Axial Skeleton
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Last updated 7:04 PM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Synarthrosis Joints
Immovable joints, present only in skull
2
New cards
4 Types of Suture Joints
Coronal, Sagittal, Lambdoidal, Squamous
3
New cards
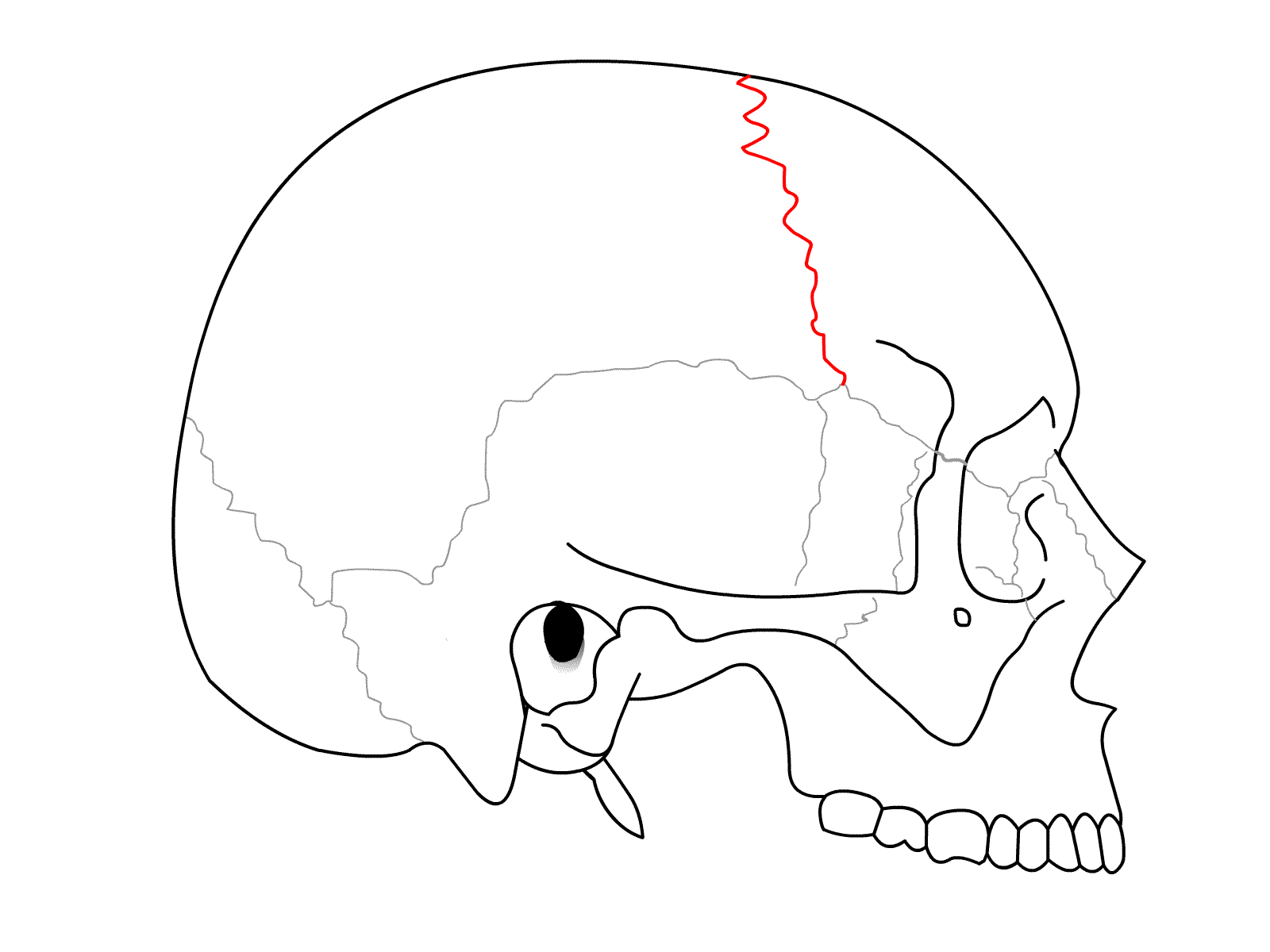
Coronal Suture
The suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
4
New cards
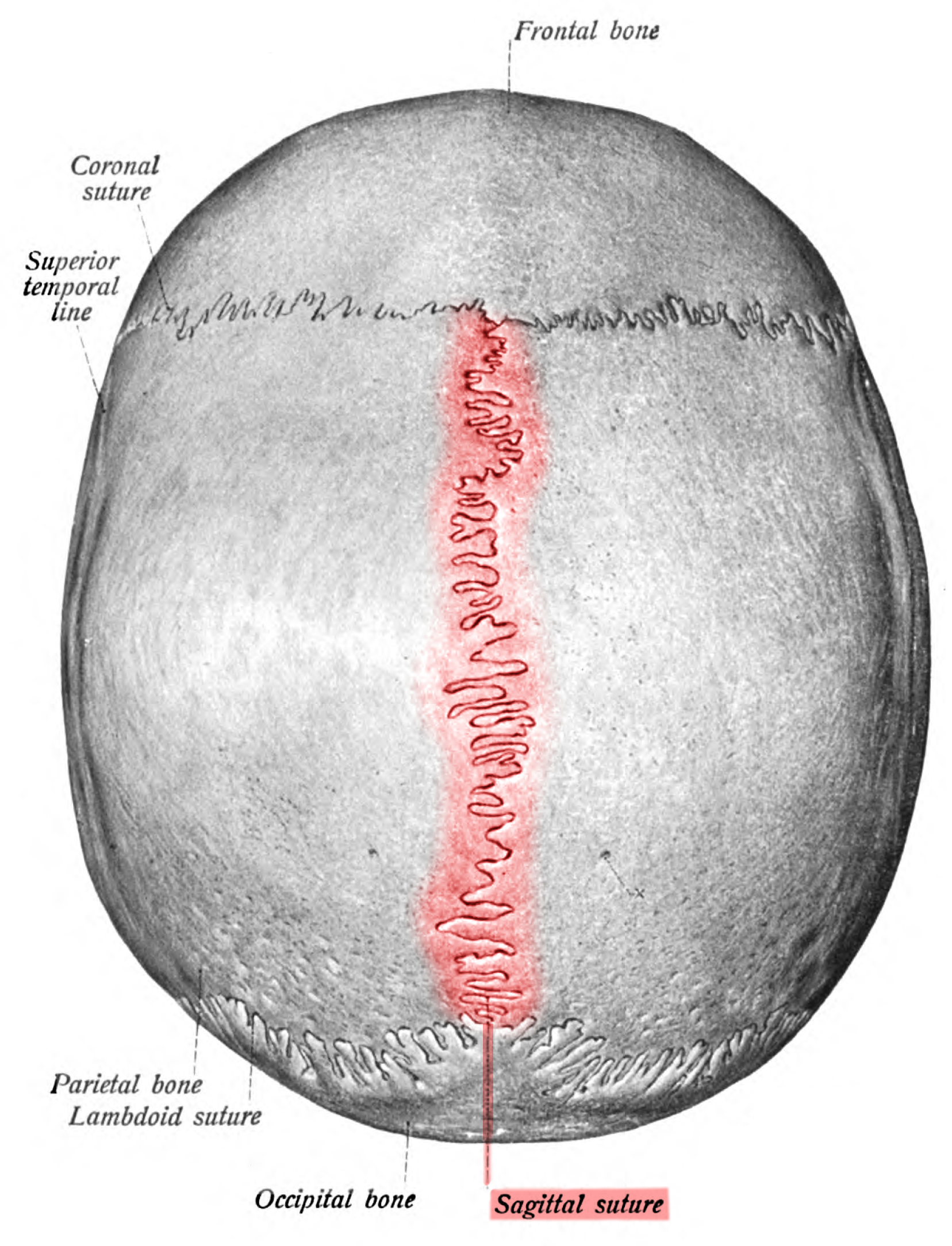
Sagittal Suture
