Circuits Test 3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
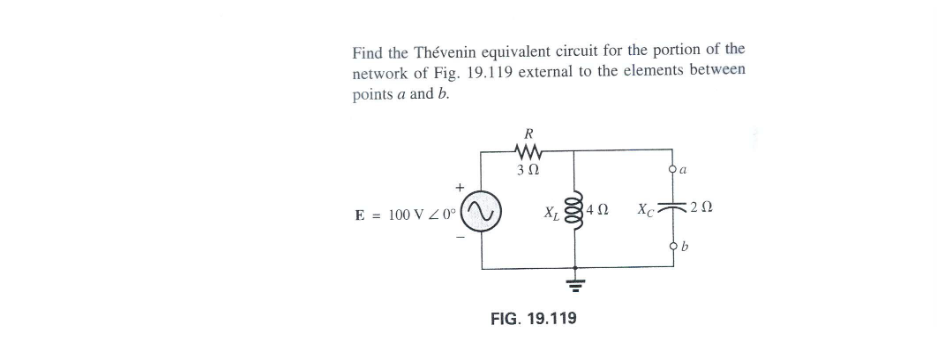
chapter 19 q1
Eth=80V<36.87
Zth=2.4Ohms < 36.87
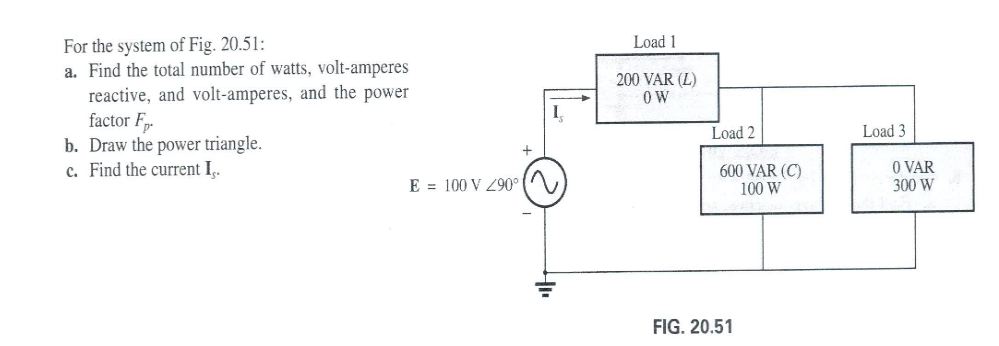
chapter 20 q1
a) Watts(add watts together) = 400 = P
VAR(add VAR together = -400 = Q
Power Factor = P/S = 400/565.7 = 0.707
S = sqrt(3200) = 565.7
b) sides 400 Watts and VAR, angle of -45 degrees
c) I=S/V = (565.69)/100 = 5.67A
Define Q (quality factor) of a circuit.(ch21 q1)
The quality factor Q of a series resonant circuit is defined as the ratio of the reactive power of either the inductor or the capacitor to the average power of the resistor at resonance
Define cutoff frequency.(ch21 q2)
The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the cutoff frequencies or half power frequencies
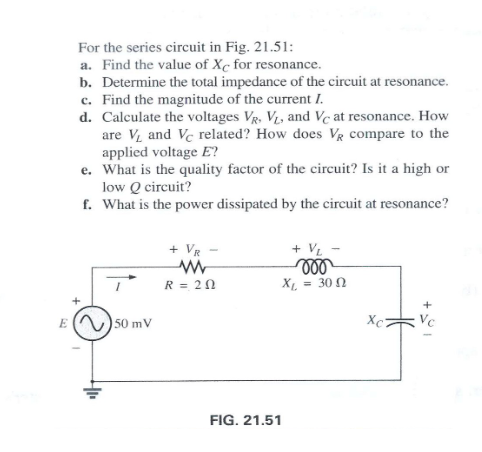
(ch21 q3)
a) resonance occurs when Xc = Xl(Xc=30)
b) series AC circuit, so Impedance adds together
2+30j-30j = 2Ohms
c)I =V/Zt = (50×10^-3)/2 = .025A
d) Vl=Vc = .75V = I*Xc
Vr = I*r = .05V
e) Qf = Xl/r = 30/2 = 15
f) P = V*I = 50×10^-3*.025 = 0.00125W
Where is the unit decibel (dB) used in industry?(ch22 q1)
The unit decibel (dB)is used in industry to
define levels of audio, voltage gain, energy,
field strength, etc.
Define Bode plot.(ch22 q2)
The curves obtained for the magnitude and/or phase angle (linear scale) versus frequency (log scale) are called Bode plots
(fig. 22.53).
