Renal & Digestive Systems
1/262
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
263 Terms
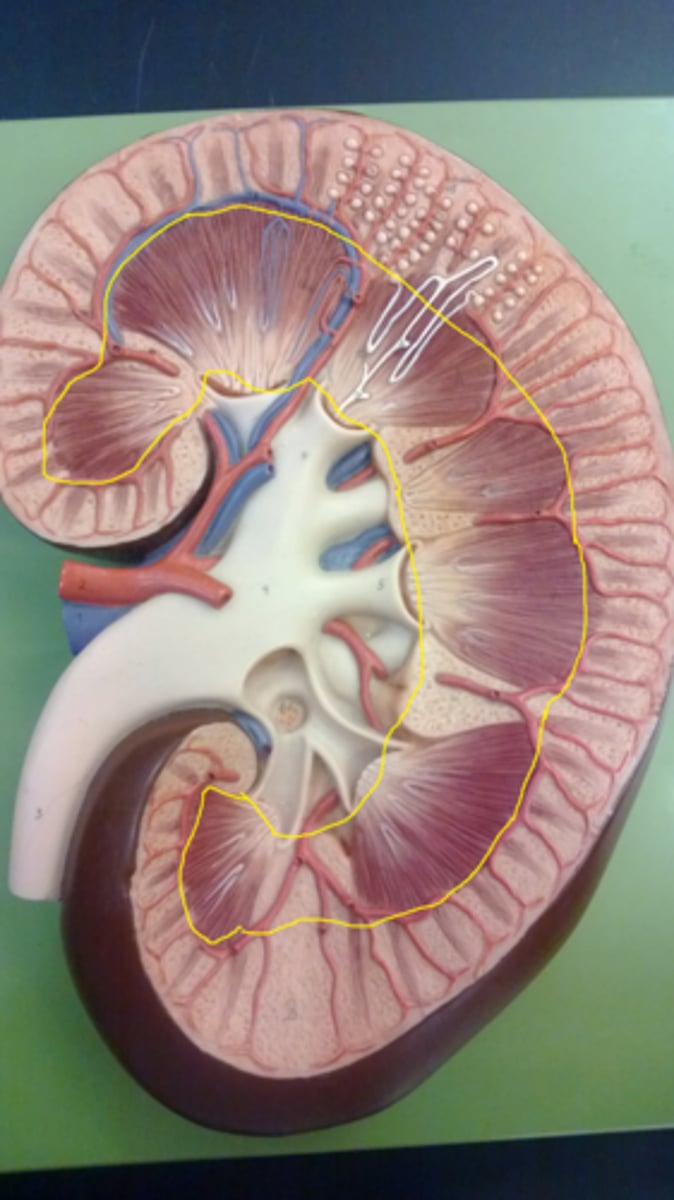
renal columns
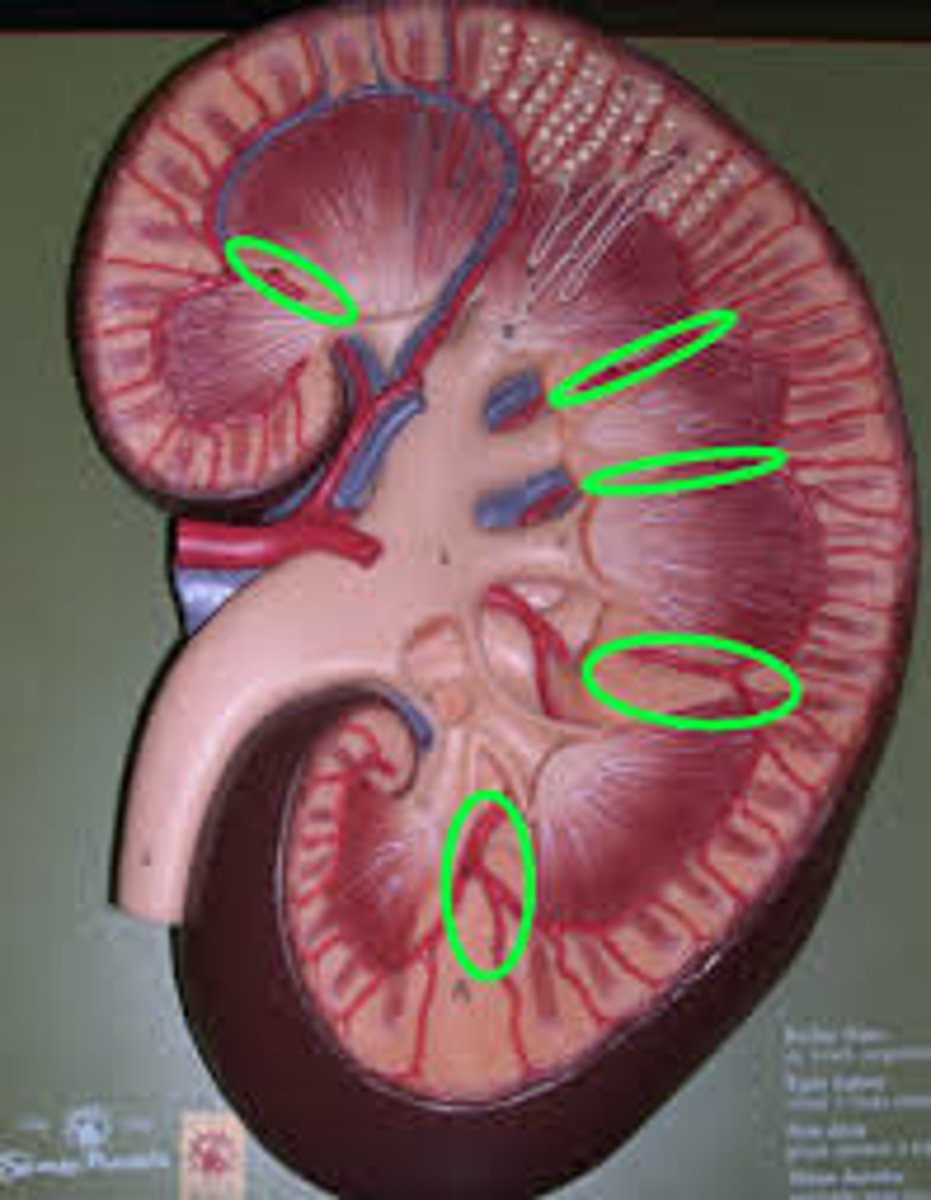
renal pyramids