The suture uniting the two parietal bones
5
New cards
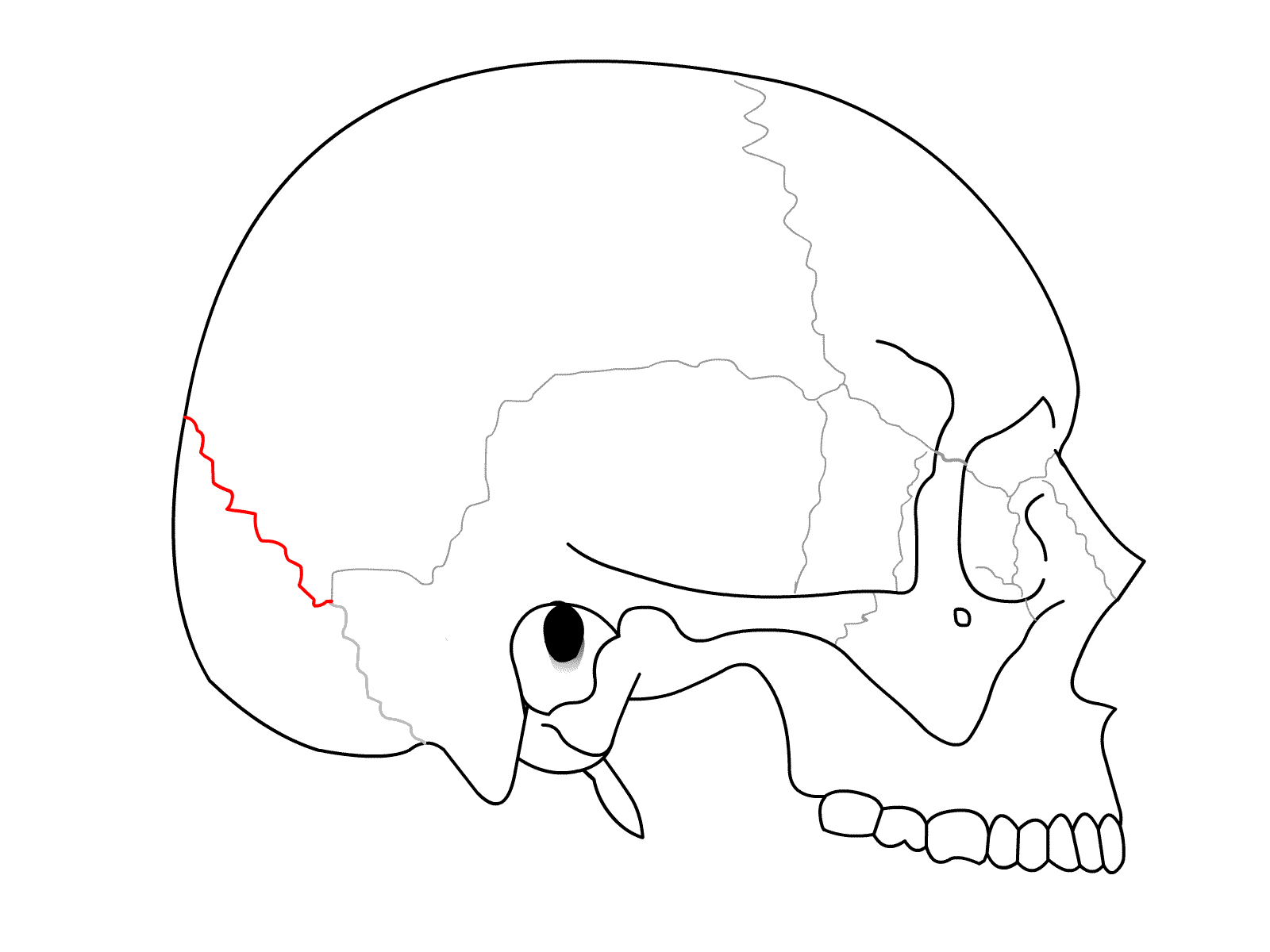
Lambdoidal Suture
Suture between the parietals and the occipital bone
6
New cards
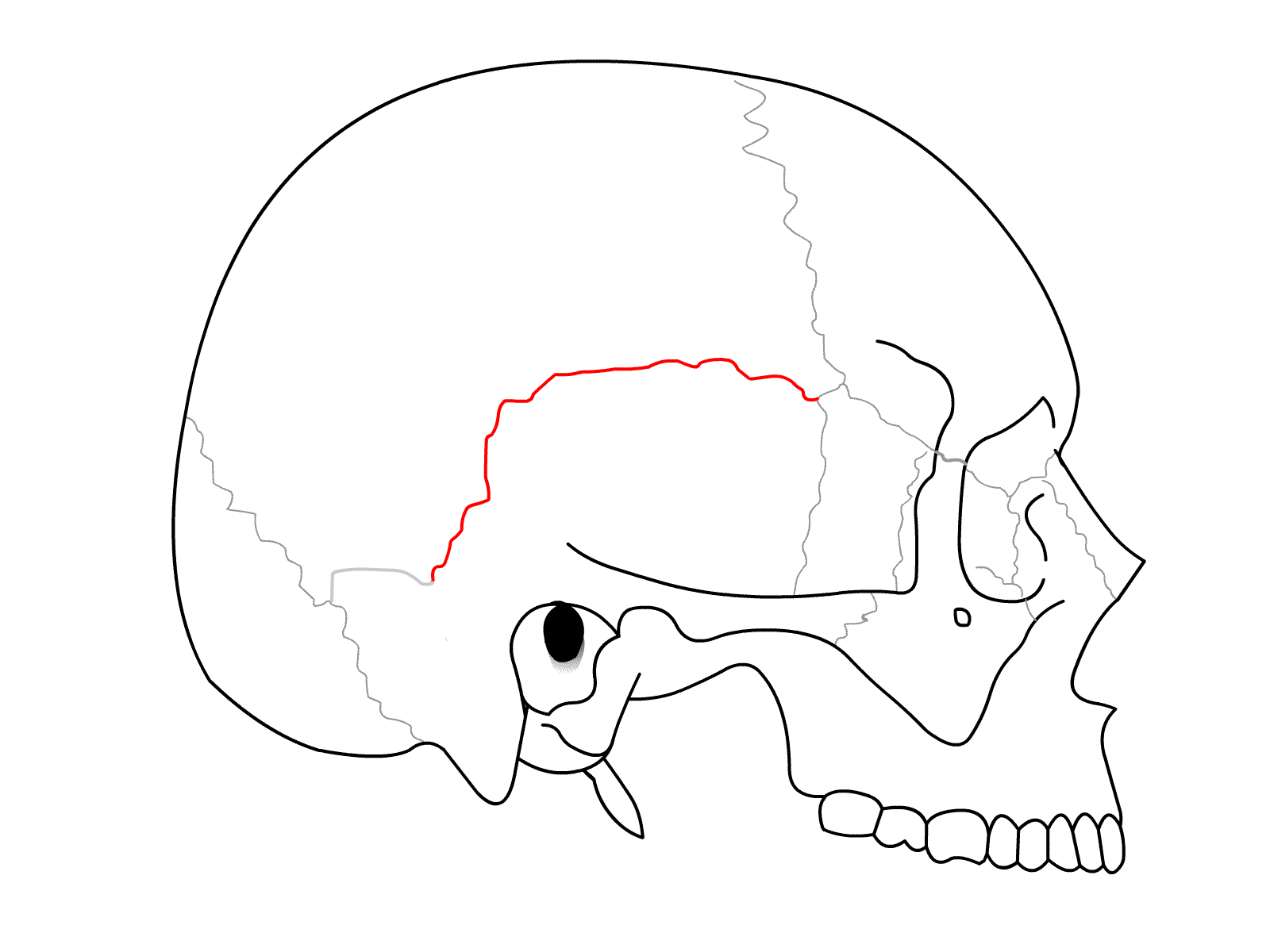
Squamous Suture
Suture between the parietals and the temporal bone
7
New cards
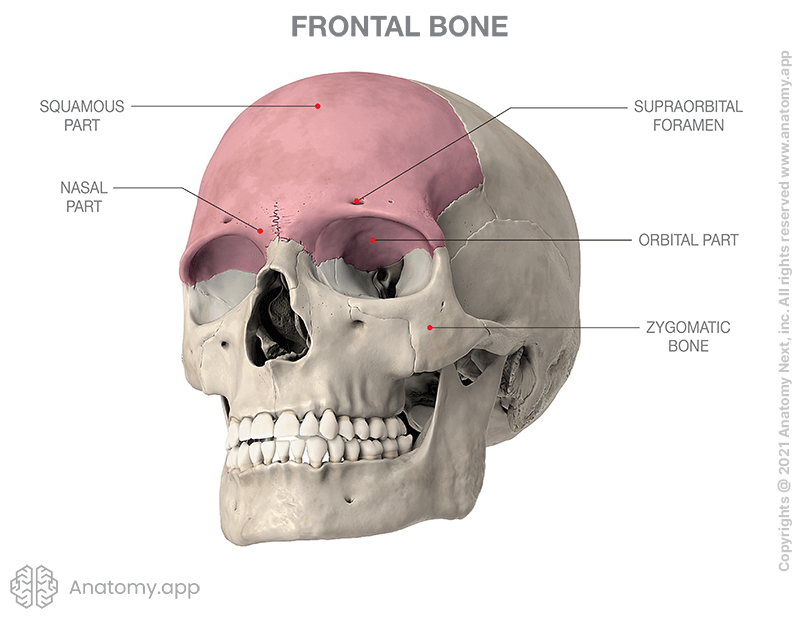
Frontal Bone
The large cranial bone forming the front part of the cranium: includes the upper part of the orbits
8
New cards
