Lecture Exam #3 Review
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 047
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
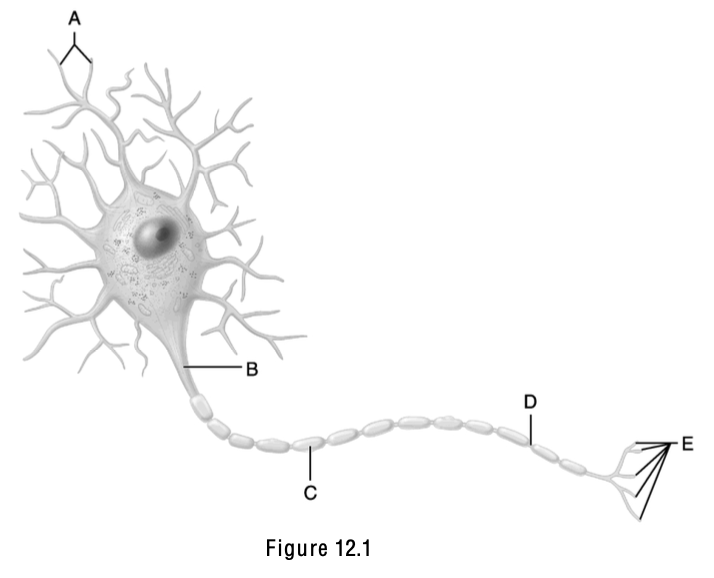
The name of this part means “little hill”.
B (Axon hillock)
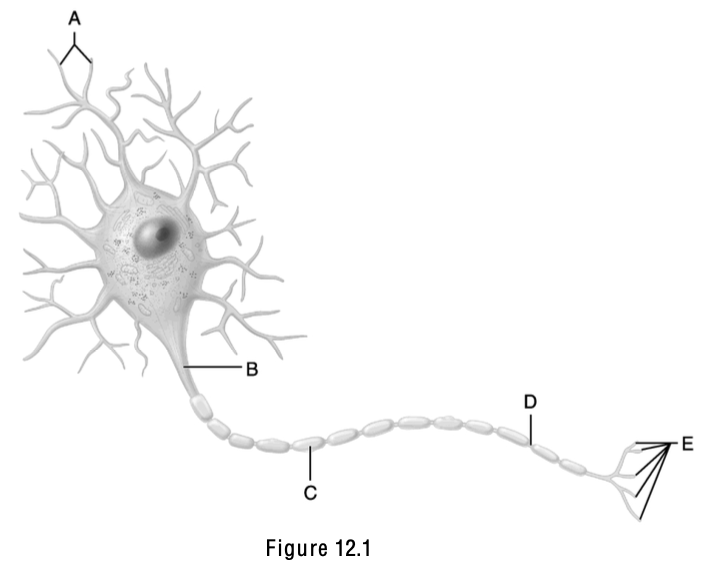
Neurotransmitters are released from this structure.
E
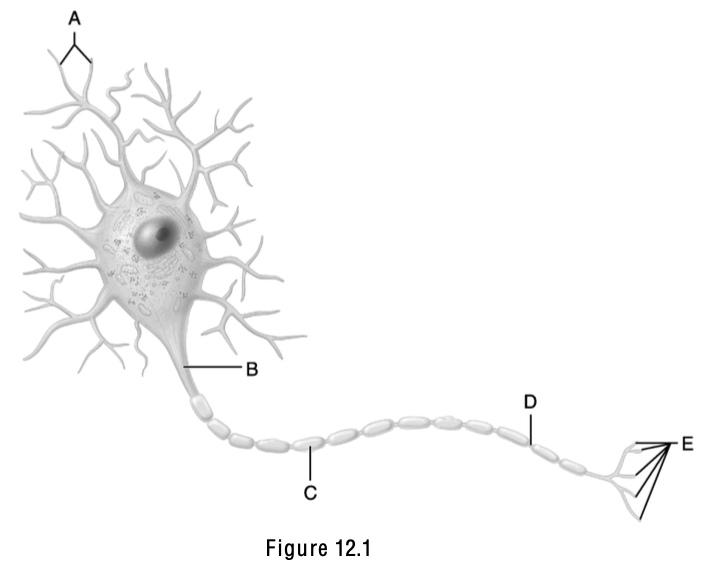
This is the node of Ranvier.
