practical 2 Structures of the Eye, Ear, Brain, and Nervous System
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Choroid (vascular) layer
Supplies blood to the retina and absorbs excess light.
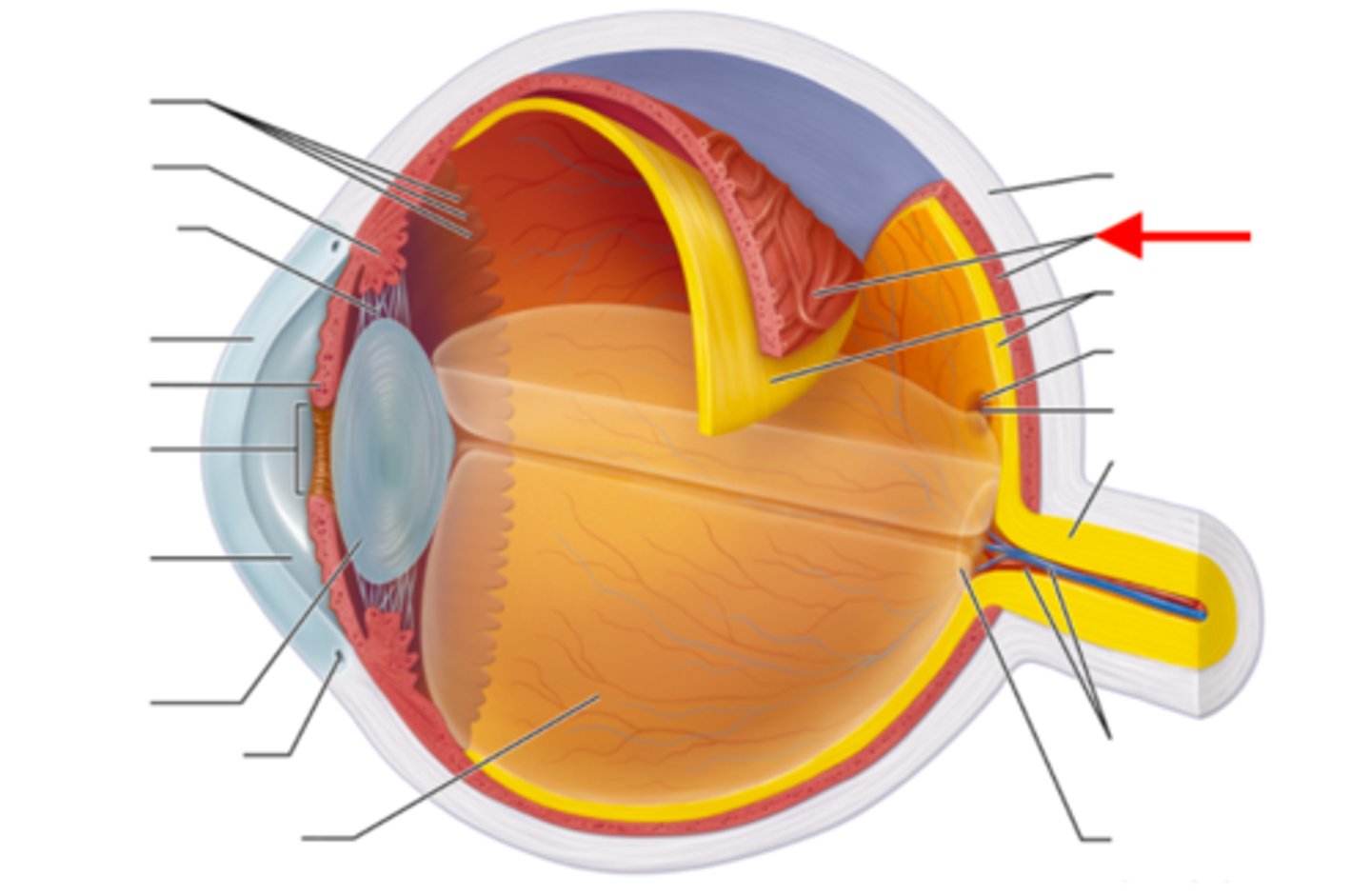
Cornea
The clear, outermost layer of the eye that helps focus light.
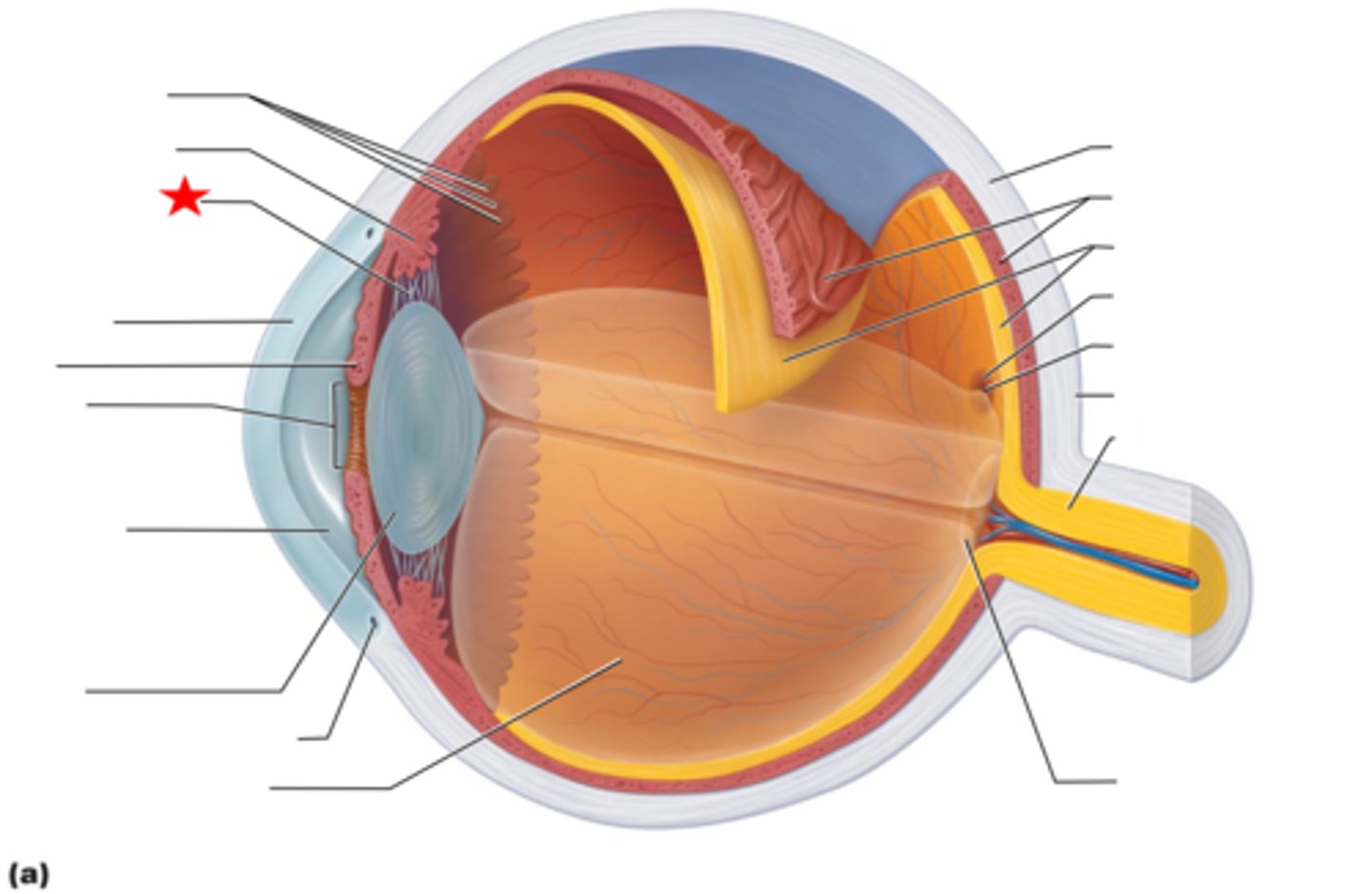
Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligaments)
Connects the ciliary body to the lens, adjusting its shape for focusing.
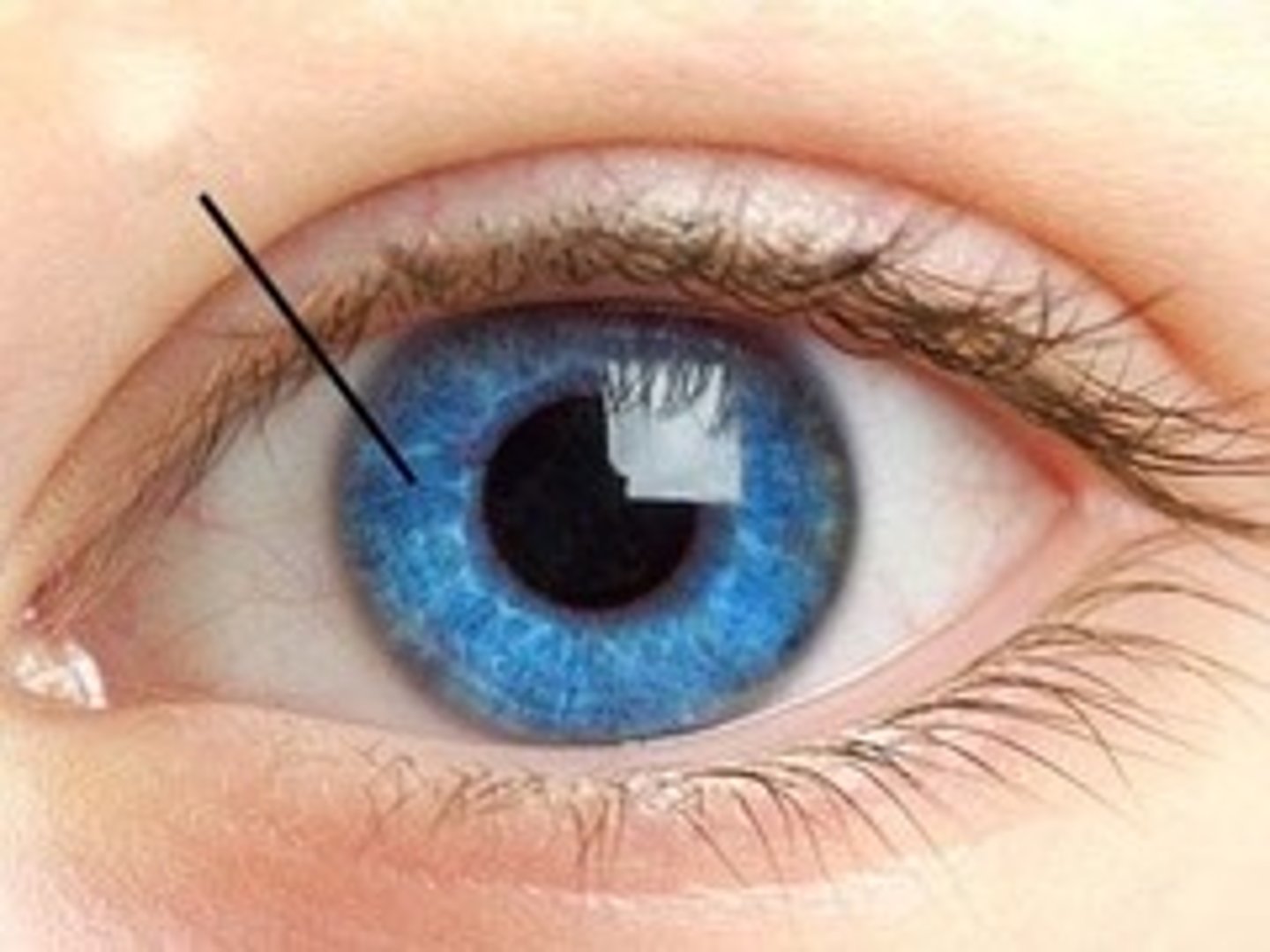
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls pupil size.
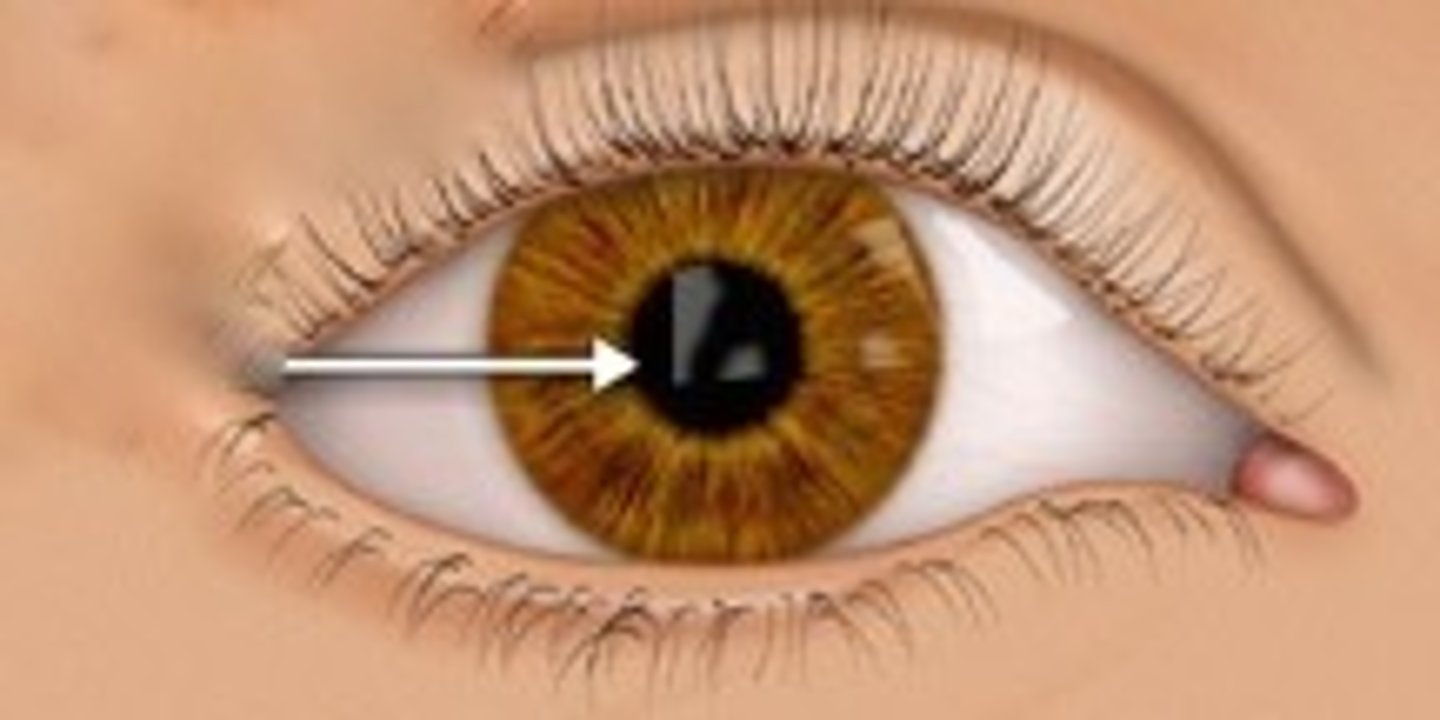
Pupil
The opening in the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
Neural (retina) layer
Contains photoreceptor cells that detect light and send signals to the brain.
