Biological Science Test 1
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:27 PM on 9/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
A flexible process used to explore a wide variety of thoughts and ideas
The Scientific Method
2
New cards
What are the 5 steps of the scientific method?
1. Make Observations
2. Formulate A Hypothesis
3. Devise A Testable Prediction
4. Conduct A Critical Experiment
5. Draw Conclusions & Make Revisions
3
New cards
Testable explanation to a question
Hypothesis
4
New cards
Supported by large body of scientific evidence
Theory
5
New cards
Describes what nature does under certain conditions
Law
6
New cards
All living things are made of _____
Cells
7
New cards
A _____ is the smallest unit of life
Cell
8
New cards
A _____ is the simplest form of a substance
Element
9
New cards
What is the nucleus composed of?
Protons and Nutrons
10
New cards
The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of _____
Electrons
11
New cards
Protons have a ___ charge
Positive
12
New cards
Electrons have a ___ charge
Negative
13
New cards
The _______ determines an atom’s identity
Atomic Number
14
New cards
In an uncharged atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of _____
Electrons
15
New cards
The number of electrons in an atom’s valence shell will determine _______
Reactivity
16
New cards
The 1st shell is full at how many electrons?
2
17
New cards
The 2nd shell is full at how many electrons?
8
18
New cards
The 3rd Shell is full at how many electrons?
8
19
New cards
Is carbon reactive?
Yes; It’s valence shell isn’t full
20
New cards
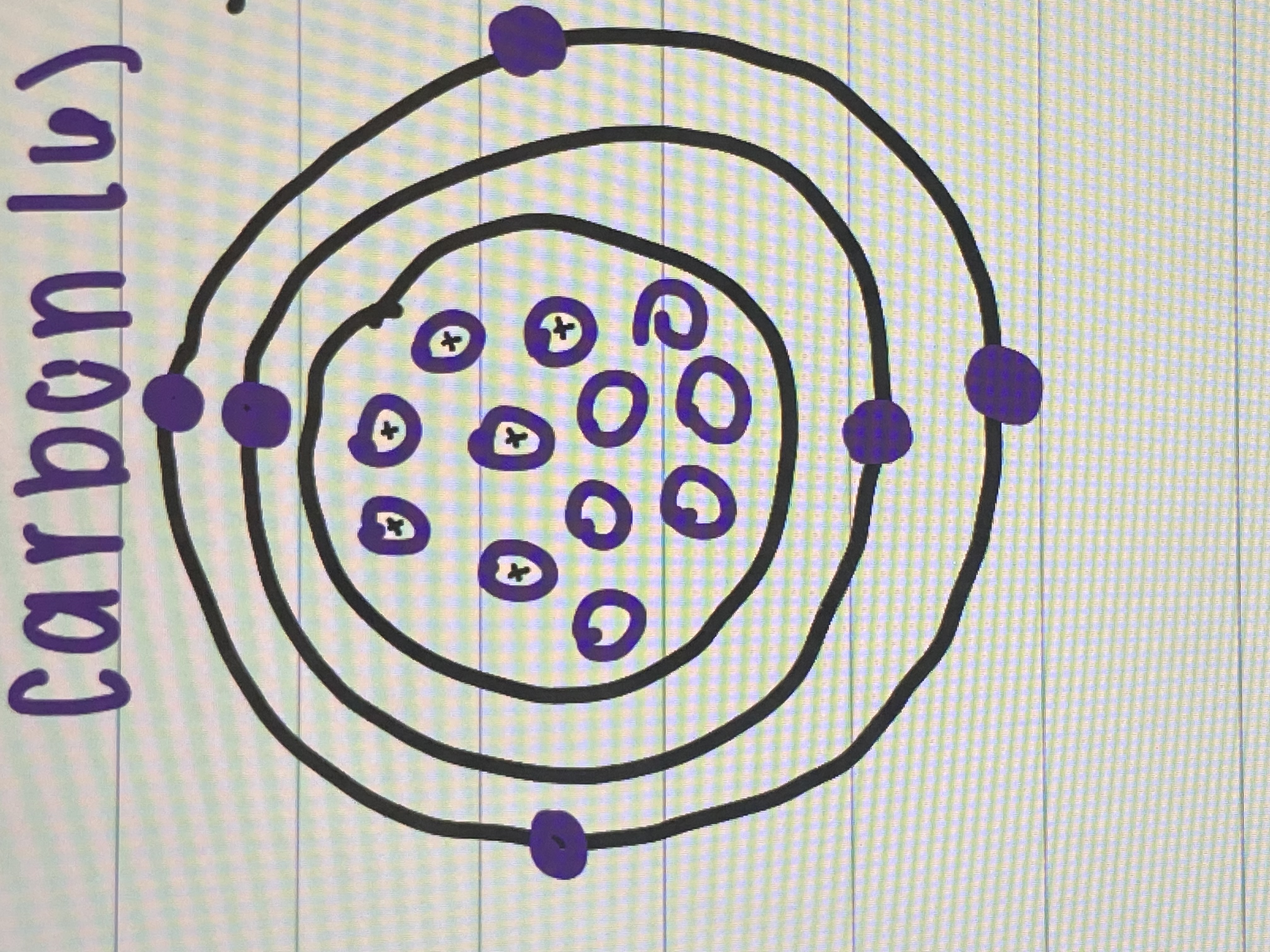
In a ____ bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons
Covalent
21
New cards
Electrons are shared unequally between atoms
Polar
22
New cards
Electrons are shared equally between atoms
Nonpolar
23
New cards
Two or more atoms chemically bonded together
Molecule
24
New cards
Substances that dissolve in water
Hydrophilic
25
New cards
Substances that do not dissolve in water
Hydrophobic
26
New cards
Is sugar hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
27
New cards
Is butter hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophobic
28
New cards
Organic molecules consist of which two atoms
Carbon and Hydrogen
29
New cards
______ are small subunits that bind together
Monomers
30
New cards
When these small subunits bind together, they for a ______
Polymer
31
New cards
What are the 4 biomolecules?
* Carbohydrates
* Lipids
* Proteins
* Nucleic Acids
* Lipids
* Proteins
* Nucleic Acids
32
New cards
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
Monosaccarides
33
New cards
What is the monomer for lipids?
Fatty Acids & Glycerol
34
New cards
What is the monomer for proteins?
Amino Acids
35
New cards
What is the monomer for nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
36
New cards
Polymer for carbohydrates
Disaccahrides and Polysaccharides
37
New cards
Polymer for lipids
Triglycerides
38
New cards
Polymer for proteins
More Complex Protein
39
New cards
Polymer for nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
40
New cards
Fast source of energy is the primary function for ______
Carbohydrates
41
New cards
Long term energy storage is the primary function for ______
Lipids
42
New cards
Muscle development is the primary function for ____
Proteins
43
New cards
Stores and transfers information is the primary function for _______
Nucleic Acids