Chapter 10- Dr. Kim
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
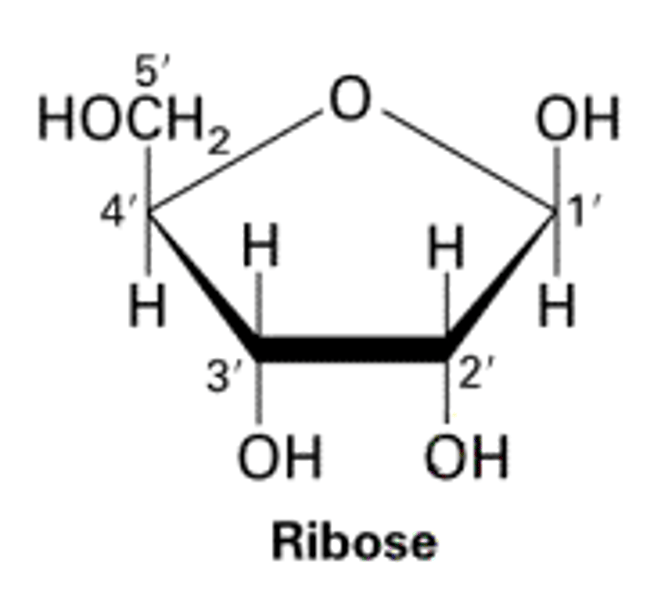
Ribose
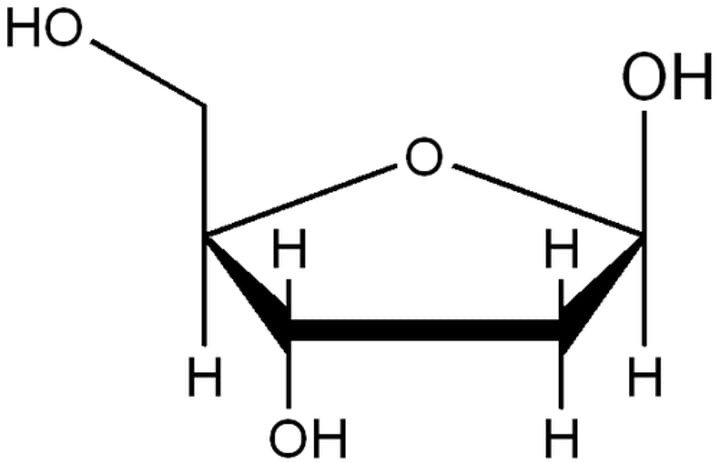
deoxyribose
What are the two purine ribonucleotides?
Adenine and Guanine
What are the pyrimidine ribonucleotides?
cytosine and thymine
How many total ribonucleotides found in RNA?
four
U=A or U=G belongs to the ____ ribonucleotides.
purine
Is DNA and RNA composed of nucleotides?
yes
What type of sugar is found in DNA?
deoxyribose
What type of sugar is found in RNA?
ribose
Is there a 2' OH group on Deoxyribose sugar?
No
There is a 2' OH group on ribose sugar.
true
What are the bases associated with DNA?
A, G, C, T
What are the bases associated with RNA?
A, G, C, U
Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester bonds in both RNA and DNA.
true
Is DNA double stranded or single stranded?
double stranded
Is RNA double or single stranded?
single stranded
There are many types of secondary structures for RNA.
true
What is the secondary structure of DNA?
double helix
Is DNA stable?
stable
Is RNA stable?
no, it is easily degraded
RNA has a primary and secondary structure.
true
RNA contains ____ in place of thymine.
uracil
How does an RNA molecule form a secondary structure?
RNA molecule folds, owing to hydrogen bonding between complementary bases on the same strand
What kind of base pairing does RNA have?
intramolecular base pairing
What are the components of the 3D rna nucleotide chain?
amino acyl acceptor arm
t-loop
d-loop
anticodon loop
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
intermediate necessary for synthesizing protein (functional product)
What kind of RNA is not easily translated into polypeptides?
Functional RNA
What are the types of functional RNA?
tRNA
rRNA
snRNAs
miRNAs
siRNAs
tRNA
bringing the correct amino acid to the mRNA
rRNA
major components of ribosomes
snRNAs
RNA processing components of spliceosome
miRNAs
regulating gene expression
siRNAs
genome defense
What is transcription the separation of?
DNA double strands
is a primer required for transcription?