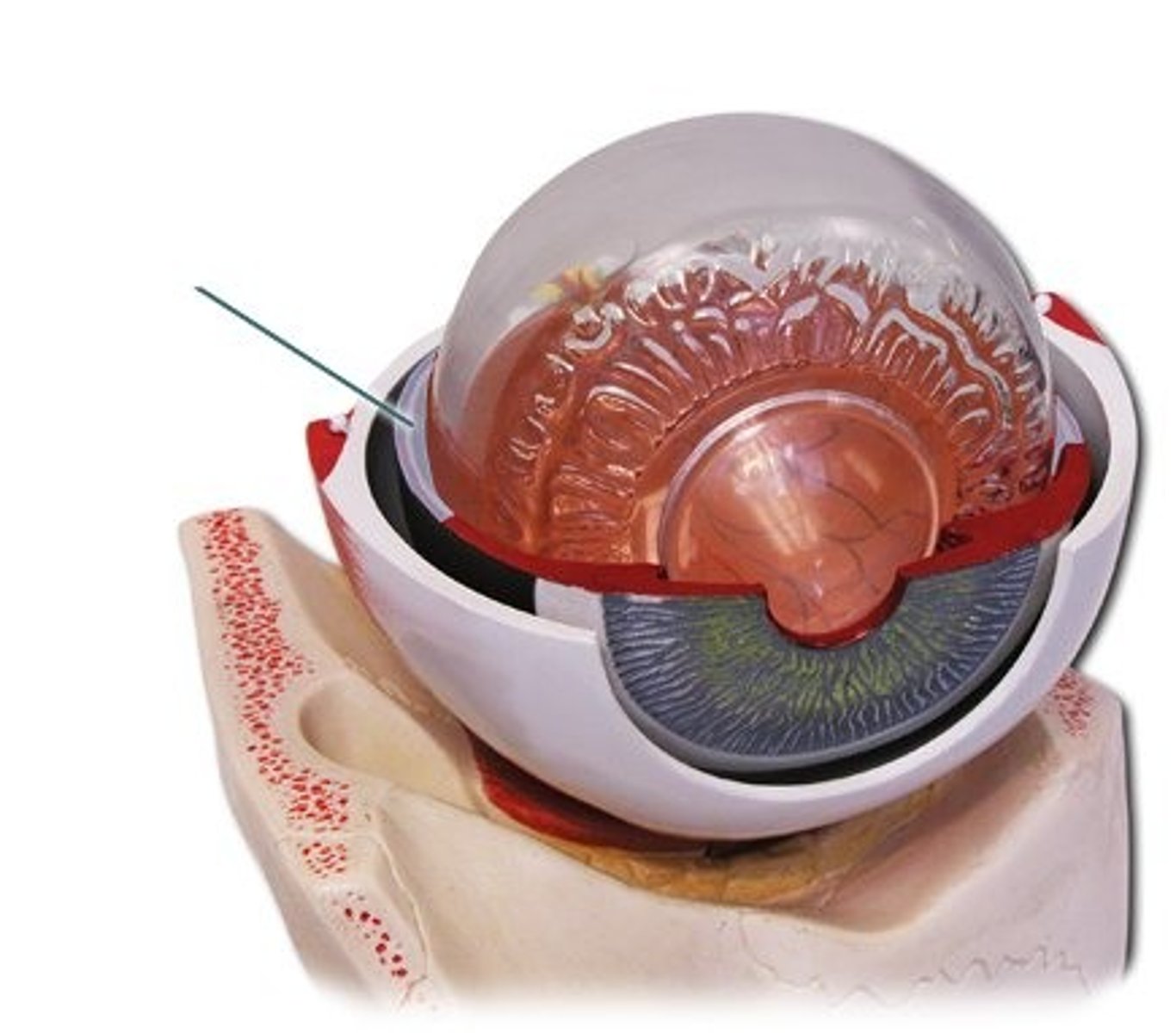
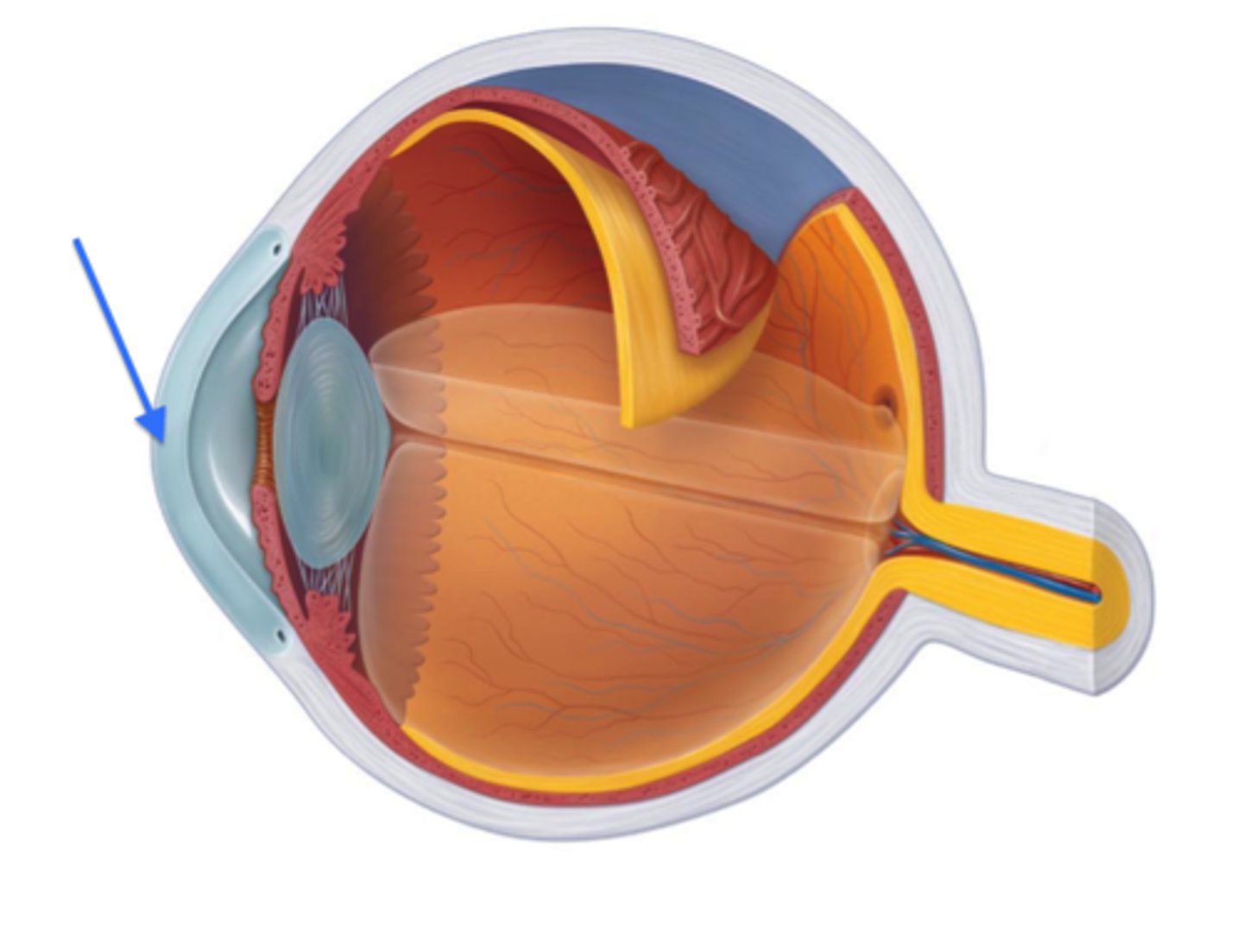
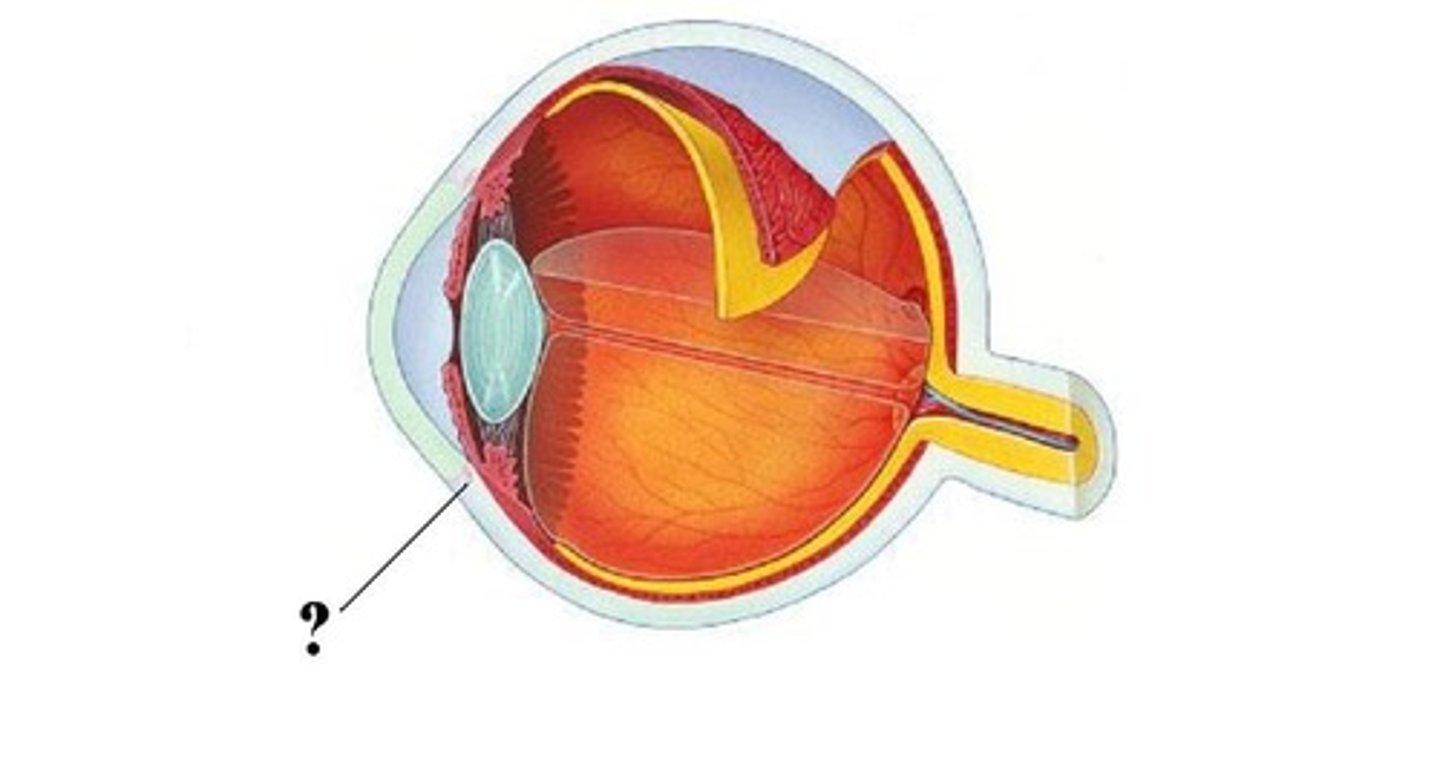
Sclera
The white, protective outer layer of the eye.
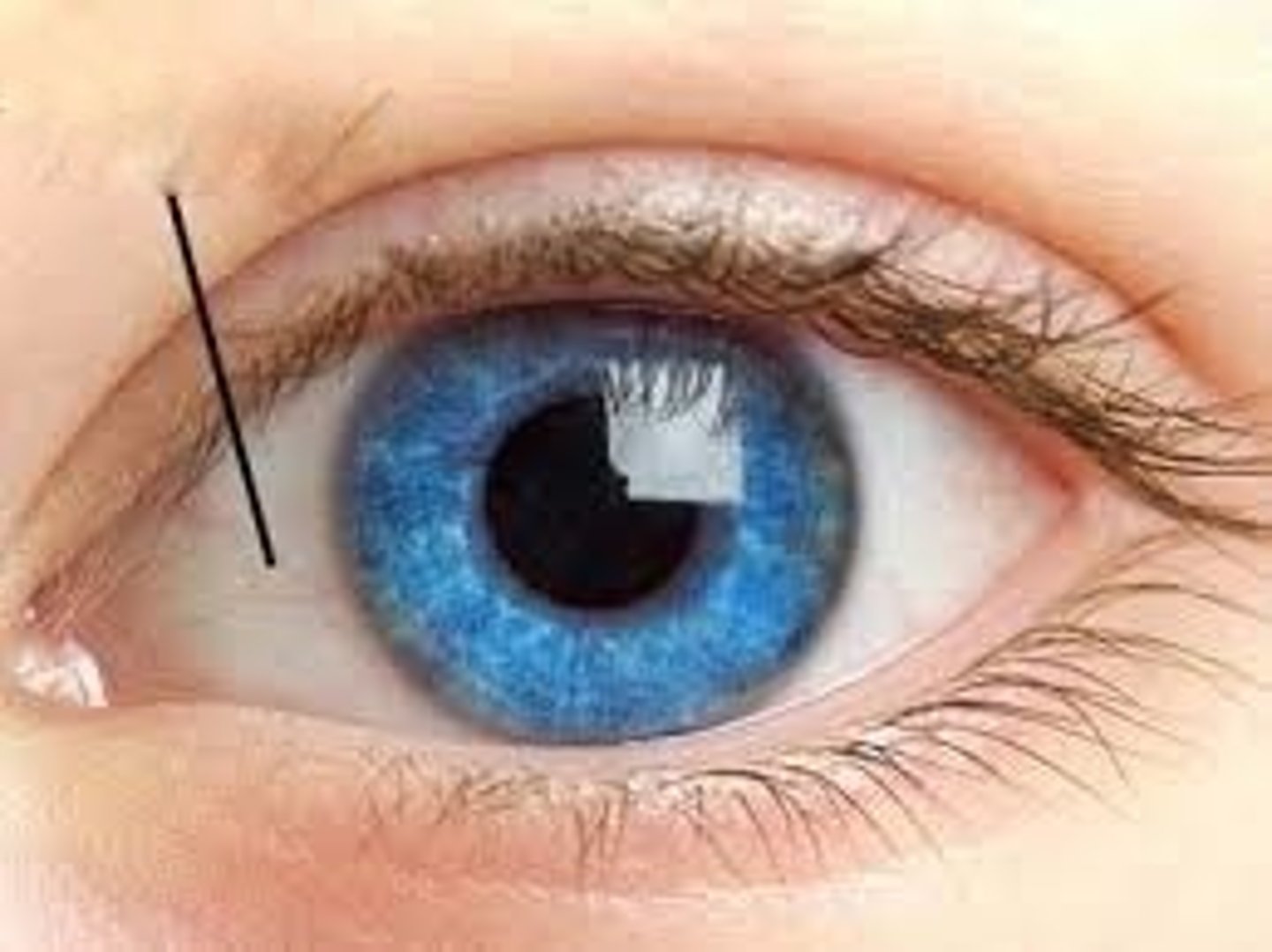
Optic disc
The 'blind spot' where the optic nerve exits the retina.