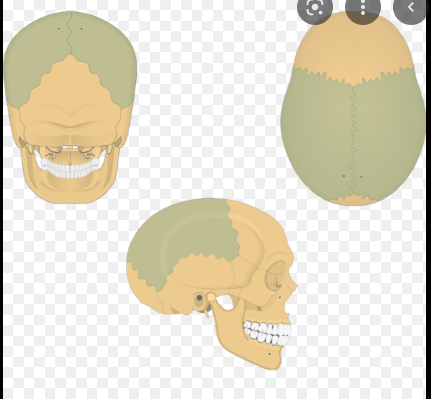
Parietal Bones
Two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
9
New cards
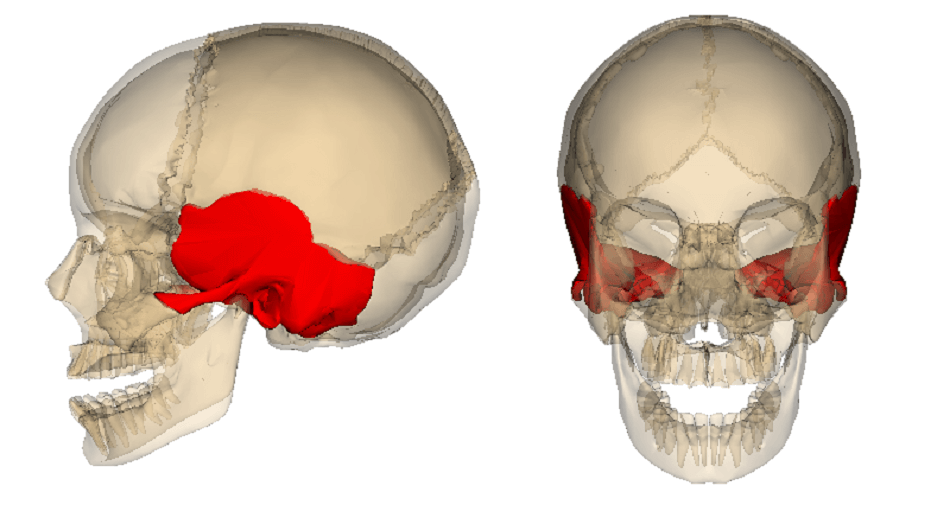
Temporal Bones
Thick bones forming the side of the human cranium and encasing the inner ear
10
New cards
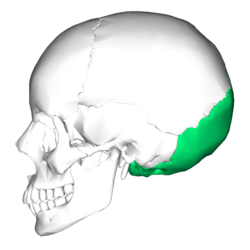
Occipital Bone
A saucer-shaped membrane bone that forms the back of the skull
11
New cards
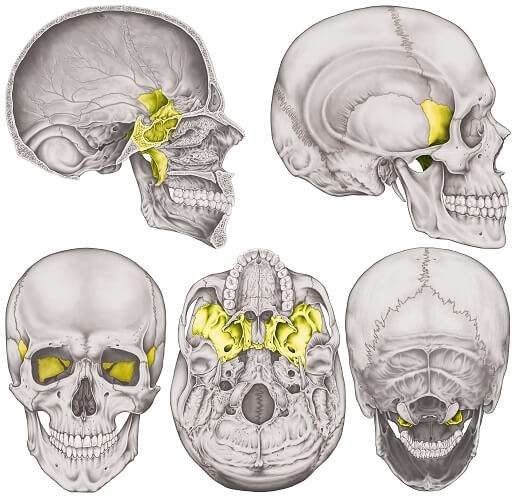
Sphenoid Bone
