A&P ch.5
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
The myocardium receives its blood supply from the
coronary arteries
The what? pumps blood into the pulmonary artery, which carries it to the lungs.
right ventricle
blood is what type of tissue
fluid tissue
the right ventricle does what
pumps blood to the lungs from the pulmonary artery
what ventricle carries blood to all parts of the body except the lungs.
left ventricle
Neutrophils
the most common type of White blood cell
CPR stands for
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Phleb/o means?
vein
lipoprotein cholesterol
good cholesterol
blood is what tissue
fluid connective tissue
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
endocardium
inner lining of the heart
Myocardium
middle and thickest layer
epicardium
outer layer of the heart
what does the serous pericardium do?
lubricates the heart and resists friction
heart muscle layers left to right
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium, pericardial cavity, parietal layer of serous pericardium, and fibrous pericardium
Atria is the? #? of the what?
2 upper chambers of the heart
What are the 2 chambers of the heart?
1 atrium and 1 ventricle
valves of the heart
pulmonary, tricuspid, aortic, mitral valves
pulmonary circulation
flows blood only between the heart and the lungs
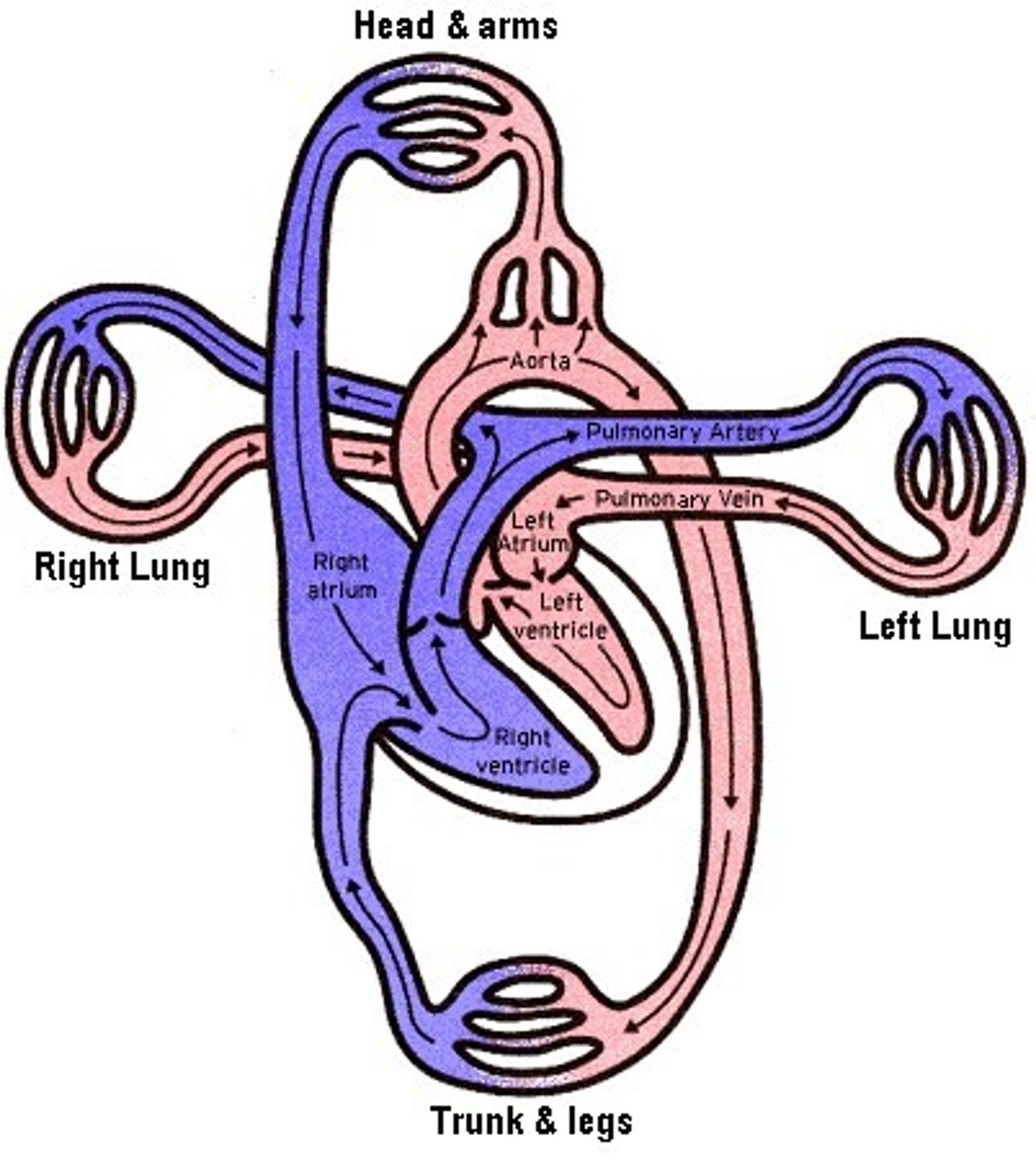
difference between pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins?