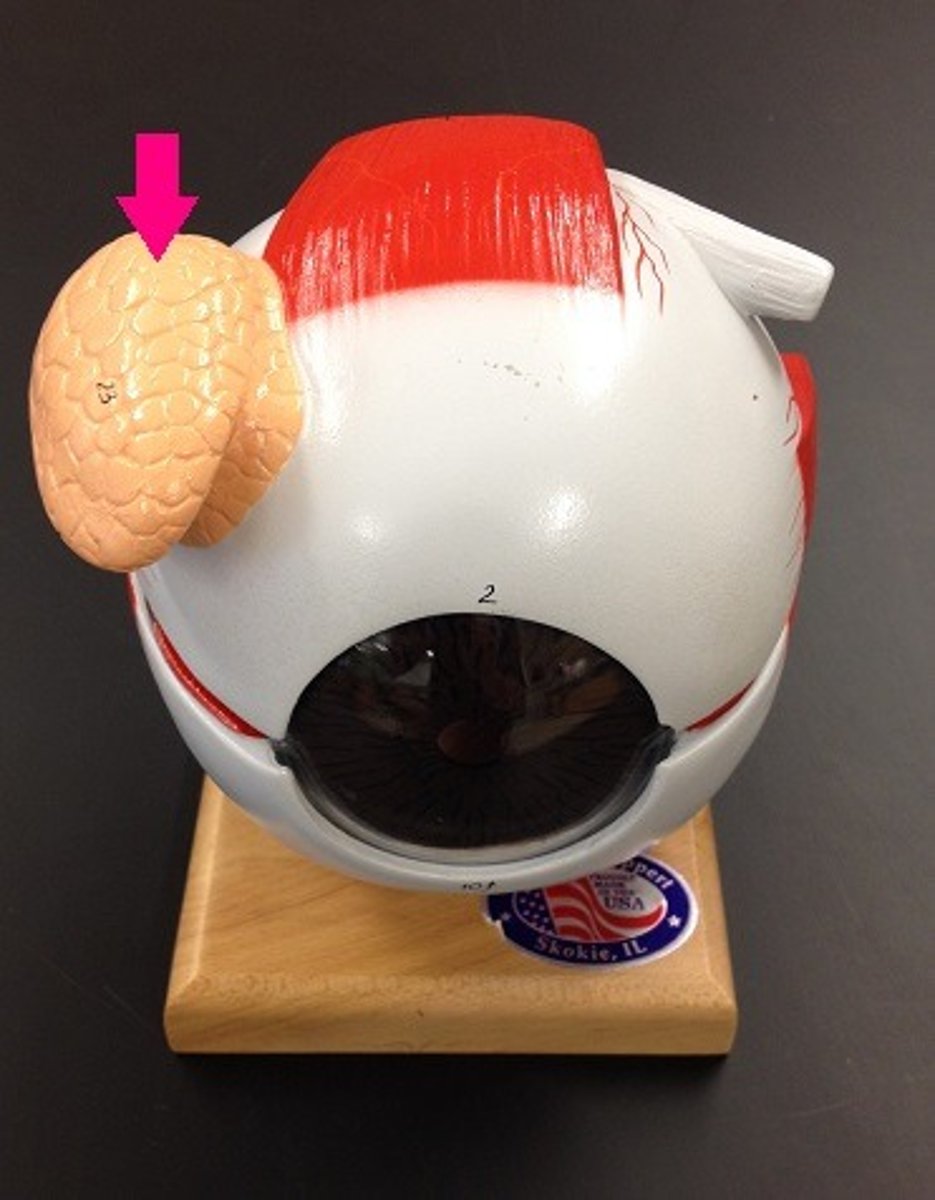
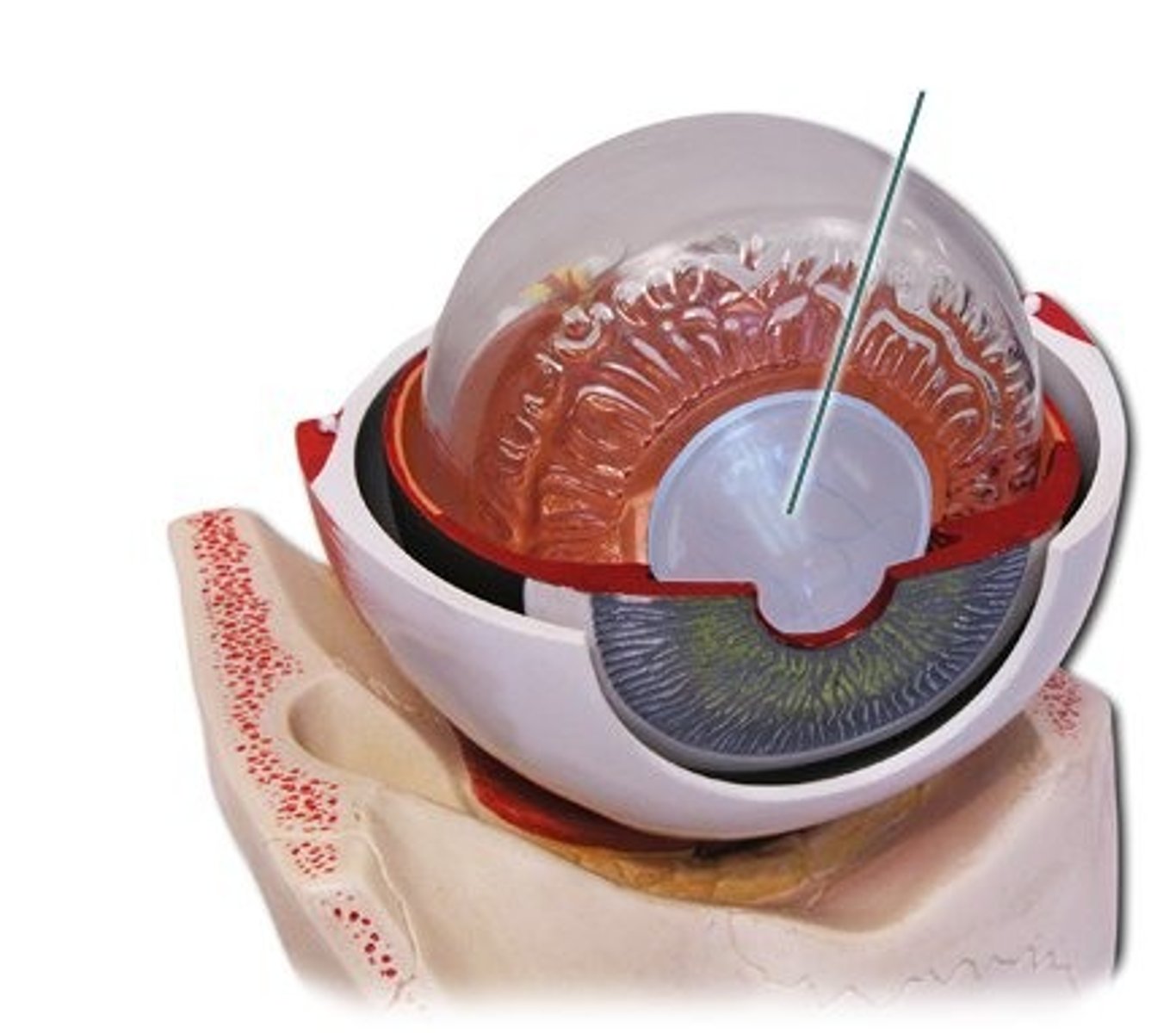
Lacrimal gland
Produces tears to lubricate and protect the eye.

Lens
Focuses light onto the retina for clear vision.
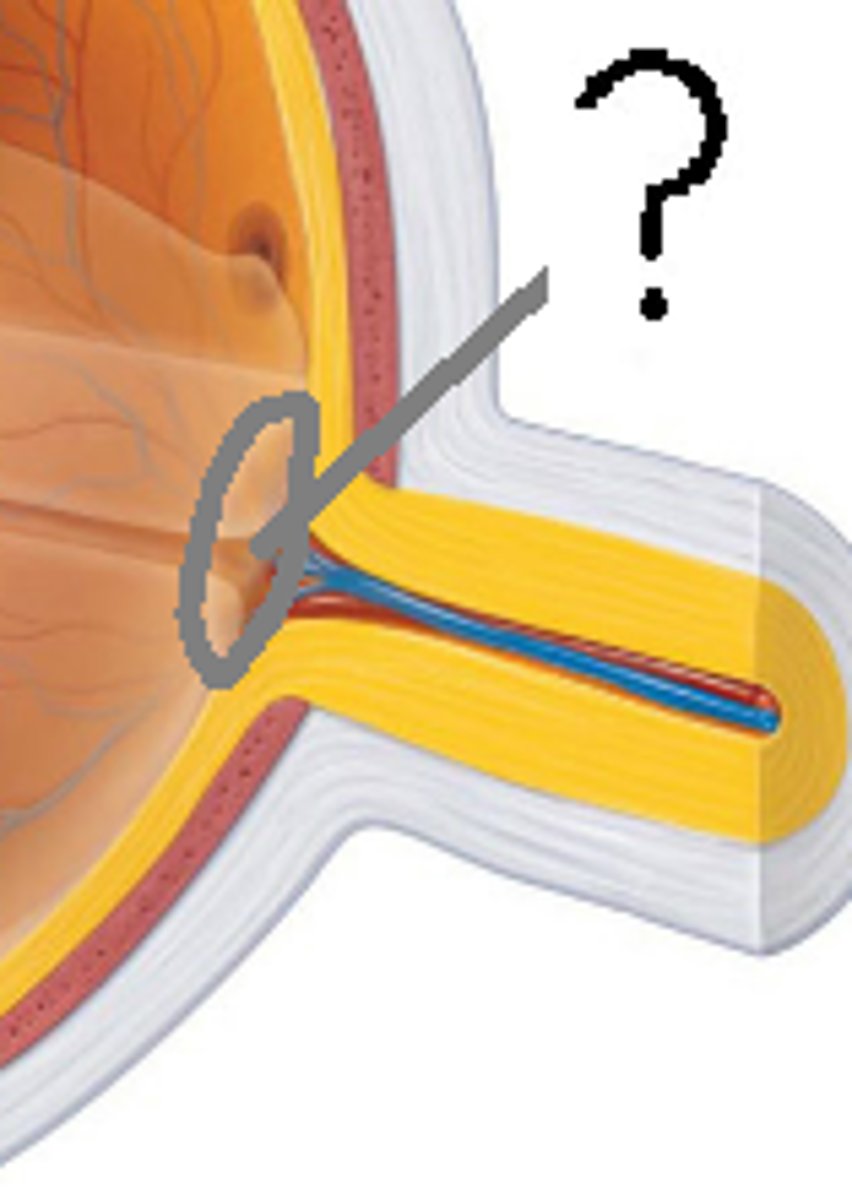
Scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
Drains aqueous humor from the eye to maintain intraocular pressure.
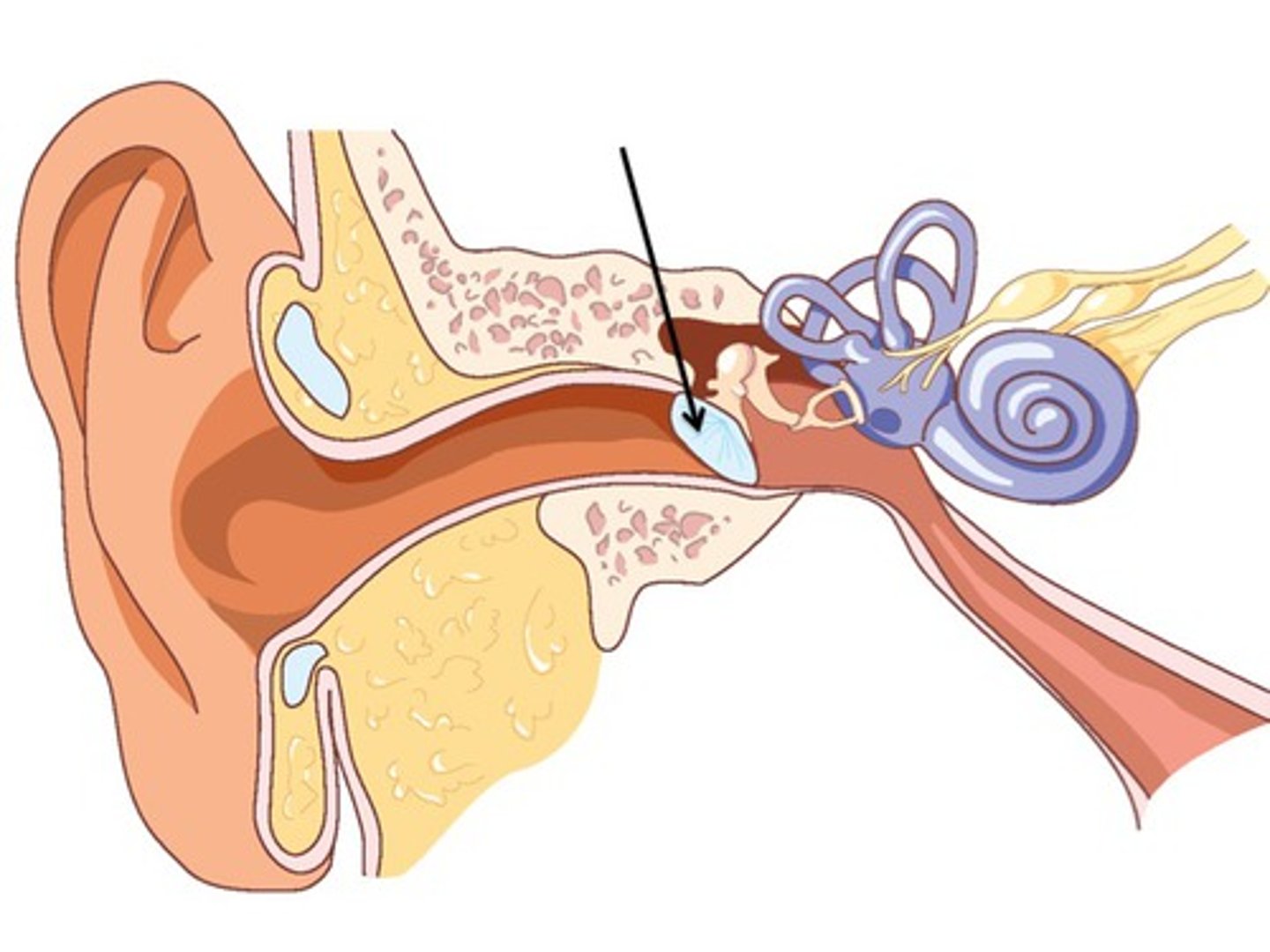
Tympanic membrane
The eardrum; vibrates in response to sound waves.
Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
Connects the middle ear to the throat, equalizing pressure.
