AP HUG Unit 2 Vocab/Concepts
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Ecumene
The areas in which people permanently settle
Ex: Many people have settled in the East Coast and stay there
Physical factors for settlement
Climate: Weathern pattern over time (People tend to lean towards warmer or moderate climates and away from colder ones and lower latitudes for rainfall)
Landforms (Is the place accessible and good for making a home? People like areas with arable land or resources)
Water bodies (Can people get water? They tend to live near lakes, rivers, etc.)
Human factors for settlement
Culture (People tend to live near people with a shared culture)
Economics (People need to get money and trade for goods)
History (Is the place known for having wars, dangers, or conflicts with nearby people?)
Politics (Do people like their amount of freedom and type of government?)
Density vs. Distribution
Distribution: WHERE people are in an area (spatial)
Density: HOW MANY people are in an area (numerical)
Arithmetic population density
Population density calculated by dividing people per a certain unit of space
Ex: There are about 38 people/km in the US
Physiological population density
An arable land population density calculated by dividing people by the amount of arable land in an area
Ex: China has a physiological population density of aboute 1310 people/arable km²
Agricultural population density
A population density measuring farmers per unit of arable land
Ex: Australia has over 325,000 people employed in agriculture and about 312,000 km² of arable land, so they have an agricultural population density of about 1 person per km² of arable land
Demographers
People who study population and the age, health, gender, ethnicity, and other factors possibly affecting how people are spread out
Carrying capacity
The amount of dependence an environment can withstand before being damaged (Depends on technology and size/type of environment)
Ex: The acre of land can only have a certain amount of wheat grown on it
Questions raised by population distribution
Political: Can the government cover and adapt for a growing or shrinking population? How can they be represented in government? Can they provide basic necessities?
Economic: Are there enough jobs for more people? Can the economy support itself? Can people take up enough jobs? Are people able to get jobs near them?
Social: Are there enough medical people to support the population? Are there enough schools for kids? Do the elderly have enough support and nursing homes?
Age structure
The portion of the total population for a certain age group
Ex: The amount of people 85+ years old in the U.S. is about 1-2%
Population pyramid
A diagram used to represent population structure by cohorts and amounts of individuals per group (often has a male and female side with margins of 5 years in an age-sex composition graph)
Can also show wealth, political stance, etc.
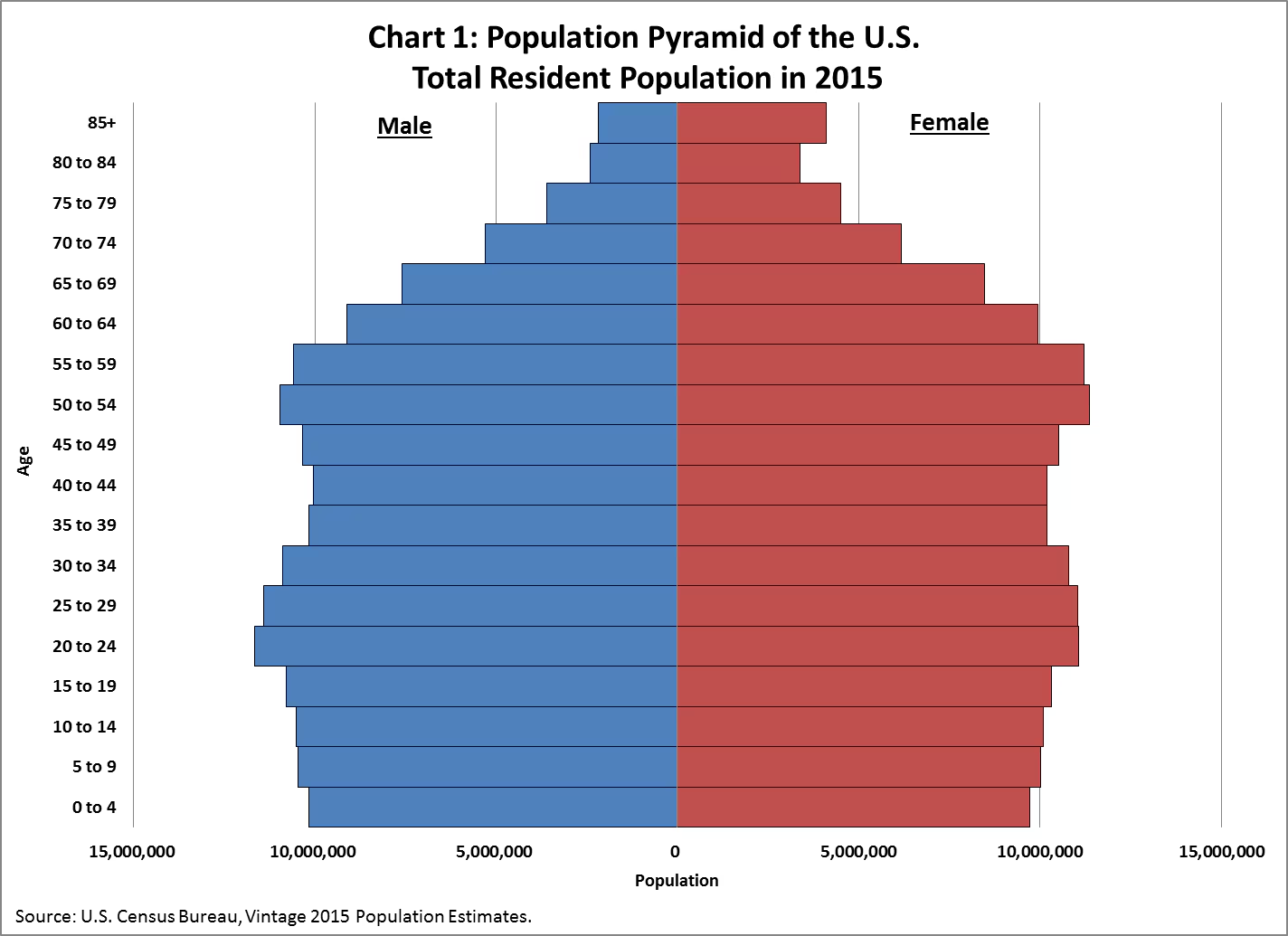
Properties of a population pyramid
Wide base and narrow head: Rapid growth (Stage 2)
Narrow base but still bigger than the rest: Slow growth (Stage 3)
Wide middle: Growth is slowing (Stage 4)
Wide head: Population is declining (Stage 5)
Random big cohort: Population boom
Sex ratio
The ratio of males to females in a population (If <1 more females if >1 more males)
Ex: The U.S. has a sex ratio of 104:100 =1.04
Thomas Malthus
An enlightenment thinker who believed that population booms (mostly the one after the Scientific Revolution) would be unsustainable and they would outgrow the food supply
He was incorrect and we improved farming methods and technologies
DTM Stage 1
Low growth
Low LE
High death/birth rates