Butterfly-shaped bone at the base of the skull, holds all other bones together
12
New cards
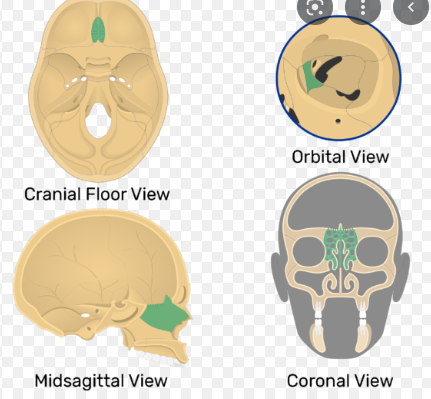
Ethmoid Bone
A small bone located between the orbits in the skull, comprising part of the sinuses
13
New cards
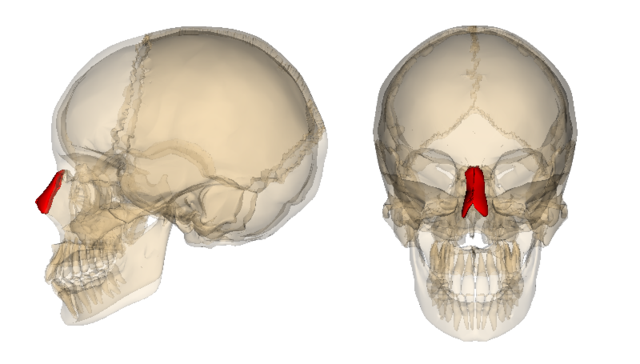
Nasal Bones
Two bones on either side of the nose, of varying shape and size depending on genetics, irregularly shaped
14
New cards
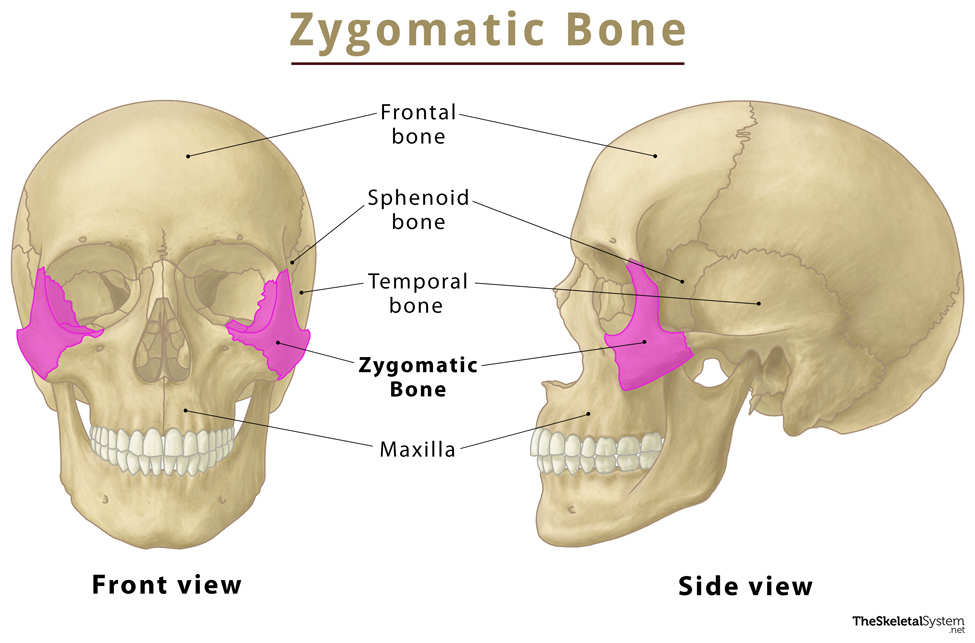
Zygomatic Bones