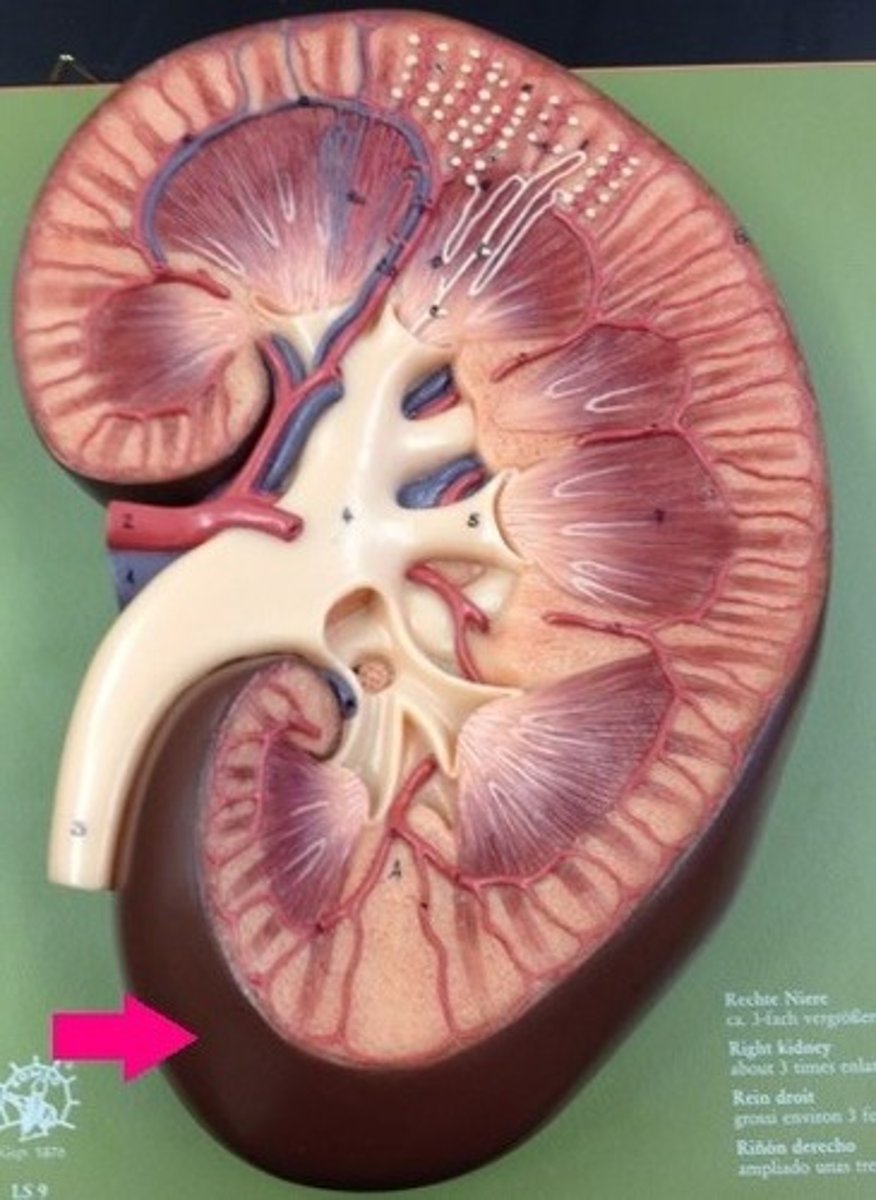
renal capsule
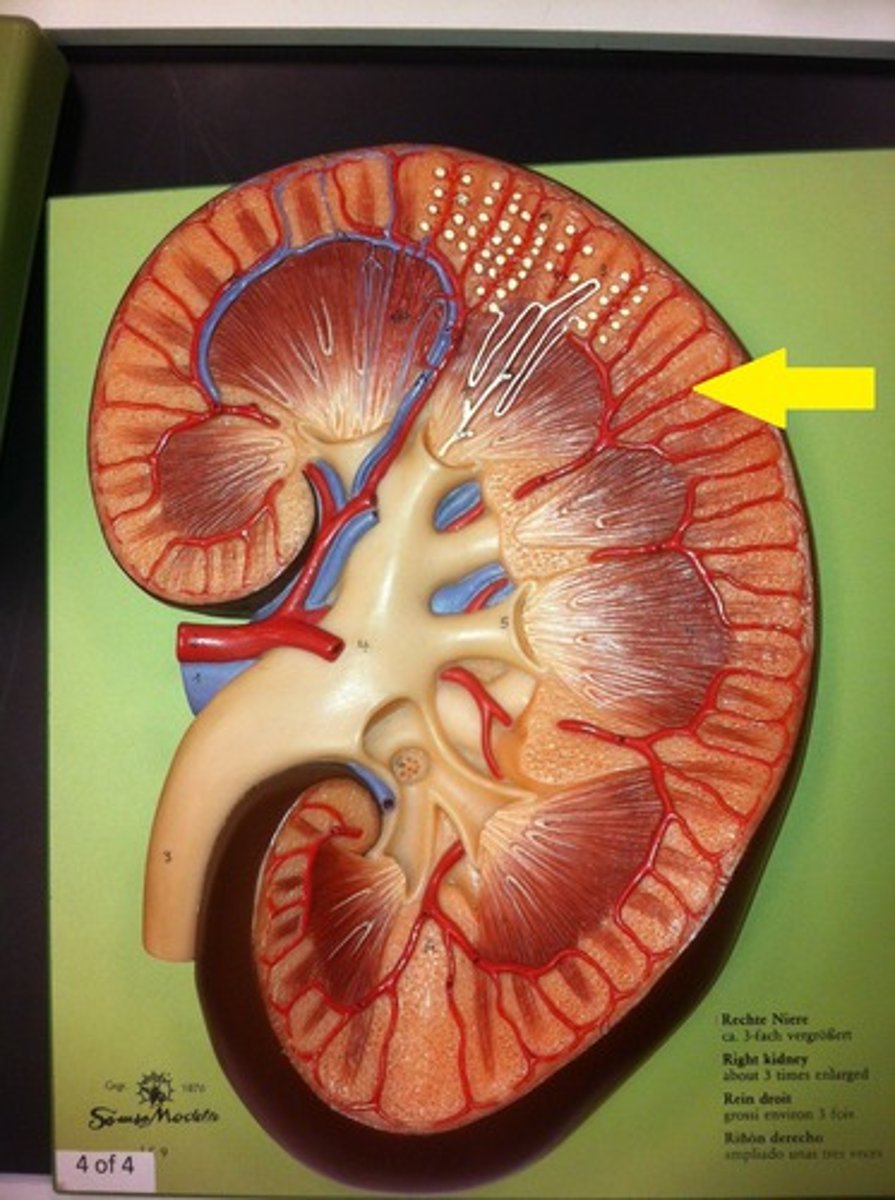
renal cortex
renal artery
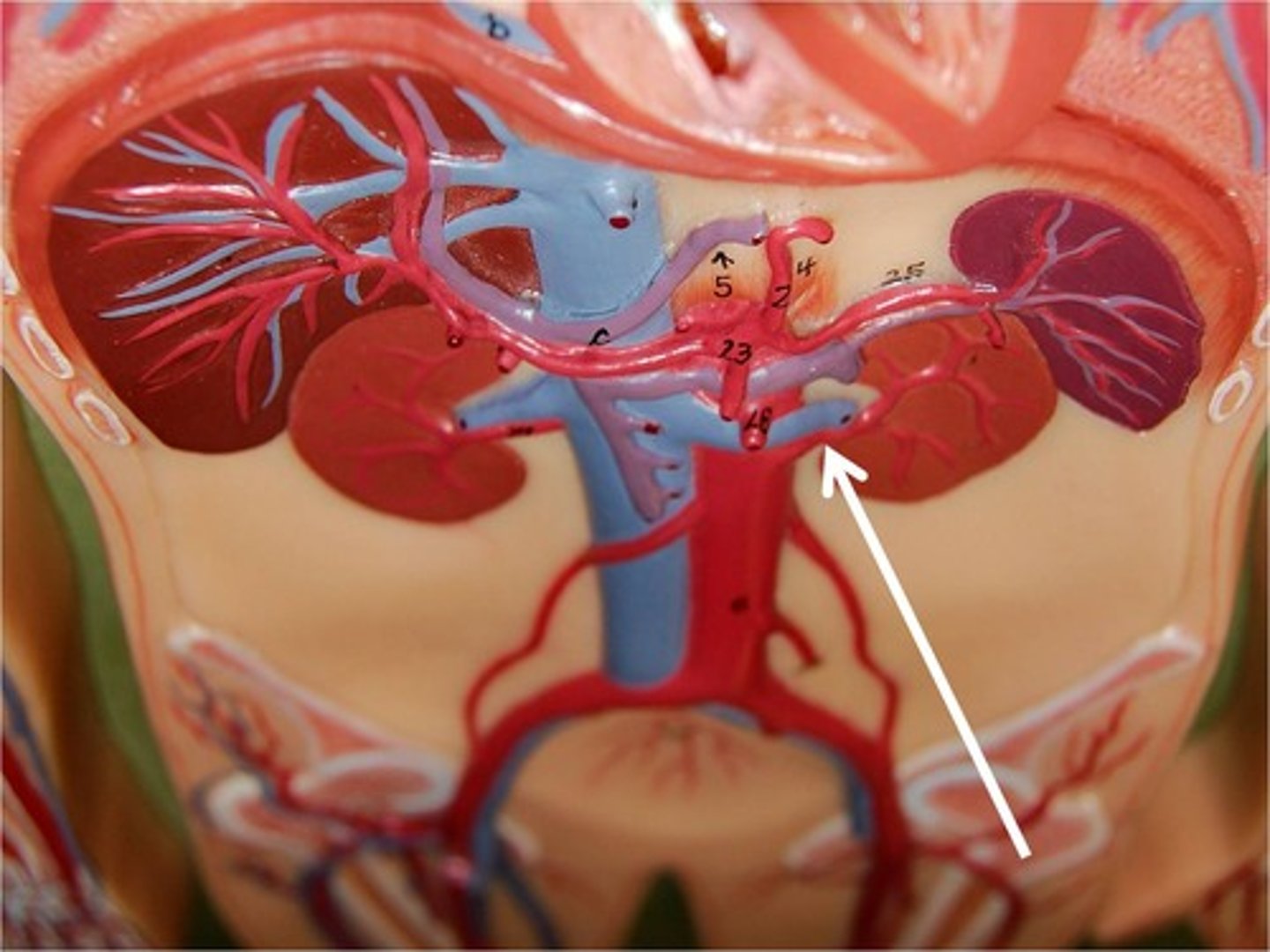
renal vein
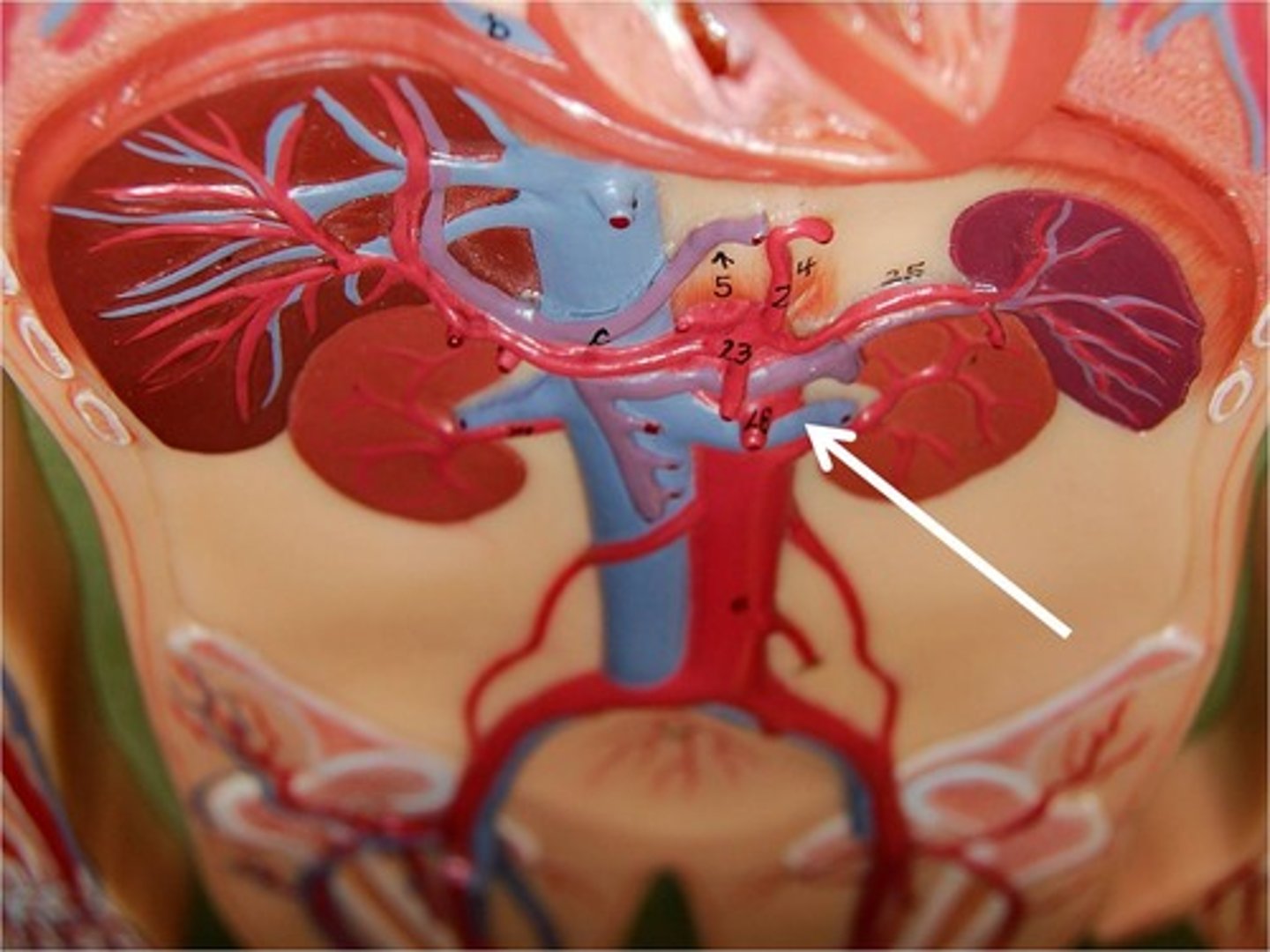
renal pelvis
