Concepts of Animal Growth
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
How big should a heifer be at calving?
She should be 82%
How big should a heifer be a breeding?
She should be 55%
Are heavier or lighter body weights at calving associated with greater milk production?
heavier body weights
What are the physical components of growth and development?
Bone, Lean, Fat
What are the chemical components of growth and development?
water, protein, lipids, ash (minerals), carbohydrates, vitamins
What is maturity?
the point in time when an animal reaches its highest level of complexity or development but it is vague and there are different types
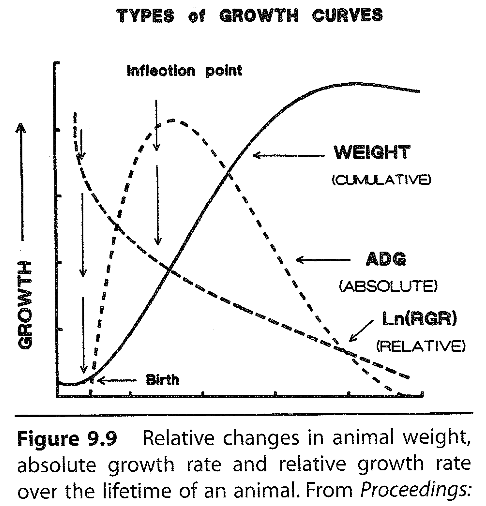
What is the general animal life progession?
conception, birth, self-accelerating postnatal growth phase, inflection point, self-retarding postnatal growth phase, maturity
What is the self-accelerating postnatal growth phase?