pulm. arteries carry deoxygenated blood and pulm. veins carry oxygenated blood
What circulation breaks all the rules?
pulmonary circulation
systemic circulation flows to whole body except?
the lungs
synotrial node is the natural what?
pacemaker of the heart
Bundle of Hiss (HISS)
ensure the heart sequence
Waves of a heart beat
p wave(early systole) QRS complex (ventricles contract) T wave (disatole)
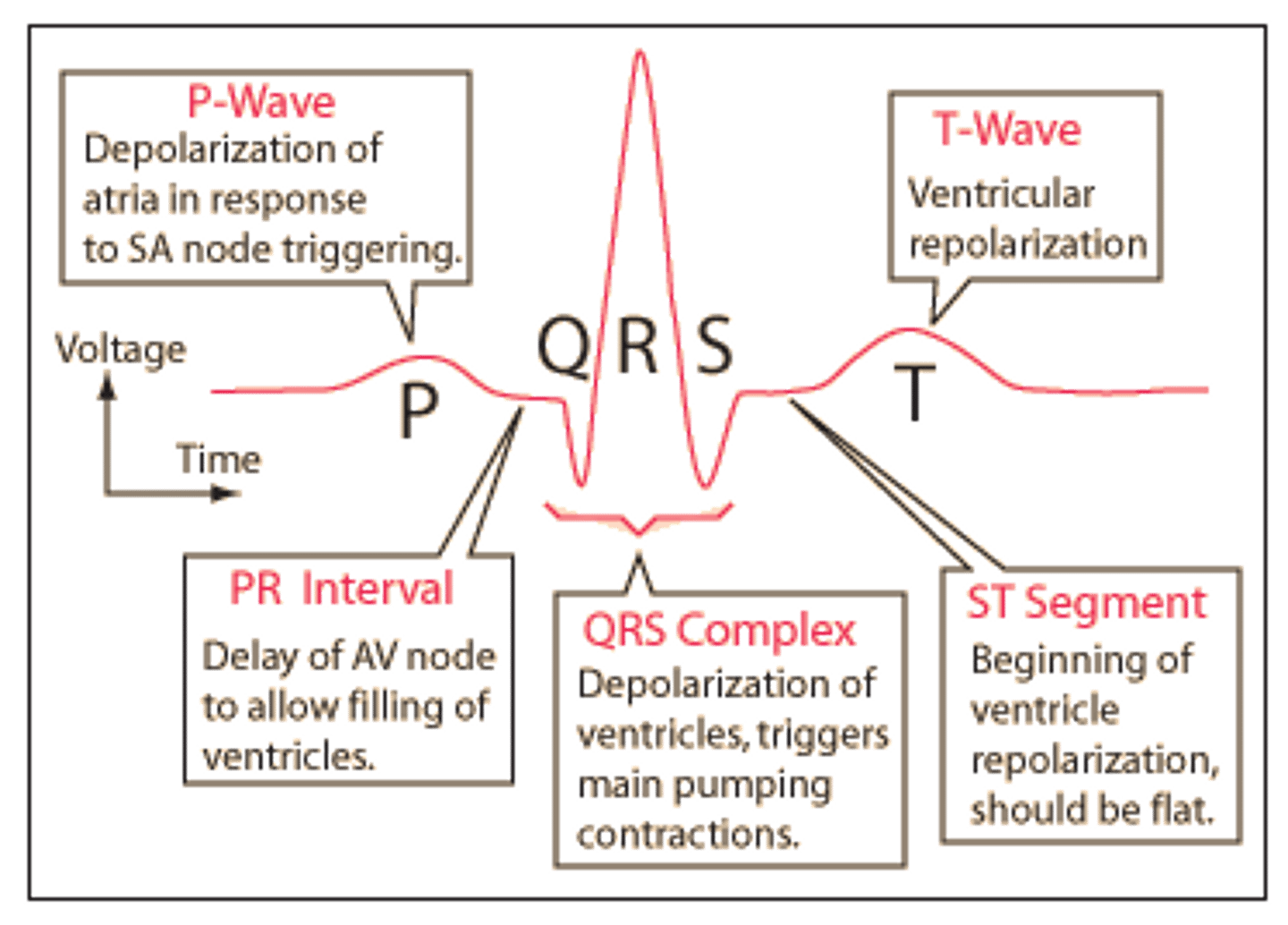
what is a normal rhythm called?
sinus rhythm
p wave and t wave are?
early systole and disatole
QRS complex in a heartbeat shows what?
relaxed ventricles contracting
what is the brady, normal, and tachy cardia numbers? example 20-50
40-60 is brady, 60-100 is normal, 100-120 is tachy
what is the largest vessel in the body
aorta
what is the smallest vessels in the body?
capillaries
superficial veins vs deep veins?
superficial veins are near the top surface and do not have corresponding arteries. deep veins in tissue, not near the top, the do have corresponding arteries
What are the 2 largest veins in the body?
superior and inferior vena cava
difference between the superior and inferior vena cava?
superior transports blood to upper portion of the HT while the inferior transports blood from the lower portion of the HT
aneurysm vs. stenosis
aneurysm is localized weakening of an artery and stenosis is abnormal narrowing of an artery
What is serum?
plasma filled after clotting is removed
what are the major blood gases?