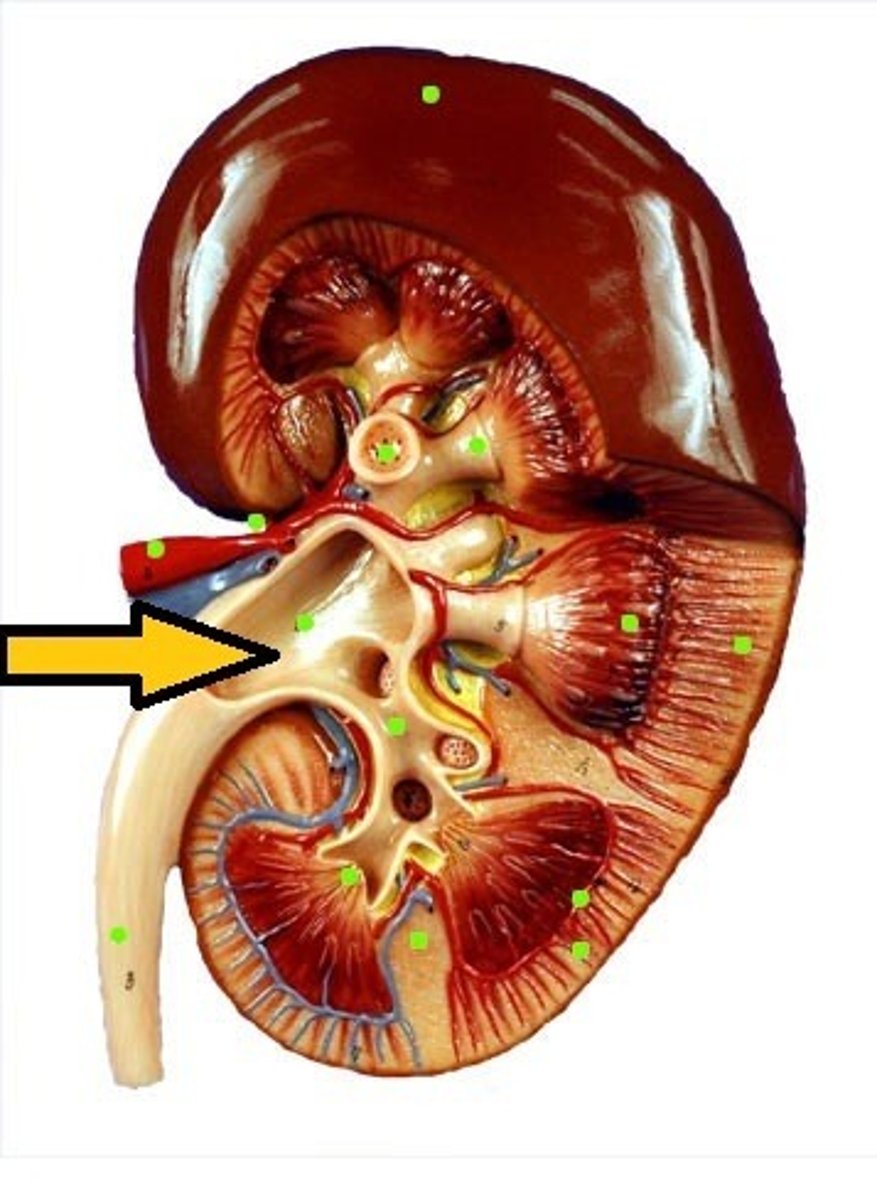
ureter
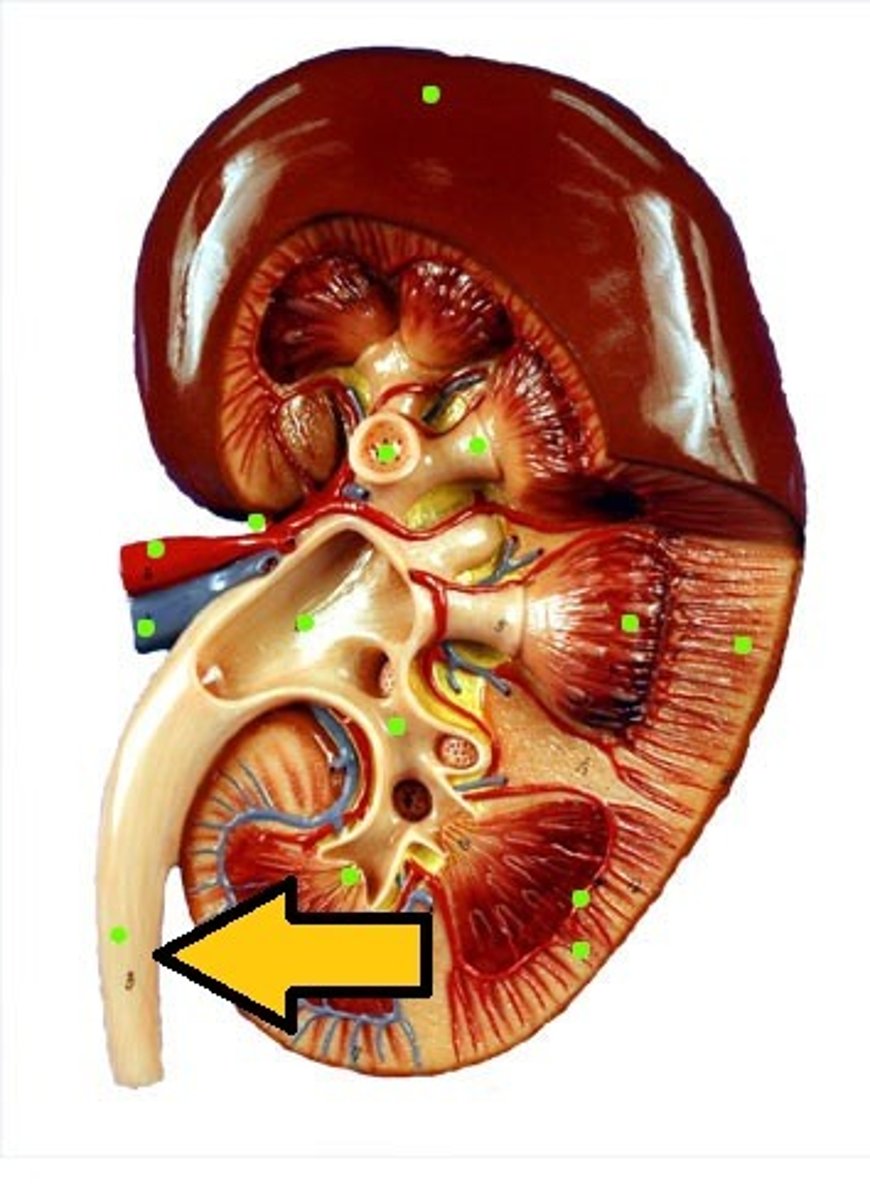
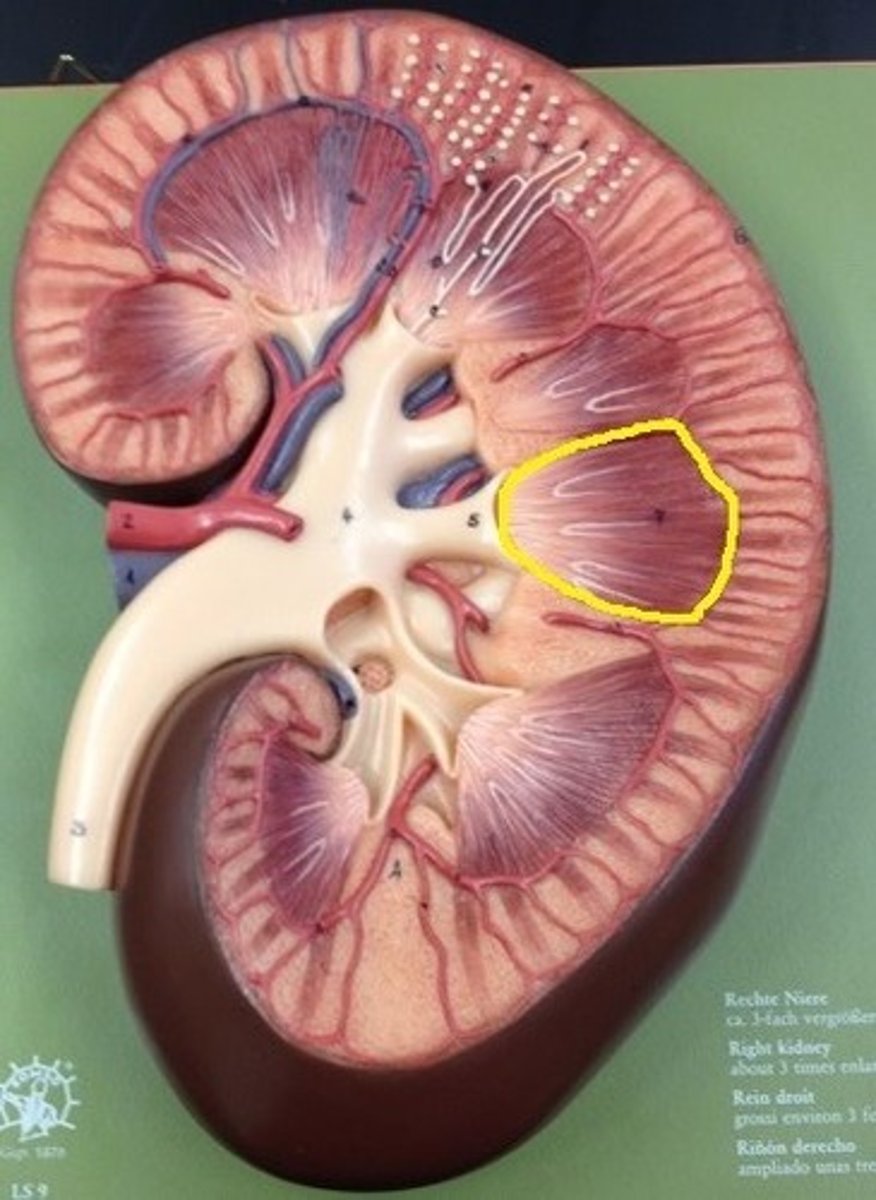
renal medulla
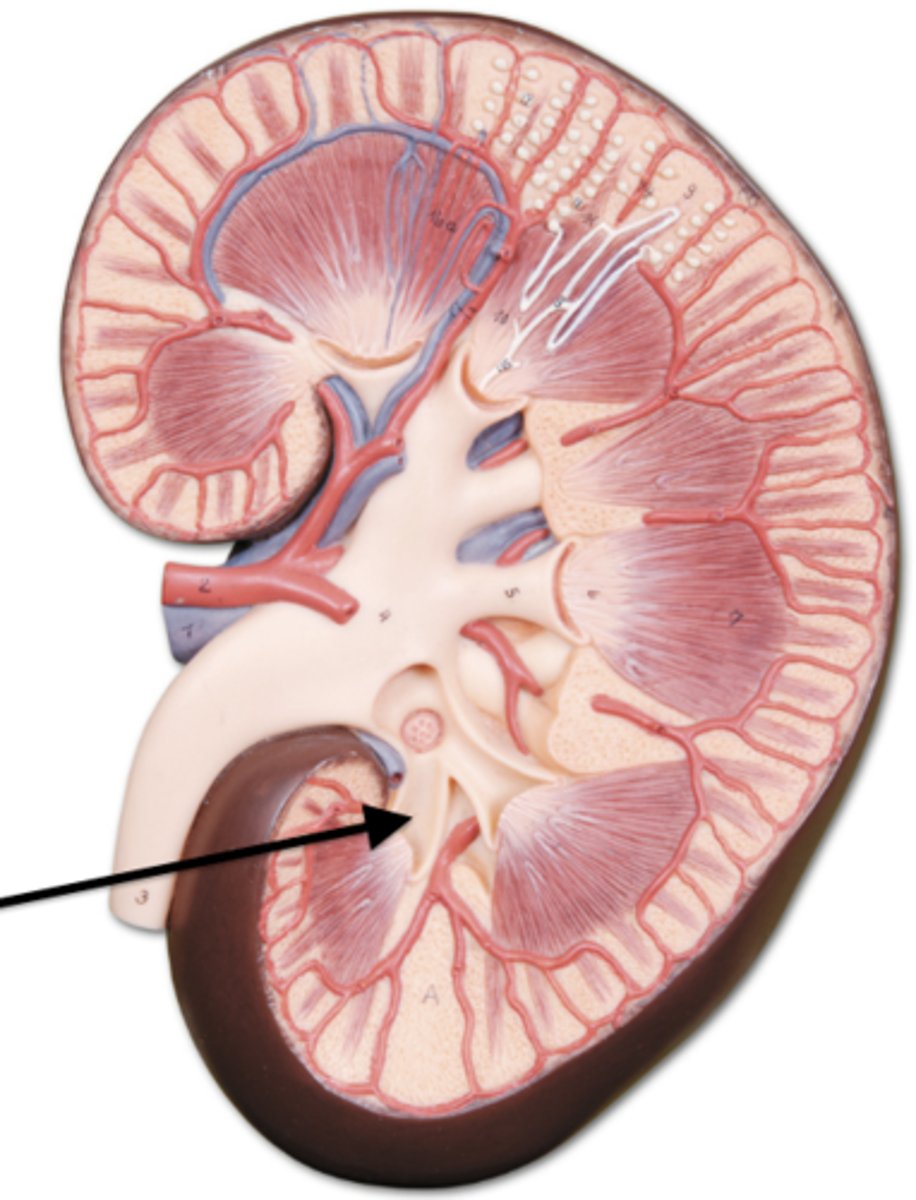
major calyx
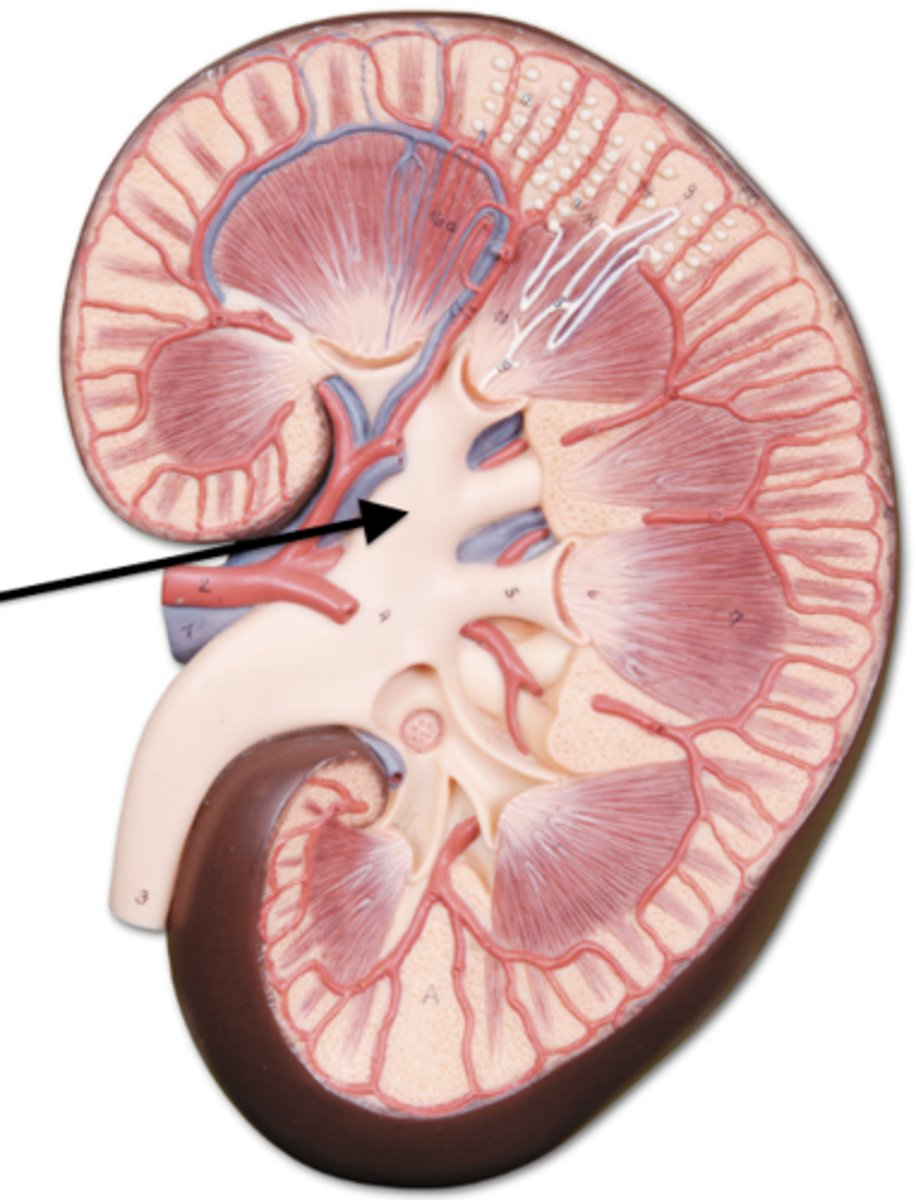
