Nucleic Acids
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Nucleic acids are the biomolecules responsible for the transfer of genetic information, which polymers are they composed of?
Nucleotide
Nucleic acids are involved in energy metabolism alongside their primary role in genetic information transfer, what are some examples of these molecules mentioned?
ATP, UTP, GTP
What are the monomers used in nucleic acids, which are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group?
Nucleotides
Depending on the parent compound they are derived from, what are the two types of heterocyclic, nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidines, Purines
The pyrimidine nitrogenous bases are characterized by a structure consisting of how many rings and how many atoms?
One ring, six atoms
The purine nitrogenous bases are characterized by a structure consisting of how many rings and how many atoms?
Two rings, nine atoms
Which pyrimidine base is described chemically as 2-oxy-4-amino pyrimidine?
Cytosine
Which pyrimidine base is described chemically as 2-oxy-4-oxy pyrimidine?
Uracil
Which pyrimidine base is described chemically as 2-oxy-4-oxy-5-methyl pyrimidine?
Thymine
Which purine base is described chemically as 6-amino purine?
Adenine
Which purine base is described chemically as 2-amino-6-oxy purine?
Guanine
What is the pentose sugar used for RNA nucleotides?
Ribose
What is the pentose sugar used for DNA nucleotides?
2-Deoxyribose
Phosphate groups of nucleotides are derived from what acid?
Phosphoric acid
Under cellular conditions, the phosphate group derived from phosphoric acid exists in which ionic form?
HPO₄²⁻
In a nucleotide, the bonds that link the three groups use the carbon atoms of the pentose sugar as the reference, which are designated with a number and what other symbol?
Prime
Nitrogenous bases are linked to which carbon atom of the pentose sugar (1’) via a glycosidic bond?
C1
What term is used to refer to nitrogenous bases that are linked to a pentose sugar?
Nucleosides
Phosphate groups are linked to which carbon atom of the pentose sugar (5’) via an ester bond?
C5
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Adenine?
Adenosine
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Adenine?
Adenosine MP
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Guanine?
Guanosine
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Guanine?
Guanosine MP
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Cytosine?
Cytidine
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Cytosine?
Cytidine MP
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Uracil?
Uridine
In ribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Uracil?
Uridine MP
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Adenine?
Deoxyadenosine
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Adenine?
Deoxyadenosine MP
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Guanine?
Deoxyguanosine
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Guanine?
Deoxyguanosine MP
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Cytosine?
Deoxycytidine
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Cytosine?
Deoxycytidine MP
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleoside formed by the combination of Thymine?
Deoxythymidine
In deoxyribonucleotides, what is the nucleotide formed by the combination of Thymine?
Deoxythymidine MP
Nucleotides are linked through their sugar and phosphate groups, what is this resulting structure referred to as?
Nucleic acid backbone
Nucleotides are linked from the 3’ carbon to the 5’ carbon via which specific type of bond?
Phosphodiester bond
What is the name given to the end of a nucleic acid with the free phosphate group?
5' end
What is the name given to the end of a nucleic acid with the free OH group?
3' end
By convention, how are nucleic acids written in terms of their ends?
5' to 3'
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)?
G, C, A, T
What is the pentose sugar found in Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)?
2-Deoxyribose
Where is DNA primarily found?
Nucleus
What is the main function of DNA?
Storage, transfer
How is DNA passed from one cell to another?
Cell division
What structure of DNA refers to the single strand nucleotide sequence, written from 5’ to 3’?
Primary Structure
What structure of DNA refers to the double stranded helix structure?
Secondary Structure
In the DNA secondary structure, if one strand runs from 5’ to 3’, how does the other strand run?
3' to 5' (anti-parallel)
What type of bonds stabilize the double stranded helix structure of DNA between nitrogenous bases of the two strands?
Hydrogen bonds
In the DNA secondary structure, the backbone is oriented outwards, where are the bases oriented?
Inwards
In double stranded DNA (dsDNA), which specific base is always paired with Cytosine?
Guanine
In double stranded DNA (dsDNA), how many hydrogen bonds link Guanine and Cytosine?
Three
In double stranded DNA (dsDNA), which specific base is always paired with Thymine?
Adenine
In double stranded DNA (dsDNA), how many hydrogen bonds link Adenine and Thymine?
Two
According to base pairing rules in dsDNA, the percentage of Adenine (%A) is always equal to the percentage of which other base?
%T
According to base pairing rules in dsDNA, the percentage of Guanine (%G) is always equal to the percentage of which other base?
%C
If human DNA contains 30% adenine, what percentage of thymine, guanine, and cytosine does it contain respectively?
30%, 20%, 20%
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in Ribonucleic acids (RNA)?
G, C, A, U
What is the pentose sugar found in Ribonucleic acids (RNA)?
Ribose
Where is RNA found within the cell?
All parts
What is the main function of RNA?
Protein synthesis
Is RNA generally more or less stable than DNA?
Less stable
What structure of RNA refers to the single strand nucleotide sequence, written from 5’ to 3’?
Primary Structure
What structure of RNA refers to the folding of a single RNA strand?
Secondary Structure
How is the folding of a single RNA strand (secondary structure) stabilized?
Hydrogen bonds
What are the three main RNA molecules involved in the conversion of genetic information into protein products?
Messenger RNA, Transfer RNA, Ribosomal RNA
Which type of RNA carries information from DNA inside the nucleus and takes it to ribosomes for protein synthesis?
Messenger RNA
Which type of RNA's sequence is used by ribosomes as the basis for the amino acid sequence of proteins?
mRNA
Which type of RNA delivers amino acids to the sites for protein synthesis?
Transfer RNA
What is the size range of Transfer RNA (tRNA) in terms of nucleotide units?
75–90
What structure is Transfer RNA (tRNA) described as having, like a 'clover-leaf'?
'clover-leaf' like
What is the three-dimensional (3D) structure of Transfer RNA (tRNA) described as?
L-shaped
Which type of RNA is a component of ribosomes?
Ribosomal RNA
What does Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) allow when messenger RNA (mRNA) enters the ribosome?
Proper binding
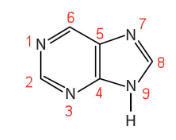
Purine
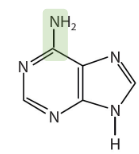
Adenine
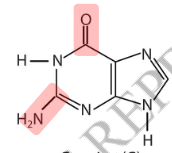
Guanine
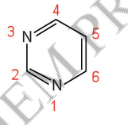
Pyrimidine
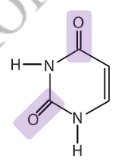
Uracil
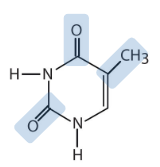
Thymine
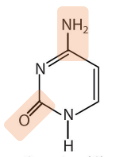
Cytosine