The Respiratory System
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What does water have in it?
Dissolved oxygen.
What is a respiratory surface?
Where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in and out of the lungs and are diffused.
What are the characteristics of a respiratory surface? (There are four).
1.) They are usually a thin, single layer of cells,
2.) Moist because the oxygen and carbon dioxide must be in a solution (liquid) for diffusion
3.) Must be in contact with an environmental source of CO2 (like water for fish)
4.) The respiratory surface must be large enough to supply every cell of an organism with oxygen
What is diffusion in the respiratory system?
The system of oxygen going in and carbon dioxide going out.
Gas exchange by . . .
Diffusion.
What is a respiratory pigment?
A protein in the blood that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide to different places. It can carry oxygen to where it's needed for cellular respiration and carbon dioxide to where it's exhaled. The human is hemoglobin.
What are the characteristics of hemoglobin
1.) 100 times more O2 then H20
2.) It is a type of red blood cell
3.) It contains iron
4.) One hemoglobin cell holds 4 O2 molecules
What are earthworm respiratory characteristics?
1.) Moist soil
2.) Thin moist skin
3.) Layered in mucus.
What are the problems with the earthworm respiratory system?
It has to be moist so if it isn't the earthworm will suffocate.
What is the respiratory system of the earthworm?
1.) O2 from the soil diffuses into the earthworm's skin.
2.) Blood in the capillaries picks up the O2.
3.) The oxygen bonds with the hemoglobin
4.) Gas exchange between the blood and cells occur where the oxygen goes to the blood and the carbon gets released.
*Unlike humans, hemoglobin is not contained in red blood cells, it instead is dissolved directly in the blood plasma.
What is the respiratory system of an amoeba?
An amoeba doesn't have a respiratory system. It instead has respiration through its cell membrane through diffusion releasing carbon dioxide and absorbing dissolved oxygen.
What is a hydra or hydridae?
A tiny freshwater animal related to jellyfish.
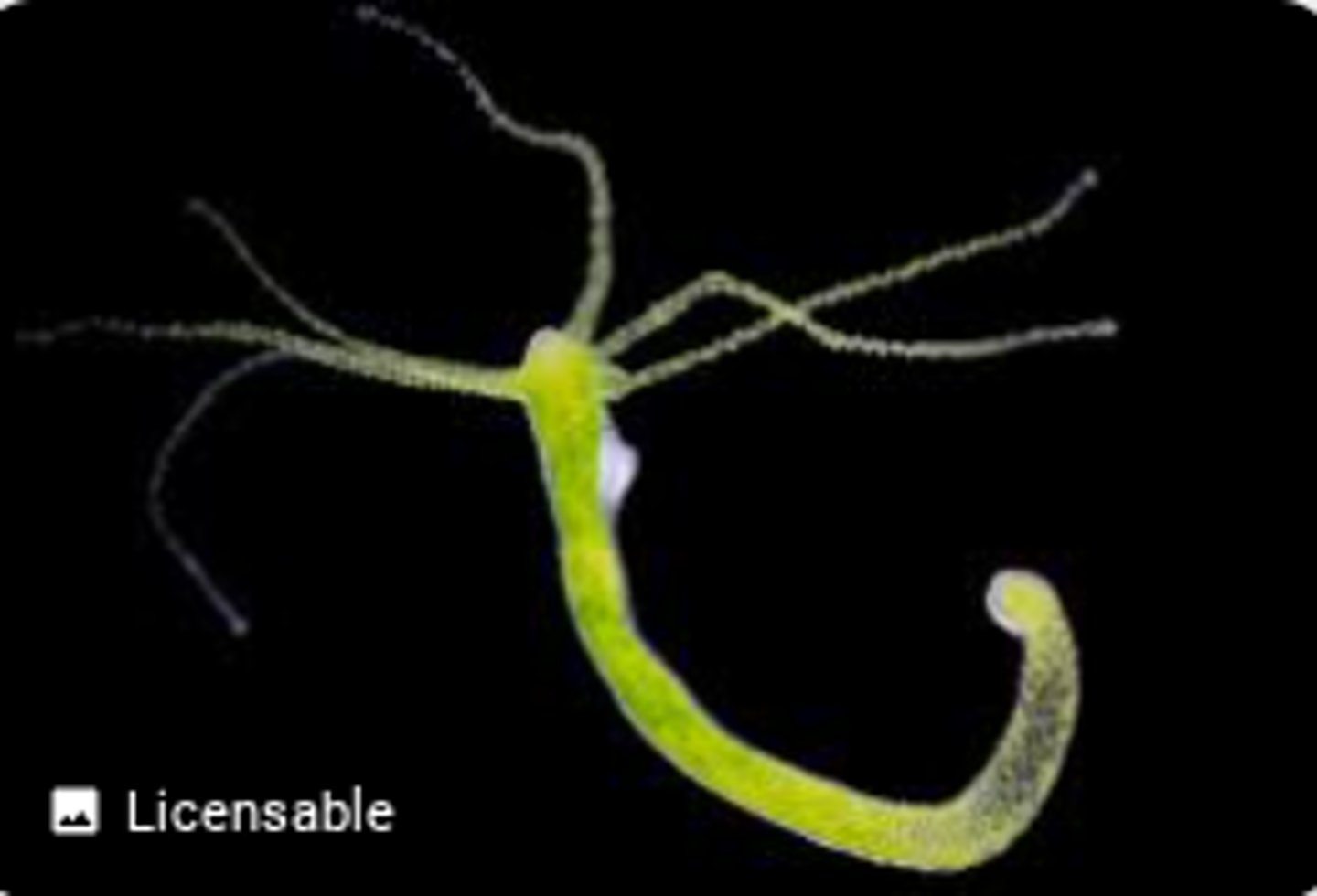
What is the respiration in a hydra?
The hydra relies on direct diffusion for gas exchange so there is no need for a direct organ to help with it. It must be in direct contact with water. It has two layers: the endoderme which is the innermost layer, and the ectoderme which is outside that. The basal disc is outside both of those and attaches to the surface (rock). The mesoglea is a thin gelatinous layer between the endoderme and the ectoderme for structural support.
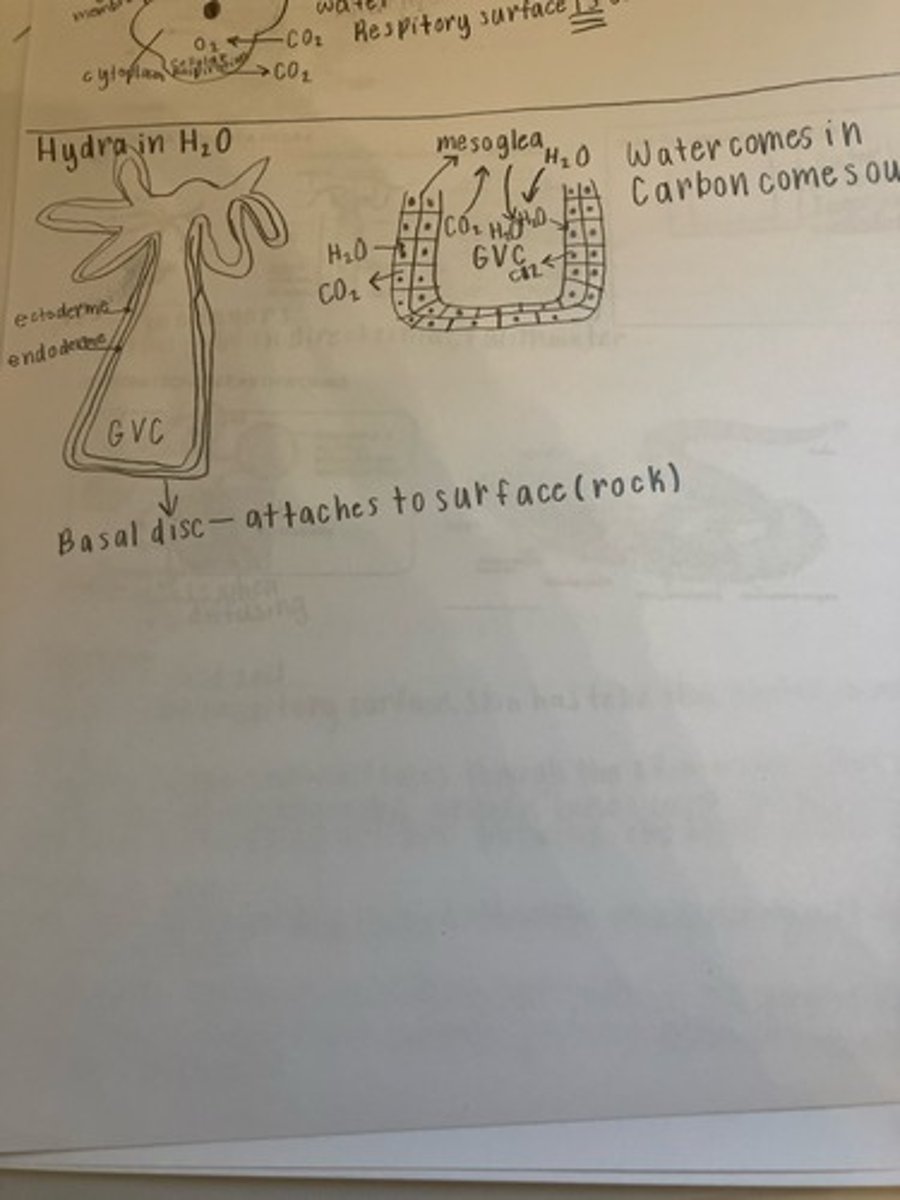
What is the endoderme?