minor calyx
glomerulus
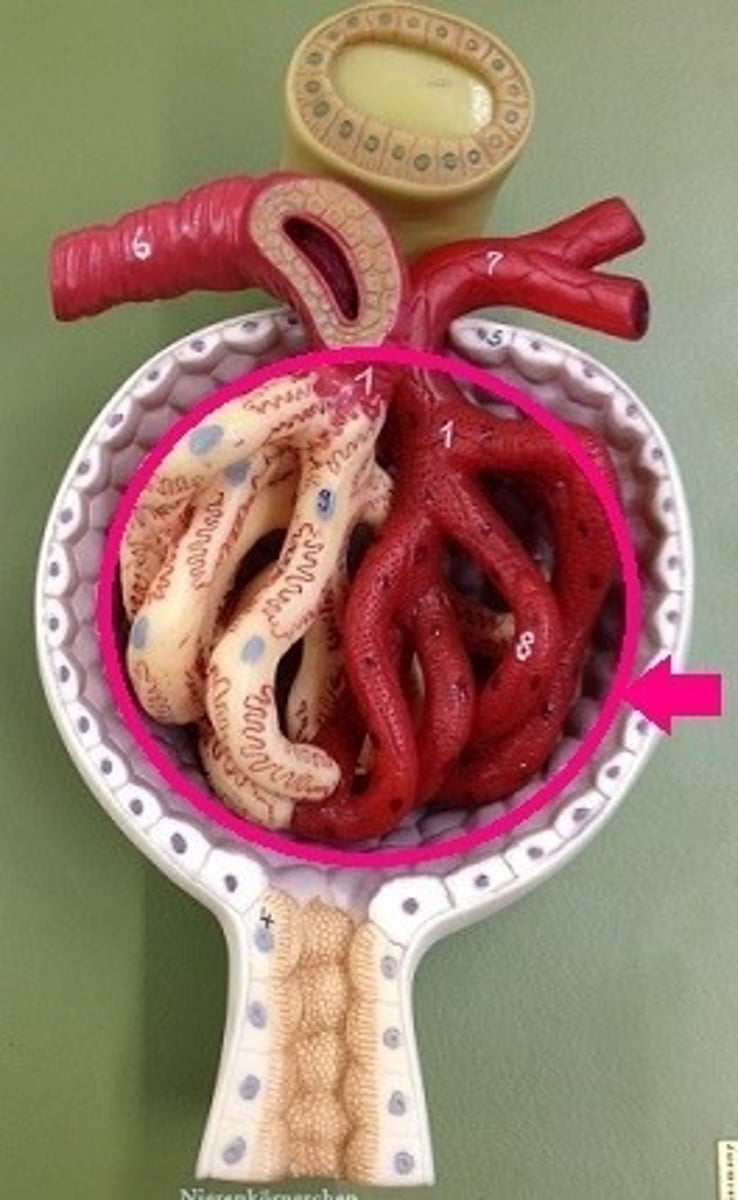
glomerular capsule
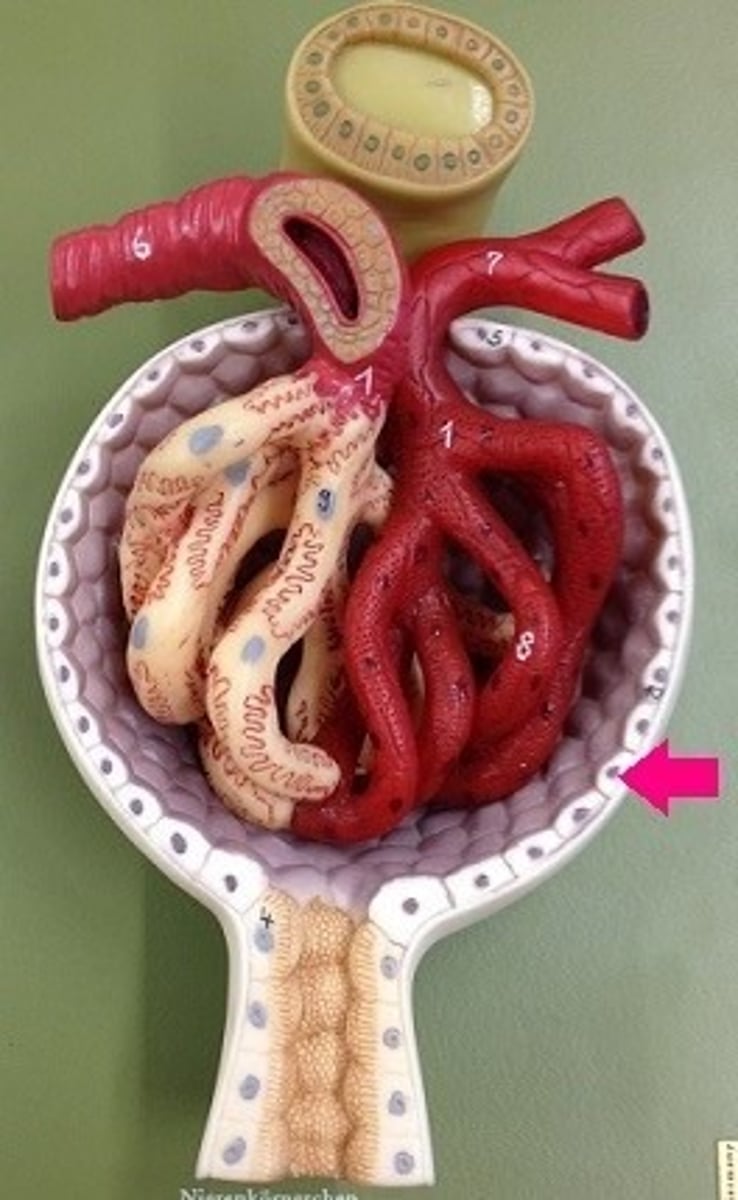
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
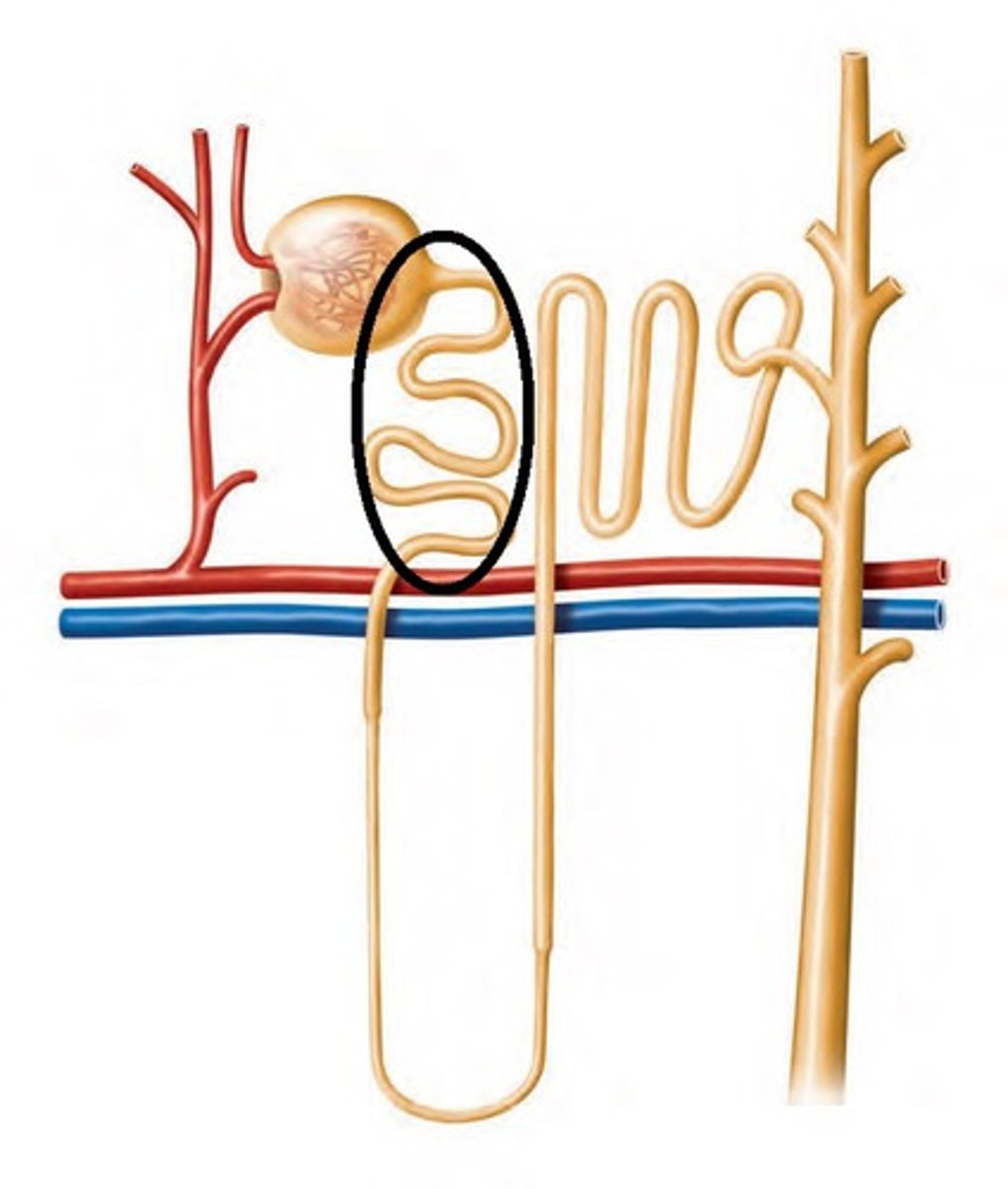