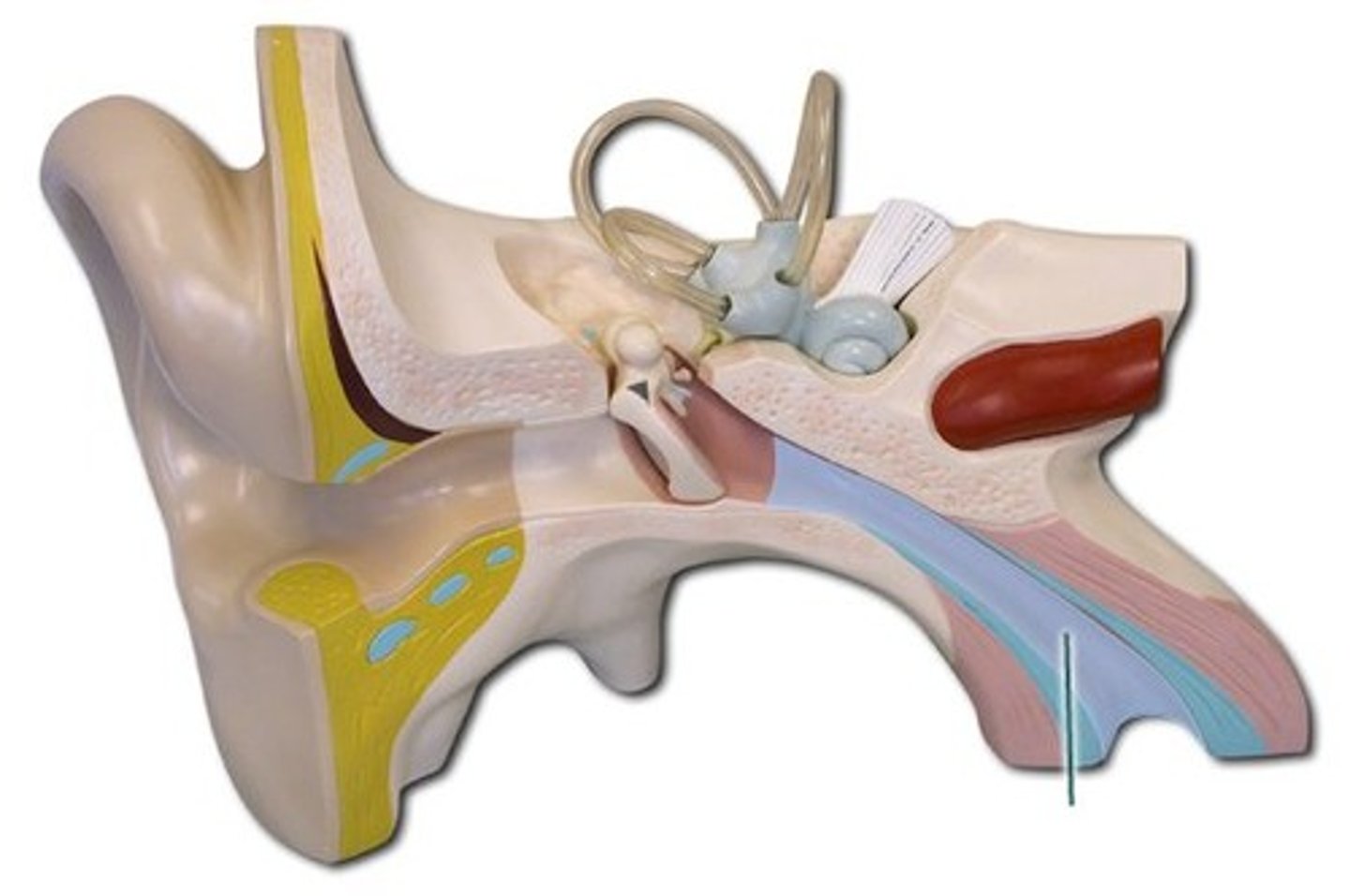
Stapes (stirrup bone)
One of the three ossicles; transmits sound vibrations to the inner ear.
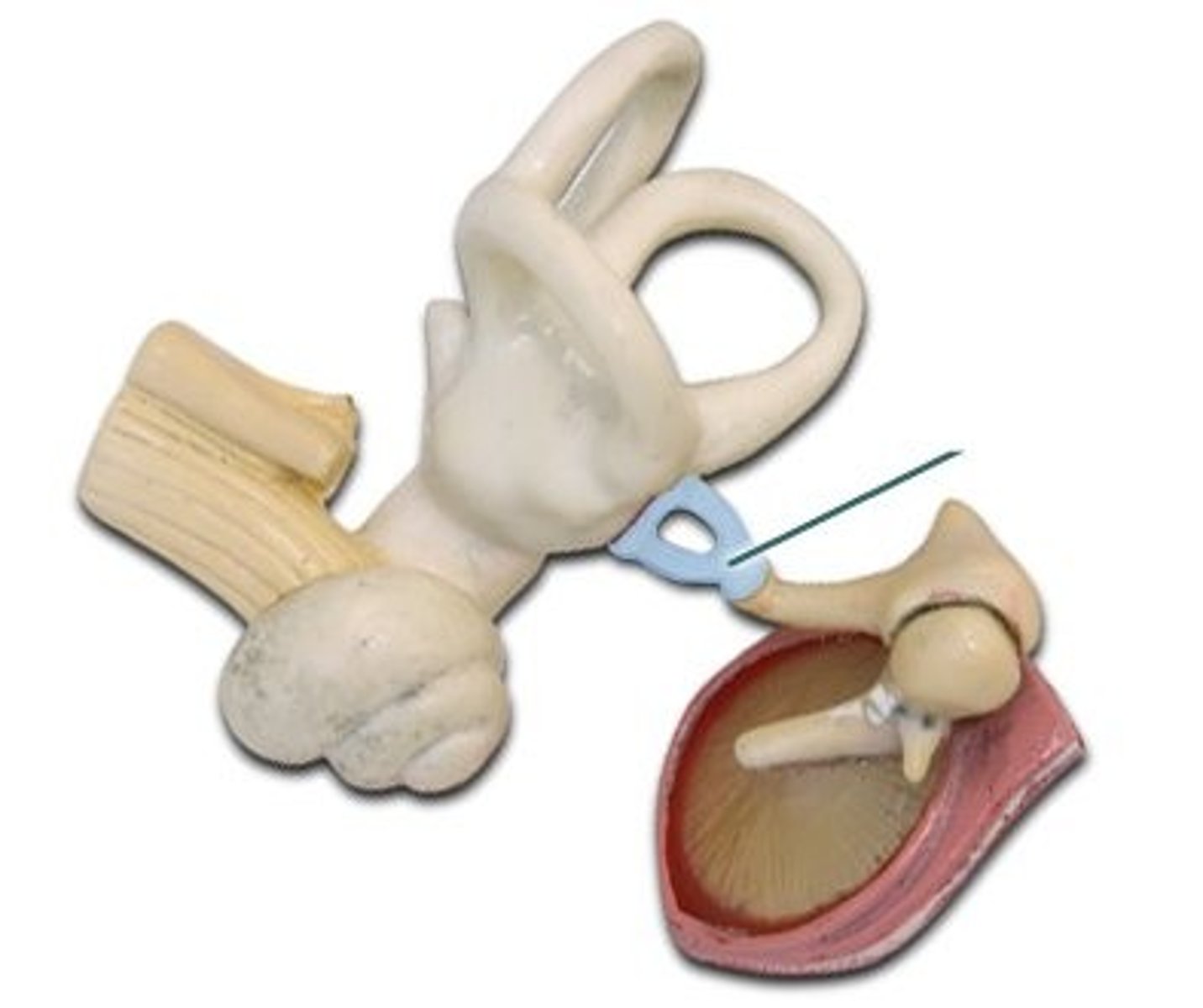
Anvil (incus)
Middle ossicle that transmits vibrations from the malleus to the stapes.
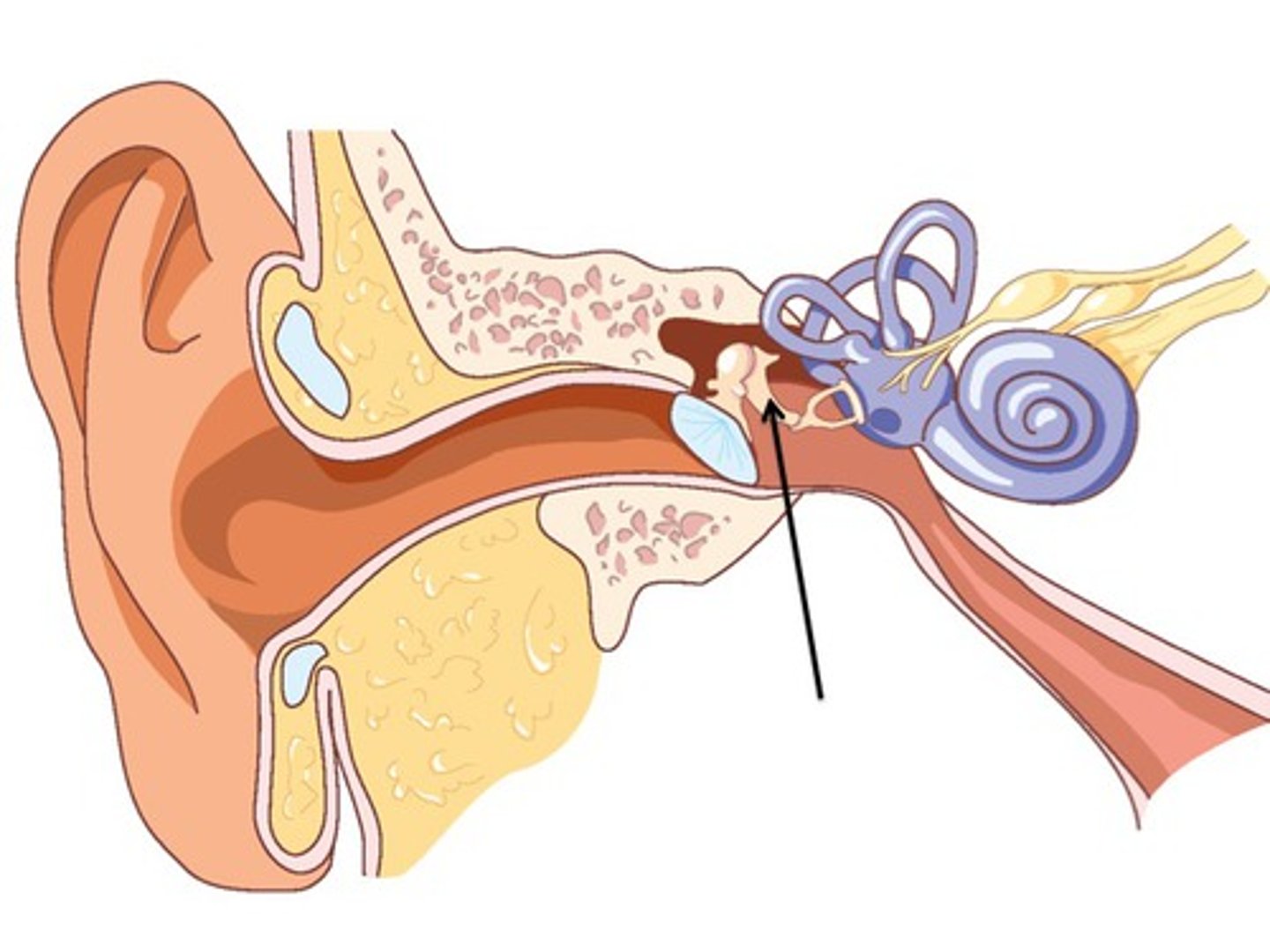
Cochlea
The spiral-shaped organ of hearing in the inner ear.
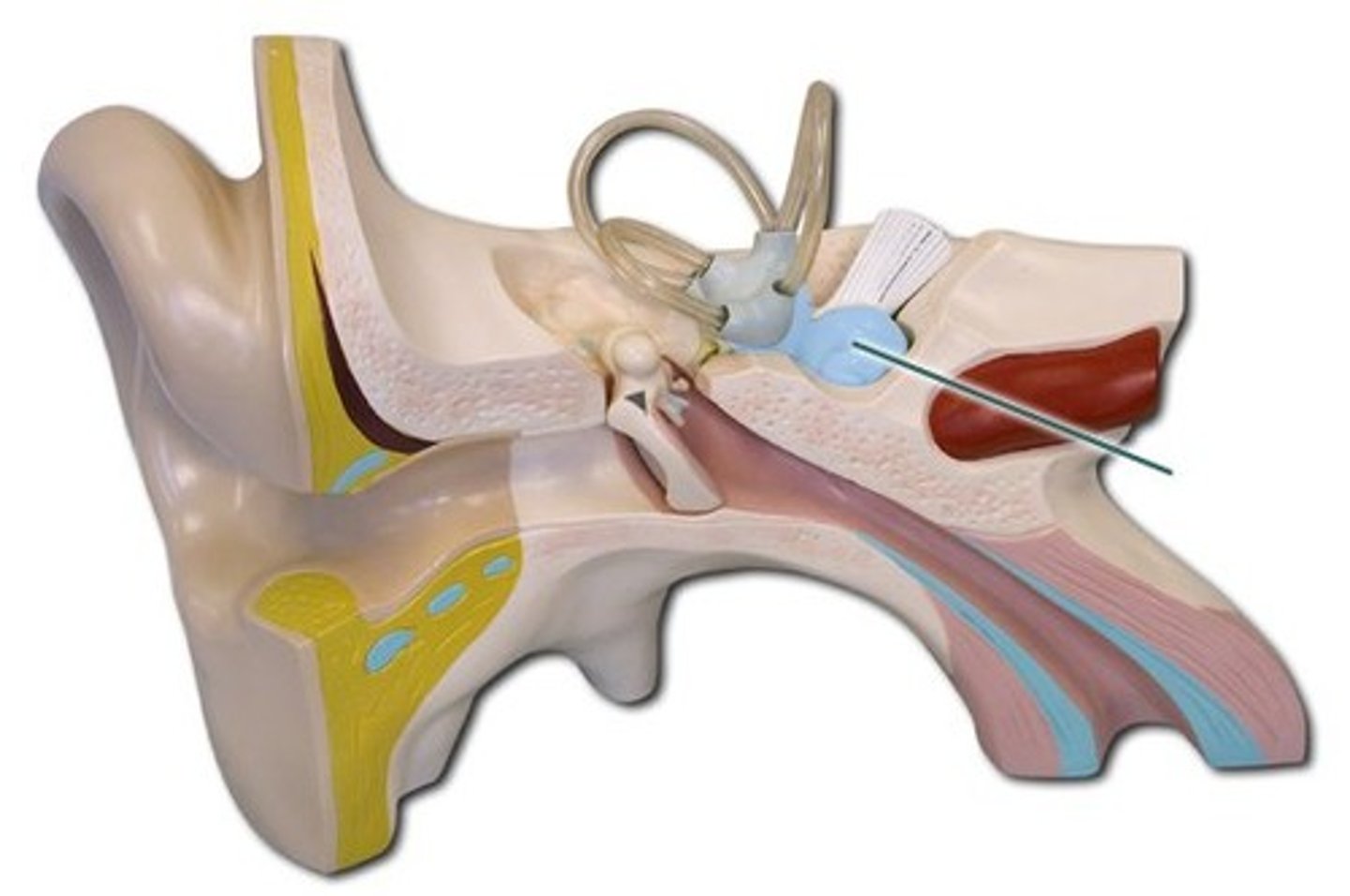
Semicircular canals
Help with balance and detecting head movements.
