Host Defenses I
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Immune response
physiological process coordinated by the immune system to eliminate foreign
substances (antigens)
antigens
any substance that can provoke a response from the immune system, causing it to produce antibodies against it
Innate barriers
the body's first line of defense against pathogens, which can be physical (like the skin and mucous membranes) or chemical (like tears, saliva, and stomach acid)
innate immunity
the body's first, non-specific line of defense against pathogens that is present from birth
lymphatic system
a circulatory system made up of lymph vessels, which are much like blood vessels
edema
tissue swelling
MALT
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; a network of immune cells located in the mucous membranes lining various body systems
granulocytes
a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that contain granules in their cytoplasm. They play a crucial role in the immune system by fighting infections and allergic reactions.
agranulocytes
a type of white blood cell that lack granules in their cytoplasm and include two main types: lymphocytes and monocytes
erythrocytes
red blood cella
leukocytes
white blood cells
neutrophils
highly phagocytic; fight many invaders, especially bacteria and viruses; fast migration
eosinophils
moderately phagocytic; attack allergens and parasites
basophils
attack allergens and parasites
phagocytosis
the process by which a cell engulfs and ingests solid particles, such as microorganisms, foreign substances, or dead cells, through a cellular eating mechanism
neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
web-like DNA structures combined with histones and antimicrobial proteins that are released from stimulated neutrophils
mast cells
phagocytic; typically stationed near body openings; play a crucial role in the immune system and allergic reaction
granules
Histamine, heparin, AMPs, pro-inflammatory enzymes
piecemeal degranulation
a slow releasing process mediated by vesicular transport of stored secretory granule contents
anaphylatic degranulation
the rapid release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells and basophils, triggered by an allergic reaction, such as in anaphylaxis
cutaneous allergic responses
an immune reaction in the skin to an allergen, causing symptoms like redness, itching, swelling, and rashes
mucosal allergic response
an overreaction of the immune system to a harmless substance (allergen) in areas with mucous membranes, such as the nose, throat, and gut
monocytes
largest agranular white blood cell; highly phagocytic once they mature into macrophages (which can be fixed or wandering); activate adaptive immune responses
monocytes
chronic infections, inflammation, disorders, certain cancers
maccrophages
mature monocytes; migrated out of circulatory system
macrophages
a type of white blood cell that acts as a "big eater" of the immune system, responsible for identifying, engulfing, and destroying pathogens like bacteria, damaged cells, and cancer cells
dendritic cells
highly phagocytic; important role in activating adaptive immune system; found in most body tissue- areas with exposure to environment
lymphocytes
B cells and T cells
interferon
What type of pathogen would illicit a cell to produce large amounts of interfero
neutrophils
which cells of the innate immune response are typically the first responders to a wound or infection?
pyrogens
What molecules are responsible for inducing a fever response during an infection?
opsonization, cytolysis, inflammation
Describe 3 outcomes of successful activation of the complement cascade.
adaptive immunity
the body's specialized immune response that targets specific pathogens and builds long-term "immunological memory" through B cells and T cells
stomach acid, lysozyme in tears and AMPs
Give one example of an innate chemical barrier defense of the human body.