descending limb of loop of Henle
nephron loop
ascending limb of loop of Henle
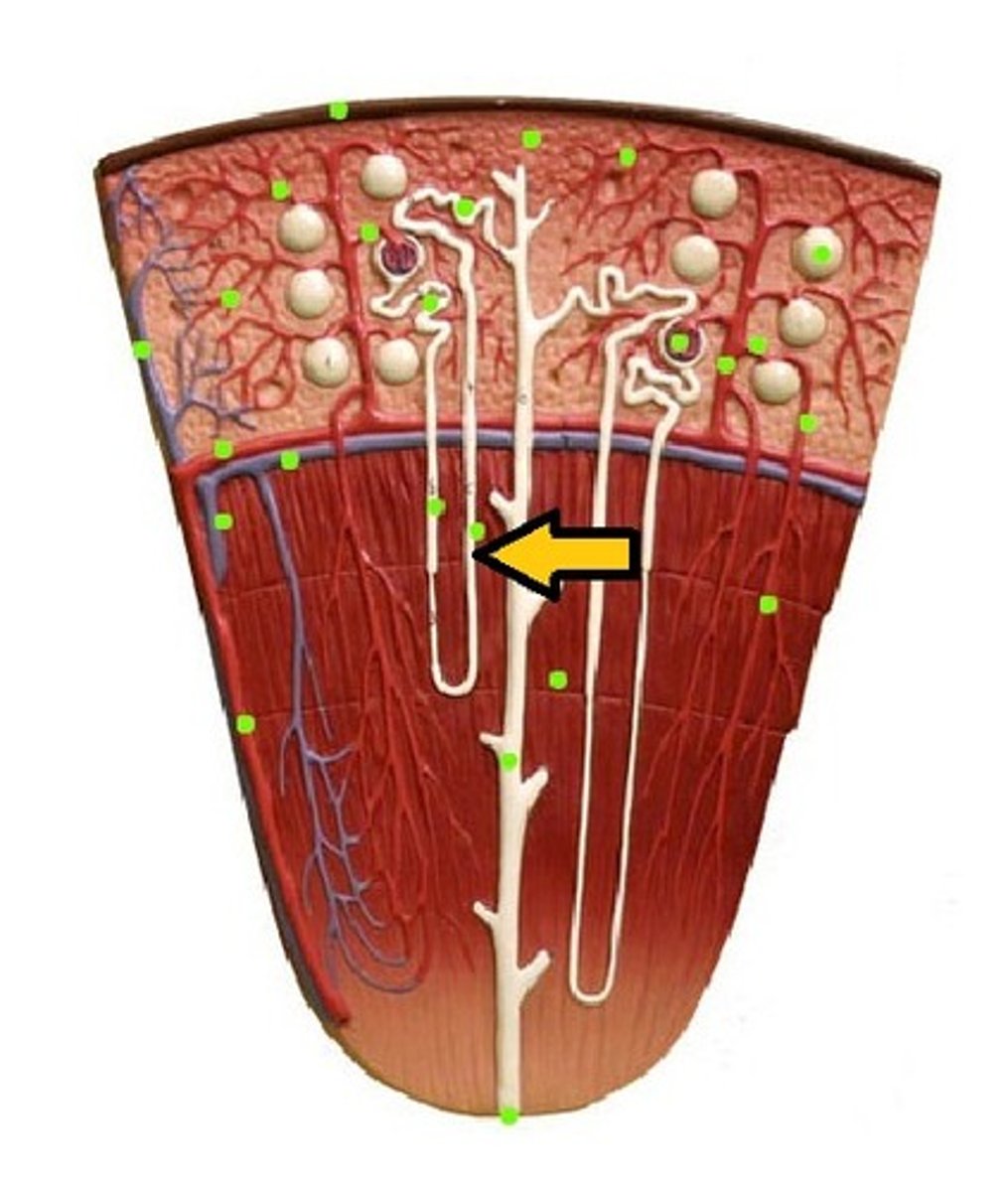
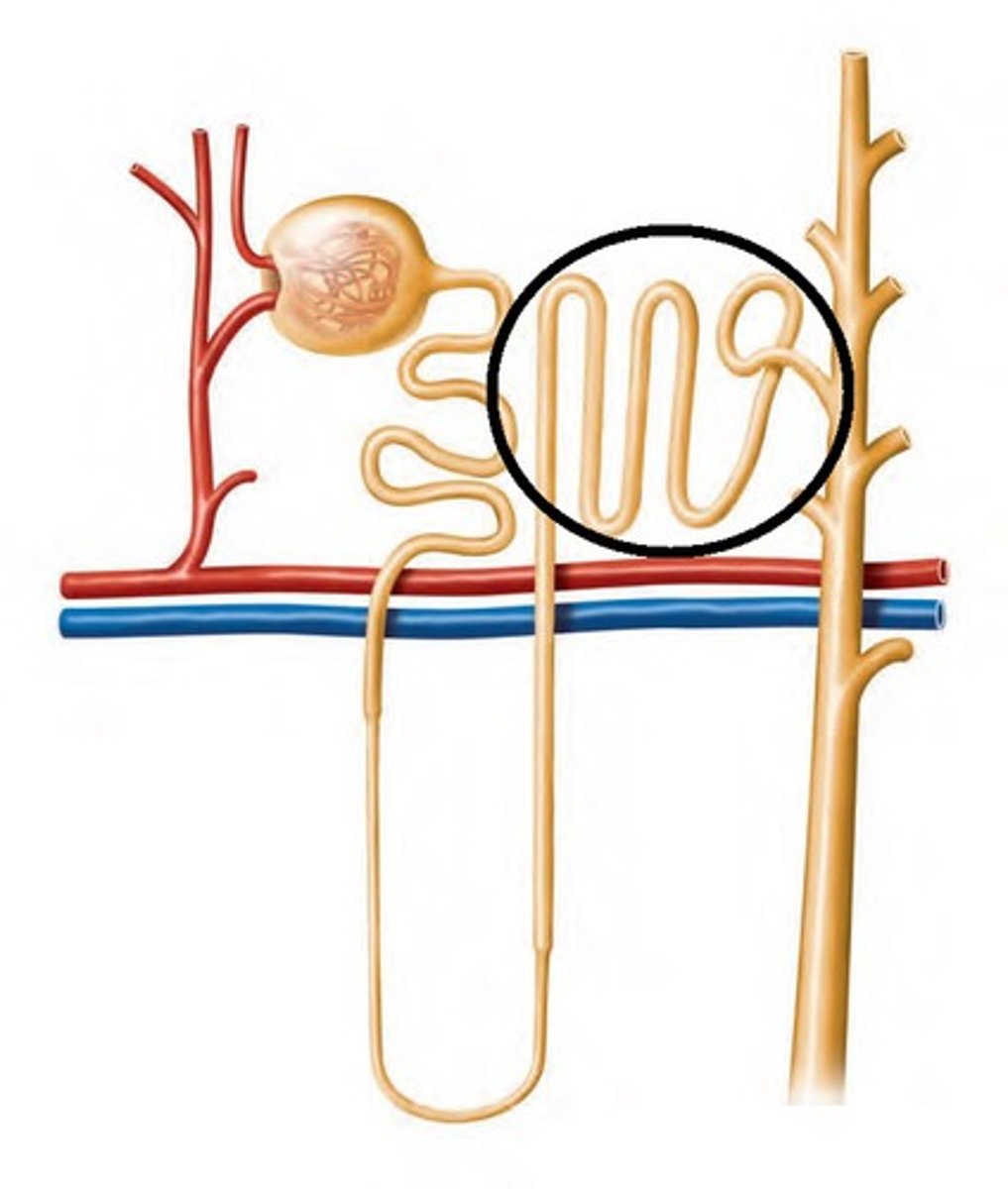
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
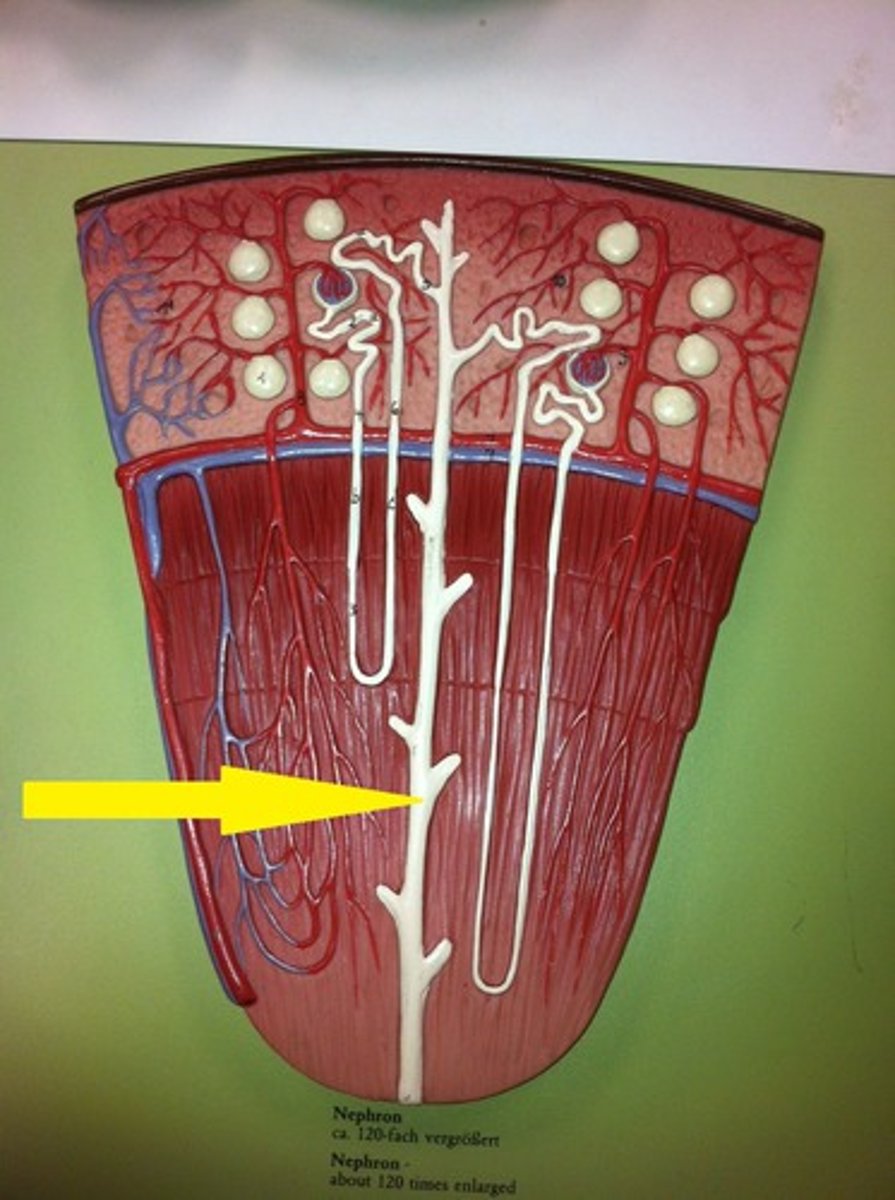
collecting duct of the nephron
the afferent arteriole in the kidney
carries blood to the glomerulus
the efferent arteriole in the kidney
carries blood away from the glomerulus
What are peritubular capillaries?