Two irregularly shaped bones on either side of the skull; form the cheekbones
15
New cards
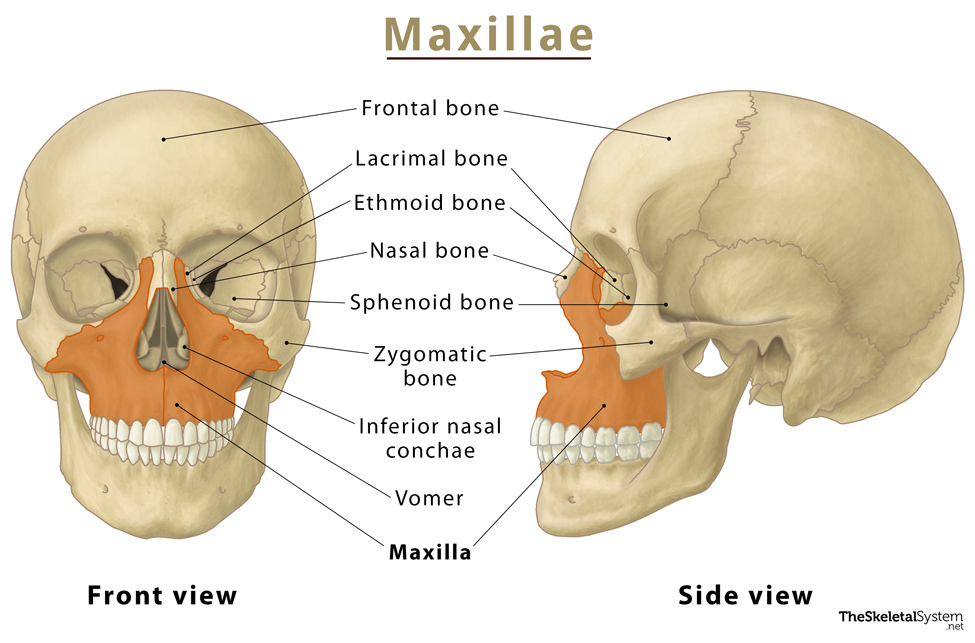
Maxillae
The bone that forms your upper jaw. The right and left halves are irregularly shaped bones that fuse together in the middle of the skull, below the nose, in an area known as the intermaxillary suture
16
New cards
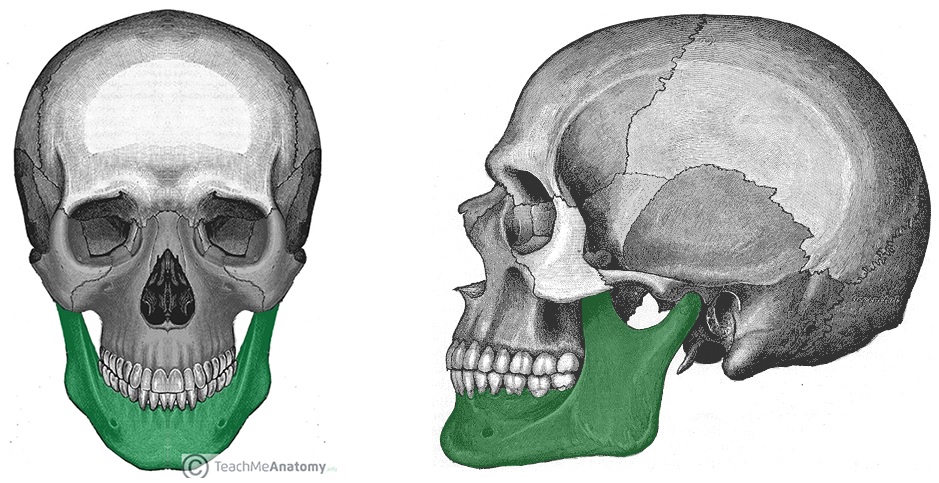
Mandible
Lower jaw bone, detached & movable, irregular bone
17
New cards
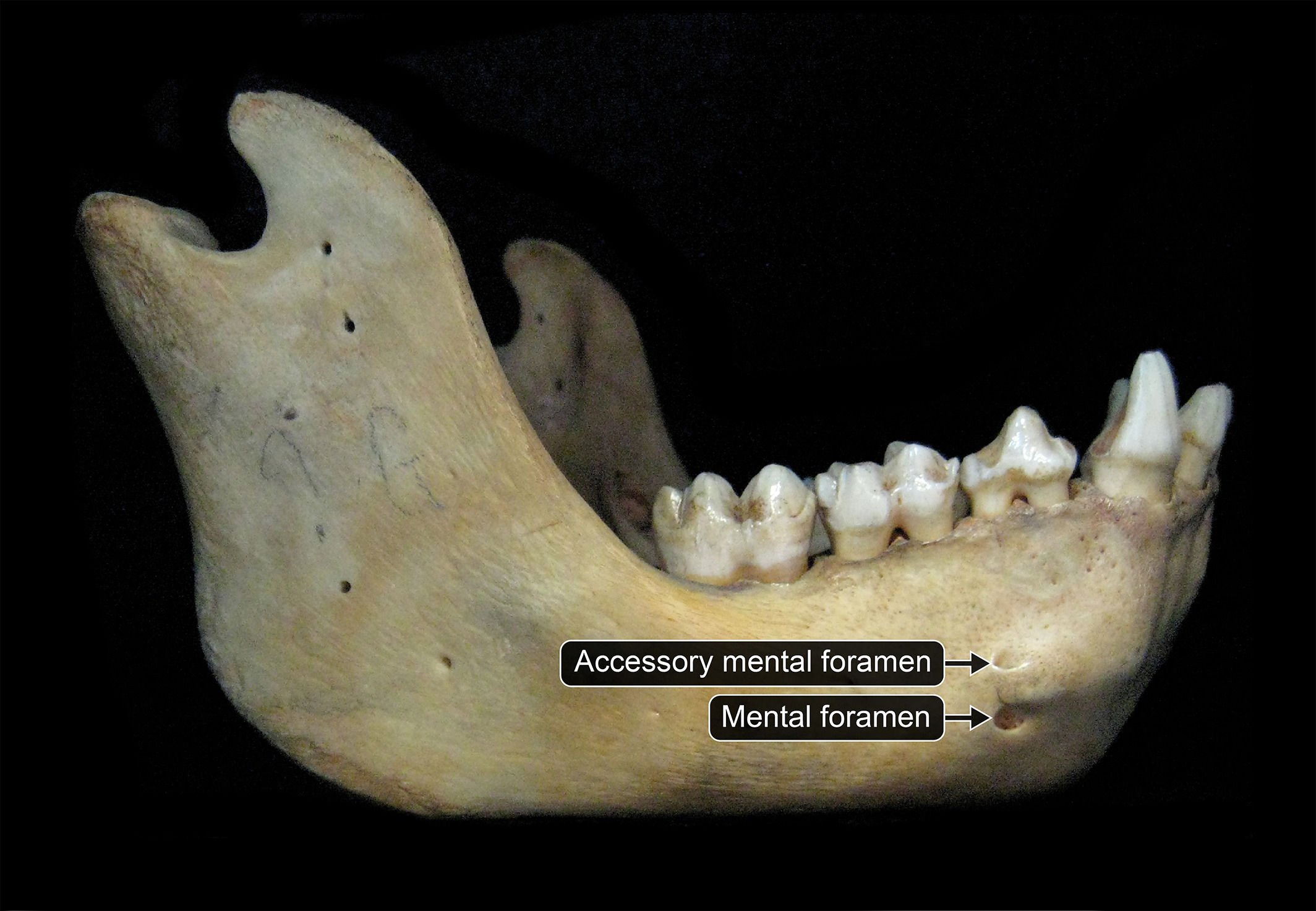
