Ch. 8 Joints - Dr. Jones
joints / articulations
where bones meet and where they come together
-gives skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
structural type of joints
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
joints / articulations
where bones meet and where they come together
-gives skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
structural type of joints
synarthroses
immovable joints
amphiarthroses
slightly moveable joints
diarthroses
freely moveable joints
sutures
[fibrous joint]
rigid, interlocking joints of skull that allow growth during youth
-contain short connective tissue fibers that allow for expansion
synostoses
[fibrous joint]
closed immovable sutures
syndesmoses
[fibrous joint]
bones connected by ligaments, bands of fibrous tissue
-short fibers offer little to no movement
-longer fibers offer a larger amount of movement
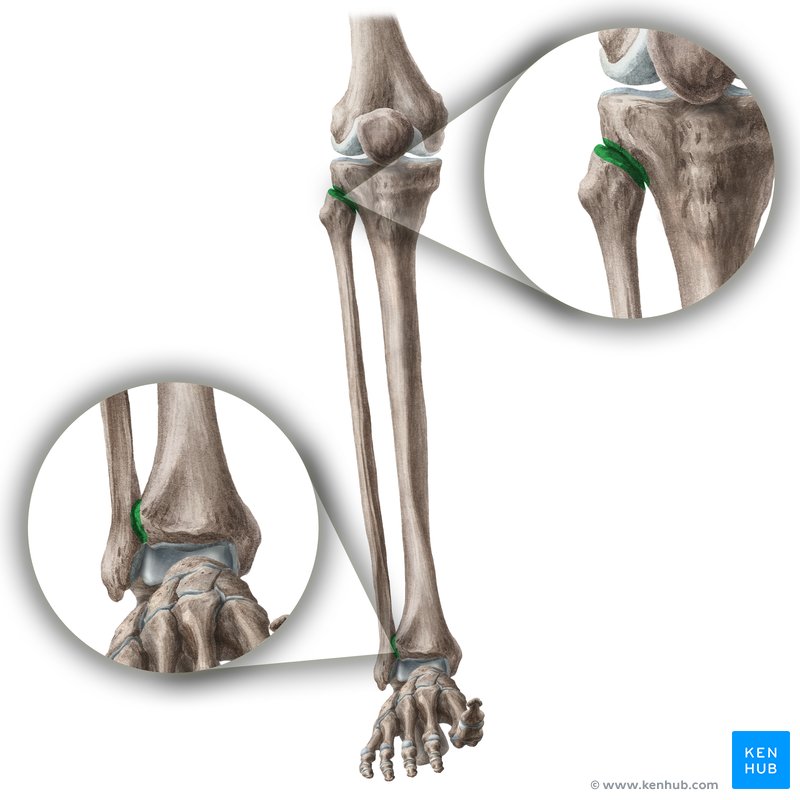
syndesmoses
inferior tibiofibular joint
fibrous joints
bones connected by dense fibrous connective tissue
-no joint cavity
-most immovable
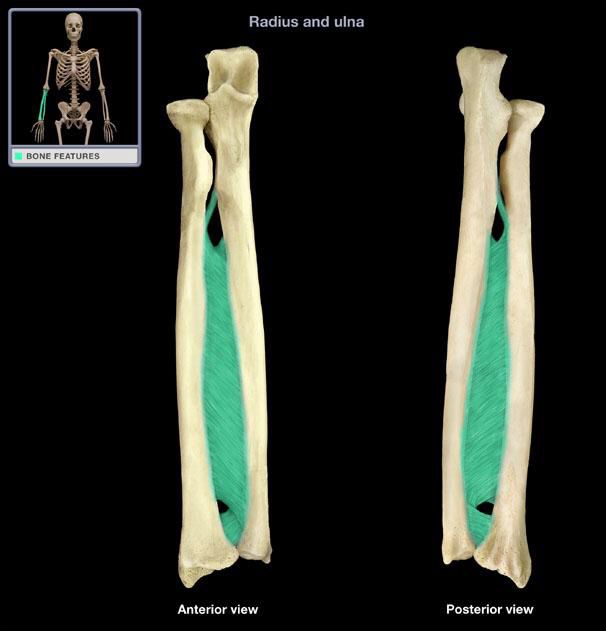
syndesmoses
interosseous membrane conneccting radius and ulna
gomphoses
[fibrous joint]
peg-in-socket joints
-teeth in alveolar joints, holding tooth in socket
-fibrous connection is periodontal ligament
cartilaginous joints
bones united by cartilage
-have no joint cavity
-not highly moveable
-2 types: synchondroses, sympheses
synchondroses
[cartilaginous joint]
unite bones with a bar or plate of hyaline cartilage
-almost all synarthrotic (immovable)
synchondroses
temporary epiphyseal plate joints
synchondroses
cartilage of first rib with manubrium (top portion) of sternum
symphyses
[cartilaginous joint]
unite bone with fibrocartilage
-strong, amhiarthrotic (slightly moveable) joints
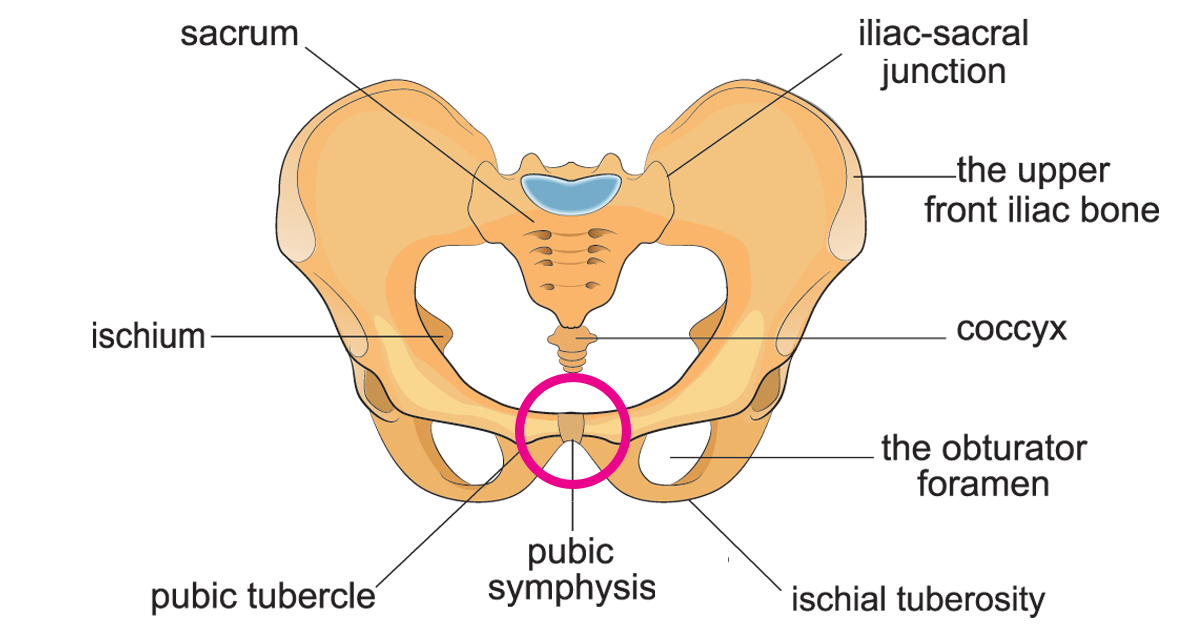
symphyses
pubic symphysis
symphyses
intervertebral joints
synovial joint
seperate bones with fluid-filled joint cavity
-all are diarthrotic (freely moveable)
-all limb joints
-have bursae and tendon sheaths