Tiny blood vessels that travel alongside nephrons.
What is the function of peritubular capillaries?
Allow reabsorption and secretion between blood and the inner lumen of the nephron.
the nephron is the
functional unit of the kidney
what does the urinary system consist of
2 kidneys, 2 ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
urine consists of
excess water, ions, metabolic wastes, and some toxic substances
What is one major function of the kidneys?
Removal of waste products from blood
How do the kidneys help maintain blood pH?
By regulating the balance of acids and bases in the blood
What role do the kidneys play in fluid and electrolyte balance?
They maintain the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body
How do the kidneys regulate blood pressure?
By releasing renin, which converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
What vitamin do the kidneys activate?
Vitamin D
where are the kidneys located
retroperitoneal, in the nonmesenteric region
the retroperitoneal is
located behind the peritoneum
what surrounds the kidneys to cushion them
adipose tissue
renal fascia
CT which anchors the kidneys to the abdominal wall
the hilum of the kidneys is where
renal arteries and nerves enter, and renal veins and ureter exit the kidneys
what are the two parts that make up the renal corpuscle
glomerulus and the glomerular capsule
podocyte
These cells form a porous membrane surrounding the endothelial cells of the glomerulus.
what are the two substances that CANNOT be filtered by the kidneys
large proteins and blood cells
filtration membranes of the glomerulus
first step in urine formation - where the blood is filtered
juxtaglomerular apparatus
Regulates blood pressure and filtration rate - site of renin production
What are juxtaglomerular cells?
The cells of the afferent artery at the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
What is the function of juxtaglomerular cells?
They are baroreceptors that secrete renin upon sensing a decrease in blood pressure.
what are the four parts of the renal tubule
proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct
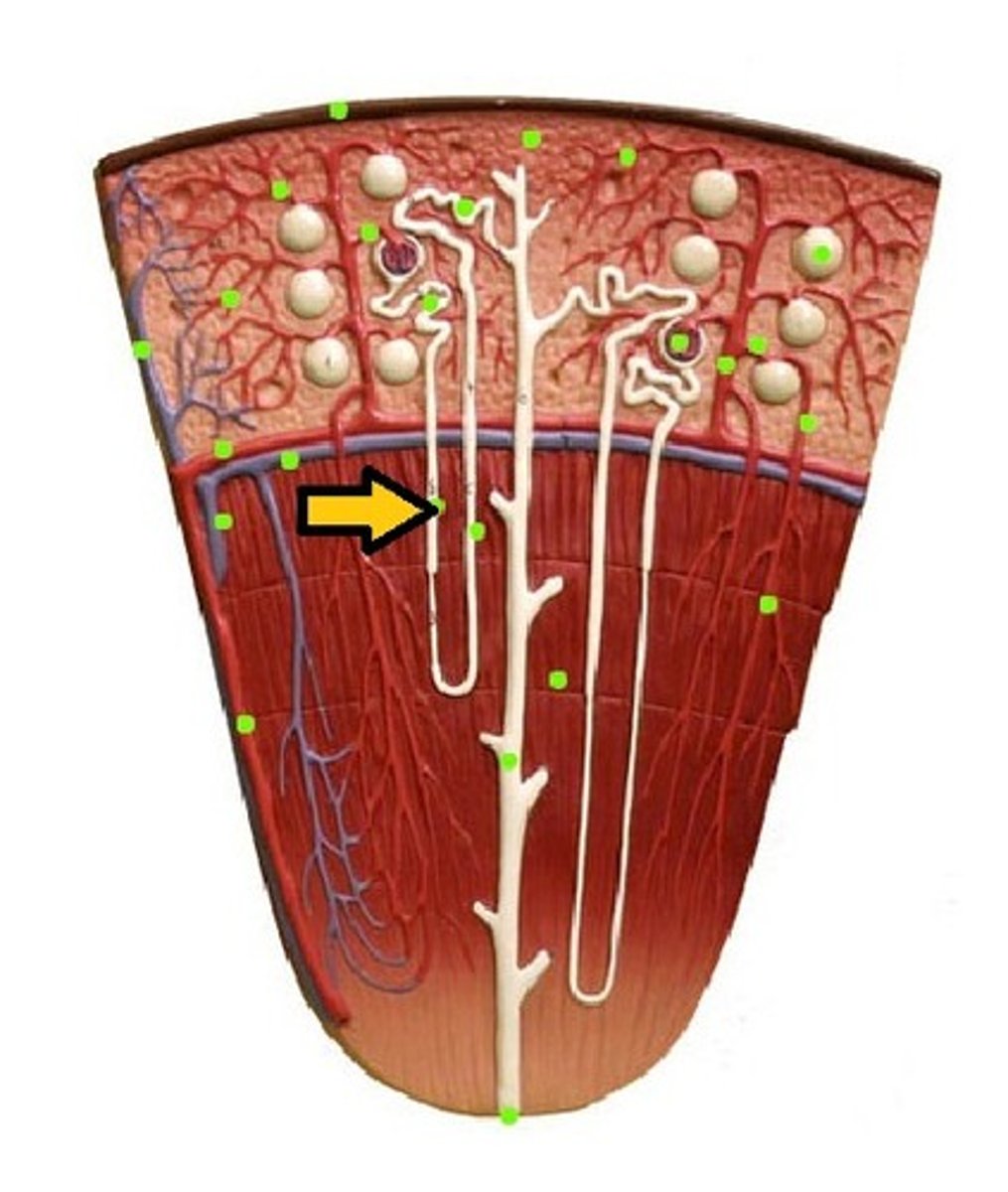
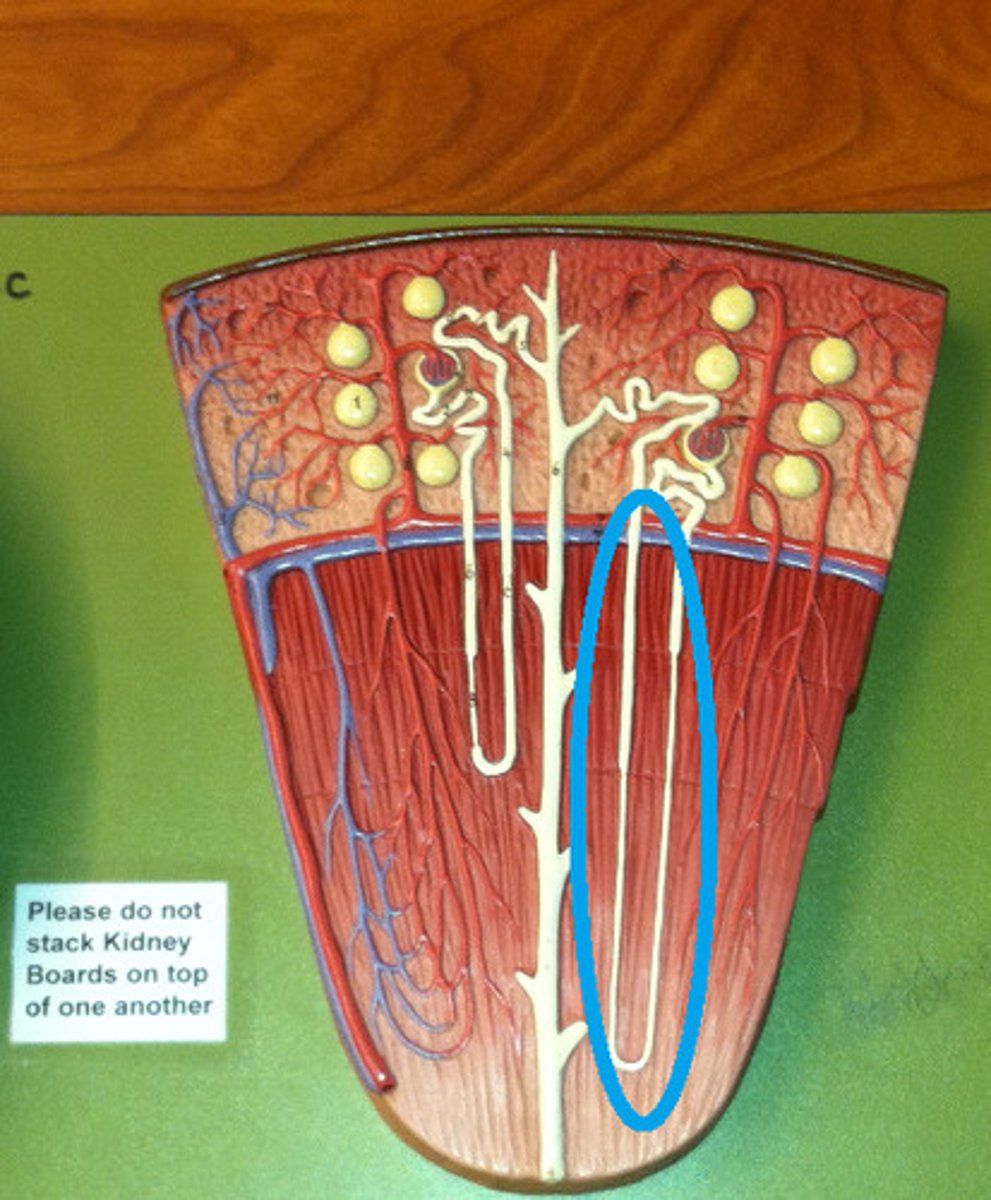
juxtamedullary nephrons
only 15% of nephrons, extend deep into the medulla
cortical nephrons
near the periphery of the cortex, do not extend deep into the medulla
renal corpuscle
filtration part of the nephron
fenestrae
- small holes in glomerular capillary walls - filter out fluid (glomerular filtrate)
filtration membrane
interface between the glomerulus and the nephron
the three steps in urine formation
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
filtration of the kidneys
movement of fluid from blood to filtrate at the glomerulus capsule
filtrate
water, small molecules, and ions that can pass through a membrane
renal fraction
part of total cardiac output that passes through the kidneys
what percent of the cardiac output passes through the kidneys
21% (average)
renal blood flow rate
rate of whole blood flow through the kidneys
renal blood flow rate formula
cardiac output * renal fraction
what is the average renal blood flow rate
1176 ml/min
renal plasma flow rate
renal blood flow rate X fraction of blood that is plasma: 650 mL/min
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the two kidneys combined
what is the total amount of filtrate produced by the kidneys in one day
180 L
glomerular filtration rate formula
renal plasma flow rate * filtration fraction
filtration fraction
part of plasma that is filtered into lumen of Bowman's capsules; average 19%
average urine production per day
1-2 L. Most of filtrate must be reabsorbed
What is filtration pressure?