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen
blood pressure is measured with mmHg. What does mmHg mean?
millimeters per mercury
bpm 40-60 is a what heartbeat?
bradycardia
60-100 bpm is
normal blood pressure range
100-120 bpm is
tachycardia
arterioles regulate what?
blood pressure
what is the largest vessel in the body?
the aorta
The cartoid artery is a major artery and carries what to where?
carries blood to the head
what is the smallest vessel in the body?
the capillaries
superficial veins vs. deep veins
near body surface and DO NOT have corresponding arteries, deep veins are in tissue away from the surface and they DO HAVE corr. arteries
what are the 2 largest veins in the body?
superior and inferior vena cava
difference from superior and inferior vena cavae?
sup. transports blood to upper portion of HT and the inf. transports blood to lower portion of HT
what are the 3 main gases?
oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen
cardiomyopathy means
all diseases of the heart muscle
what is CAD, CHD, and IHD (relating to heart)
coronary artery disease, coronary heart disease, and ischemic heart disease
what is angina meaning?
chest pain due to lack of blood flow
ischemia meaning?
insufficient supply of oxygen due to no blood flow
myocardial infarction (MI) means a?
heart attack (complete block of cor. arter. by plaque buildup)
CHF results to edema what is CHF and edema mean?
congestive heart failure and edema is swelling
carditis and endocarditis meaning?
carditis is inflammation of the heart and endocarditis is inflammation of the inner lining of the heart
left-sided heart failure is?
systolic or diastolic failure
right-sided heart failure happens because?
often the result of left-sided heart failure, causes fluid buildup
a defective heart valve is also know as a?
heart murmur
valvular heart disease prevents what?
prevents heart valves from opening and closing properly
valvular stenosis means?
narrowing, stiffening, or thickening of the valves
protrusion of a heart valve is known as?
mitral valve prolaps
what is it called when a valve doesn’t close tightly
mitral valve regurgitation
arrhythmia is?
irregular heartbeat
cardiac arrest is?
total loss of normal rhythm
asystole mean?
flat line
palpitation is
a pounding or racing heartbeat w/ or wo/ rhythm
arterial fibrillation(a-fib)
a fib is tachycardia
ventricular fibrillation (v-fib)
rapid, irregular, heartbeat
hypertension vs. hypotension
hyper. high blood pressure vs. low blood pressure
essential hypertension is?
consistant high blood pressure with and unknown cause
secondary hypertension means?
a medical problem but improves when problem is resolved
malignant hypertension vs. pulmonary hypertension?
malignant is very high blood pressure vs. high blood pressure in the lungs
orthostatic hypotension means?
low blood pressure from standing up
hemostasis means?
to stop or control bleeding
embolism is?
sudden blockage of blood vessel by embolus
aneurysm is?
balloon-like or weakening of an artery walls
stenosis means?
narrowing of an artery by plaque or commpression
atherosclerosis means
hardening from plaque
phlebitis
inflammation of veins
varicose veins are?
swollen veins
thrombus means?
blood clot on interior wall of artery or veins
occlusion means?
blocking or closing of an opening
venous thromboembolism is a?
blood clot in the vein which breaks off and travels
dyscrasia means?
abnormal condition or state
-penia means?
decrease, loss
bacterial infection entering your bloodstream is known as?
sepsis
thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis mean?
thrombocytopenia means decrease in # of platelets and thrombocytosis means increase in # of platelets in the blood
what is the fatty substance that travels through the blood to all body parts?
cholesterol
hyperlipidemia
elevated cholesterol and other fatty substance
LDL or low density lipid is what type of cholesterol?
bad cholesterol
HDL or hight density lipid is what type of cholesterol
good cholesterol
leukemia meaning?
cancer by progressive increase of leukocytes (white blood cells)
anemia
low erythrocytes (red blood cells)
hemochromatosis is?
iron-overload disease where the intestines absorb to much iron
angiography is what type of diagnostic procedure?
x-ray of blood vessels after contrast is injected
duplex ultrasound is what type of procedure?
imaging of blood vessel and the flow of blood through the vessels
what do they use to record the heart electrically?
electrocardiogram
what is a compliance treatment?
following dr’s orders no matter what