No (replication only)
What are three components of transcription?
template DNA, NTP, transcription apparatus
information transfer
through complementary pairing of bases
What is the name of the template strand?
non-coding (non-sense) strand
non-template strand
mRNA sequence
mRNA sequence is the same as the ______ strand
coding/sense
What is RNA transcribed from?
one DNA strand
What end are nucleotides always added to of the RNA molecule?
3' end
Initiation of RNA synthesis does not require a primer.
true
Where does DNA unwind at in the RNA molecule?
at the front of the transcription bubble
What region is the promotor found in?
5' regulatory region
What is name of the site where the first base is transcribed?
initiation site (+1)
What are the core enzymes in the initiation step of prokaryotes?
alpha, beta, beta', theta
Which holo-enzyme is not a core enzyme?
sigma
alpha (core enzyme)
help assembly/ promote interactions with regulatory proteins
Beta (core enzyme)
active in catalysis
Beta prime (core enzyme)
binding to DNA
Theta (core enzyme)
enzyme assembly
What enzyme is known to correct positioning of the holoenzyme, binding to -35 and -10?
sigma
Around what region does the sigma enzyme separate the DNA strands?
-10 region
When does the sigma enzyme dissociate?
after transcription begins
Different sigma factors recognize different sets of _____.
promoters
When is RNA transcription initiated in bacteria?
when core RNA polymerase binds to the promoter with the help of sigma
Many RNAs can be simultaneously transcribed from a ____.
gene
When there is presence of a nucleus, such as eukaryotes, what is the consequence?
separated transcription and translation
What occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotes?
RNA processing
What is the primary transcript in eukaryotes?
pre-mRNA
What is the primary transcript in prokaryotes?
mRNA
Eukaryotic genome is the presence of a ____.
nucleus
RNA polymerase I
large rRNAs
RNA polymerase II
pre-mRNA, some snRNAs, snoRNAs, some miRNAs
RNA polymerase III
tRNAs, small rRNAs, some snRNAs, some miRNAs
RNA polymerase IV
some siRNAs in plants
What are the promoters of genes transcribed by?
RNA polymerase II
Where is the TATA box region?
-30 bp region
TFII
transcription factor of RNA polyermase II
What is the TATA binding protein?
TBP
_____ is apart of the TFIID complex.
TBP
What protein attracts other GTFs and RNA polymerase II?
TBP
PIC
pre-initiation complex
______ + ______= Pre-initiation complex
RNA polymerase II + GTFs
CTD
C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase
What happens with to the interactions with GTFs when phosphorlyated?
the GTFs are weakened
Which of the following is true of RNA compared to DNA?
RNA has a hydroxyl group on 2'-carbon atom of its sugar component
When RNA is transcribed from a gene, which strand of DNA is used?
the template strand
The transcription unit includes three essential regions. What is the proper order of these regions?
promotor, RNA coding sequence, terminator
What would the result be if a specific sigma subunit were mutated?
RNA polymerase would fail to initiate transcription at the promoter specific to the sigma subunit
The bacterial holoenzyme binds to which part of the promoter?
-10 and -35 consensus sequence
In rho-dependent transcription termination, the rho factor binds to _____.
mRNA
In eukaryotes, what initially binds to the TATA box on the DNA template?
TFIID
What is the ribsome binding site on prokaryotic mRNA?
shine-dalgarno sequence
Where is the start codon in prokaryotic transcription?
5' end
Where is the stop codon located during prokaryotic transcript?
3' end
In Eukaryotic transcription, what end does the cap add to?
5' end
Eukaryotic RNA processing is _______.
cotranscriptional
What are the three characteristics of RNA processing in eukaryotes?
capping
splicing
polyadenylation
splicing
removal of introns and joining of exons
polyadenylation
addition of 100s of adenine nucleotides
What does not require a coding sequence and is removed from mature RNA in eukaryotic transcription?
intron
During capping, what is the 7-methyl guanine added to?
5'-5' phosphate
Where is the polyA tail added?
3' end
What are the two functions of CAP?
protects RNA from degradation (increased stability)
required for ribosome binding (translation)
How many total places are there for methylation?
3 places
What are conserved regions related to?
intron splicing
What is the splicing machinery called?
spliceosome (molecular complexes)
What type of RNA is apart of the spliceosome?
small nuclear RNA (snRNA)