The innermost layer of a hydra
What is the ectoderme?
The outer layer of a hydra
What is the mesoglea?
The layer sandwiched in between the ectoderme and endoderme to provide structural support for the hydra's respiratory system.
What is the respiratory system in grasshoppers?
THE BLOOD DOES NOT TRANSFER GASES!
1.) Air enters and leaves through spiracles into the tracheal tubes (the tips of the tubes are moist for gas exchange).
2.) For inhalation the abdomen expands and air comes in.
3.) For exhalation the abdomen contracts and the air moves out.
What are the characteristics of the respiratory system in a grasshopper? More specifically the respiratory surfaces?
The tracheael is the respiratory surface and the tracheole is the system of branching tubes that terminate at the end.
What are the complications with the grasshopper respiratory system?
Drowning occurs when the body is submerged not the head.
Cell respiration
Coverts glucose and oxygen into energy
Respiration
Facilitates gas exchange between an organism and its environment
What are the qualities of air?
21% of the atmosphere is oxygen. Internal respiratory surfaces keep it moist for land organisms
What are the qualities of water?
3-5% is dissolved oxygen
What are examples of respiratory surfaces?
Alvelous, Skin, Gills, Tracheal System
What are the tracheal used for?
Grasshoppers breathe using a tracheal system, not lungs, with oxygen entering through spiracles (holes on the body sides) into tubes (tracheae) that branch into tiny tracheoles, delivering oxygen directly to cells. It is used for gas exchange.
What are spiracles?
Openings on the side of a grasshopper on the abdomen that regulate air inhalation and exhalation.
What are the characteristics of the fish respiratory system?
Gills are fin filaments of skin that grow out of the body and are rich in blood vessels.
What is the process of the fish respiratory system?
1.) Water passes over the gills and the oxygen that is dissolved in the water diffuses across the gill membrane into the blood in the capillaries.
2.) The CO2 from the blood passes out from the gills and into the water.
-Gills can remove 80% of the oxygen from the gill membrane into the blood of those capillaries.
What is a capillary?
In the respiratory system, a capillary is a tiny blood vessel wrapped around the alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs, forming a network that enables gas exchange
What is the problem with the fish respiratory system?
Must be a continuous flow of water or gills will dry out and fish will suffocate.
What is the first of the three phases of gas exchange?
Breathing: Gas exchange between the lungs and the blood.
What is the second of the three phases of gas exchange?
Transport: The blood transports oxygen to the cells. Carbon dioxide from the cells enters the blood and goes to the lungs.
What is the third of the three phases of gas exchange?
Cellular respiration: The cells use oxygen for aerobic respiration and the carbon dioxide is a waste gas for cell respiration. It is the process where oxygen and glucose produces energy and then releases carbon dioxide and water as waste to exhale.
What are the three functions of the nose?
1.) To filter air using mucus and nose hairs.
2.) Warms air by using the blood in the capillaries.
3.) Moistens air using mucus.
Where is the pharynx located and what is the function?
The pharynx is located behind the mouth and the nasal cavity. It is the common passage for air, food, and liquids. The adenoids and tonsils are located there. It is used for defense.
What is the function of the larynx?
It is the voice box. It is made of mostly cartilage. The vocal cords vibrate as air passes through. It controls air flow during breathing, protects the airway during digestion of food, but the main one is that it produces sound.
What is the trachea?