articular cartilage
[synovial joint general feature]
-hyaline cartilage covering ends of bones
-prevent crushing of bone ends
joint (synovial) cavity
[synovial joint general feature]
small, fluid-filled space unique to synovial joints
-minimize friction
articular (joint) capsule
[synovial joint general feature]
-external fibrous layer: dense irregular connective tissue hold everything in position
-inner synovial membrane: loose connective tissue that makes synovial fluid to lubricate joint
synovial fluid
viscous slippery filtrate of plasma and hyaluronic acid that lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage
fatty pad
cushioning between fibrous layer of capsule and synovial membrane or bone
-found in synovial joint
articular discs (menisci)
ensure tight fit between bone
-reduce wear and tear
bursae
“pillow” of synovial fluid that act as lubrication
-reduce friction where ligaments, muscles, skin, tendons, or bones rub together
tendon sheath
elongated bursae wrapped completely around tendons subjected to friction
shape of articular surfaces, ligament number and location, muscle tone
factors influencing stability f synovial joints
gliding movements
one flat bone surface glides or slips over another similar surface (slide alongside each other)
angular movements
increase or decrease angle between two bones
-movement along sagittal plane
flexion
decreases the angle of the joint
extension
increases the angle of the joint
hyperextension
movement beyond anatomical postion
abduction
away from midline
adduction
toward midline
circumduction
involves flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction; moving in a cone in space
rotation
turning of bone around its own long axis toward midline or away from it
medial
rotation toward midline
lateral
rotation away from midline
supination
palms face anteriorly
-radius and ulna are PARALLEL
pronation
palms face posteriorly
-radius ROTATES OVER rulna
opposition
movement of thumb
dorsiflexion
bending foot toward shin
plantar flexion
pointing toes
inversion