No migration
Often young population
Ex: Rural Bangladesh, Amazon Rainforest
DTM Stage 2
Increasing growth
Increasing but still low LE
High birth rate but lower death rate
Out-migration
IMR and MMR decrease
Young population
Ex: Sri Lanka, Peru, Ethiopia
DTM Stage 3
Out-migration
Lots of people are born
Lower birth and death rates
Medium LE
Ex: India, China, Mexico
DTM Stage 4
Slowing growth
Decreasing birth rates but slightly lowered death rates
In-migration
Balanced population
Peak LE
Ex: USA, Canada
DTM Stage 5
Population decline
Birth rates fall below death rates and death rates increase
Aging population
Lowered LE
Ex: Japan, Germany
Crude birth rate(CBR)
Total # of live births in an area for every 1000 people alive
Crude death rate(CDR)
Total # of deaths per 1000 people in an area
Total fertility rate(TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have
Where people live
Midlatitudes
Near fresh water
Near resources
Arable land
Low altitudes
Agglomeration effects
Businesses/necessities that grow around a shared industry in the same area
Ex: glass beaker factory near an Amgen area of biotech labs
Rate of natural increase (RNI)
(Crude birth rate - crude death rate)/10
Demographic (population) change
Births - deaths + immigration - emigration
True fertility rate(TFR)
The number of births that live to childbearing age (technically adolescence) and heavily affected by IMR
Doubling time
The time it takes a population to double (Longer for more developed country)
Formula is 70/RNI
Pro-natalist/expansive population policies
Policies encouraging women to have children
Ex: Kamala Harris’ $6000 tax credit
Anti-natalist/restrictive population policies
Policies discouraging or preventing women from having children for economic/political reasons
Ex: One-child policy in China
Eugenic population policies
Policies limiting or preventing people of a certain ethnic or cultural group from having children in an attempt to limit or eliminate their population (typically motivated by ignorance or prejudice)
Ex: Nazi Germany
War’s effects on births
Causes a birth deficit (due men on the front line/ parents creating a better life for kids)
Often followed by a baby boom (followed by a baby bust until echo)
When boomers have children it causes an echo
Ex: Boomers in USA
Dependency ratio
Amount of people dependent on an area’s workforce (working age people)
(% under 15 + % over 64) to % working age
Ex: (20%+20%):60% = 40:60
Epidemiological Transition Model
Corresponds with DTM
Stage 1: Pestilence(disease) and famine — high CDR, low LE
Stage 2: Receding Pandemics(like AIDS) — decreasing CDR, increasing LE
Stage 3: Degenerative and Human-Created Diseases(chronic) — stable CDR, increasing LE
Stage 4: Delayed Degenerative Diseases(really old people) — low CDR, peak LE
Stage 5: Reemerging of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases (due to a use of antibiotics) — LE decreases
Migration
The permanent or semi-permanent relocation of people
Ex: I move from TO to NYC
Remittances
Money sent by migrant workers from one country to country of origin (usually to support family members)(also hurts the economy of the country money is sent out of)
Ex: Workers from Mexico go to the United States and send money back to their families in Mexico
Cyclic movement
Short periods away from home, nomadism, commuting (happens in most active people’s lives)
Ex: I go from home to TOHS, then other places
Periodic movement
Long periods away from home
Ex: Migrant workers, military, college
Transhumance
The movement of livestock in accordance to the seasons
Ex: Bird migration in spring
International vs. internal/intranational migration