D
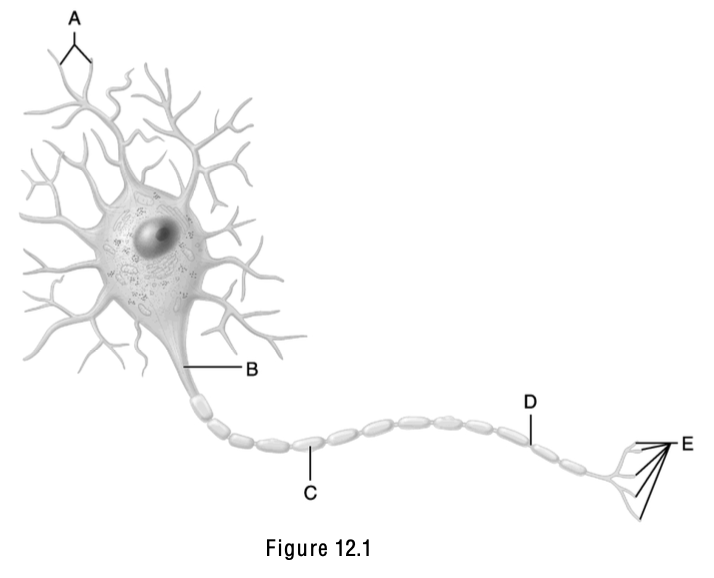
Axodendritic synapses occur between “E” and this structure.
A
True/false; A neuron is a collection of nerve fibers in the PNS.
False
True/false; Most neurons are multipolar neurons.
True
True/false; The somatic nervous system is considered to be the involuntary nervous system.
False
True/false; Microglia are ciliated to help circulate CSF.
False, ependymal cells are ciliated, not microglia.
A somatic motor neuron carries
a. information, such as pain, from the viscera in the ventral cavity to the CNS.
b. motor commands to the skeletal musculature
c. information that signals muscle contraction in the organs in the ventral cavity
d. information from the skin to the CNS
b. motor commands to the skeletal musculature
Which of the following is not a characteristic of neurons?
a. high metabolic rate
b. longevity
c. ability to survive without oxygen
d. inability to divide
c. ability to survive without oxygen
Which of the following is the correct path an impulse takes across a synapse?
a. dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, axon of postsynaptic neuron
b. axon of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
c. axon of postsynaptic neuron, dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft
d. synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron, axon of presynaptic neuron
b. axon of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
Of the following, which is the only structure that is in the PNS, as opposed to the CNS?
a. a ganglion
b. white matter
c. perineurium
d. epineurium
a. a ganglion
The entire nerve is surrounded by a tough fibrous sheath called the
a. endoneurium
b. ectoneurium
c. perieneurium
d. epineurium
d. epineurium
This region of the brain regulates body temperature, hunger, and thirst.
a. hypothalamus
b. cerebrum
c. cerebellum
d. thalamus
a. hypothalamus
Both the cerebrum and this structure have an outer cortical layer of gray matter.
a. hypothalamus
b. cerebrum
c. cerebellum
d. thalamus
c. cerebellum
The fourth ventricle lies between the pons and what other structure of the brain?
a. hypothalamus
b. cerebrum
c. cerebellum
d. thalamus
c. cerebellum
This portion of the brain is the largest part of the diencephalon and forms the upper and lateral walls of the third ventricle.
a. hypothalamus
b. cerebrum
c. cerebellum
d. thalamus
d. thalamus
Nearly all communication to the cerebral cortex must pass through this structure
a. hypothalamus
b. cerebrum
c. cerebellum
d. thalamus
d. thalamus
True/false; the hypothalamus, in addition to the cerebral cortex, is in control of emotional responses.
True
True/false; the Reticular Activating System (RAS) contains structures that regulate and cause emotional responses
False
It is easy to mix up the terms sulcus and gyrus (on the cerebral cortex). The difference between these two structures is that
a. a sulcus corresponds to a folia on the cerebellum, whereas a gyrus corresponds to a fissure
b. a sulcus is the same as a fissure on the cerebral cortex, whereas a gyrus is a lobe
c. a gyrus is a ridge, and a sulcus is a groove
d. a sulcus is a groove, and a gyrus is a deeper groove
c. a gyrus is a ridge, and a sulcus is a groove
The cell bodies located in the anteriormost region of the spinal cord’s gray matter belong to this group
a. somatic motor
b. visceral sensory
c. visceral motor
d. somatic sensory
a. somatic motor
The visual association area of the cerebral cortex is located in the
a. insula
b. frontral lobe
c. occipital lobe
d. parietal lobe
d. parietal lobe
The function of the blood-brain barrier is to
a. prevent all contact between bloodborne molecules and brain tissue
b. keep neurons from innervating blood vessels
c. help protect the central nervous system
d. provide an impenetrable barrier between blood and brain, because the brain gets all its nourishment from the CSF
c. help protect the central nervous system
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by choroid plexuses in all the following locations except the
a. central canal
b. lateral ventricle
c. fourth ventricle
d. third ventricle
a. central canal
The subarachnoid space lies between what two layers of meninges?
