Music Elements and Theory: Sound, Rhythm, and Form
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What begins the process of sound?
The vibration of an object.
How is sound transmitted to our ears?
Through sound waves created by vibrations.
What are the four main properties of musical sounds?
Pitch, Dynamics, Tone Color, Duration.
What determines the pitch of a sound?
The frequency of vibrations.
What is a Tone in music?
A definite pitch named after the first seven letters of the alphabet (a, b, c, d, e, f, g).
What is an interval in music?
The distance between two tones.
What is an octave?
Two tones that are eight pitches apart.
What does 'dynamics' refer to in music?
The relative loudness or softness of a sound.
What is a crescendo?
A gradual increase in loudness.
What is a decrescendo (diminuendo)?
A gradual decrease in loudness.
What is tone color (timbre)?
The quality that identifies an instrument's or voice's sound.
What does duration refer to in music?
The length of time a musical sound lasts.
What is the role of a Listening Outline?
To point out notable musical sounds and features before listening.
What is the voice range based on?
Physical makeup and training.
What are the classifications of female voice types?
Soprano, Mezzo-soprano, Alto.
What are the classifications of male voice types?
Tenor, Baritone, Bass.
What produces sound in string instruments?
Vibrating strings.
How is pitch changed in brass instruments?
By the pressure of the player's lips and the length of the instrument.
What is the main characteristic of percussion instruments?
Sound is produced by striking or shaking the instruments.
What are the main orchestral woodwinds?
Flute, Clarinet, Oboe, Bassoon, Saxophone.
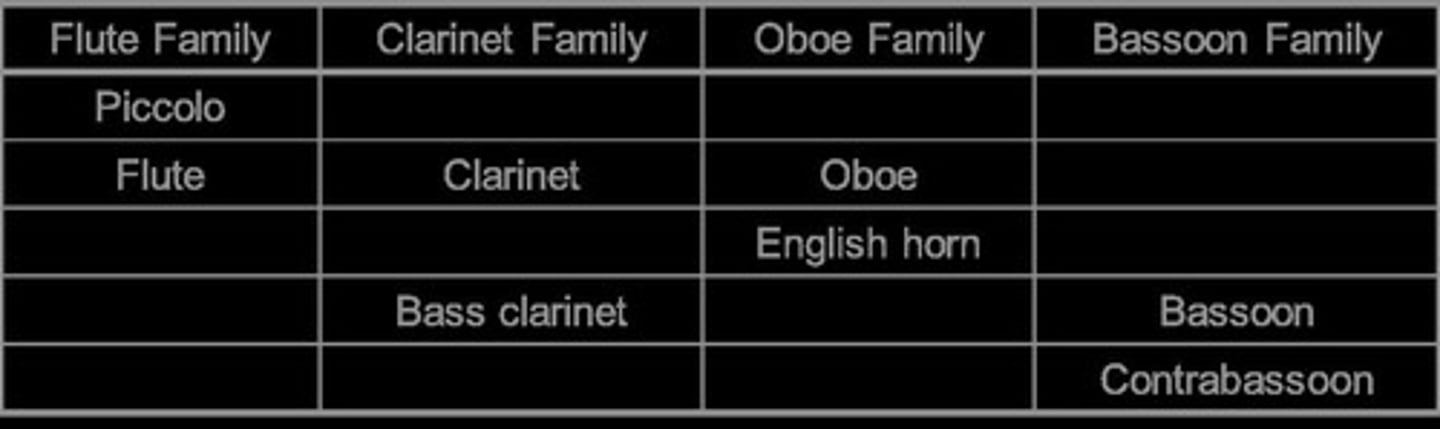
What is a keyboard instrument?
An instrument such as a piano or organ that produces sound by pressing keys.
What is rhythm in music?
The particular arrangement of note lengths or the flow of music through time.
What is a beat in music?
A regular recurrent pulsation that divides music into equal units of time.
What is meter in music?
The organization of beats into regular groups.
What does 'accent' mean in music?
A note that is emphasized or played louder than the notes around it.
What is syncopation?
A rhythmic concept where the emphasis is placed on unexpected beats.
What is syncopation in music?
when an 'off beat' note is accented.
What does tempo refer to in music?
refers to the speed of the beat; how fast or slow music flows.
What are tempo markings indicated by?
indicated by Italian terms.

What is a metronome used for?
indicates the exact tempo.
What is the Grand Staff in music notation?
consists of a treble clef and a bass clef.
What do ledger lines represent in music notation?
added lines above or below the staff to notate pitches outside the standard range.
What is the purpose of rests in music?
indicate notated silence in music.
What does a time signature indicate?
indicates the meter of a piece of music, showing how many beats per measure.
What is a melody?
a series of single tones that add up to a recognizable whole.
What are the two types of chords in harmony?
Consonant (stable, restful) and Dissonant (unstable, tense).
What is a triad in music?
the simplest chord made up of three notes.
What is the tonic triad?
built on the 1st scale tone and is the most stable chord.
What is modulation in music?
the process of moving from one key to another within the same piece of music.
What defines a key in music?
it centers a piece of music around a central tone, scale, and chord.
What is the difference between major and minor scales?
Major scales have a bright, happy sound, while minor scales have a dark, sad sound.
What does a key signature indicate?
sharps or flats in a piece of music, determining its key.
What is musical texture?
layering of sound by voices or instruments.
What is monophonic texture?
a single layer of sound produced by one voice or instrument.
What is polyphonic texture?
multiple melodies beginning at different times.
What is homophonic texture?
one melody with harmony, all beginning at the same time.
What is musical form?
organization of musical elements in time.
What are the three techniques that create musical form?
Repetition, contrast, and variation.
What is ternary form in music?
three-part structure, typically labeled as ABA'.
What is binary form in music?
two-part structure, typically labeled as AB.
What are the historical periods of Western art music?
Middle Ages, Renaissance, Baroque, Classical, Romantic, 20th Century to 1945, and 1945 to present.