period of time in which an animal has reached a level of complexity that enables it to grow rapidly like ruminant development
What is the inflection point?
the maximum growth rate, puberty, exponential portion of growth curve
What is the self-retarding postnatal growth phase?
growth begins to slow, maybe due to reduction in ability to deposit protein
What is a cumulative/distance growth curve?
consecutive measurements in dependent variable (total weight) plotted against change in independent variable (time)
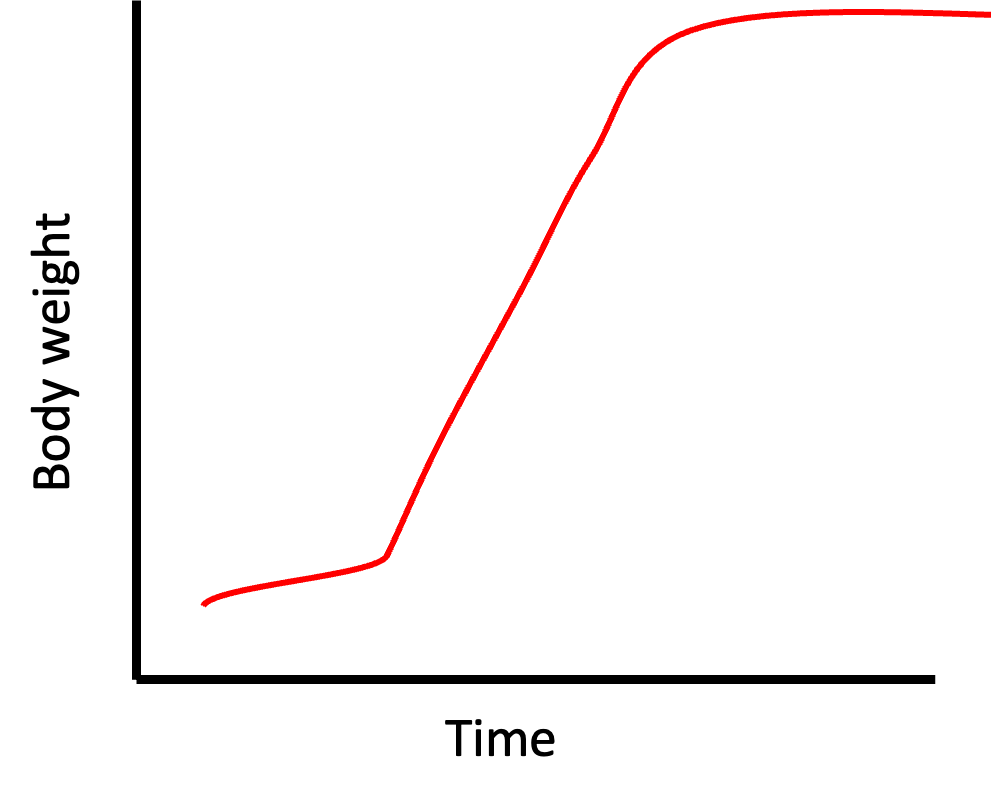
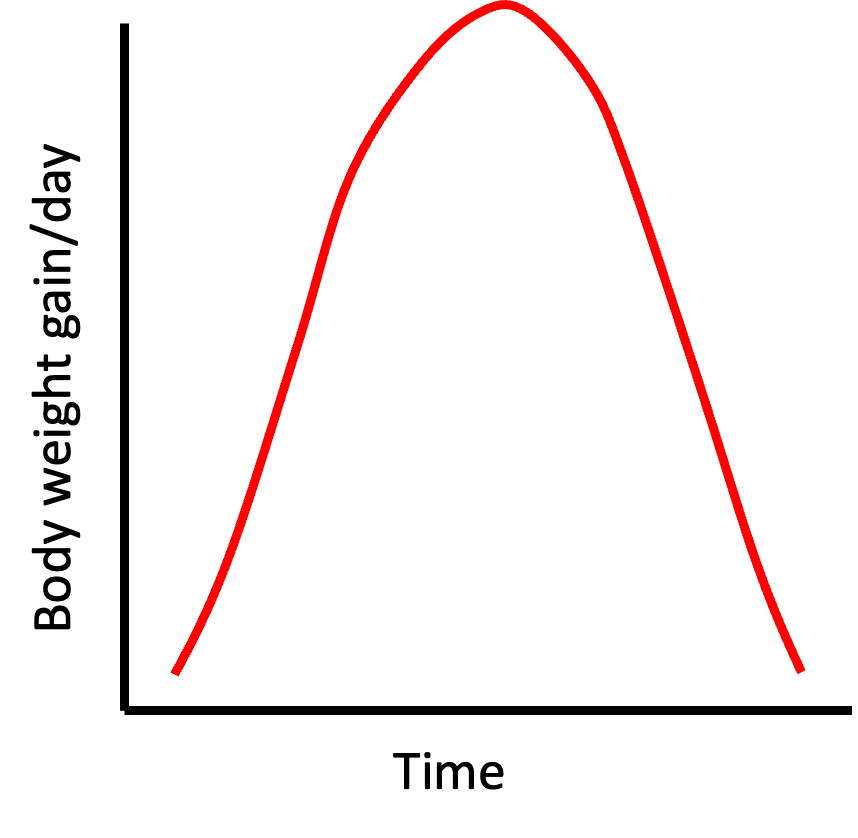
What is an incremental/velocity/absolute growth curve?
consecutive changes (not total amount) in the dependent variable (weight) against a series of consecutive time intervals
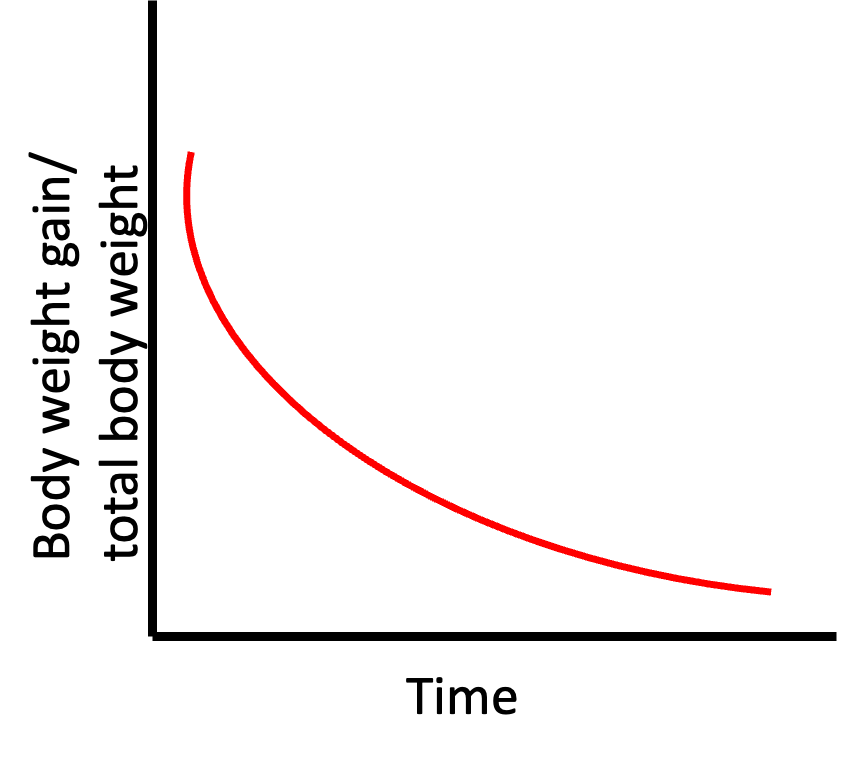
What is a relative growth curve?
consecutive changes in the RATE of growth against total weight (or cumulative growth)
Look at the type of growth curves?
