Social Psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:09 PM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
1
New cards
Brewer and Gardner’s 3 types of self
Individual, relational and collective
2
New cards
Tajfel and Turner split identity into 2 types
Social and personal
3
New cards
Social identity
Group membership
4
New cards
Personal identity
individual traits
5
New cards
Individual self
personal traits
6
New cards
relational traits
assimilates you to others e.g mum
7
New cards
collective
group membership e.g student
8
New cards
The age children develop self awareness
1 & 1/2 or 2
9
New cards
Gallup’s test for self awareness
mirror test
10
New cards
Public self
social image
11
New cards
private self
thoughts, feelings, attitudes
12
New cards
Heightened self awareness
If you know you are happy or sad you become more happy or sad
13
New cards
We store self knowledge using
schemas
14
New cards
self-schematic
important part of self schema
15
New cards
aschematic
less important part of self schema
16
New cards
Control theory of self regulation
set yourself standards and see if you meet them
17
New cards
self-discrepancy theory
3 self schemas: actual, ideal and ought
18
New cards
Social comparison theory
compare to others to gauge self performance
19
New cards
downwards social comparison
seeking worse people to make yourself feel better
20
New cards
upwards social comparison
compare ourselves to someone better - often dismiss
21
New cards
Medvec olympic study
bronze medalists looked significantly happier than silver medalists
22
New cards
Social identity theory
we use different self concepts based on contextual factors
23
New cards
self categorisation theory
how social identity theory works cognitively
24
New cards
Attribution
process of assigning a cause to our own and other’s behaviour
25
New cards
top down processing is
theory driven
26
New cards
category
organised hierarchically (associative network) - fuzzy sets of features organised around a prototype
27
New cards
prototypes
cognitive representation of typical defining features of a category (average category number)
28
New cards
casual attribution
an inference process through which perceivers attribute an effect to one or more causes
29
New cards
The naive scientist is
logical and tests hypotheses
30
New cards
Naive scientist 3 principles (need to)
form a coherent view of the world, gain control over environment and needs to identify internal and external factors
31
New cards
Attributional theory is
casualty of success or failure
32
New cards
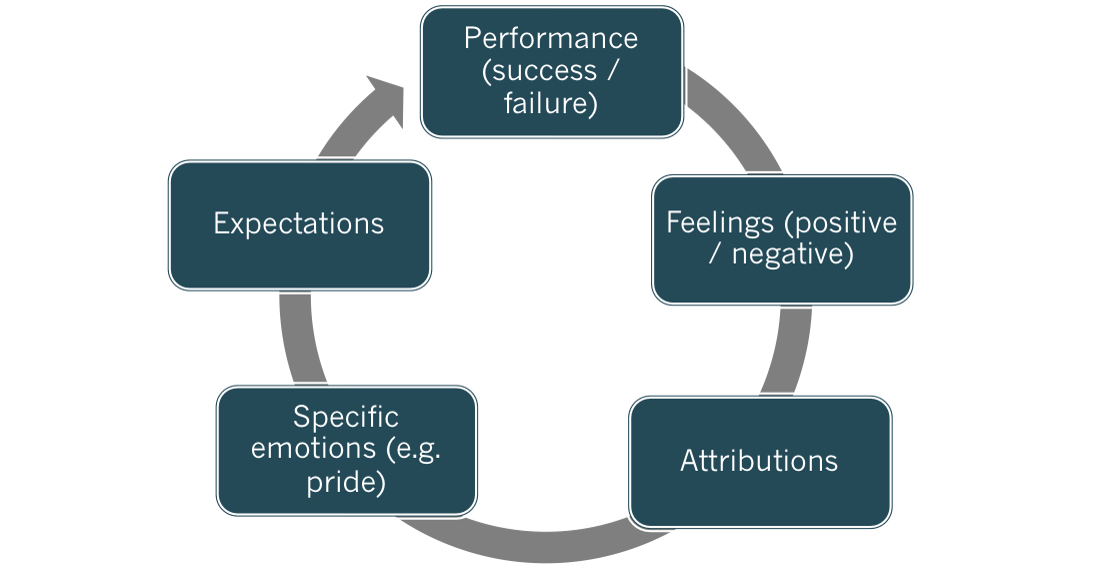
Attributional theory
33
New cards
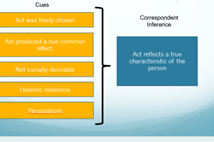
Correspondent inference theory
34
New cards
Co -variation model
use multiple observations to try to identify factors that co-vary with behaviour
35
New cards
Naive psychologist theory
Heider 1958
36
New cards
Attributional theory
Weiner 1979
37
New cards
Correspondent inference theory
Jones and Davis 1965
38
New cards
Covariational model
Kelley 1967
39
New cards
3 components of the co variation model
consistency, distinctiveness, consensus
40
New cards
Attributional biases
systematic errors indicative of shortcuts, gut feeling, intuition
41
New cards
false consensus reasoning
we seek out those that are similar
42
New cards
fundamental attribution error
tendency to attribute behaviour to enduring dispositions
43
New cards
Example of fundamental attribution error
expecting the quiz master to be knowledgeable
44
New cards
Actor-obsever bias
see someone else as rude, see yourself as having a bad day
45
New cards
self-serving bias
success due to internal factors failure due to external factors
46
New cards
Heuristics
mental shortcuts
47
New cards
Why do we use heuristics?
