Market Structures (3.1) - Monopoly
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Monopoly
A market structure in which there is only one firm who controls the entire output of the industry.
Assumptions/features of Monopolies
One firm in the industry: Only one firm exists within the industry so there is no distinction between firm and industry. The first supplies the entire output of the industry.
Profit maximisation: it is possible for the firm to earn SNP’s in both the short run and the long run. A firm aims to make maximum profits and this is the point where MC=MR
Barriers to entry exist: If a monopoly market structure is to exist in the long run, there cannot be freedom of entry into the industry. The creation of barriers to entry prevent the entry of new firms into the industry.
Unique good or service sold: A monopoly market structure sells a unique good or service to consumers and there are no substitutes for consumers to purchase.
Price maker/ setter
A firm with a monopoly that gives it the power to influence the price it charges as the good it produces does not have perfect substitutes.
Implications of the assumptions of monopolies
Short run equilibrium and long run equilibrium are the same. Hence, there is only one position.
The monopolists face a downward sloping demand curve and as such the monopolist must lower price to sell more goods.
Due to the level of market power that monopolies have, as well as their ability to exploit the consumer, government monitoring is far more common with monopolies than any other market structure. This is to prevent the monopoly from engaging in practices that are against the publics best wishes.
Natural Monopoly
A natural monopoly occurs in industries where high fixed costs and significant economies of scale make it most efficient for a single firm to supply the entire market. These are often subject to government intervention to protect consumers and ensure fair prices.
Illegal Monopolies
Maintain their monopoly positions through anti-competitive practices. I.e. price limiting, mergers + acquisitions.
Barriers to entry
Restrictions which prevent new firms from entering an industry.
Barriers to entering a monopoly market
Legal/statutory Monopoly: Other firms may not be allowed into the industry because the government gives a firm the sole right to supply a particular good or service.
Ownership of a patent/copyright: if a firm has the sole right to a manufacturing process, then no other firm can compete with it. Other firms are not allowed to use this patent until the time period for it has expired which gives the firm a temporary monopoly.
Large capital investment: In some industries the minimum size of a firm required to operate efficiently is so large that there is no room for competitors once one firm has established itself. Competitors are discouraged from entering because of the high initial start up costs as only large firms will be able to fund the necessary investment.
Mergers
Brand proliferation
Aggressive pricing tactics: price limiting
Advantages of Monopolies
Economies of Scale: Monopolies gain a cost advantage due to their large scale of operations. Eg. Discounts for bulk buying.
Guarantee supply of Product/service: It is unlikely that monopolies will go bankrupt therefore they ensure the provision of goods and/or services.
Employment: This ensures stable employment and job security for employees.
Potential for Innovation: The SNP’s that are earned by monopolies can be reinvested into R&D, which will lead to consumers getting better products.
Disadvantages of Monopolies
Higher Prices: Monopolies can charge higher prices, compared to perfect competition because there is no competition.
Lower Output Produced: Monopolies with similar costs to a firm in perfect competition may produce a lower output compared to a firm in Perfect Competition. Scarcity results in higher prices. Consumer choice is restricted as there are no alternatives available.
Inefficiency/Wasteful of resources: A monopolist does not produce at the lowest point of the AC curve. This results in monopolies wasting scarce resources.
Lack of innovation: The lack of competition means that a Monopolist does not have to innovate or develop new products or services. Consumers don’t benefit from better and updated products.
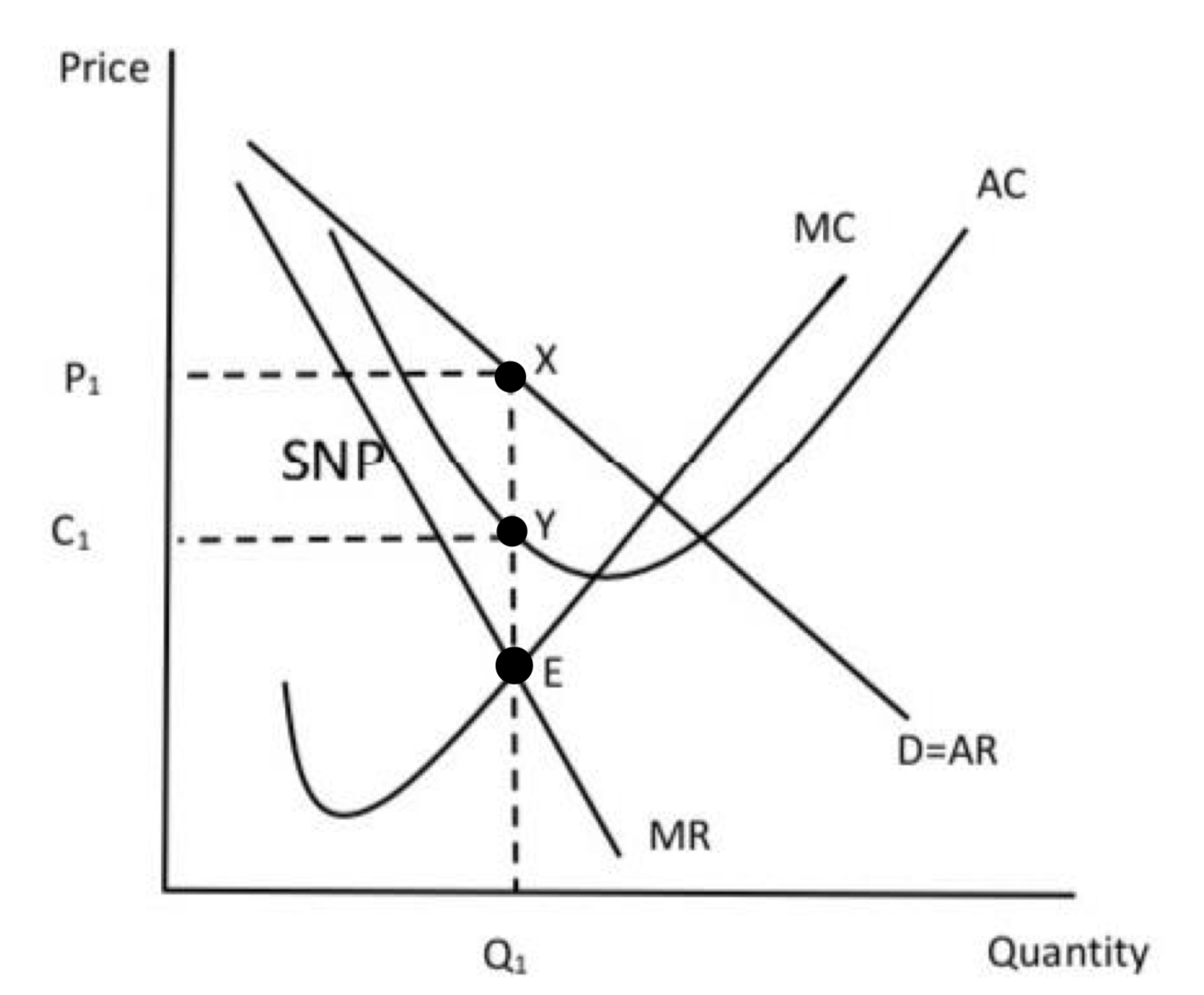
Long run and short run Equilibrium of a Monopolist
Super Normal Profits → Average Revenue exceeds Average Costs (AR > AC), will continue to earn SNP’s as barriers to entry exist.