Is a growth more realistic as a stair step or smooth?
stair step because growth is not linear
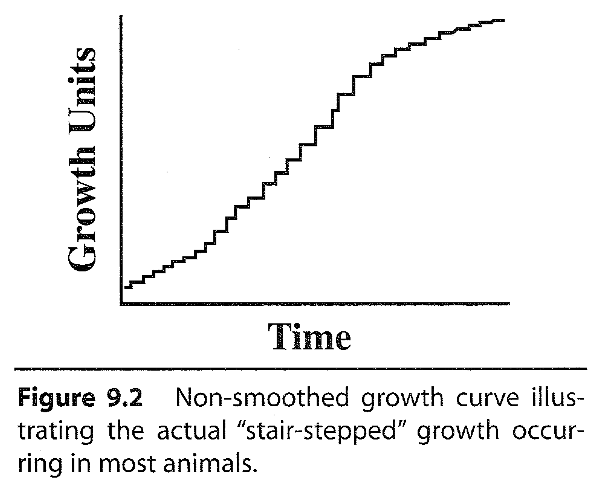
What is the average daily gain?
amount of weight gained each day between two time points
What is weaning weight?
[(weaning wt. - birth wt.)/days of age at weaning X 90] + birth wt.
What is the weaning ADG?
(actual weaning wt. - birth wt.) / calf age, da.
What is yearling ADG?
(actual yearling wt. - actual weaning wt.)/number of days between weights
What is 205-day adjusted weaning wt.?
(ADGw x 205) + Birth wt. + Age of Dam adjustment factor
What are the adjustment factors for Age of Dam?
Adjustment factors | |||||
Age of dam, years | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5-10 | 11+ |
Male calf | +60 | +40 | +20 | 0 | +20 |
Female calf | +54 | +36 | +20 | 0 | +18 |
What is 365-day adj. wt.?
(ADGy x 160) + 205-day wt. adjusted for dam age
What is weight per day of Age (WDA)?
steer wt./days of age
What is the prenatal bovine growth curve?
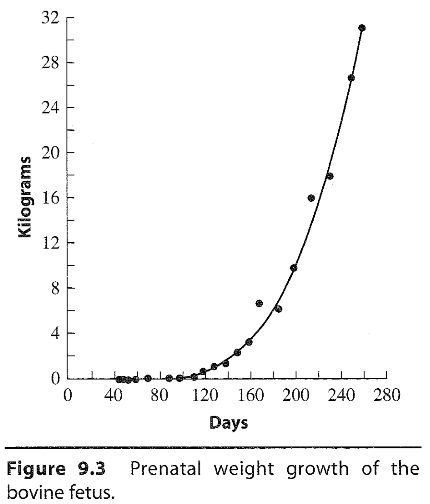
What does the alternative growth segments look like?
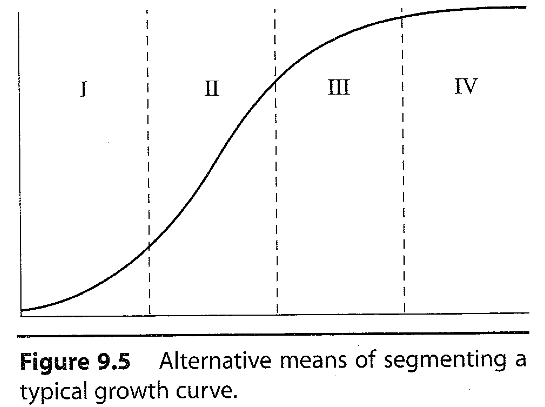
What is the first growth phase?
5-20% of total growth completed, slow growth of all tissues, in the order of organs>bone>muscle>fat
What is second growth phase?
