation)=P(price level) x Y(real GDP)
Increase in human capital causes
increase in economic growth
Increase in demand causes
increase in equilibrium price
Increase in supply causes
decrease in equilibrium price
Increase in consumer spending causes
increase in real GDP
Increase in interest rates causes
decrease in investment
Increase in inflation causes
Decrease in real wages
Increase in discouraged workers causes
decrease in unemployment rate
Increase in aggregate demand causes
increase in price level
Increase in short run aggregate supply causes
decrease in price level
Increase in government spending causes
increase in real GDP
Increase in taxes causes
decrease in disposable income
Increase in marginal propensity to consume causes
decrease in the spending multiplier
Increase in interest rates causes
decrease in bond prices
Increase in money supply causes
Decrease in nominal interest rates
Increase in reserve requirement causes
decrease in money supply
Increase in central bank purchasing bonds causes
increase in money supply
Increase in interest on reserves causes
decrease in aggregate demand
Increase in inflation causes
decrease in real interest rates
Increase in deficit spending causes
increase in real interest rates
Increase in deficit spending causes
Increase In real interest rates
Increase in capital stock causes
Increase in economic growth
Increase in appreciation causes
decrease in net exports
Increase in interest rates causes
increase in net capital inflow
Comparative advantage
a country makes a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country
Investment
business spending on physical capital, never personal investing
Full employment
when there is only structural and frictional unemployment
Long run self adjustment
when there’s a positive or negative output gap, SRAS will eventually shift
Fiscal policy
government changes government spending and/or taxes, which shifts AD
Monetary policy
when there are limited reserves, central banks can influence interest rates by changing the reserve requirement discount rate, or by doing open market operations, which shifts AD
Open market operations
buying and selling government securities to either increase or decrease the money supply (buying increases and selling decreases), when central banks buy or sell bonds
Crowding out
deficit spending leads to higher real interest rate and less investment
Capital inflow
High interest rates decrease investment but attract more foreign capital
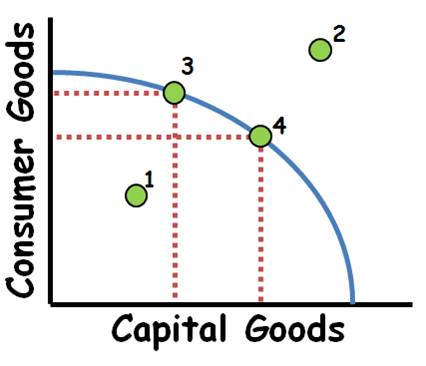
Production possibilities curve
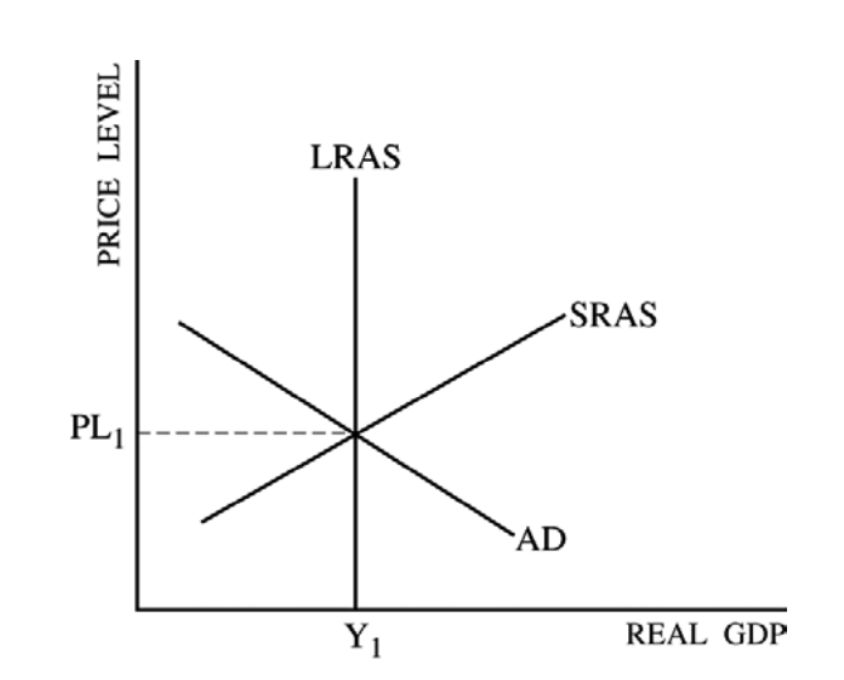
AD/AS (full employment)