Design a R-C low-pass filter to have a cutoff frequency of 500 Hz using a
resistor of 1.2KΩ. Then sketch the resulting magnitude (normalized plot of
Av versus f) (see Fig. 22.20) for 0 Hz, 250 Hz, 500 Hz, and 1KHz (ch22 q3)
fc = 1/(2pi*R*C): c=1/(2pi*f*r) = 26.6uF
draw diagram with input terminals, R and C in series, and output terminals around C
Y axis starts at 1, and reduces to .707 at 500Hz, and at 1k is slightly below that.
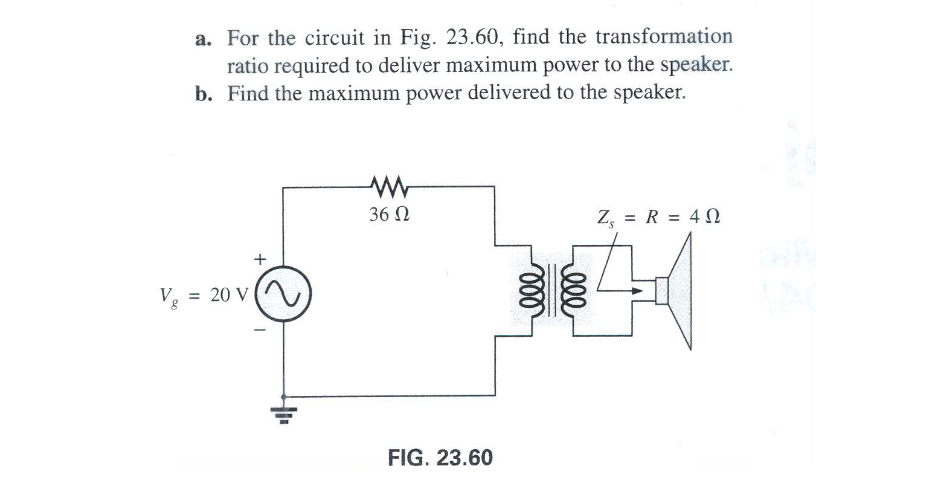
(ch23 q1)
Zp = a² *Zs
36=a²*4 9=a²
a=3
Pout = Pin =20²/ 36 = 11.11
What are the four reasons three phase systems are
preferred over single phase systems?(ch24 q1)
3 phase systems are prefered because they allow for thinner, lighter conductors and supporting structures.
They also allow for smoother opperation of motors, and allow for self starting motors.

(ch24 q2)
a) Vl = Vphase*sqrt(3) = 120.1V
b) loads are balanced, so Vphaseload = Vphase = 120.1V
c) Iu = Vphase/ Zload = 12A
d) phase current = line current = 12A
Name four systems where pulse signals are used.(ch25 q1)
A vast array of instrumentation,
communications systems, computers, radar
systems, and TV remotes use pulse signals
Define duty cycle of a pulse waveform(ch25 q2)
The duty cycle is defined as: pulse width/period x 100
The duty cycle provides a percentage indication of the portion of the total period encompassed by the
pulse waveform.
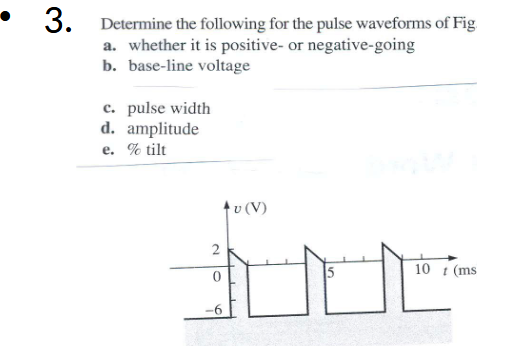
(ch25 q3)
a) positive going
b) -6 V
c) 1V
d) 8V
e) 28.57%
Name five non-sinusoidal waveforms.(ch26 q1)
DC, square, sawtooth, rectified, and triangular waves are common non sinusoidal waves.
Explain the three basic parts of a Fourier series? (ch26 q2)
Fourier series consist of DC, sine, and cosine terms
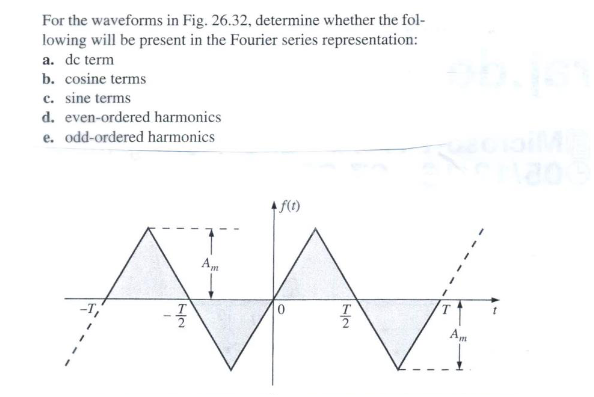
(ch26 q3)
a)No
b)No
c)Yes
d)No
e)Yes