75% of total growth reached, organs reach mature size, bone growth completed, maximal muscle growth, slow fat accumulation
What is the third growth phase?
80-90% of growth attained, organ and bone growth complete, accumulation of fat begins
What is the fourth growth phase?
90-95% of additional growth as fat and 5-10% of gain is muscle
What is allometric growth?
the comparison of the growth rate of a body component to the growth rate of the entire body where Y= a+bX, Y = log weight of specific tissue, X = log weight of total carcass, a = constant, b=growth coefficient
In allometric growth what does it mean when b>1?
the tissue component is growing at a faster rate than the whole body (high impetus)
In allometric growth what does it mean when b<1?
the tissue/component is growing at a slower rate than the whole body (low impetus)
In allometric growth what does b=1 mean?
the tissue/component is growing at the same rate as the whole body (average impetus)
What is diphasic?
when growth coefficients may be generated for tissues over a shorter period of time and therefore, may yield dramatically different and sometimes contrasting coefficient
What is monophasic?
muscles or tissues that have growth coefficients that are constant over time
When does isometric growth occur?
from birth until 2-3
When does allometric growth occur?
from 3 months until 11-12 months and return to isometric until conception
What is isometric growth?
exact opposite of allometric growth, the proportions of the organism stay relatively similar and the mature organism looks like a bigger version of the young version of the organism
What is allometric growth?
unequal growth rate in different portions of the body of an organism that gives rise to the final shape, growth of a particular structure at constantly greater rate than the whole
What are the changes in body part deposition?
brain, bone, muscle, fat
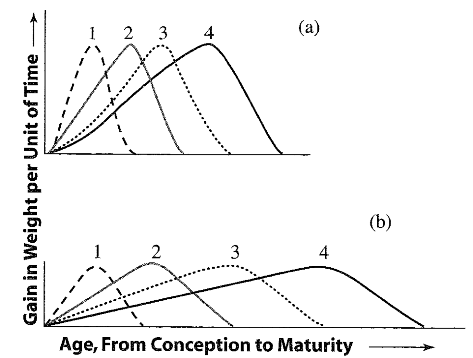
What is the priority of nutrient use?
the brain and CNS, bone, muscle, fat
What are the changes from birth to maturity?
changes in body form - proportions, changes in body measurements - carcass length longissimus muscle area subcutaneous fat thickness, changes in body components - body weight empty body weight dressing percentage carcass weight, changes in carcass components, changes in chemical composition, factors affective composition - genetics species sex nutrition
What is the influence of livestock sex on growth?
males have higher growth, then castrated males, then females
What is animal conformation?
the proportional shape of an animal or carcass, a visual assessment of the desirability of animals and/or carcasses, meat animals usually have better conformation than dairy or multipurpose animals
look at this graph
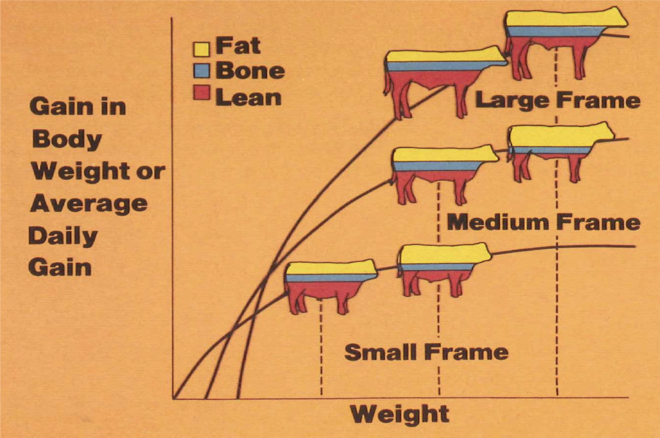
what is body weight?
live weight of animal
what is empty body weight?
live weight minus digestive system contents
what is carcass weight?
live weight minus internal organs, hide/pelt, feet and head
what is dressing percentage?
carcass weight divided by live weight
what is the empty steer body composition?
the liver has the highest amount of carbs because it is a glucose storage site, skeleton has the most mineral, muscle has the more moisture, adipose tissue has the most lipids
What are the % chemical composition of steer fat depots?
intermuscular has the most amount of water, kidney has the most amount of fat, intermuscular also has the most amount of protein
What are the differences in muscle distribution % among ruminant animals?
bison bulls have more proximal pelvic limb %, merino ram has most spinal column % and abdominal wall %,