neuro 206 lecture 2; studying the nervous system
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
what are neural circuits
organized ensembles of neurons that process specific kinds of information
what are synaptic connections that underlie neural circuits typically made of
neuropil
what are neuropil
the regions between nerve cell bodies where most synaptic connectivity occurs; consists of a dense tangle of dendrites, axon terminals, and glial cell processes
what are the basic constituents of all neurons circuits
afferent neurons, efferent neurons, and interneurons
how do afferent and efferent neurons different
flow of information in neural circuits
afferent neurons
nerve cells that carry info from the periphery TOWARD the BRAIN or spinal cord (Arrive at CNS)
afferent neurons are also known as
sensory neurons
efferent neurons
nerve cells that carry info FROM the BRAIN or spinal cord (Exit CNS)
efferent neurons are also known as
motor neurons
afferent neurons and efferent neurons are collectively referred to as
projection neurons
what are projection neurons known for
their axons extend for a significant distance beyond their cell body and connect with distal targets
what do interneurons do?
participate only in local aspects of circuit function, based on their relatively short axons and the restricted targets with which they connect
interneurons are also known as
local circuit neurons
signals in neural circuits are based on
the chemical neurotransmitter released by receptors in the postsynaptic domain
types of signals neurons can transmit
excitatory signals and inhibitory signals
excitatory signals
enhance electrical activity in the target neuron and make it more likely that the target neuron will relay signals to additional neurons in the circuit via excitatory neurotransmitters
inhibitory neurons
diminish electrical activity in the target neuron far below the threshold necessary for it to transmit electrical signals to additional neurons in the circuit via inhibitory neurotransmitters
modulatory neurotransmitters
modify the thresholds in target neurons, which then changes the effectiveness of either excitatory or inhibitory signals
what is the myotatic reflex also known as
knee-jerk reflex
what are the afferent neurons in the myotatic reflex
sensory neurons with cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia and send axons peripherally that terminate in sensory endings in the skeletal muscles
what are the targets of the afferent neurons in the myotatic reflex
motor neurons that relay the output activity of the circuit and control the muscles that make the knee jerk
the myotatic reflex circuit has what type of output
divergent
what does having divergent output mean?
there are distinct types of efferent neurons in the circuit
what are the distinct types of efferent motor neurons in the myotatic reflex output circuit?
one type of motor neuron projects to the flexor muscles in the limb, and the other to extensor muscles
what are the functional implications of having divergent output in a neural circuit (myotatic reflex)
flexors and extensors have opposing actions, so there must be one signal that causes the extensor to contract and flexor to relax. there also needs to be interneurons that modulate the input-output signal to turn one of the excitatory inputs into an inhibitory input
the interneurons in the myotatic reflex are…
spinal cord interneurons
summarize the myotatic reflex circuit
hammer taps, stretches tendon, which stretches sensory receptors in leg extensor muscles
sensory neuron synapses with and excites motor neuron in the spinal cord; also excites spinal interneuron
interneuron synapse inhibits motor neuron to flexor muscles
motor neuron conducts AP to synapses on extensor muscle fibers, causing contraction
flexor muscle relaxes because the activity of its motor neuron has been inhibited
leg extends
techniques to study the nervous system
electrophysiological recording
calcium imaging
fMRI
what are the different kinds of electrophysiological recordings?
extracellular recording
intracellular recording
extracellular recording
Electrical activity of neurons can be observed and measured directly via electrodes placed near a neuron to record action potentials
intracellular recording
Electrical activity of neurons can be observed and measured directly via electrodes by accessing the inside of a neuron to record action potentials as well as subthreshold potentials
in terms of the recordings created, how do extracellular and intracellular recordings differ?
extracellular recordings only record action potentials; intracellular recordings record both action potentials and subthreshold potentials

This is an example of what type of recording?
extracellular
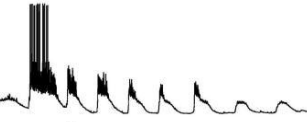
This is an example of what type of recording?
intracellular
classical extracellular recording was done with
a single electrode
pros and cons of extracellular recording
high temporal resolution (< 1 ms)
direct measurements of neural activity
invasive
can only measure a few cells at a time
what is temporal resolution?
length of time between distinct measurements

this picture depicts what analytical tool?
multielectrode array
what are multielectrode arrays?
a grid of tightly spaced microscopic electrodes which generally have 1000 sites
what do multielectrode arrays allow for?
enable recoding from 100s to 1000s of cells
what is the main issue with multielectrode arrays?
very invasive
what is the rationale behind using calcium imaging as a tool to study the nervous system
calcium levels inside a cell rise during an AP and gradually return to baseline after the AP; AP causes transient changes in intracellular Ca2+, thus you can measure activity of a cell during different processes based on Ca2+ levels
how does calcium imaging work?
fluorescent calcium indicators (“GCaMP”) enable activity measurement in specific cell types at high spatial resolution.
when Ca2+ binds to calmodulin, creates a conformational change that activates GFP and causes the cell to fluoresce
calcium imaging relies on what kind of measurement?
relative measurement
assess activity by finding the change in fluorescence divided by the baseline level
pros and cons of calcium imaging
high spatial resolution (single cell)
can image multiple cells at once
ok temporal resolution ( > 100 ms)
invasive
limited observation depth (1 mm into tissue)
fMRI stands for…
functional magnetic resonance imaging
what does fMRI do?
measures changes in blood oxygenation related to activity
what is the mechanism behind how fMRI works?
neural activity changes the ratio of oxygenated hemoglobin (oxyHb) and deoxygenated hemoglobin (deoxyHb) in blood (because oxygenated blood goes to active parts of the brain)
oxyHb is diamagnetic but deoxyHb is paramagnetic → radio frequency absorption and emission in a magnetic field changes → effect of emission on magnetic field that we measure changes
pros and cons of fMRI
noninvasive
low temporal resolution
low spatial resolution
fMRI maps show…
the results of a statistical test at each voxel
how are p-values represented chromatically in an fMRI map?
Very low p-values are dark red and progress to blue as it increases, and high p-values remain gray
What do different p-values mean?
low p-values reflect changes likely not due to chance
how do you study a complex system
step 1: observation
step 2: perturbation
step 2a: activate
step 2b: remove
what are ways you can use perturbation to deactivate neurons?
lesions
drugs
optogenetic inhibitors
what is lesion?
removal of brain tissue to assess the causal role of a brain area (if something stops working due to the area being removed, that area is essential for that function)
what are the issues with lesion?
takes long, brain can recover, permanent
how are drugs helpful with studying the brain?
enable faster assessment of functional roles
example of how drugs were used to study nervous system
muscimol (GABA receptor agonist) is injected into the motor cortex to see what role GABA plays in establishing movement and balance by inhibiting GABA’s activity in the system
what are optogenetic inhibitors
can selectively inhibit specific neurons/cellular functions in cells of interest via inserting light-activated ion channels or pumps to hyperpolarize neurons
halorhodopsin
Cl- channel optogenetic inhibitor; lets Cl- into the cell
archaerhodopsin/bacteriorhodopsin
H+ channel optogenetic inhibitor; lets H+ leave the cell
optogenetic inhibitors enable
even faster, genetically-targeted inactivation
what are ways you can use perturbation to activate neurons?
electrical stimulation
channelrhodopsin
how does electrical stimulation allow us to study the brain?
activate neuronal population, so local stimulation activated muscles in different body parts and thus are connected
what are channelrhodopsins?
light-gated ion channels that undergo conformational changes that let cations pass through when hit by light
what can channelrhodopsin be used for?
to rapidly activate genetic subsets of cells