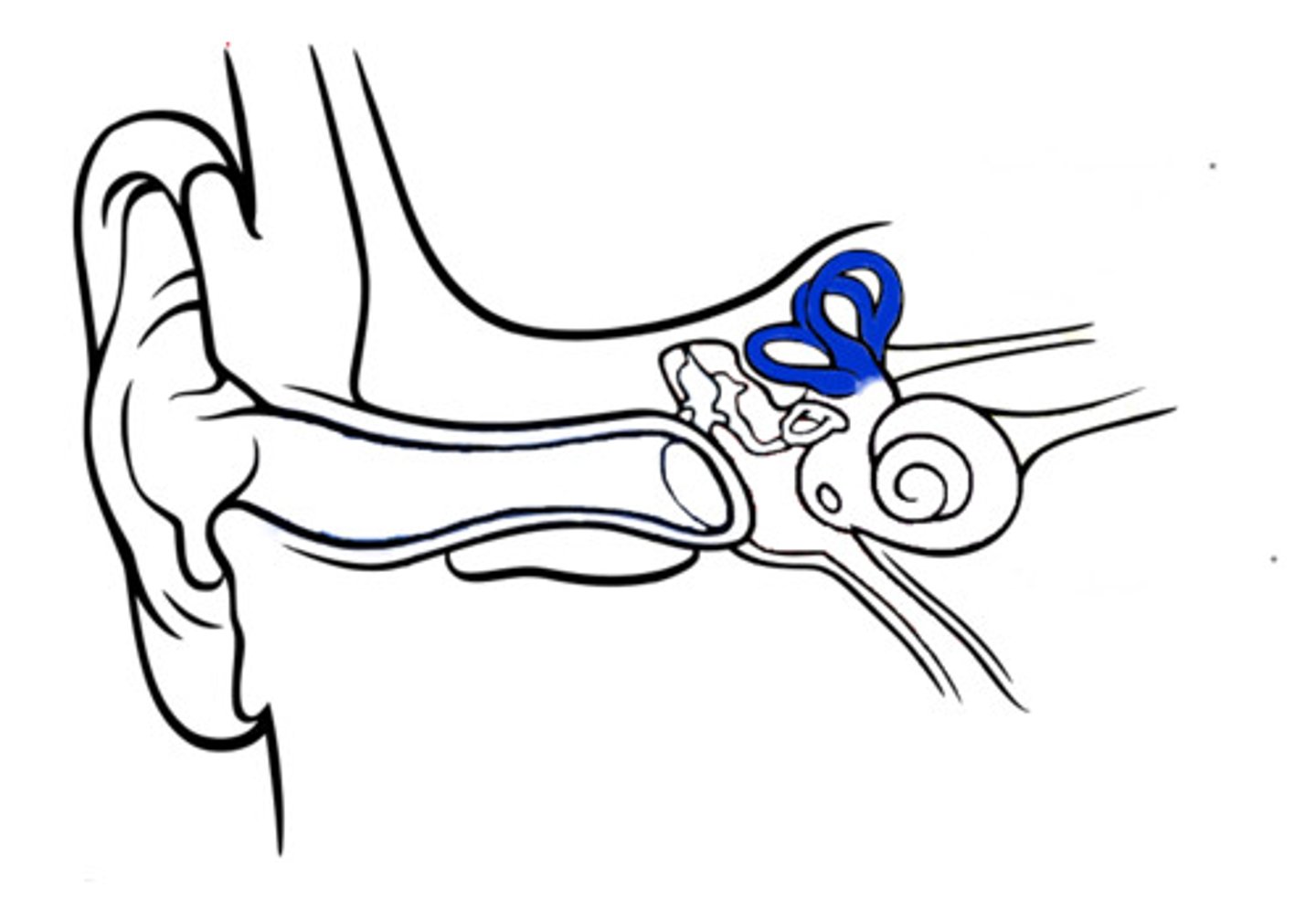
Optic chiasma
The crossing point of optic nerves for visual processing.
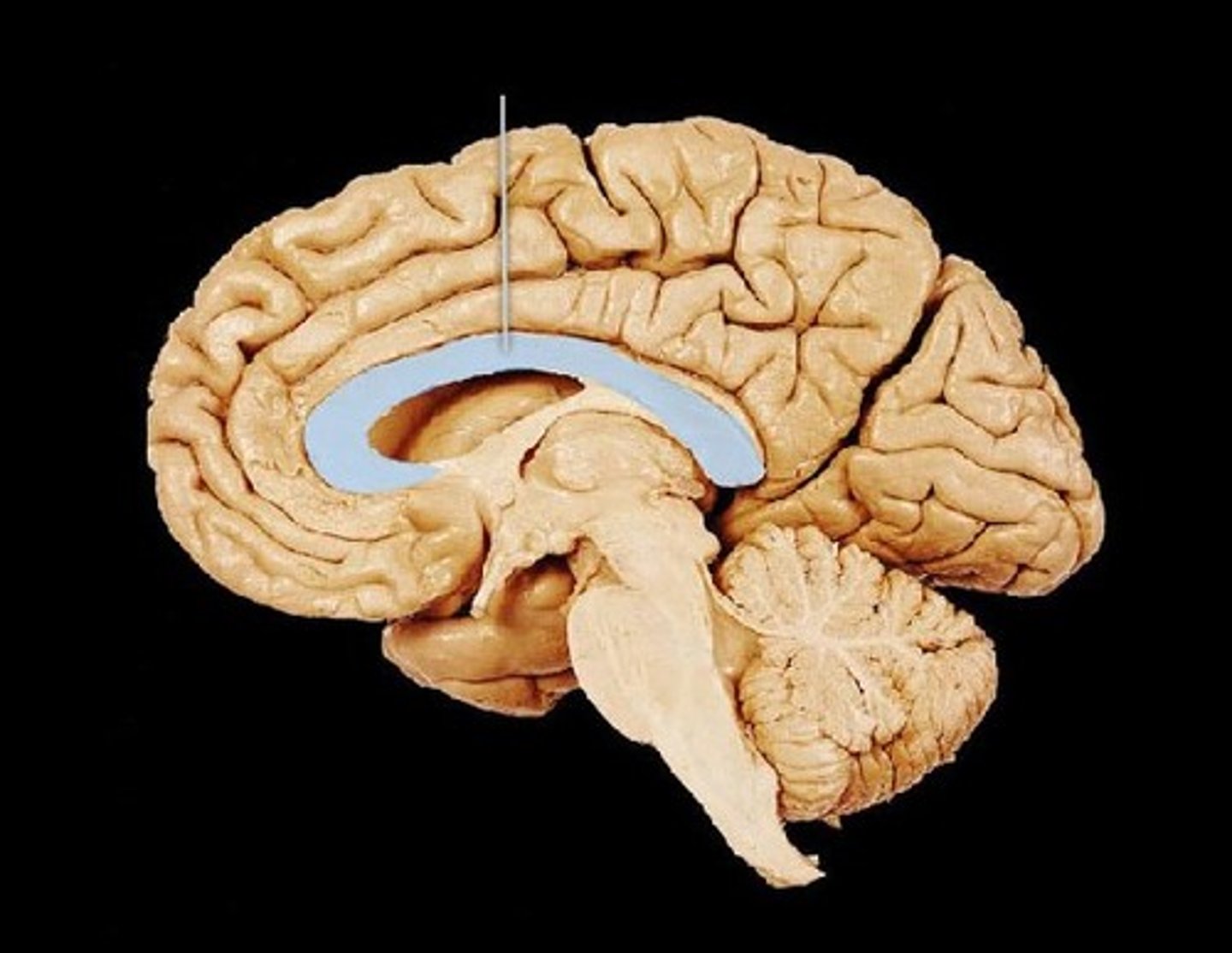
Corpus callosum
Connects the left and right brain hemispheres.
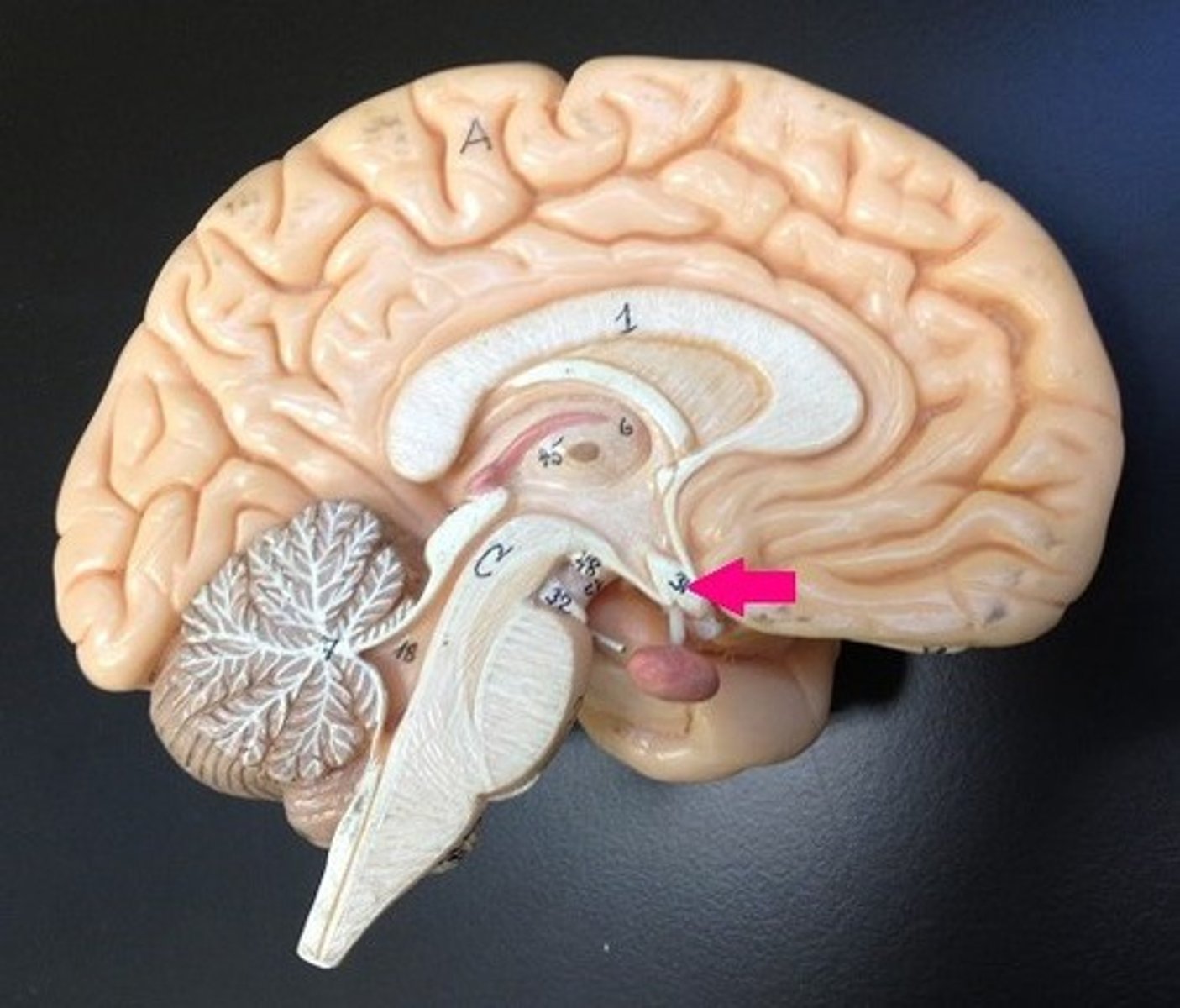
Corpora quadrigemina (superior and inferior colliculi)
Involved in visual and auditory reflexes.
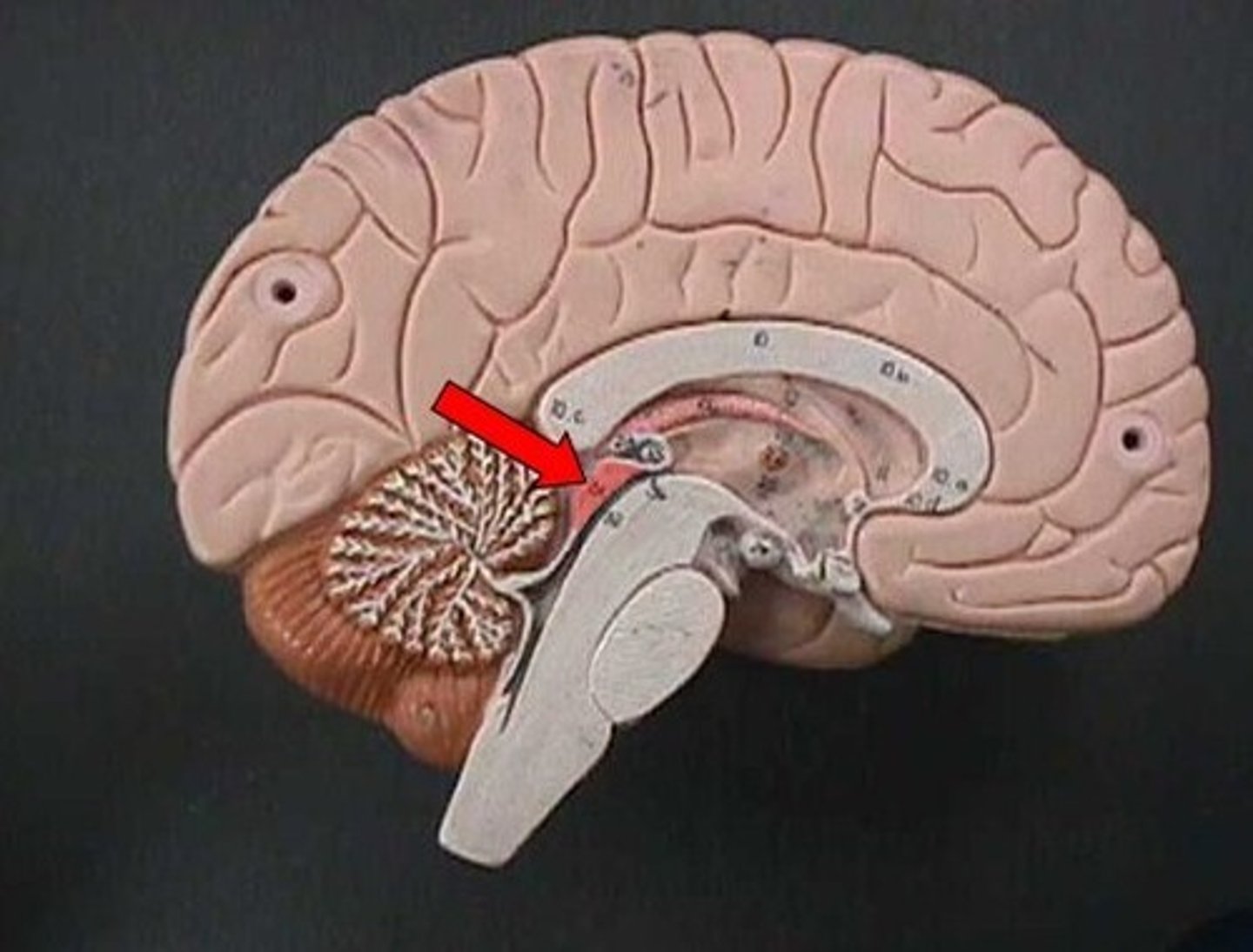
Pons
A brainstem structure that relays messages between the brain and spinal cord.