a. dura and epidural
b. arachnoid and pia
c. arachnoid and bone of skull
d. arachnoid and dura
b. arachnoid and pia
The cauda equina
a. describes the radiating patterns of projection fibers
b. is a series of nerve roots in the lumbar and sacral regions
c. is confined to the thoracic & cervical segments of the spinal cord
d. consists of hair like the tail of a horse
b. is a series of nerve roots in the lumbar and sacral regions
Two parts of the brain that are most involved in emotions are the
a. medulla and cerebellum
b. red nucleus and substantia nigra
c. cingulate gyrus and hypothalamus
d. superior and anteiror colliculi
c. cingulate gyrus and hypothalamus
The only one of the meninges that follows the brain surface into a cerebral sulcus is the
a. dura mater
b. pia mater
c. arachnoid mater
d. alma mater
b. pia mater
Which of the following grooves separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum?
a. lateral sulcus
b. central sulcus
c. transverse sulcus
d. longitudinal fissure
c. transverse sulcus
Which of the following statements about an axon is false?
a. it carries nerve impulses toward the cell body
b. it has a uniform diameter
c. it is also referred to as a nerve fiber
d. it has branches
a. it carries nerve impulses toward the cell body
A man walking barefoot stepped on a piece of glass. His foot jerked upward in which type of reflex?
a. visceral; monosynaptic stretch reflex
b. somatic; polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
c. somatic; monosynaptic withdrawal reflex
d. visceral; polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
b. somatic; polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
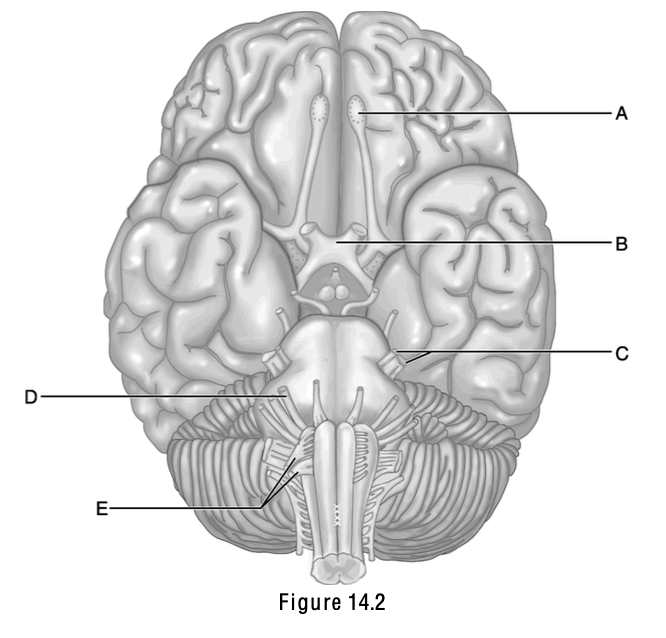
This nerve, whose name bears the fact that it has three major branches, is cranial nerve V.
C (trigeminal nerve)
This carries nerve filaments from the organ of smell.
A (olfactory nerve)
This is the point where the nerve fibers coming from the retina cross over, which is reflected in its name.
B (optic chiasma)
This nerve innervates muscles of facial expression.
D (facial nerve)
True/false; both the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions are part of the somatic motor nervous division.
False
True/false; when you flex your biceps, you are calling on the somatic sensory portion of the nervous system.
False
True/false; all of the following are exteroceptors: tactile corpuscles, lamellar corpuscles, and tactile epithelial cells
True
True/false; one of the largest branches of the sacral plexus is the sciatic nerve
True!
True/false; A nerve plexus is formed by interconnected dorsal and ventral rami of spinal nerves
False
True/false; the sequence of brachial plexus components from medial to lateral is as follows: roots, trunks, divisions, cords.
True!