Mental Foramen
Entry points in the mandible bone for blood vessels
18
New cards
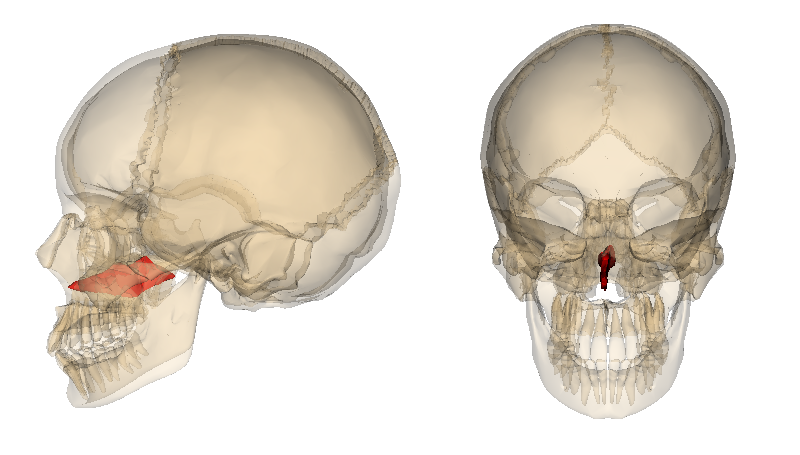
Vomer
Thin trapezoidal bone of the skull forming the posterior and inferior parts of the nasal septum
19
New cards
Inferior Nasal Concha
Small irregularly shaped bones in the sides of the nasal canal
20
New cards
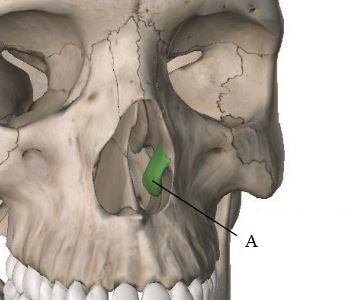
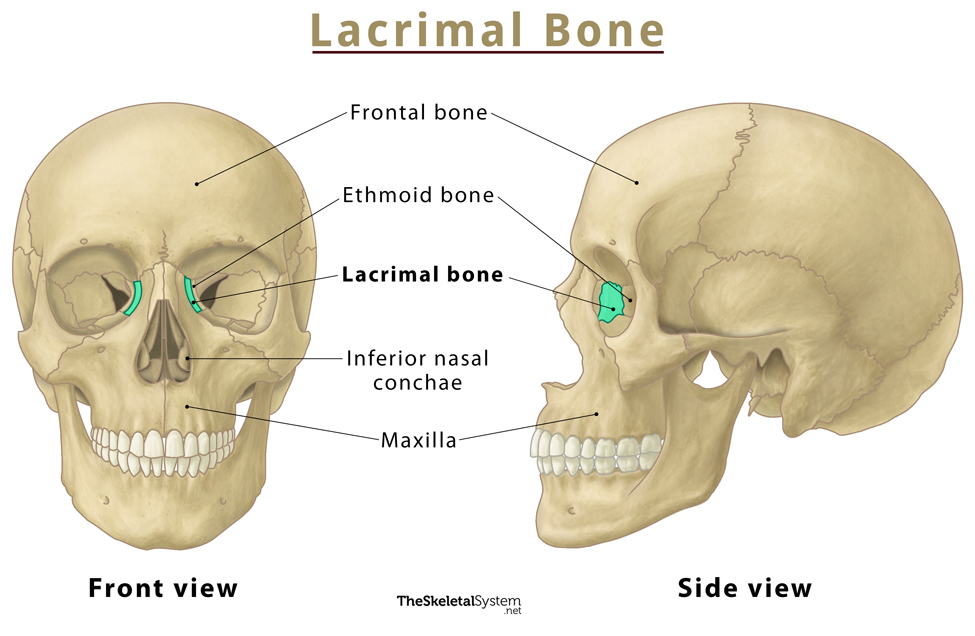
Lacrimal Bone