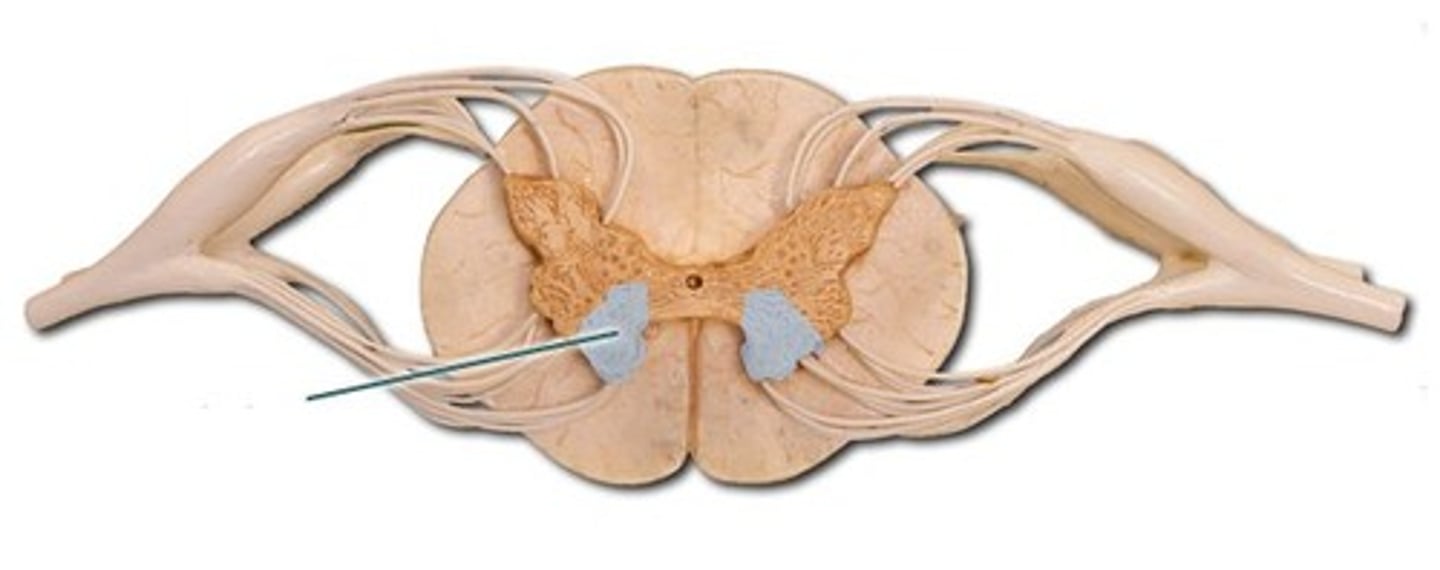
Ventral horn of the spinal cord
Contains motor neurons that send signals to muscles.
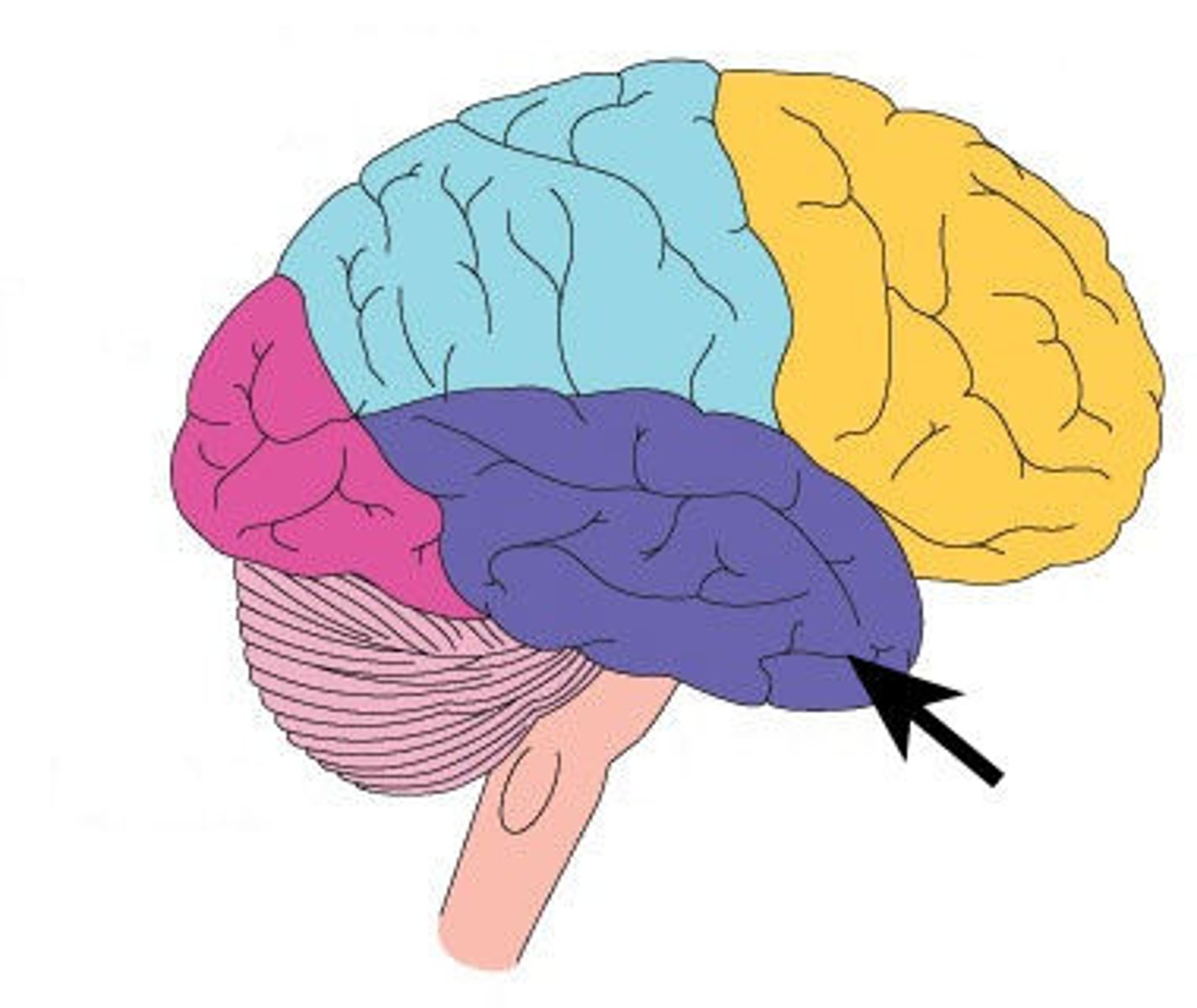
Temporal lobe
Processes auditory information and memory.
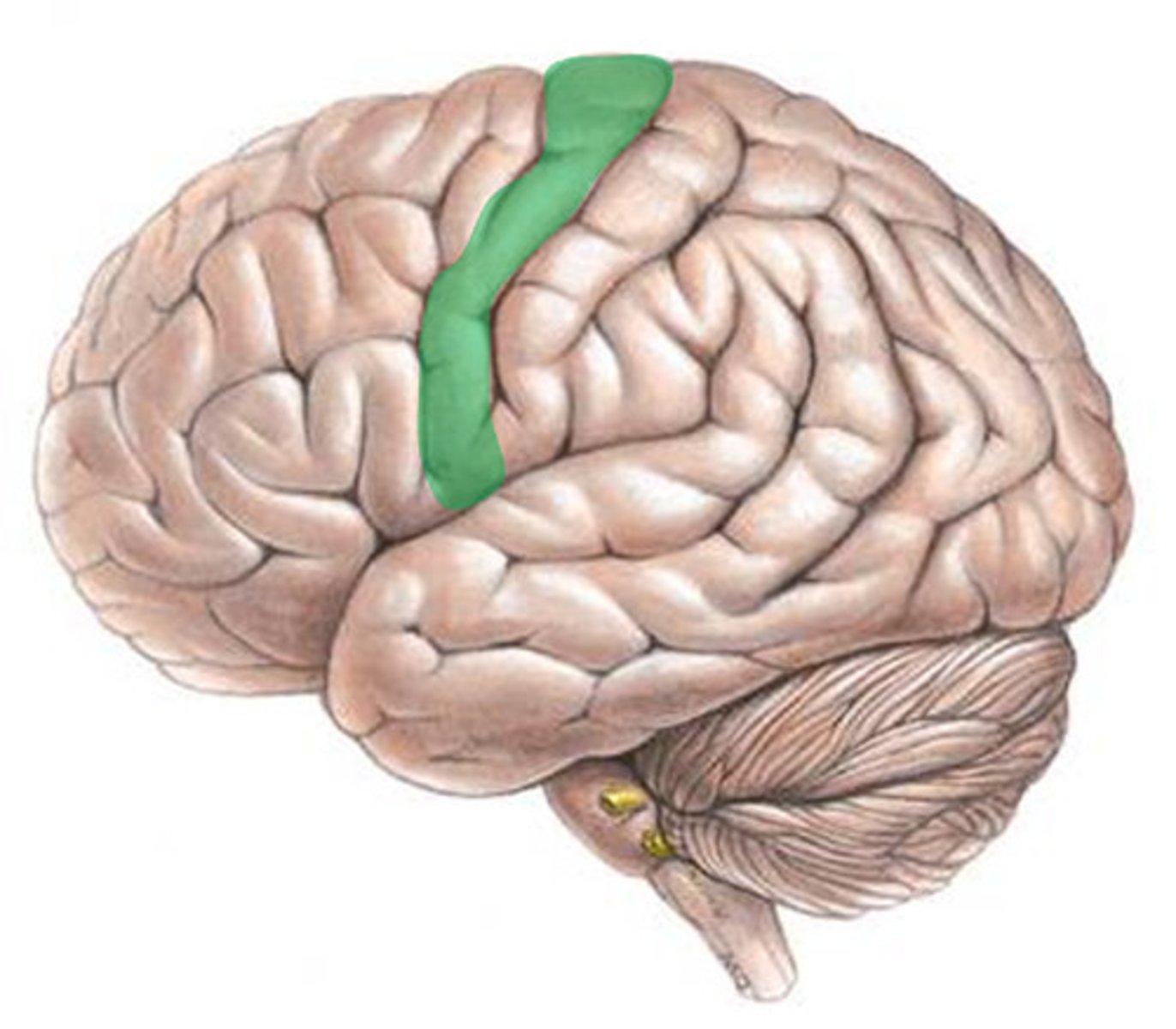
Gyrus
A ridge on the brain's surface that increases surface area.
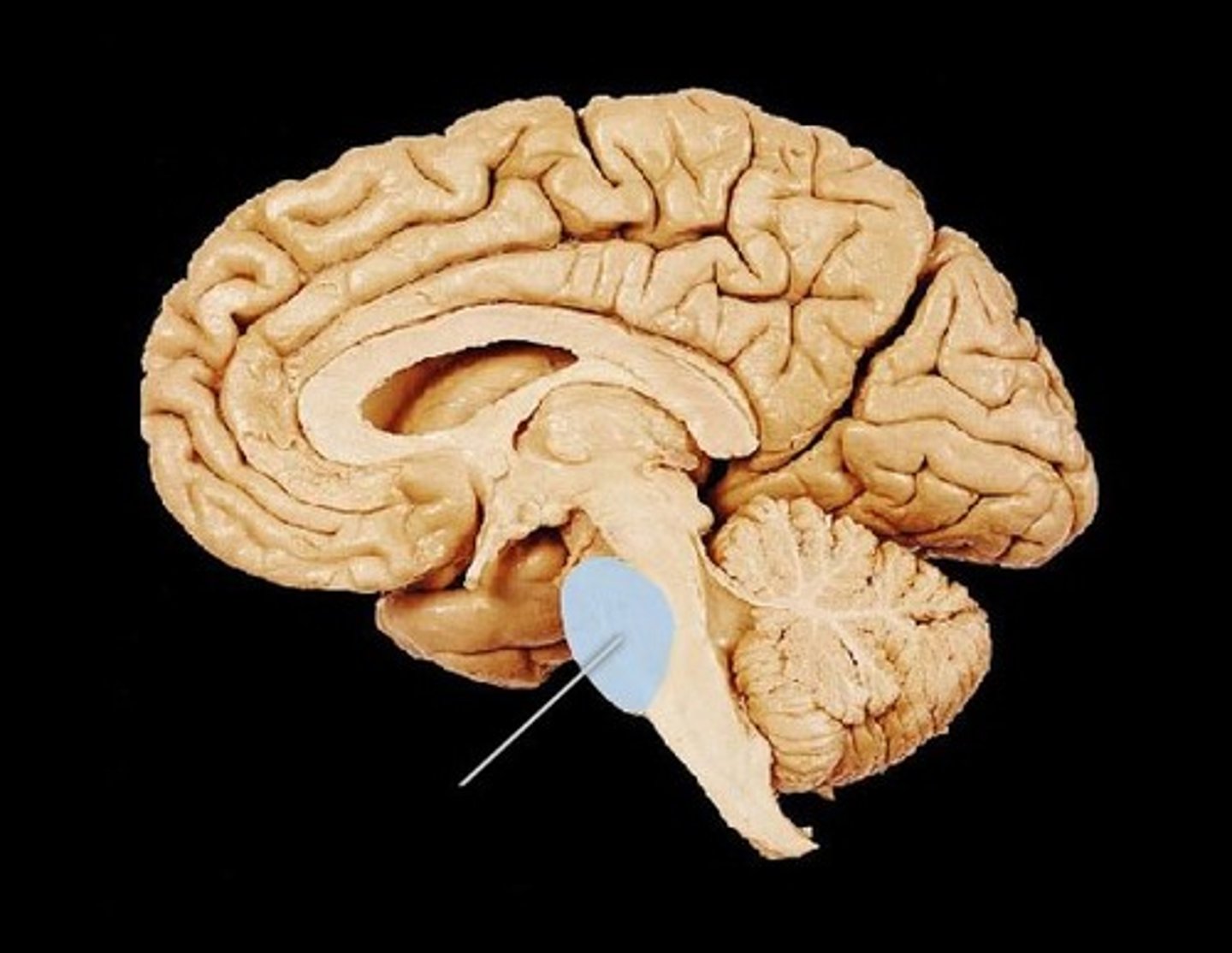
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis, hunger, and hormone release.