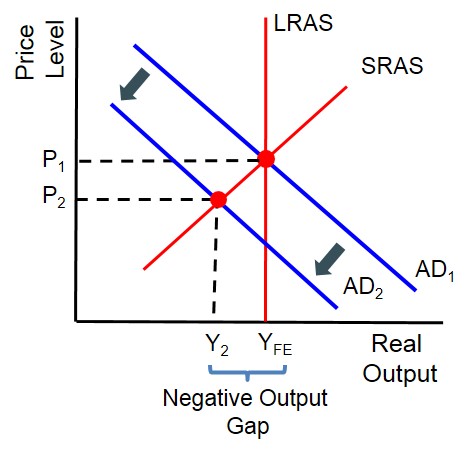
AD/AS negative output gap (equilibrium is left of LRAS)
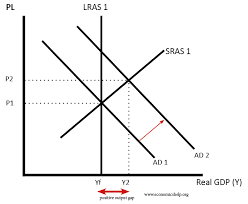
AD/AS positive output gap (equilibrium is right of LRAS)
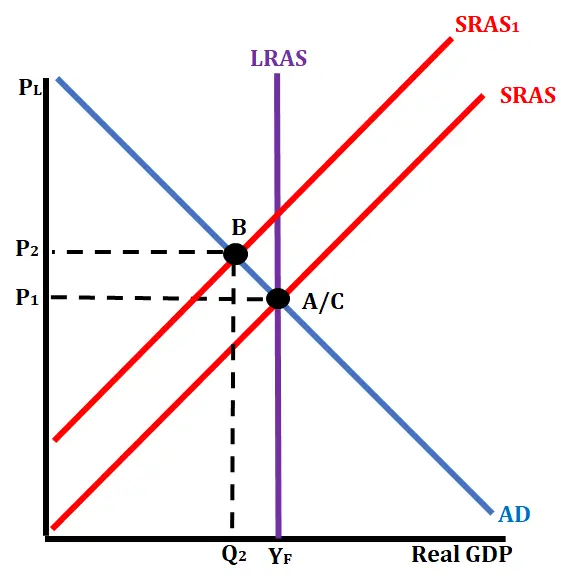
AD/AS Recession self adjust (SRAS moves right, AD moves left)
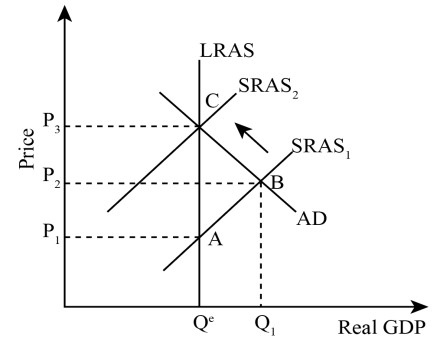
AD/AS Inflation self adjust (SRAS moves left, AD moves right)
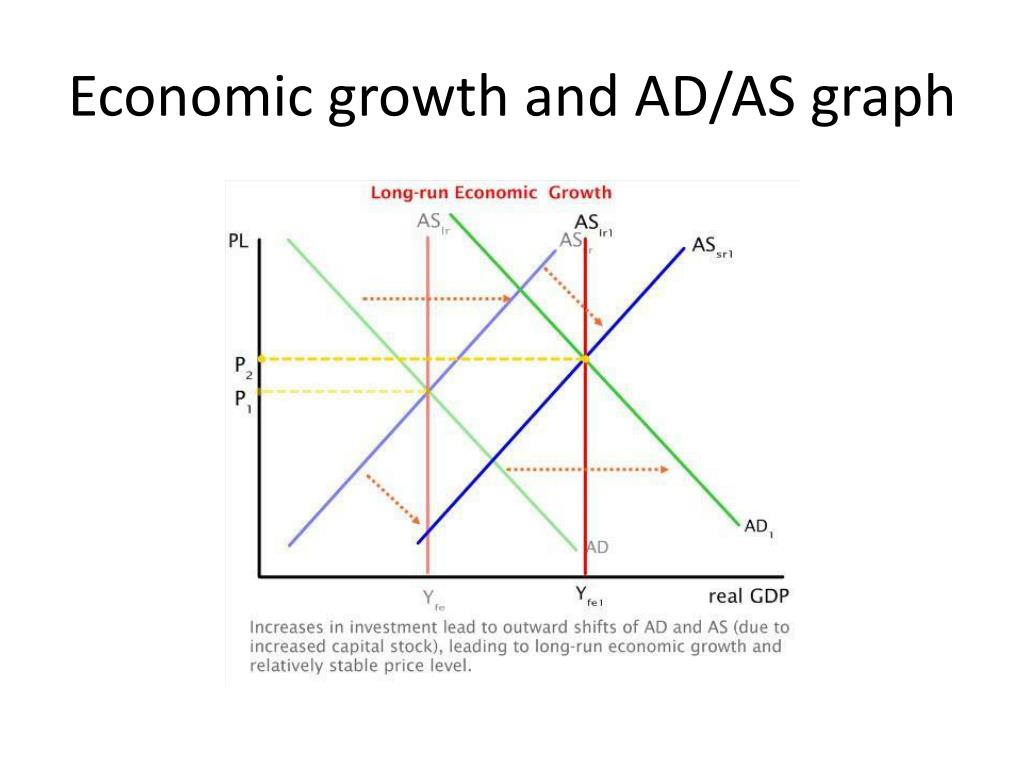
AD/AS economic growth (LRAS shifts right, AD and SRAS shifts right)
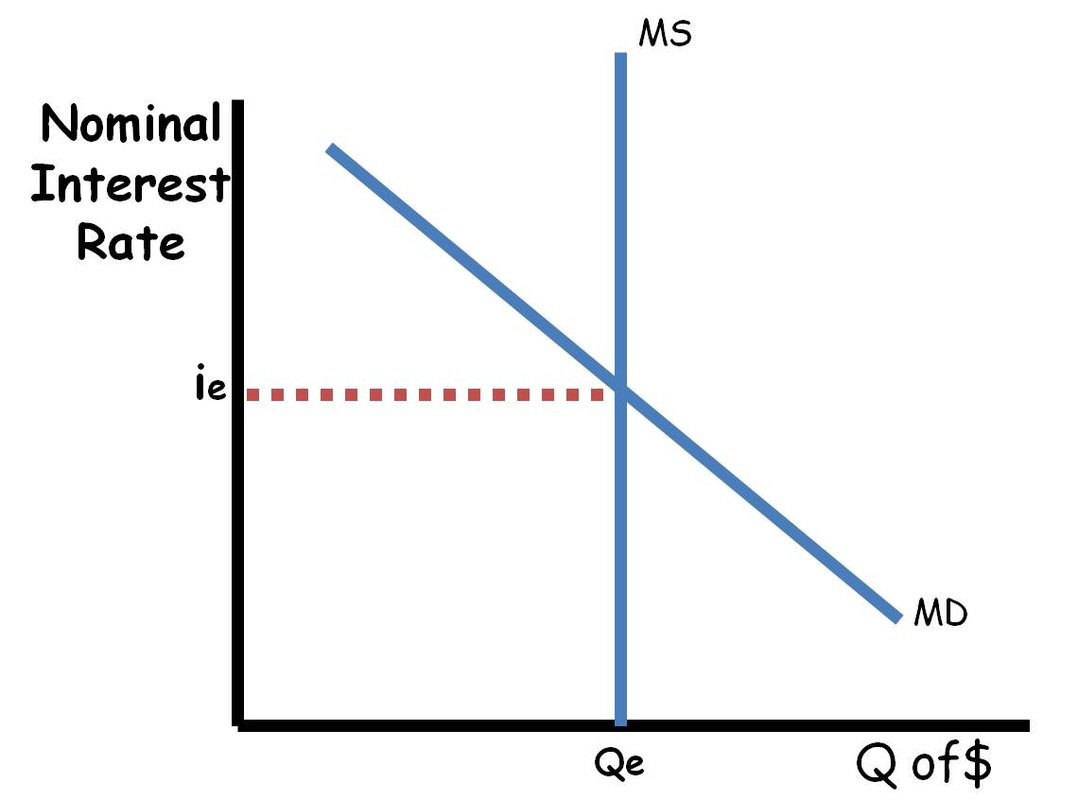
Money market
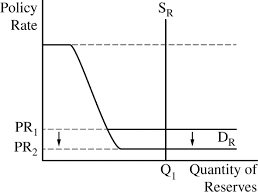
Reserve market
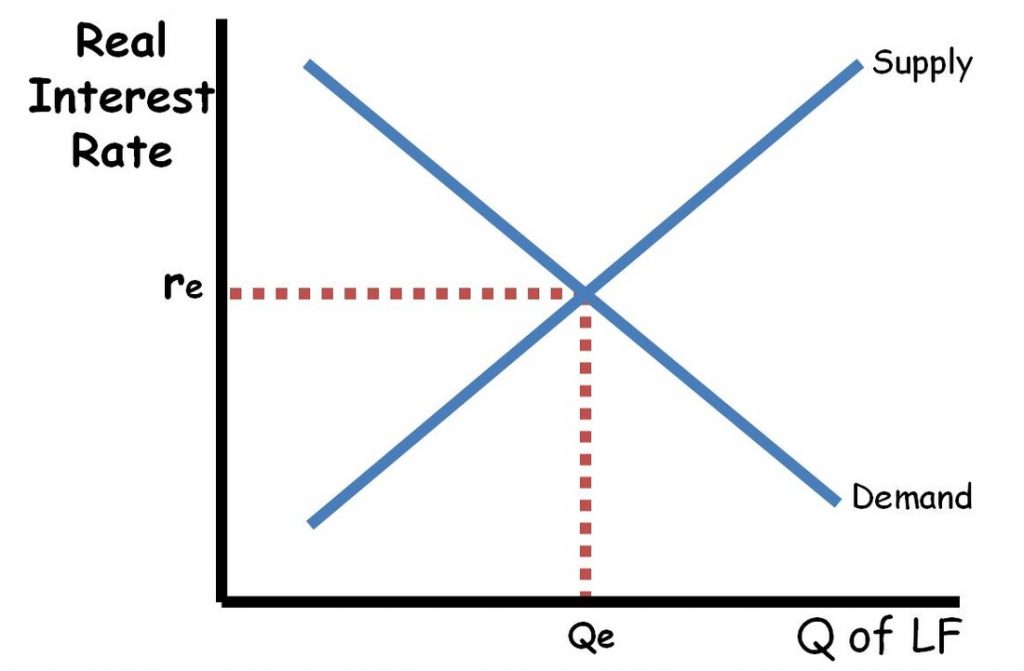
Loanable Funds
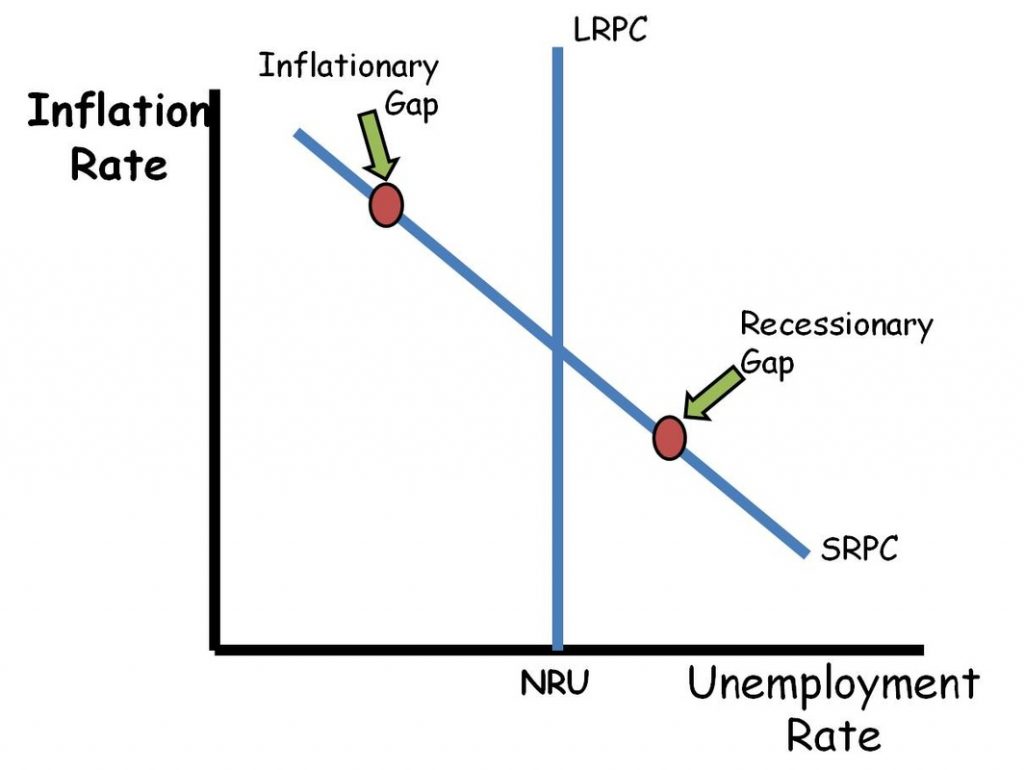
Phillips Curve
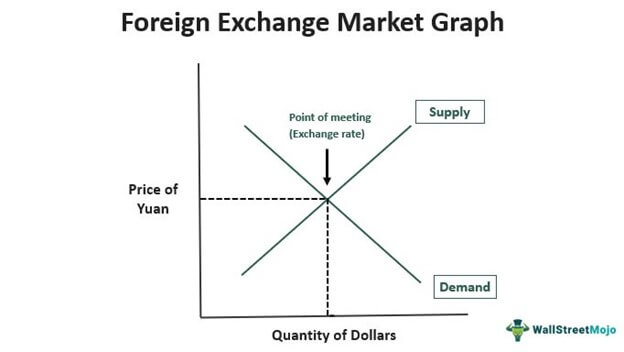
Foreign exchange
Change in price level
moves the point on the AD curve
Factors that shift AD to the right (increase)
increased consumer confidence, business optimism, increased government spending, tax cuts, reduced interest rates, increased net exports
Factors that shift AD to the left (decrease)
decreased consumer confidence, business pessimism, reduced government spending, tax increases, increased interest rates, decreased net exports
Factors that shift SRAS to the right