It is 12 cm long and 2 1/2 cm wide. It is composed of 16-20 c-shaped rings of cartilage that keeps it open. It's function is to provide a clear, unobstructed airway for the passage of air in and out of the lungs, thereby facilitating respiration.
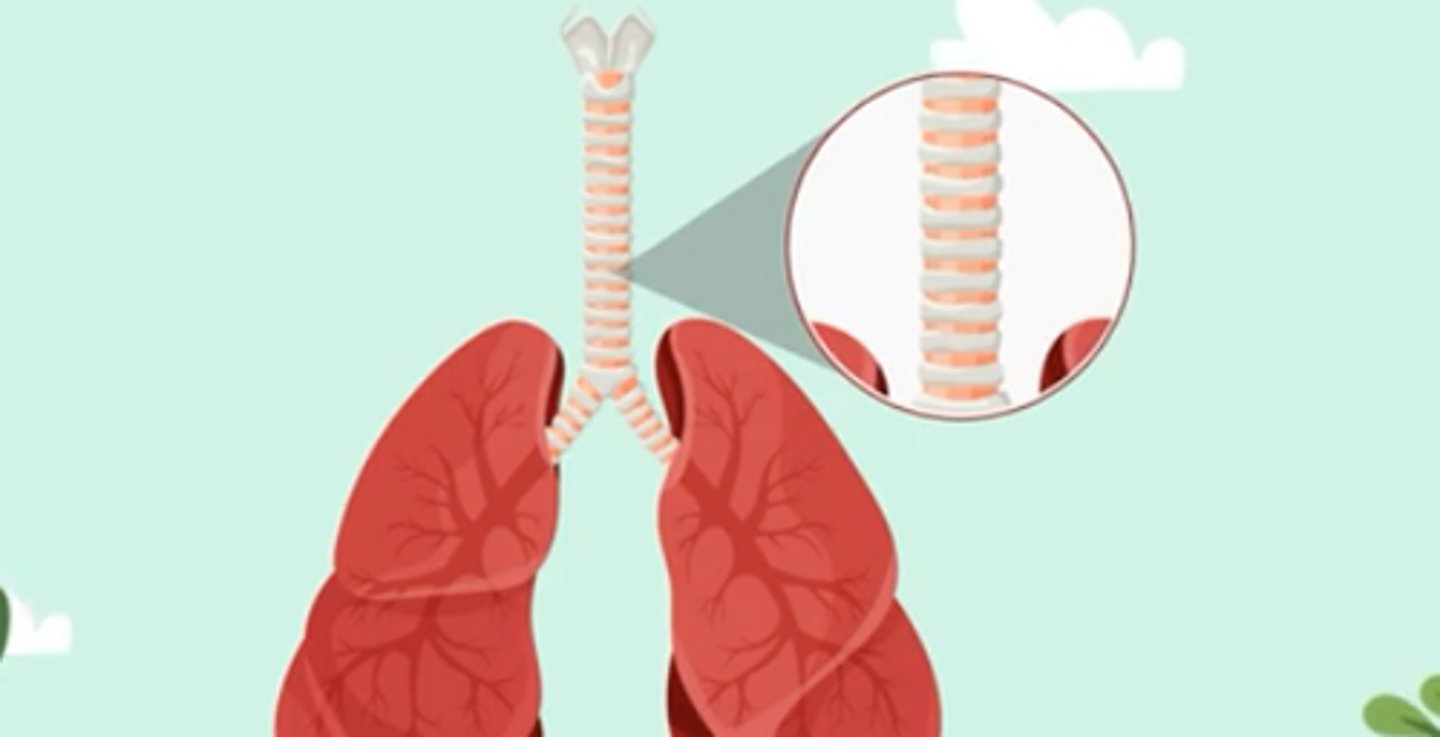
What is the bronchus/bronchi?
Cartilage ring tubes that divide into smaller and smaller tubes. They act as transport tubes to transport oxygen to the lungs and take the carbon dioxide out. The smallest ones transport oxygen to the alveoli.
What are bronchioles?
The smaller branches of bronchi.
What are alveoli?
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. There are millions of them per lung and they are surrounded by the capillary network. When you inhale they expand with oxygen. Then, the oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood while carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood into the alveoli. The walls are membranes.
What is diffusion?
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What is the epiglottis?
A flap that flips down to cover the entry to the trachea and the larynx during swallowing.
What does a respiratory pigment do?
Increases how much oxygen can be transported.