CH220C Aldol Condensation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are we studying in the adol condensation lab?
the synthesis of trans-p-anisalacetophenone via an aldol condensation rxn
what is an aldol reaction?
an addition rxn of an enol or enolate to a carbonyl compound such as aldehyde or ketone
what is the product of just the aldol reaction and what does this turn into, generally?
a beta-hydroxy carbonyl compound
it produces an alpha,beta-unsaturated compound
how is the enolate formed in the reaction?
the OH- grabs an alpha proton, forming a negative charge on the alpha carbon
does acetophenone or p-anisaldehyde have alpha hydrogens?
only acetophenone
the compound that has alpha hydrogens is _______________ and will be converted into _____________ by NaOH
nucleophilic, enolate
is an enolate resonance stabilized?
yes!
at elevated rxn Ts, why does an a,B-unsaturated compound form?
it is more energetically stable due to the creation of extended conjugation (pi-way, single-double-single-double, etc.)
do we need to preform the enolate? why/why not?
no
because only acetophenone has alpha carbons, so only one enolate is formed
what is the general rxn for the aldol condensation? *be able to draw out the complete mechanism*
acetophenone + p-anisaldehyde + NaOH + heat --> 3-hydroxy-3-(4-methyoxyphenyl)-1-phenylpropan-1-one --> trans-p-anisalacetophenone + H2O
describe the 6 steps of the procedure for the aldol condensation
1. add .2mL p-anisaldehyde, .2mL acetophenone, and 1mL ethanol to a 5mL conical vial w/ a small rice stirbar
2. add 3 drops of 50% NaOH soln
3. stir for 10 min until soln solidifies (takes <5 min) reaction is completed when stir bar can no longer rotate
4. while rxn is stirring, set up buchner filtration apparatus
5. filter solid product, rinse w/ cold ethanol
6. save the product for next week for mass MP, and IR
is the aldol condensation lab hard? how can you fail?
no! it is very simple and quick
you can fail if you add the wrong reactants
how do you know the rxn is complete?
the stir bar can no longer rotate
in general, how do you use the IR?
1. clean plate w/ isoproponal before and after
2. allow plate to air dry
3. inspect underside of press for contamination
4. turn press indicator until 1/2way green (if red, unscrew-anvil can crack)
rate of increase should be no more than _____________ for mel temp
2°C per min
what is the solvent for this reaction?
ethanol
aldol reactions are important ways to form new _____________________
carbon-carbon bonds
what is an aldol?
a molecule that contains both aldehyde and alcohol functional groups
what is the pka of the protons of the alpha carbon?
about 18-20 pka (pretty acidic for a C = C can be deprotonated to become nucleophilic)
is NaOH capable of deprotonating an alpha carbon w/ protons?
yes
why are the H's on the alpha carbon so acidic?
because the conjugate base is resonance stabilized
how are new C-C bonds formed in aldol condensations?
nucleophilic carbons (w/ formal negative charges) can attack a carbonyl carbon (electrophilic)
what protonates the negative oxygen intermediate?
water
how can a dehydration rxn occur?
there are still 2 acidic Hs on the molecule to grab to form a more stable double bond
is the final product cis or trans, why?
trans- more stable isomer
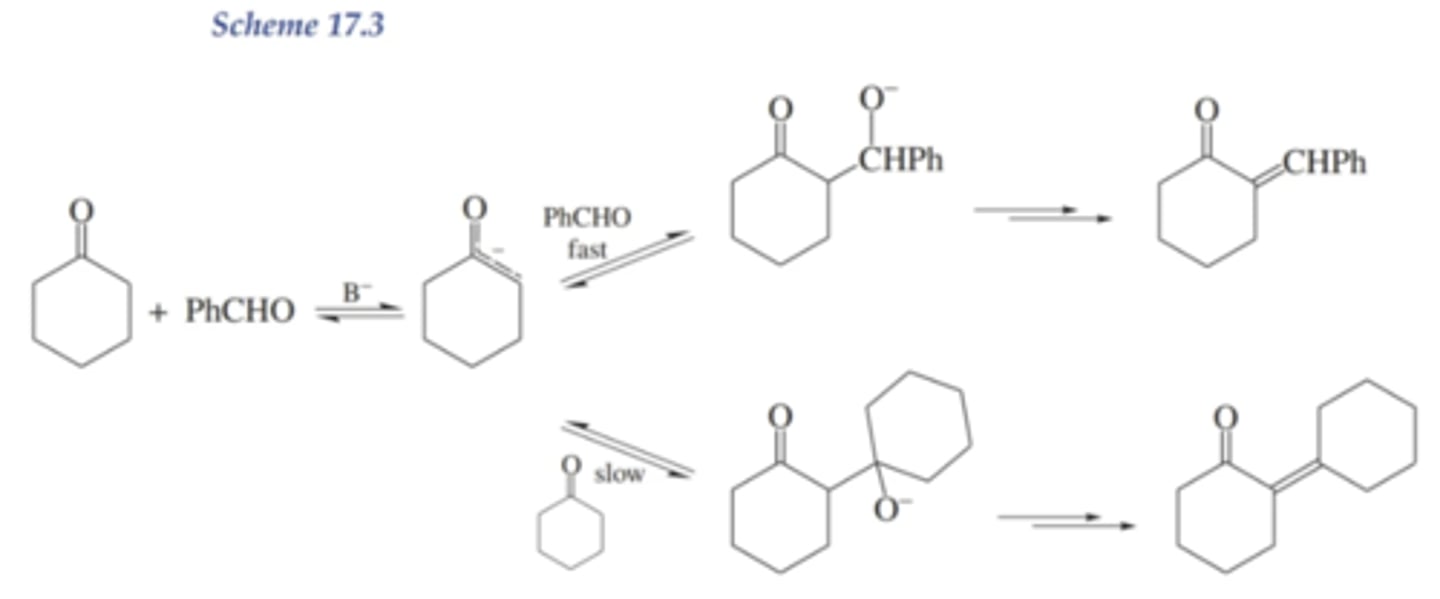
Could the enolate ion from acetophenone add to another acetophenone molecule?