sole of foot faces medially
eversion
sole of foot faces laterally
elevation
lifting body part superiorly
-shrugging shoulders
depression
lowering body part
-opening jaw
protraction
mandible juts out
retraction
mandible is pulled toward neck
femoropatellar joint
-allows gliding motion along femur during knee flexion
tibiofemoral joint
lateral and medial joint
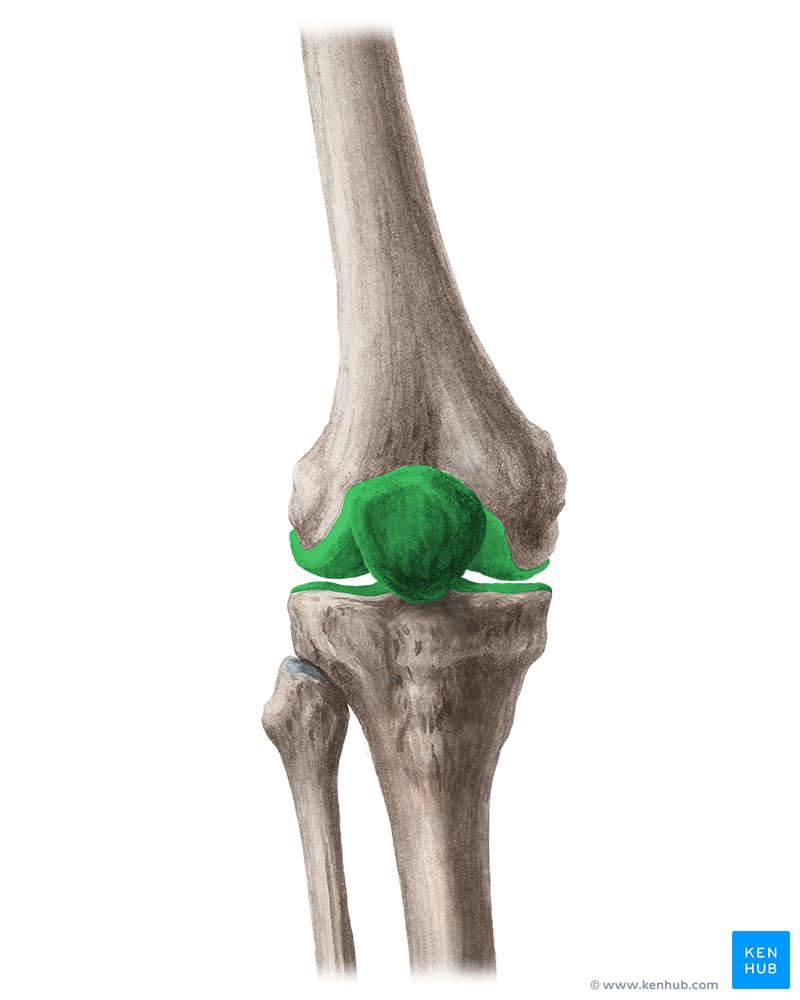
hinge joint
allows flexion, extension, and some rotation when knee is partly flexed
fibular/tibial collateral ligaments, oblique popliteal ligament, arcuate popliteal ligament
acts as straps for support (more mobility, need more stability)
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
-attaches to anterior tibia
-prevents forward sliding of tibia and stops hyperextension of knee
posterior cruciate ligament
-attaches to posterior tibia
-prevents backward sliding of tibia and forward sliding of femur
collateral ligaments, cruciate ligaments, cartilages (menisci)
common knee injuries (3 C’s)
cartilage tears
tearing menisci, due to compression and shear stress
-repaired with arthroscopic surgery
arthroscopic surgery
minimally invasive surgery; meniscectomy
sprains
reinforcing ligaments are stretched or torn, partial tears repair very slowly because of poor vascularization
dislocations (luxations)
bones forced out of alignment
-accompanied by sprains, inflammation, and difficultly moving joint
subluxation
partial dislocation of a joint
bursitis
inflammation of bursa, usually caused by blow or friction
tendonitis
inflammation of tendon sheaths, typically caused by overuse
arthritis
inflammatory or degenerative diseases that damage joints
osteoarthritis
most common type of arthritis
-seen mostly in females due to hormones
-degenerative “wear and tear” arthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disease of unknown cause (immune system attacks own cells)
gouty arthritis
deposition of uric acid crystals in joints and soft tissues, more common in males
-typically affects joint at base of great toe (hallux)