The pressure gradient responsible for filtration.
What does filtration pressure do?
It forces fluid from the glomerular capillary across the membrane into the lumen of the glomerular capsule.
pressures that contribute to filtration pressure
glomerular capillary pressure, capsule hydrostatic pressure, blood colloid osmotic pressure
glomerular capillary pressure (GCP)
blood pressure inside capillary, moves fluid out of capillary and into the glomerular capsule
Capsule hydrostatic pressure (CHP)
pressure of filtrate already in the lumen of the glomerular capsule
blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)
osmotic pressure caused by proteins in blood
capsule hydrostatic pressure is a(n)
inward pressure movement - forces filtrate back into glomerular capillaries
blood colloid osmotic pressure is a(n)
inward pressure movement
BCOP is always greater at the
end of the glomerular capillary than at the beginning
Net filtration pressure is equal to
10 mmHg
what two ways are required to regulate glomerular filtration rate
intrinsic and extrinsic regulation
intrinsic regulation of the GFR is regulated via
autoregulation
extrinsic regulation of the GFR is regulated via
sympathetic nervous system and secreted hormones
myogenic mechanism
mechanism for renal autoregulation in which smooth muscle cells in afferent arterioles contract in response to elevated blood pressure
tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism
Mechanism for renal autoregulation in which the macula densa senses increased load and causes constriction of the nearby afferent arteriole, increasing resistance to maintain constant blood flow.
when does extrinsic regulation of the glomerular filtration rate occur
severe conditions such as dehydration or hemorrhage
sympathetic stimulation of the GFR
constricts arteries and afferent arterioles --> decreasing renal blood flow and filtrate formation
how does the secretion of renin affect GFR
forms angiotensin II which stimulates vasoconstriction, decreasing blood flow to the kidney
where does most reabsorption occur in the nephron
proximal convoluted tubule
what is the descending loop of the nephron most permeable to
water
what is the ascending loop of the nephron most permeable to
Na+, NOT permeable to water
the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts water permeability are regulated by
aldosterone, antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and atrial nitruiretic peptide
range of urine concentrations
65 mOsm/kg - 1200 mOsm/kg
what three factors affect volume and concentration of urine
countercurrent mechanisms, medullary concentration gradient, and hormonal mechanisms
countercurrent mechanism
Occurs when fluid flows in opposite directions, materials may be exchanged as they pass
What is the countercurrent multiplier?
A mechanism that enhances the concentration of urine in the kidneys.
Where does the countercurrent multiplier occur?
In the nephron loop.
What is the result of the countercurrent multiplier in the medulla?
It creates a high concentration of solutes in the interstitial fluid.
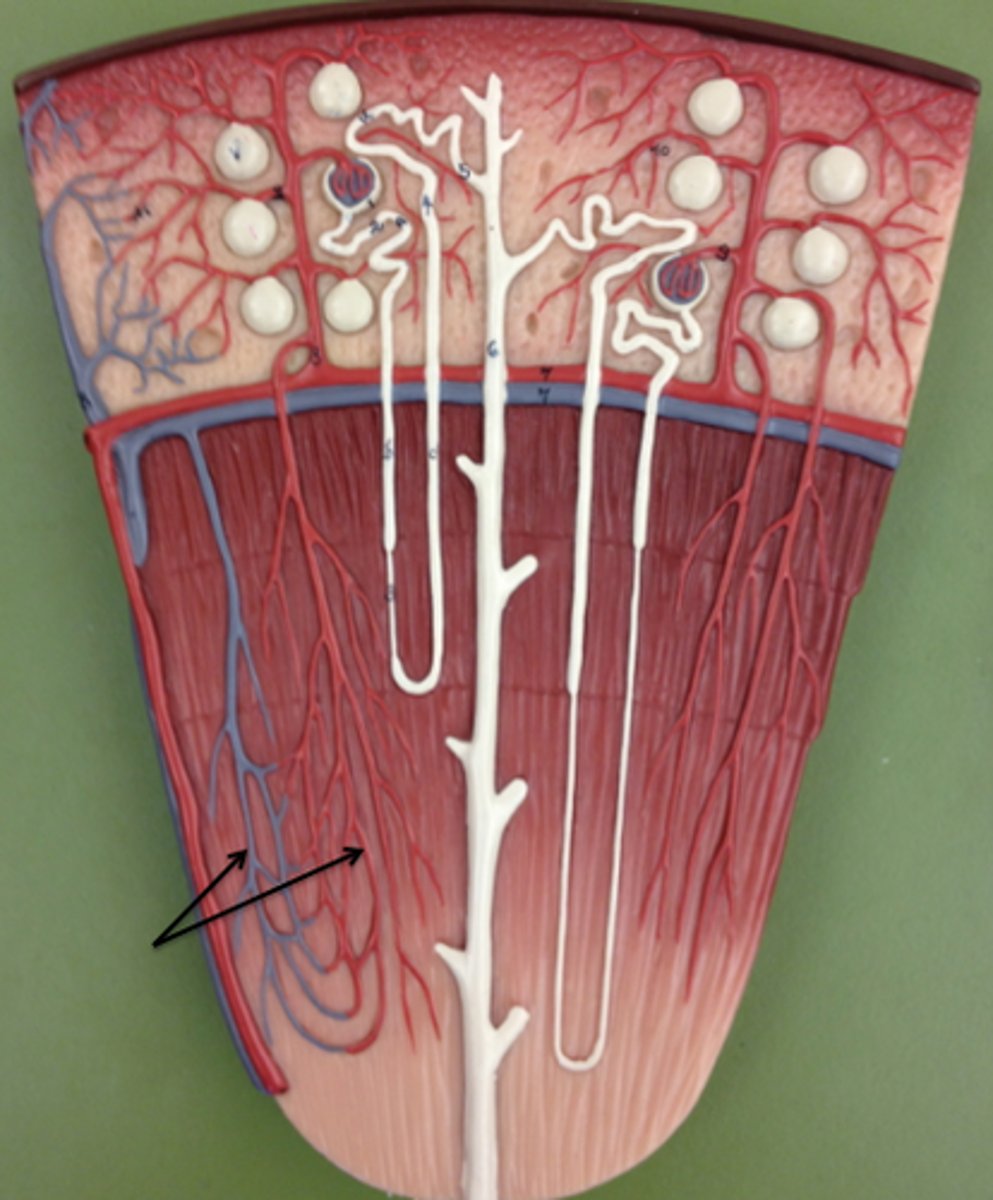
countercurrent exchanger
maintains the high solute concentration in the interstitial fluid in the vasa recta
vasa recta
The capillaries that surround the tubules of the nephron. Reclaims reabsorbed substances, such as water and sodium ions.

what is the purpose of the countercurrent multiplication in the kidneys
create an osmotic gradient to reabsorb water from tubular fluid and produce concentrated urine
the proximal convoluted tubule filtrate reabsorption
remains relatively constant
the distal convoluted tubule filtrate reabosorption
is tightly regulated, can quickly change depending on body conditions
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
a hormone cascade pathway that helps regulate blood pressure and blood volume
When is RAAS (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system) activated?
initiated under low blood pressure conditions
where is renin secreted from
juxtaglomerular cells
renin converts into
angiotensinogen into angiotensin I