yes
why isn't the product formed by the rxn of the enolate w/ another molecule of acetophenone the major product?
because the addition to aldehydes is faster than to ketones, so p-ansialdehyde is the preferred electrophile
the other rxn is much slower
What is the Cannizzaro Reaction?
side reaction when 2 molecules of anisaldehyde reacts with NaOH to form a carboxylic acid on one aldehyde an alcohol on the other
what is the problem with mixed aldol reactions?
there are multiple potential enolates and electrophilic carbonyls, so multiple products are made that are hard to separate
what are 2 ways to solve the problem of mixed aldol rxns?
1. prepare enolate on its own before (NaOH - not strong enough, equilibirum to left) (LDA- strong enough)
2. only use one aldol w/ alpha protons, have one aldol be a better electrophile (WE ARE DOING THIS)
why are aldehydes better electrophiles than ketones?
less steric hindrance
what data are we collecting in the aldol condensation?
MP, % yield, IR
is the final product a solid?
yes
what is the main source of product loss in the aldol rxn?
transfer issues because it is microscale (very small)
what are we looking for on the IR?
carbonyl peak
no methyl peak
no OH peak
what are the symptoms, prevention, and first aid for the ingestion of methanol?
S: inebriation, drowsiness, coughing, headache, dullness, weakness, vertigo, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, blindness
P: do not eat or drink in lab
FA: if vomiting occurs, keep head lower than hips, get medical attention if needed
why do we add 100% alcohol?
to prevent the reaction from reversing (we add it in excess)
why do we add sodium bicarbonate into ice water?
add the sodium bicarbonate w ice water bc is an exothermic rxn (i think)
methanol
possible mutagen
sulfuric acid solution
known carcinogen
sodium sulfate
carcinogen, mutagen
diethyl ether
Possible mutagen
what makes a-hydrogen more acidic
stabilization through inductive effects and resonance
why can we use NaOH to perform reaction rather than needed a strong base like LDA
Because steric and electronic effects. Aldehydes are better electrophiles than ketones bc steric hinderance
What are two ways in which the a-carbon atoms can become nucleophilic
- deprotonation to form enolate ion
- keto–enol equilibration, called tautomerization, to give an enol
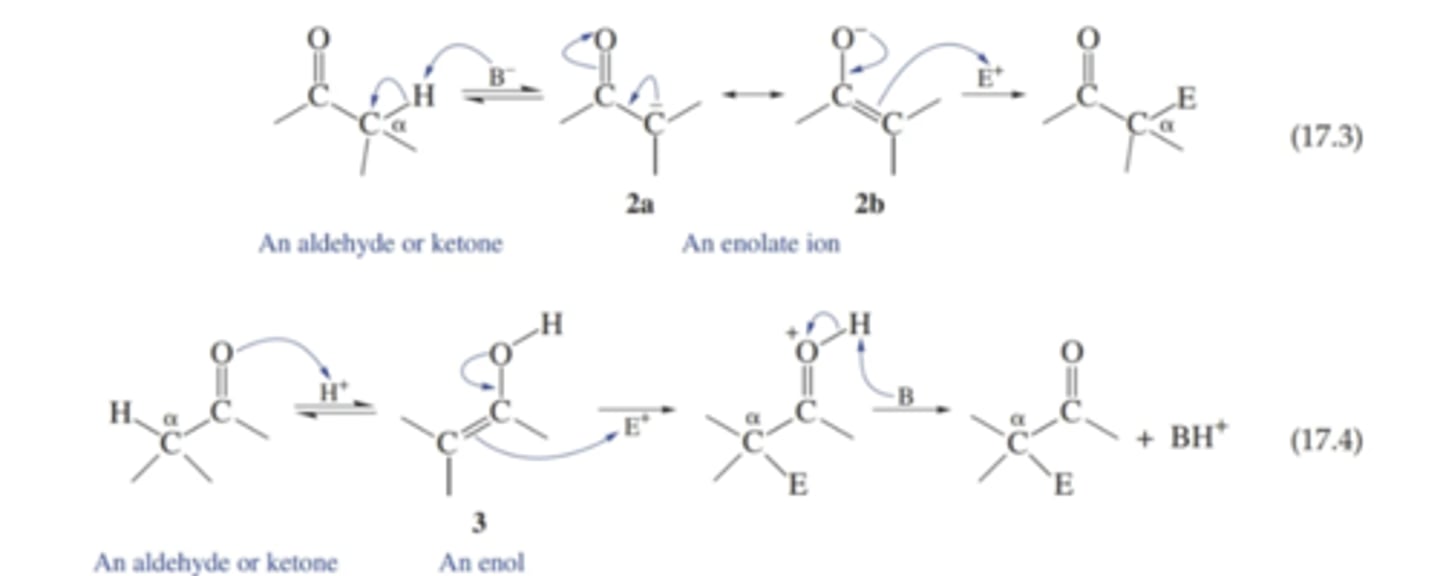
What is a mixed or crossed-aldol condensation
two different carbonyl compounds are the reactants