An example of an encapsulated receptor is
a. a tactile epithelial cell (Merkel disc)
b. a tendon organ
c. a hair follicle receptor
d. a lamellar corpuscle (pacician corpuscle)
b. a tendon organ - technically correct, just not frequently used as an example
d. a lamellar corpuscle (pacician corpuscle)
Sensory input from the skin would follow the
a. sympathetic nerve pathway
b. dorsal root of nerves
c. ventral root of spinal nerves
d. pathway of parasympathetic neurons
b. dorsal root of nerves
Which nerve supplies most of the muscles of the posterior forearm?
a. radial
b. axillary
c. median
d. ulnar
a. radial
If one likens a spinal nerve to the trunk of a tree, then the two roots of this tree are the dorsal and ventral roots. What would represent the first and largest branches of this tree?
a. ventral and dorsal rami
b. rami communicantes
c. dorsal and ventral root ganglia
d. the bracial plexus
a. ventral and dorsal rami
The major nerve plexus to the upper limbs is the
a. cervical plexus
b. lumbar plexus
c. brachial plexus
d. sacral plexus
c. brachial plexus
Contraction rate of the diaphragm is controlled by which nerve?
a. trochlear
b. vagus
c. trigeminal
d. phrenic
d. phrenic
Mixed cranial nerves containing both motor and sensory fibers include all of the following except the
a. vestibulocochlear
b. trigeminal
c. facial
d. vagus
a. vestibulocochlear
Which of the following nerves does not arise primarily from the brachial plexus?
a. radial
b. median
c. ulnar
d. phrenic
d. phrenic
Spinal nerves exiting the spinal cord from the level of L4 to about S5 form the
a. femoral plexus
b. thoracic plexus
c. sacral plexus
d. lumbar plexus
c. sacral plexus
The main nerve to the anterior thigh is the
a. obturator
b. sural
c. sciatic
d. femoral
d. femoral
Which nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus?
a. ulnar
b. median
c. musculocutaneous
d. radial
d. radial
The only cranial nerve that travels into the abdomen is the
a. glossopharyngeal
b. vestibulocochlear
c. hypoglossal
d. vagus
d., vagus
Starting at the spinal cord and proceeding laterally, the subdivisions of the brachial plexus are
a. trunks, divisions, cords, rami
b. rami, divisions, cords, trunks
c. divisions, rami, trunks, cords
d. rami, trunks, divisions, cords
d. rami, trunks, divisions, cords
The general visceral motor division of the peripheral nervous system.
a. parasympathetic division
b. sympathetic division
c. autonomic nervous system
c. autonomic nervous system
Division of the ANS responsible for the fight-or-flight response.
a. parasympathetic division
b. sympathetic division
c. autonomic nervous system
b. sympathetic division
Divisions of the ANS most active during vigorous exercise.
a. parasympathetic division
b. sympathetic division
c. autonomic nervous system
b. sympathetic division
This division can also be called the craniosacral division.
a. parasympathetic division
b. sympathetic division
c. autonomic nervous system
a. parasympathetic division
True/false; preganglionic fibers are myelinated, whereas postganglionic fibers are unmyelinated
True!
True/false; parasympathetic stimulation of blood vessels causes vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure.
False
True/false; sympathetic trunk ganglia contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons and are located in the dorsal root of the spinal cord.
False (Sympathetic trunk ganglia contain the cell bodies of MOTOR neurons)
All of the following have only sympathetic innervation except the
a. blood vessels
b. sweat glands
c. salivary glands
d. arrector pili
c. salivary glands
Which of the following cranial nerves does not supply the parasympathetic fibers to the head?
a. glossopharyngeal
b. facial
c. oculomotor
d. vagus
d. vagus
The sympathetic system causes
a. decreases blood glucose, heart rate, and blood pressure, and increased peristalsis
b. decreased blood glucose and peristalsis, and increased heart rate and blood pressure
c. increased blood glucose, heart rate, and blood pressure, and decreased peristalsis
d. increased blood glucose and peristalsis, and decreased heart rate and blood pressure
c. increased blood glucose, heart rate, and blood pressure, and decreased peristalsis
The trunk ganglia contain what kind of cell bodies?
a. postganglionic parasympathetic
b. preganglionic parasympathetic
c. preganglionic sympathetic
d. postganglionic sympathetic
d. postganglionic sympathetic
Identify the correct sequence of structures through which preganglionic sympathetic fibers pass.
a. dorsal root to gray ramus communicans to sympathetic trunk ganglion
b. ventral root to sympathetic trunk ganglion to white ramus communicans
c. ventral root to white ramus communicans to sympathetic trunk ganglion
d. dorsal root to sympathetic trunk ganglion to gray ramus communicans
c. ventral root to white ramus communicans to sympathetic trunk ganglion
Parasympathetic postganglionic fibers of the head are located within the
a. facial nerve
b. trigeminal nerve
c. vestibulocochlear nerve
d. accessory nerve
b. trigeminal nerve
Which autonomic division increases heart rate?
a. somatic
b. cranial
c. parasympathetic
d. sympathetic
d. sympathetic
In which system do nerve cell bodies lie closest to the organs being innervated?
a. sympathetic
b. somatic motor
c. parasympathetic
d. visceral sensory
c. parasympathetic