it’s quick and easy
48
New cards
Availability heuristics
judge how frequent something is based on ease of thinking of examples
49
New cards
Representative heuristic
judge based off a small sample
50
New cards
Anchoring heuristic
judge based off examples (salesman)
51
New cards
Attitude
a relatively enduring organisation of beliefs/ a general feeling or evaluation
52
New cards
3 component model for attitude
ACB
53
New cards
ACB stands for
Affective (feelings), cognitive (beliefs), behavioural (actions)
54
New cards
simple dimension attitude
I love dogs
55
New cards
complex dimension attitude
I love that dogs are friendly but they smell
56
New cards
Attitudes become stronger if
they are complex and evaluated frequently
57
New cards
Katz 4 functions of attitude
knowledge, utilitarian, ego-defensive and value expression
58
New cards
mere exposure effect
repeated exposure of a stimulus - enhancement of preference for that stimulus
59
New cards
instrumental conditioning
behaviour repeated if you get a positive consequence eg positive praise
60
New cards
our attitudes come from self perception theory - Bem
gain knowledge about ourselves by infering fromm our own behaviour
61
New cards
reliability
consistent results over time
62
New cards
validity
results are true
63
New cards
Lapiere 1934 racial prejudice study
92% of resturants said they wouldn’t serve a chinese couple when actually 95% did without hesitation
64
New cards
Attitudes usually predict
behaviour but not always eg smokers thinking smoking is unhealthy
65
New cards
Things that impact how well attitude predicts behaviour
whether it is formed through direct experience and how specific the asked questions are
66
New cards
cognitive dissonance
a person has 2 or more thought that don’t fit in together
67
New cards
How to change an attitude
reduce importance, add an element, change one element
68
New cards
Dual process model central route
When message is followed closely, considerable cognitive effort expended
69
New cards
Dual process model peripheral route
When arguments not well attended to; peripheral cues
70
New cards
systematic processing
When message is attended to carefully; scan & consider available arguments
71
New cards
heuristic processing
Use cognitive heuristics - e.g., ‘statistics don’t lie’
72
New cards
How knowledge of attitudes are used in the real world
adverts
73
New cards
A group
2 or more individuals having a face to face interaction
74
New cards
Types of groups
strong interpersonal relationships e.g families, groups formed to fulfill tasks eg offices
75
New cards
groups based on large social categories
women, america
76
New cards
groups based on weak social relationships
people who dont like taylor swift, people from Nottingham
77
New cards
transitory groups
people
78
New cards
social facillitatuion
triplett found that people go faster when racing or being timed when alone
79
New cards
audiences are ‘merely present’
entirely passive and unresponsive audience that is only physically present
80
New cards
species that go faster when other members of their group are doing the same
kangeroos, monkeys and horses (pays et el)
81
New cards
social inhibition
sometimes the presence of an audience can wosren performance, bond and titus
82
New cards
Zajonc’s Drive theory
Audiences make anxious people better on tasks they are already good at and worse on ones they normally struggle with
83
New cards
Evaluation apprehension
Social facilitation is an acquired effect based on percieved evaluations of others
84
New cards
Evaluation apprehension is unnecessary
for social facilitation
85
New cards
Distraction-conflict theory
People do worse on a task when distracted by others
86
New cards
social loafing
when someone outs in less effort beacuse they are being judged as part of a group
87
New cards
Geen on social loafing
when other people om the group don’t put in effort it makes you loose motivation too
88
New cards
How to reduce social loafing
identifiability and individual responsibility
89
New cards
collective effort model
people put in effort if they think their effort will have impact and if they could get good rewards
90
New cards
group problem solving
better results in smaller groups when ideas are critiqued
91
New cards
Janis’ ‘groupthink’
where opositions’s to poor group decisions are supressed to maintain harmony
92
New cards
social norms
unwritten rules of how to behave in society
93
New cards
social influence
when attitudes/behaviours are influenced by other people
94
New cards
Sherif autokinetic effect
people use judgements of others as a framework in ambiguous situations
95
New cards
Asch line judgement conformity
33%
96
New cards
Asch line anonymous conformity
12\.5%
97
New cards
normative influence
want to fulfill other’s expectations - surface compliance
98
New cards
informational influence
believe others have correct opinions - true cognitive change
99
New cards
majority influence
produces public compliance via social comparison
100
New cards
minority influence
produces indirect, private change in opinion; conversion effect as a consequence of active consideration of minority point of view