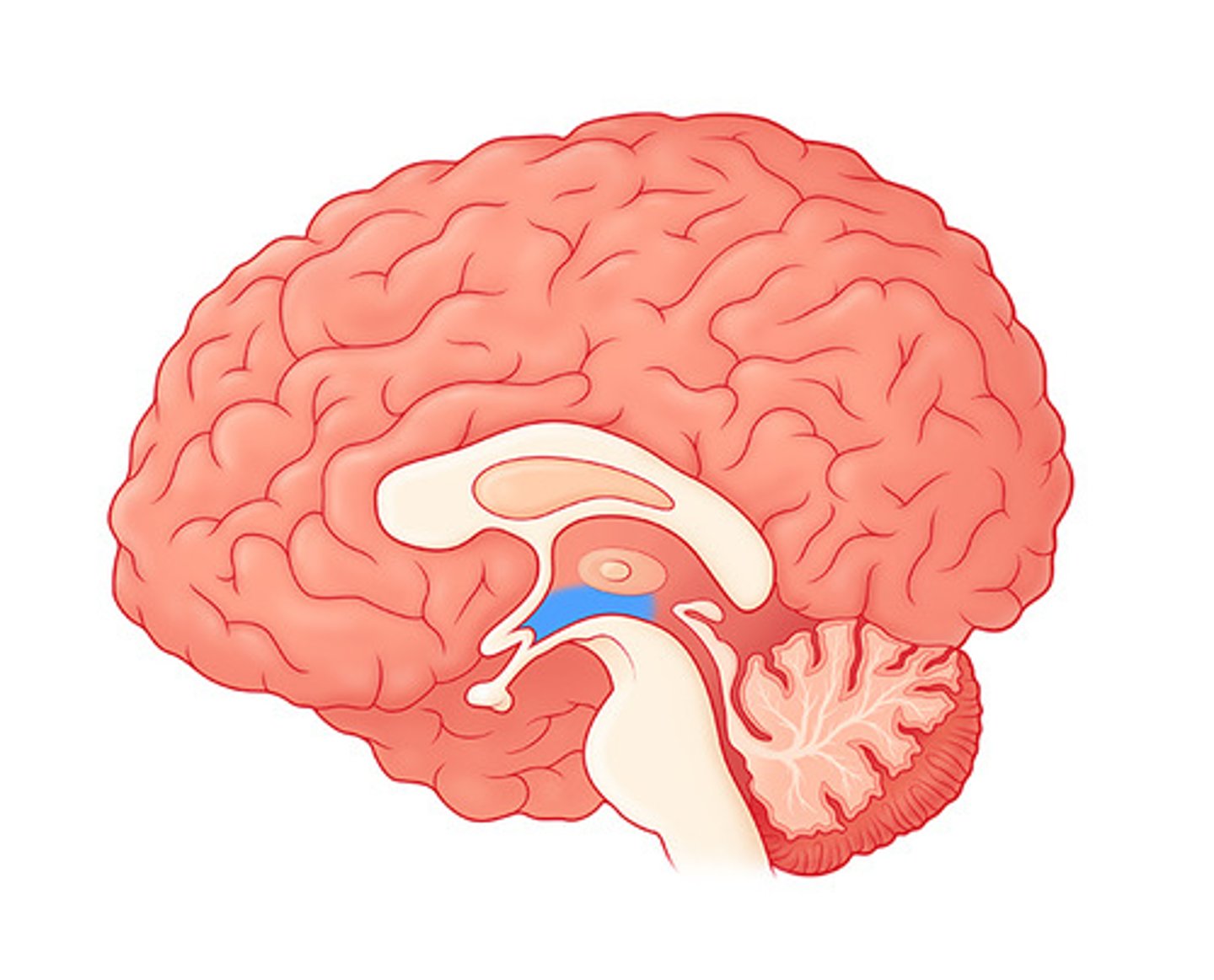
Pituitary gland
The 'master gland' that controls other endocrine glands.
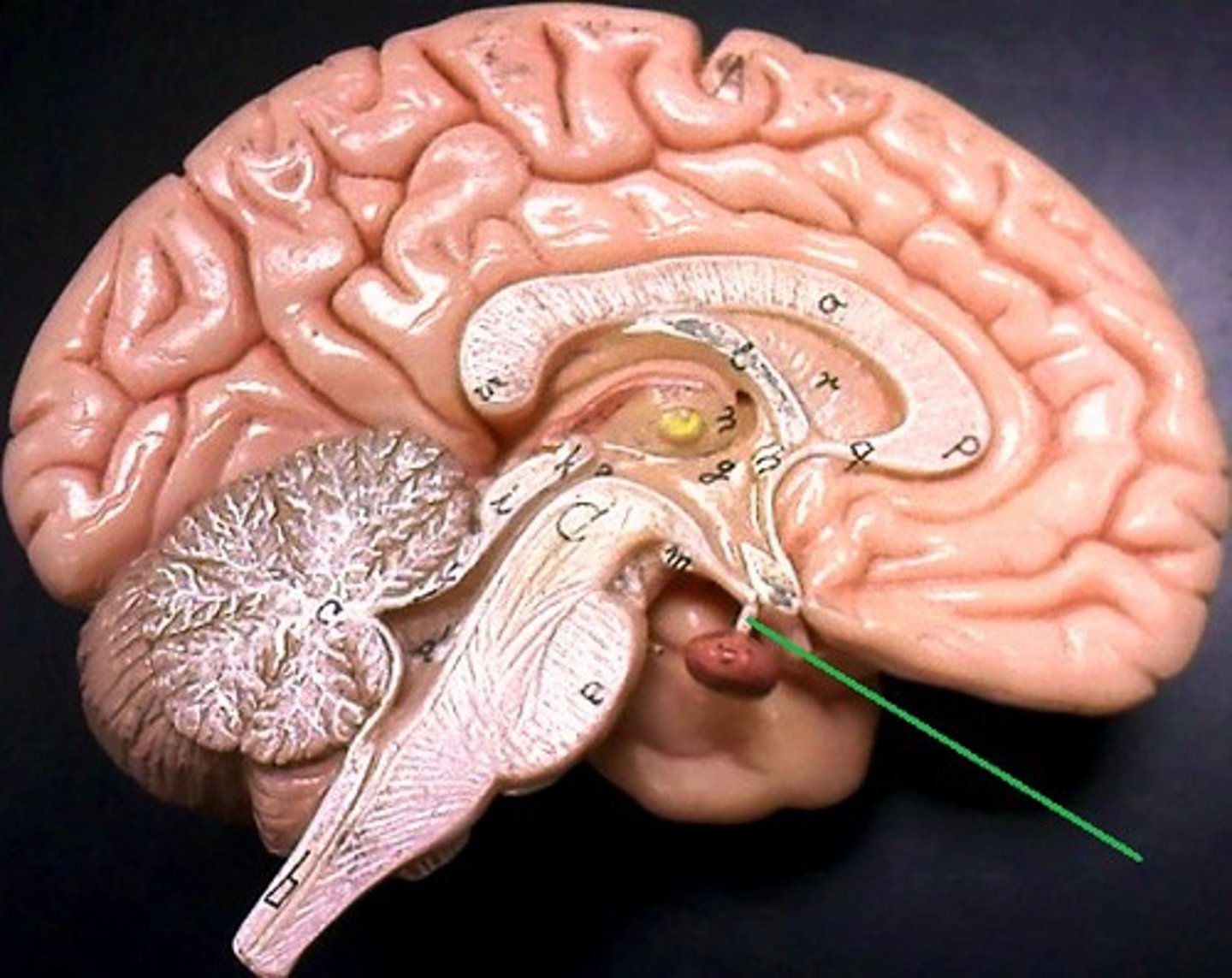
Olfactory nerve (CN #1)
Carries smell information to the brain.
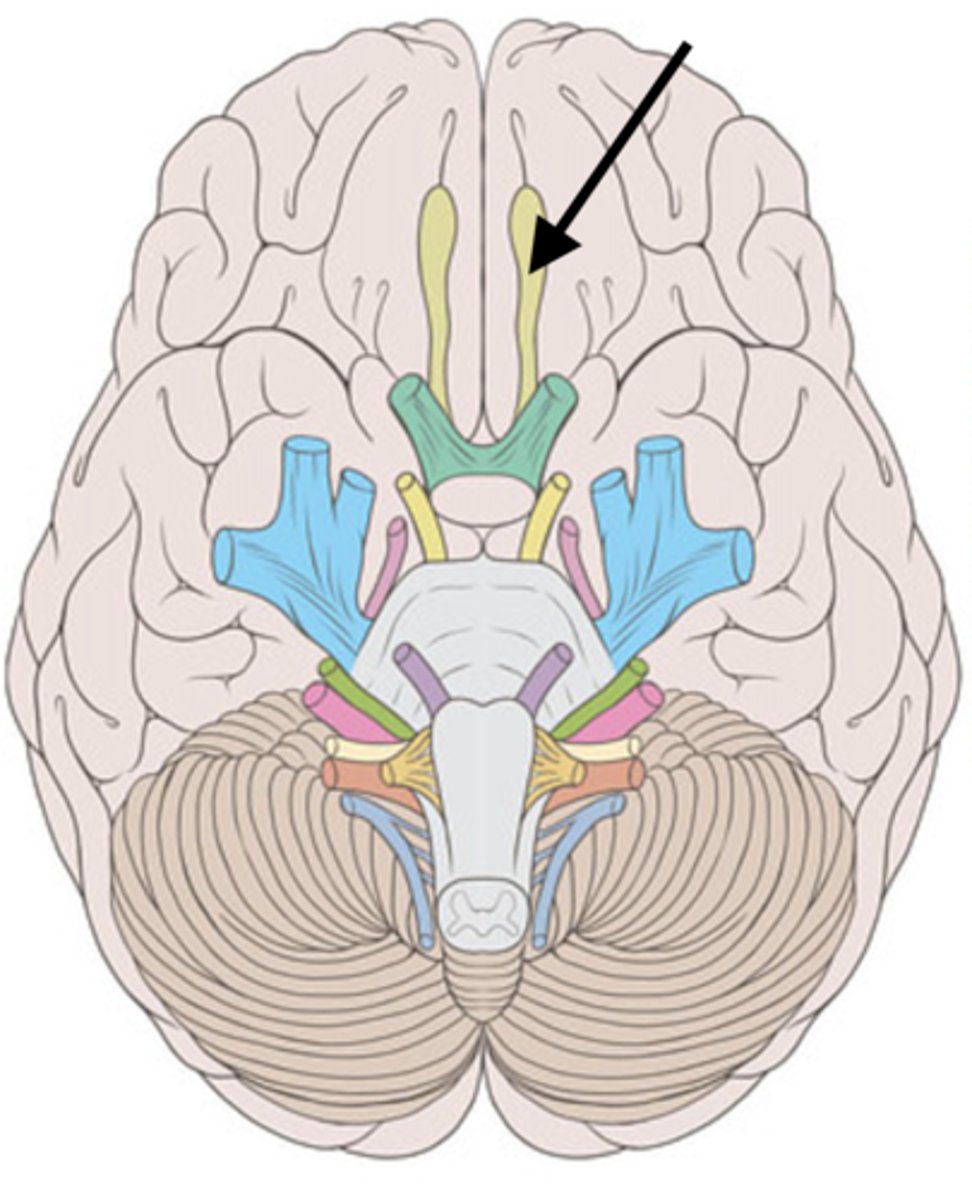
Dorsal root ganglion of spinal cord
Contains sensory neuron cell bodies.
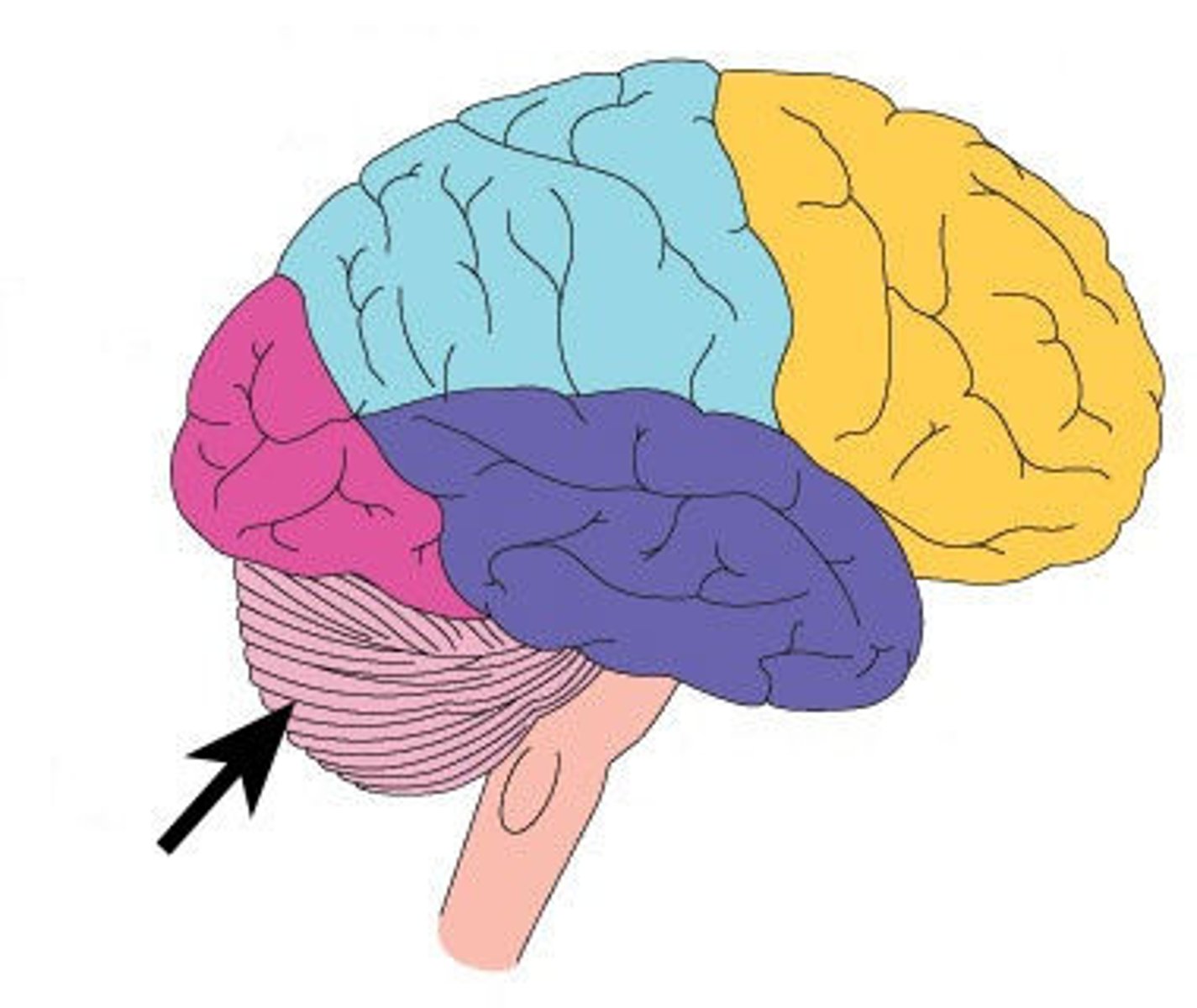
Cerebellum
Controls coordination and balance.