Small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts; drains eyes to nasal
21
New cards
Foramen Magnum
The large opening at the base of the cranium through which the spinal cord passes
22
New cards
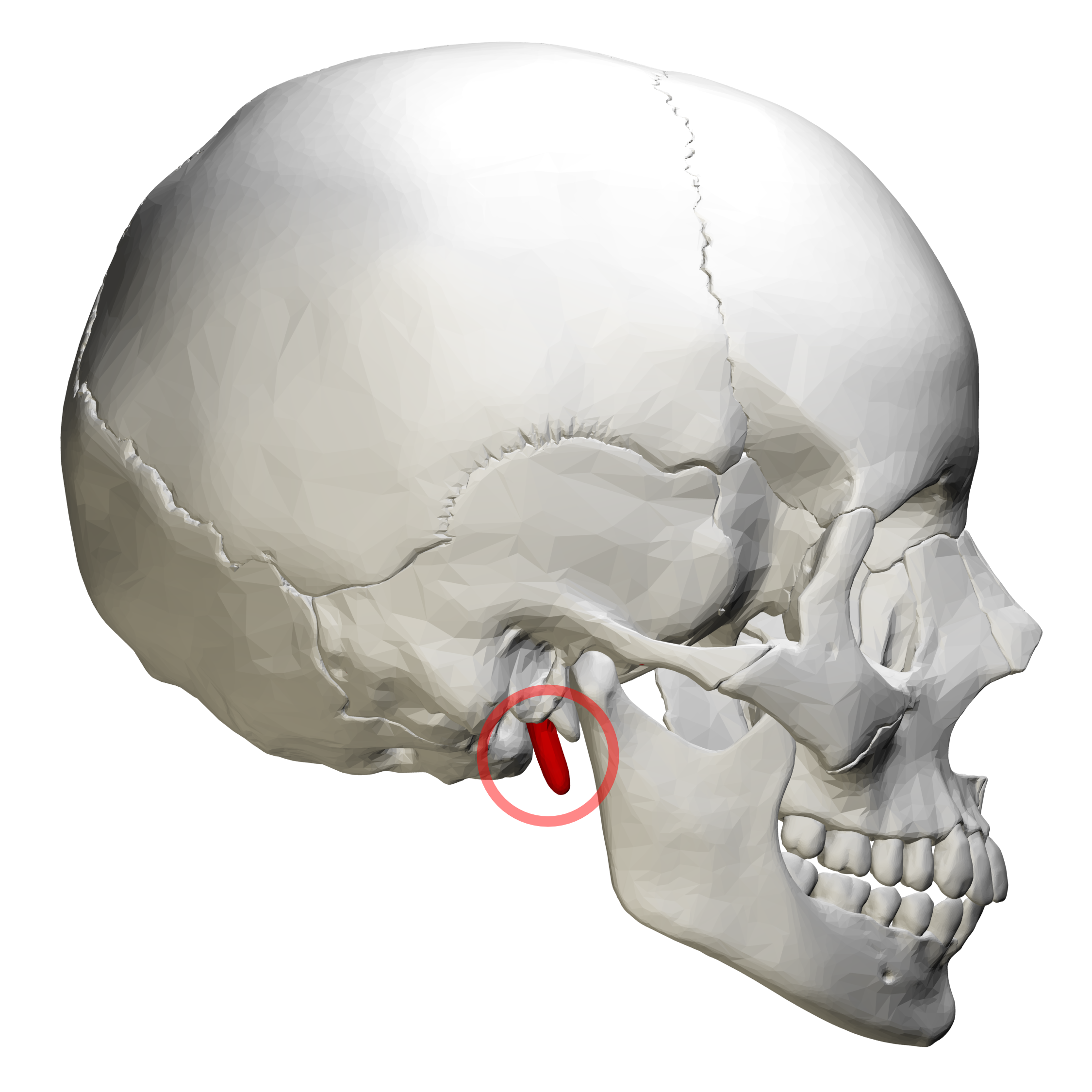
Styloid Process
Extends from the base of the temporal bone
23
New cards
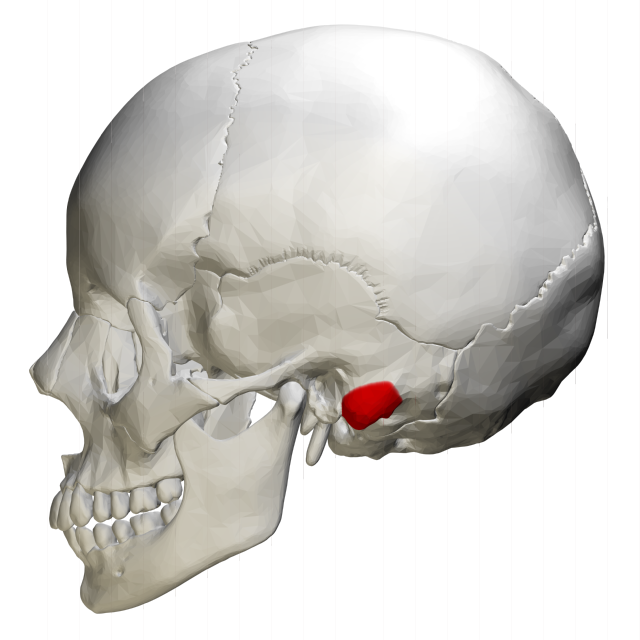
Mastoid Process
A smooth conical projection of bone located at the base of the mastoid area of the temporal bone. It allows the attachment of muscles.