International migration: Migration from one country to another
Ex: Movement from Spain to Portugal
Internal/intranational migration: Movement from one area of a country/area to another area in the same country/area
Ex: Movement from LA to Phoenix
Counter migration
The idea that as people move in, others tend to move out
Ex: People in Texas leaving because Californians are moving in
Forced migration
Involuntary migration due to political issues
Ex: Pilgrims moving out of England because they were religiously persecuted by the government
Voluntary migration
People choose to move for better opportunity, lifestyle, etc.
Ex: Mr. Daigneault moves to TO
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
Every migrant flow generates a return or counter-migration
The majority of migrants move a short distance
When migrants do travel long distances they usually move in steps
Migrants who move long distances tend to choose big cities
Urban residents are less migratory than people of rural areas
Families are less likely to make international moves than young adults
Gravity Model
Mathematical model of interaction between places
Formula: (Population of City 1 x Population of City 2)/Distance²
Push/pull factors
Factors that either draw people in to somewhere or make them want/need to leave
Push include: Natural disasters, war, economic, social, cultural, environmental or political issues
Pull include: Kinship links, chain migration, and social, cultural, political, or economic opportunity
Internally displaced people vs. refugees
Internally displaced: Had to move because of a push factor but still lives in same country
Refugees: Had to move because of a push factor but lives in different country
Kinship links
When migrants pull other family members into moving to the same place
Chain migration
When one person moves, then drawing another person, then another person, etc.
Causes immigration waves and results in ethnic enclaves(like Koreatown)
Distance Decay Model
Model emphasizing that friction of distance reduces interaction between places as they get farther apart (relates to Gravity Model)
When women are educated
They are able to better care for the children they have
The have children later in life because they are continuing their education
They often want to utilize their education so they have fewer children in order to work
Maternal mortality rate
Number of female deaths related to pregnancy per 100,000 live births
Intervening obstacle
A negative obstacle that stops migrants from reaching their intended destination
Ex: Migrants run out of money on their journey
Intervening opportunity
A positive pull factor that encourages migrants to go elsewhere from their intended destination
Ex: A migrant from Florida going to California finds that land is cheaper in Texas
ESPN
Stands for economic, social, political, and environmental and can be used to analyze factors and consequences at a higher level
Determinants of an aging population
Crude birth rates
Infant mortality rates
Total fertility rates
Crude death rates
All change life expectancy
Census designated place
Unincorporated areas not grouped in a county and possibly cities/town
Neo-Malthusian Theory
The modern theory that human population growth will eventually exceed the local environment’s ability to grow enough food to support them and that overpopulation needs to be addressed immediately
Ex: South Sudan has too large a population to support its own population
Types of checks on population
Preventive: Choices by humans to reduce population growth
Ex: Moral restraint, birth control
Positive: Checks on population causes by the environment and nature
Ex: Disease, natural disasters, starvation