natural killer cells
a type of white blood cell in the innate immune system that identifies and kills abnormal cells, such as virus-infected cells and tumor cells
cytotoxic
release specialized proteins; proteins that incapacitate cells structurally and functionally and trigger an inflammatory response
apoptosis
programmed cell death, a natural process where a cell triggers its own death to eliminate unnecessary or damaged cells for the health of the organism
defense and signaling molecules
Eliminate the invading pathogen or limit its spread until the adaptive immune system responds
cytokines
small proteins secreted by immune and other cells that act as chemical messengers to coordinate and regulate immune responses
chemokines
signaling molecules; attract WBCs
chemotaxis
cell movement in response to chemical stimuli
chemokines
subset of cytokines that primarily act as a "call to action," attracting and guiding immune cells to a specific location
interleukins
key communicators in the immune system, regulating immune responses by promoting or suppressing inflammation, activating immune cells, and influencing their growth and differentiation
hematopoiesis
production of new blood cella and platelets
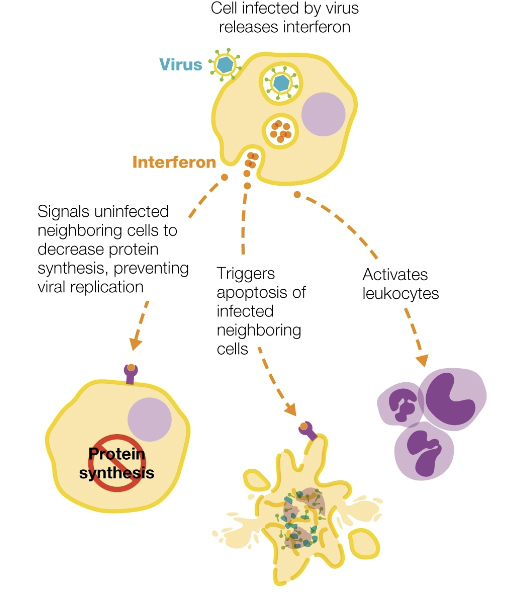
interferons(IFNs)
“interfere” with viral replication; activated innate and adaptive immune reponses to other pathogens
IFN-y
produced by NK cells and certain T cella to activate macrophages
IFN-a and IFN-B
made by virus infected cells
tumor necrosis factor (TNFs)
regulate immune cells and inflammation; capable of killing tumor cells
TNF-a
produced mainly by macrophages, induces inflammation
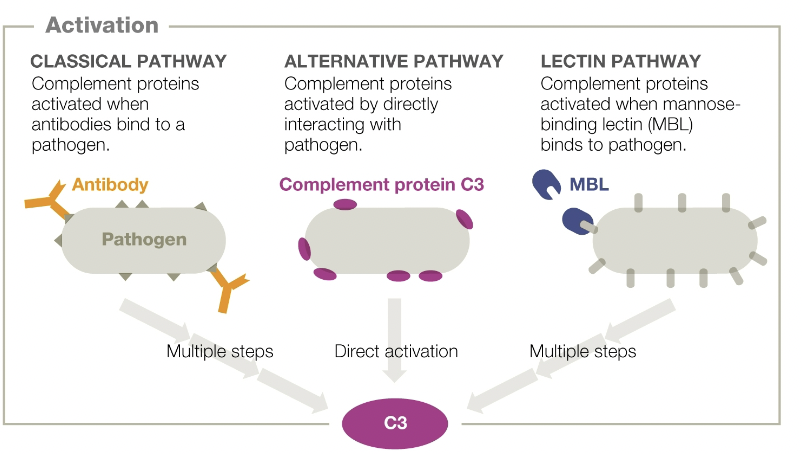
classical pathway
complement proteins activated when antibodies bind to a pathogen
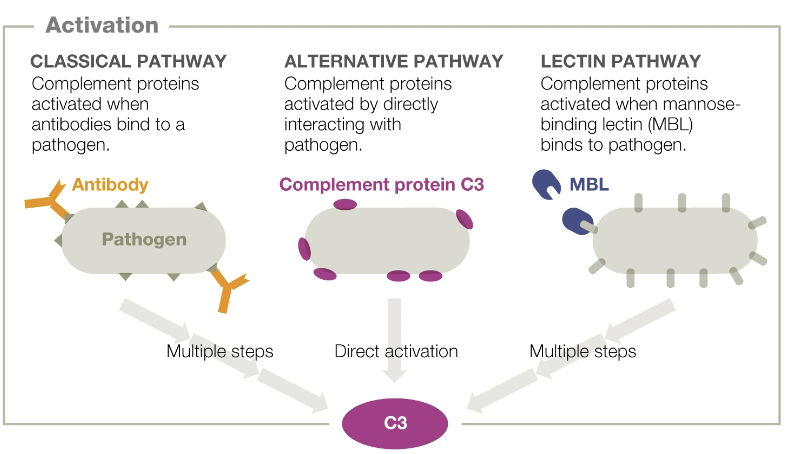
alternative pathway
complement proteins activated by directly interacting with pathogen
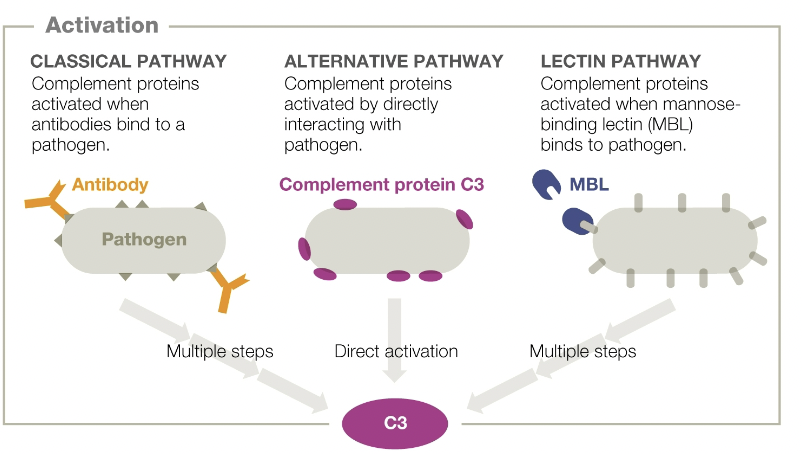
lectin pathway
complement proteins activated when mannose-binding lectin (MBL) binds to pathogen
opsonization
complement protein tags pathogen for phagocytosis
cytolysis
complement proteins form membrane attack complex (MAC) in pathogen’s plasma membrane. Water and ions rush through MAC and lyse cell
inflammation