24
New cards
External Auditory Meatus
Hole in the side of the cranium which forms the ear canal
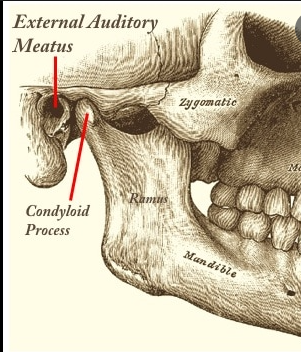
25
New cards
External Occipital Protuberance
Small bump on occipital bone which serves as a muscular attachment point
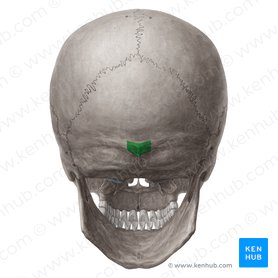
26
New cards
Palatine Bones
Two bones in upper jaw, forming roof of mouth/hard palate
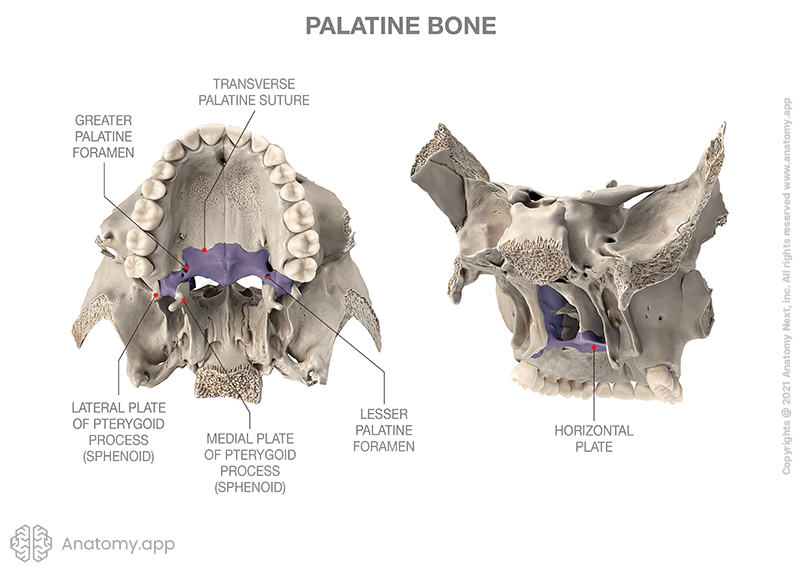
27
New cards
Vertebral Column
26 bones in total; Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, and Coccyx
28
New cards
Cervical Spine
Seven bones; bifid spinous (two bumps); first bone is called Atlas, second is called Axis.
29
New cards
Atlas Vertebra
First cervical vertebra, holds up skull, allows for nodding motion
30
New cards
Axis Vertebra
Second cervical vertebra, allows for head-shaking motion, has a structure called a dens which is a bump.
31
New cards
Thoracic Vertebrae
Articulate with ribs, look like giraffe's face, downward spinous
32
New cards
Lumbar Vertebrae
Largest and strongest of the vertebrae; looks like moose's face; square spinous
33
New cards
Sacrum
Wedge-shaped bone consisting of five fused vertebrae forming the posterior part of the pelvis; permits articulation of two hip bones; contains many foramen for nerves
34
New cards
Coccyx
Tailbone; points inferiorly in those with birth canals, anteriorly in those without
35
New cards
Vertebral Discs
Discs of cartilage between vertebrae which absorb shock
36
New cards
Vertebral Fusion
The placing of a vertical rod between two vertebrae, keeping the disc in place while eliminating the ability for those two vertebrae to bend
37
New cards
Herniated Disc
A painful slip of the fibrocartilage of the disc between spinal vertebrae; occurs most often in the lumbar region; causes disc to put pressure on spinal cord
38
New cards
Scoliosis
An abnormal lateral curve to the vertebral column
39
New cards
Kyphosis
An abnormal backward curve to the vertebral column; observed most commonly in the elderly due to muscular atrophy
40
New cards
Rib Cage
12 pairs of ribs (24 in all), plus sternum
41
New cards
Sternum
Flat bone which connects all ribs in the anterior face of the ribcage; Manubrium (top), body (middle, part with most of the rib connections), Xiphoid Process (very bottom tip, can break off during CPR and puncture lungs)
42
New cards
True RIbs
7 pairs-- connect directly to sternum
43
New cards
False Ribs
5 pairs, including floating ribs-- connect indirectly to sternum
44
New cards
Floating Ribs
2 pairs-- don't connect to sternum at all, connect only to thoracic spine; technically also false ribs
45
New cards
Inner Ear Bones
Hammer, anvil, stirrup; malleus, incus, stapes
46
New cards
Malleus
Hammer ear bone
47
New cards
Incus
Anvil ear bone
48
New cards
Stapes
Stirrup ear bone
49
New cards
Manubrium
Top of sternum
50
New cards
Rib Facets
The part of the rib which articulates with the thoracic spine
51
New cards
Floating ribs are false ribs
Why are there 7 pairs of true ribs, 5 pairs of false ribs, and 2 pairs of floating ribs when there are only 12 pairs of ribs in all?