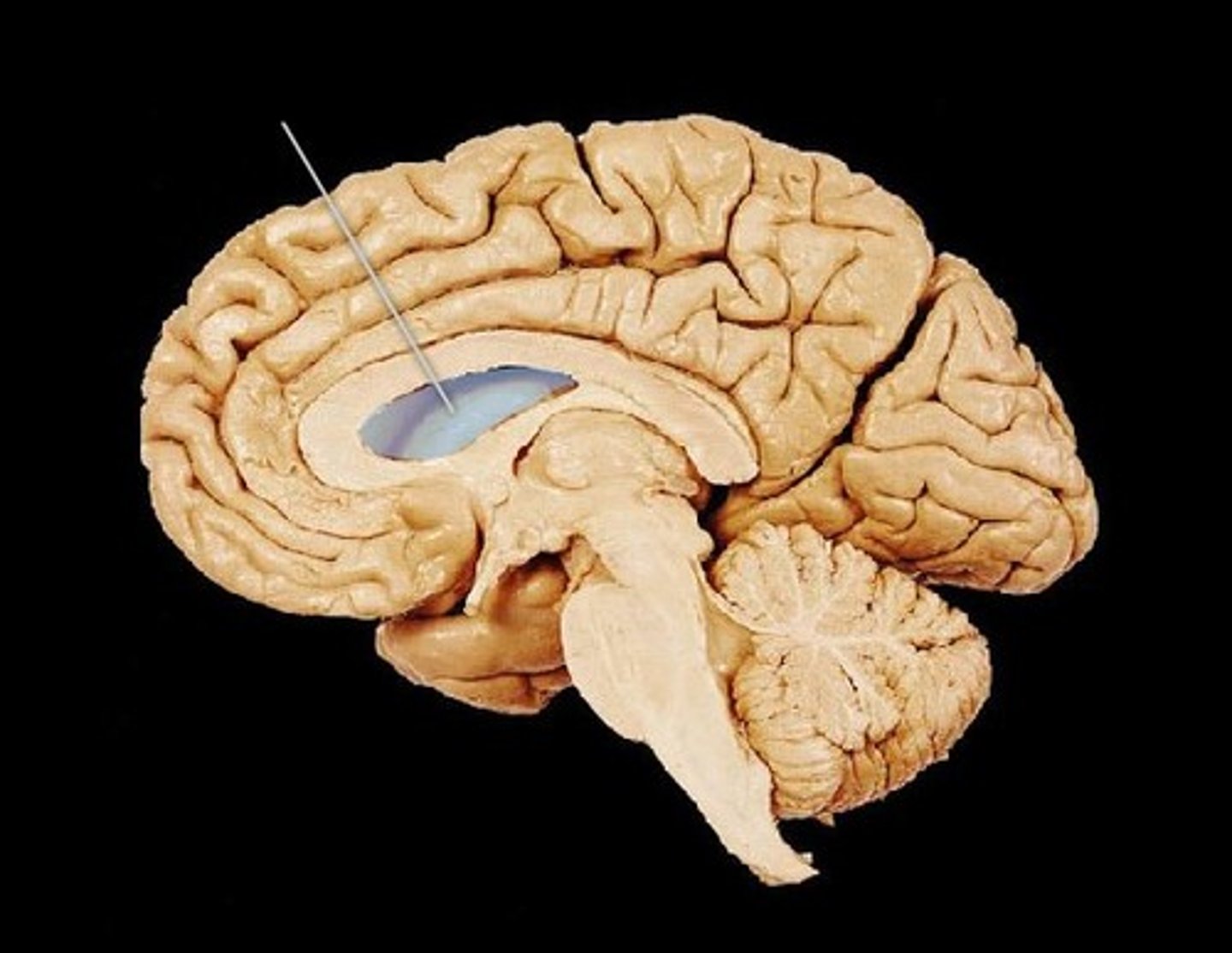
Ventricles of the brain
Cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that cushion the brain.
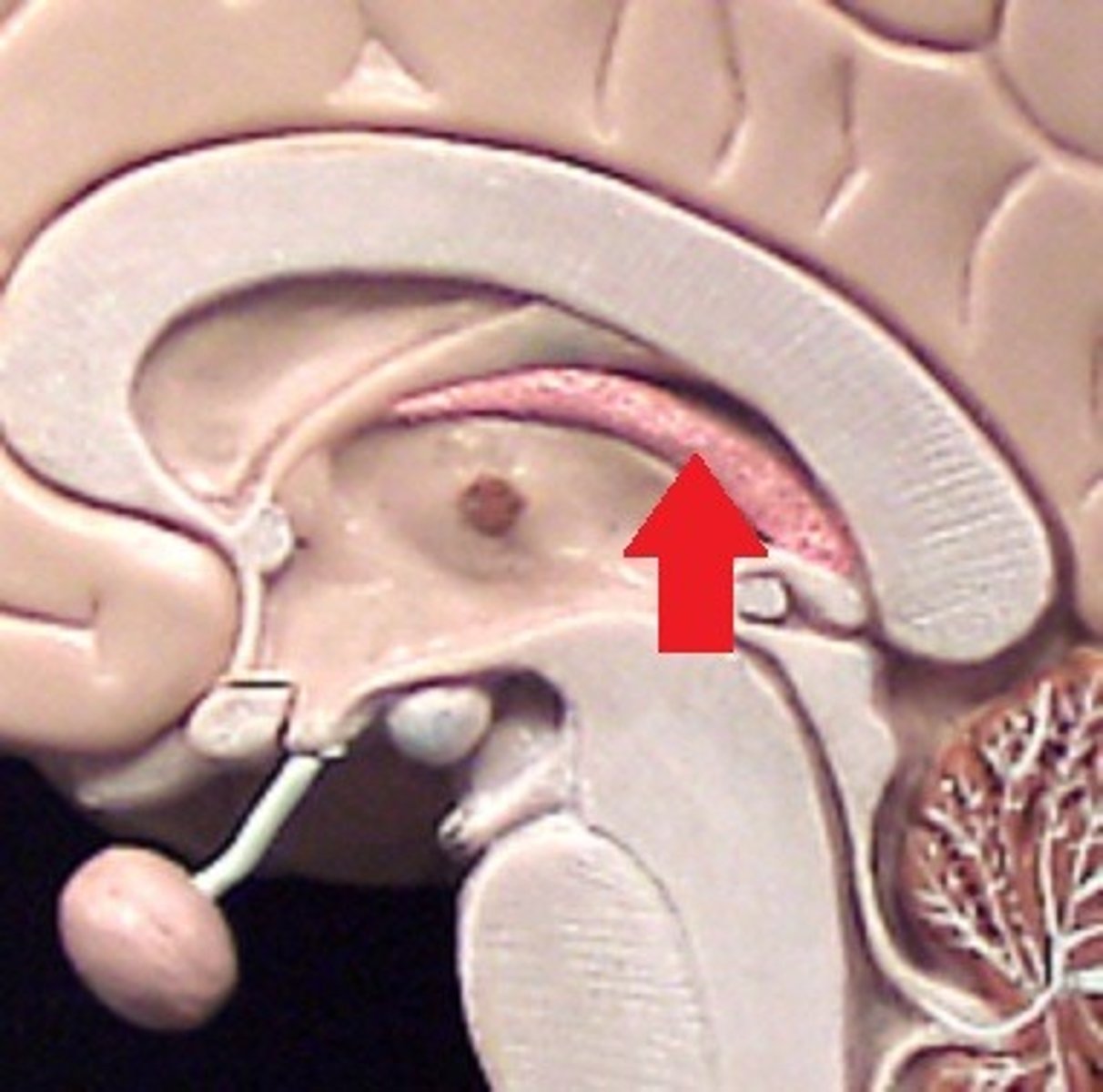
Choroid plexus of ventricle
Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
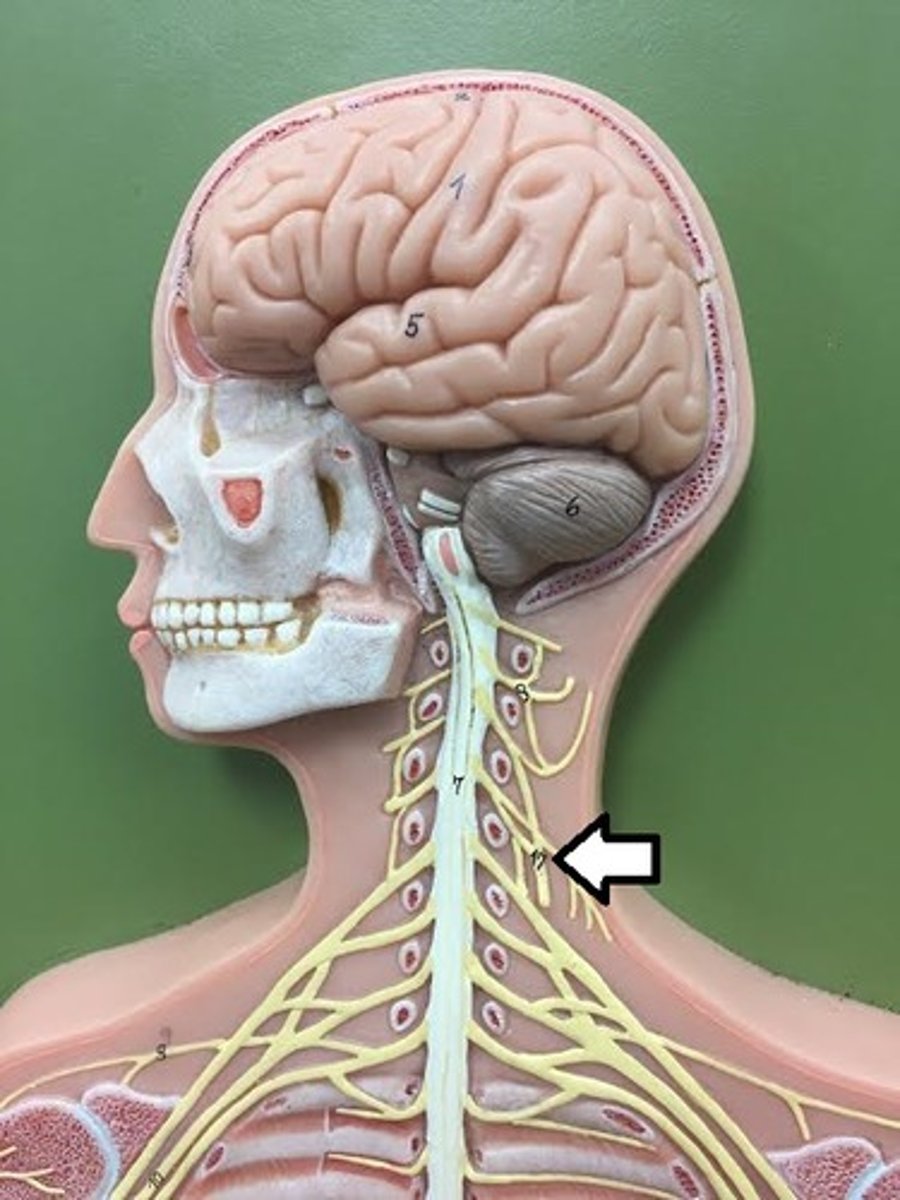
Phrenic nerve
Controls the diaphragm for breathing.
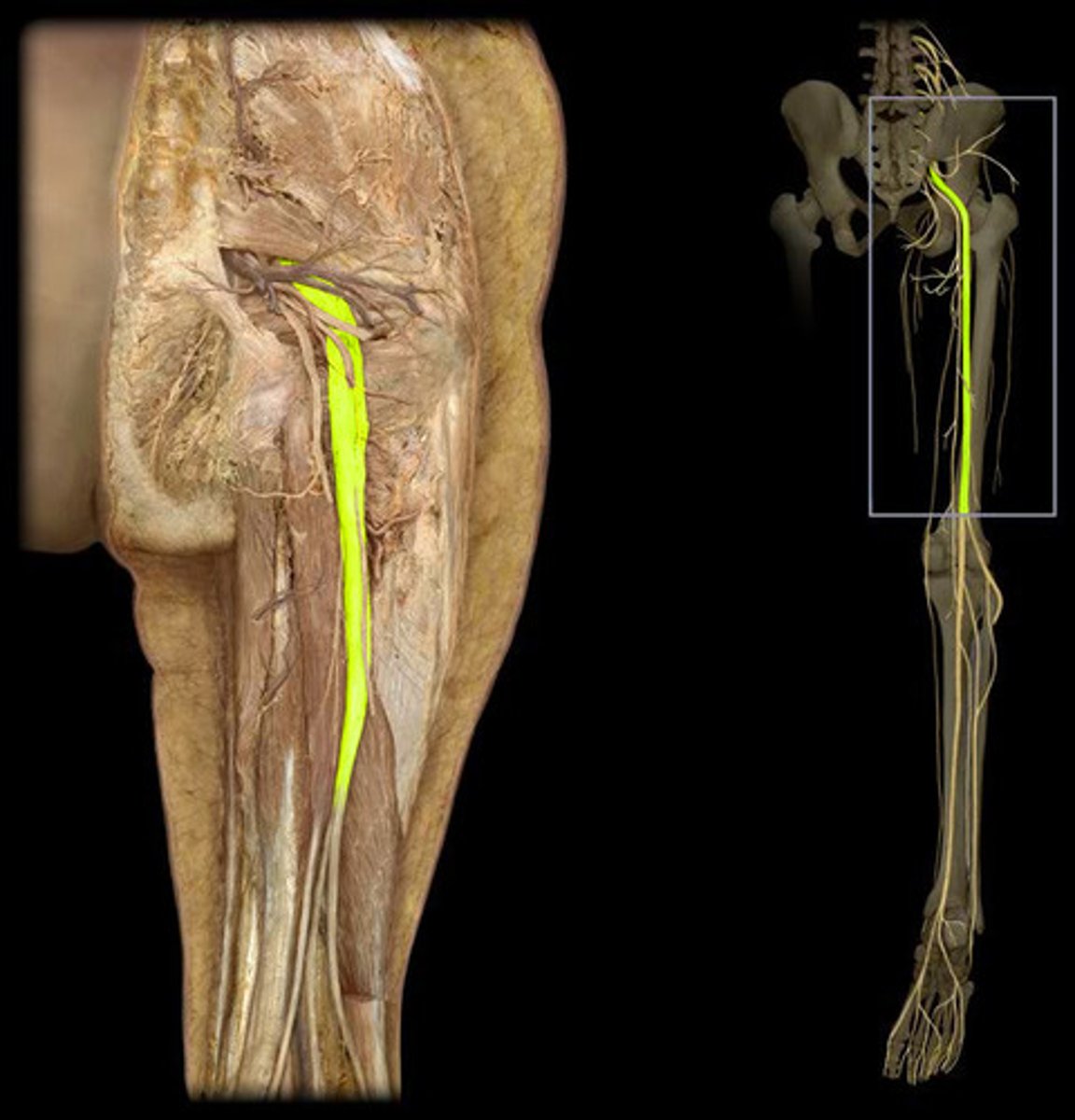
Sciatic nerve
The largest nerve in the body, running down the leg.