decreases in wages, increased productivity, decreased regulation, lower inflation expectations
Factors that shift SRAS to the left
increase in wages, increased energy prices, decreased productivity, increased regulation, higher inflation expectations
Shifts money supply curve right
Expansionary monetary policy: central bank increases money supply through open market operations, lowering RR, or lowering discount rate
Shifts money supply to the left
contractionary monetary policy: central bank decreases money supply by selling bonds, raising RR, or raising discount rate
Shifts money demand curve right
increase in real GDP, increase in price level
Shifts money demand curve left
decrease in the price level, decrease in real GDP, advancements in money technology such as more use of credit cards
Loanable funds supply curve shifts right
Increased saving, government policies that encourage savings, government policies that encourage investment, foreign investment
Loanable funds supply curve shifts left
decreased saving behavior, increased government deficit, decrease in financial security risk, decreased foreign investment
Loanable funds demand curve shifts right
increased borrowing, increased confidence (businesses and consumers expecting higher returns on investments), tax incentives, crowding out (government increases borrowing)
Loanable funds demand curve shifts to the left
decreased investment opportunities, reduced business confidence, economic slowdown, increased corporate tax rates
Long run Philips curve shifts right
Philips curve shifts are the same as Natural Rate of Unemployment shifts: increase in structural unemployment
long run Philips curve shifts left
decrease in frictional unemployment
Short run Phillips curve shifts right
all shifts are due to changes in AS, SRPC shifts the opposite direction of AS negative supply shocks shifting AS to the left, increased expected inflation shifting AS to the left
Short run Phillips curve shifts left
AS curve shifts right due to positive supply shocks or decreased expected inflation
Exchange rate increases
decrease in money supply due to tightening monetary policy, this causes appreciation
Exchange rate decreases
increase in the money supply due to central banks increasing the amount of money in circulation, leading to depreciation
Money demand shifts right in foreign exchange
increase in demand for that country’s currency, foreign countries with higher incomes, higher interest rates, supply decrease
Money demand shifts left in foreign exchange
decrease in the demand for the currency, decrease in foreign income, decrease in foreign prices, negative investor sentiment