Price → The firm produces at Q1 and sells at P1
Equilibrium → Occurs at point E where Marginal cost equals Marginal Revenue (MC=MR) and Marginal Costs is rising (MC cuts MR from below)
Costs → Shown at point C1
Scarcity → The firm is not making efficient use of scarce resources because they don’t produce at the lowest point on the Average Cost Curve.
remember specs
Price Descrimination
When the same goods or services are sold to different consumers (in different markets) at varying ratios between marginal cost and the price. The price difference is not due to differences in the cost of production.
Conditions needed for price discrimination to occur
Some Monopoly/market power: Firms must have some ability to alter the market price by exercising control over its demand, supply or both. If freedom of entry existed into the industry, competitors would enter where the firm was charging the higher prices and earning SNP and this would continue until normal profit was being earned.
Separation of markets: The markets must be distinct and separate. This ensures that the good bought in the low-priced market cannot be offered for resale in the higher priced market (no resale between markets)
Different Consumer Price Elasticities of Demand: Different Consumers display different sensitivities to price I.e. they have different price elasticities of demand. Consumers with the greater PED are charged the lower priced market for their goods.
Characteristics of a consumer needed for a monopolist to price discriminate
Consumer Indifference/ Inertia: The difference in price mag be so small that consumers are indifferent and so don’t mind paying the slightly higher prices.
Consumers ignorance: Consumers may be unaware that the good is available elsewhere at a lower price.
Consumer Attitudes to the Goods: A consumer may be willing to pay a higher price for a good which he considers to be in fashion / provide status. e.g. people and their desire to buy ‘branded’ products.
Regulation
The controlling of an activity or process, usually by means of rules and legislation.
Positive effects if regulation
Improves public welfare:
Companies can be closed:
Corrects market failure:
Negative effects of regulation
Impedes profitability:
Net cost on society:
Time consuming/ inefficient:
Deregulation
Removing barriers to entry into a market. This results in more suppliers/ competition into the market which causes lower prices.
Positive effects of deregulation on consumers of the good/service
Lower Prices: Increased competition resulting from the entry of new firms will result in consumers benefitting from more competitive prices.
Increased availability of service: Following an increase in supply of an industry, the ease with which a consumer can avail of a service also increases.
Positive effects of deregulation for employees in the industry
Job Opportunities: New suppliers may offer increased employment opportunities to workers currently in the industry.
More motivated Workforce: Competition may pressurise the workforce to become more productive in their jobs which would lead to higher efficiencies.
Positive effects of Deregulation on the profits of existing firms
Increased Profits: If the existing businesses can meet the new competition and expand their business activities the business may experience economies of scale and earn more profit as a result.
Negative effects of deregulation on the consumers of the goods/services
Decline in Standards of service: The service provided by the semi state company may deteriorate in quality in an effort to save costs.
Disruption to Supply of Service: The fear of workers about the effects of competition may cause them to engage in industrial disputes disrupting the service for consumers.
Negative Effects of Deregulation on Employees in the industry
Reduced Job Security: Public Sector employees have a lot of job security. The biggest risk to employees is the loss of their job through rationalisation of services.
Changes in Conditions of Employment: The firm may change the conditions of employment for its employees.
Price limiting
When a firm with monopolistic power or a government sets A maximum or minimum price for a good or service, i.e price floor or price ceiling.
The Negative Effects of Deregulation on the Profits of Existing Firms
Decreased Profits: If existing businesses experience a loss of business, their market share falls resulting in a loss of profits.