complement proteins recruit leukocytes, releasing signals that cause ________
inflammation
innate immune response that develops after tissue damage
recruit immune defenses to injured site, limit spread of infectious agents, deliver oxygen, nutrients and chemical factors required for tissue recovery
why does our immune system employ inflammation
redness, pain, localized heat, swelling, and sometimes loss of function
what are some cardial signs of inflammation
vascular changes
chemical alarm signals released by damaged cells and leukocytes increase blood flow and vessel permeability
leukocyte recruitment
cytokines recruit leukocytes. Neutrophils arrive first, followed by monocytes, which mature into macrophages. Neutrophils and macrophages phagocytize invaders and recruit other leukocytes
resolution
inflammation signals decrease; tissue repair initiated
vasodilation
the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow
exudate
a fluid that leaks from blood vessels into nearby tissues, composed of cells, proteins, and other solid materials; associated with inflammation
vasoactive molecules
substances that cause blood vessels to widen (dilate) or narrow (constrict), influencing vascular tone and permeability; pro-inflammatory/active pain receptors
chemoattractants
chemical substances that induce directional movement in cells, guiding them toward higher concentrations of the substance
margination
leukocytes slow as they roll along vessel wall; eventually leukpcytes adhere to vessel wall
diapedesis
leukocytes change shape; leukocytes squeeze out of vessel
macrophage maturation
inflammation- resolution
return of capillaries to normal state; damaged vessels repaired
angiogenesis
the natural process of forming new blood vessels from existing ones
fever
abnormally high systemic body temp
pyrogens
fever-inducing agents
hypothalamus
what do cytokines signal to raise body temp
low grade fever
enhances antiviral effects of interferons, promotes tissue repair, limits growth of certain pathogens
interferon
cell infected by virus releases ________
interferon
signals uninfected neighboring cells to decrease protein synthesis, preventing viral replication
interferon
triggers apoptosis of infected neighboring cells
interferon
activates leukocytes