AP Bio Unit 1 - only the stuff idk
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Carb elements
C (H2O)
Carb monomers
simple sugars monosaccharides
Carb shape
hexagonal
Are carbs polar or nonpolar? What does this do to their solubility?
polar — dissolve well in water
what is the structure of monosaccharides?
simple ring sugars
examples of monosaccharides (2)
glucose + fructose
function of monossacharides
quick energy
two monosaccharides combined
disaccharides
two examples of disaccharides
sucrose and lactose
polymers of carbs + their function
complex sugars (polysaccharides) — store energy and provide structure
4 examples of polysaccharides and their functions
Starch = how store energy in plants
Glycogen = how store energy in animals
Cellulose = make up cell walls
chitin = make up exoskeletons of insects
sucrose
disaccharide; table sugar
what is lactose in?
milk
Where do animals and plants store carbs and energy?
plants: central vacuole
animals: muscles and liver
identify this
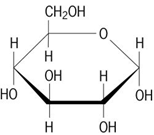
Carbohydrate
Are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic? what does this mean?
hydrophobic —> nonpolar, insoluble in water
3 functions of lipids
insulation and long term energy storage (fat) and cell membrane
two types of lipids
fats and oils
monomers of lipids
fatty acids and glycerol
elements of lipid
Hydrocarbons (CH) + a few Oxygens on the ends
ALSO phospholipids have Phosphorus
Phospholipids
structural component of cell membrane
What is the phosphate head? What is the phosphate tail?
head = ionic —> hydrophilic
tail = hydrophobic —> hide between heads
steroids
cholesterol and sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone)
What are cholesterol and sex hormones made of?
4 fused rings
identify:
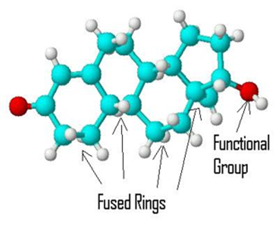
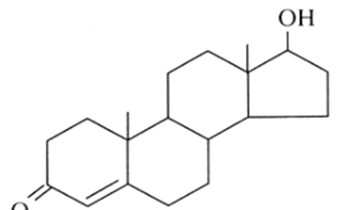
steroid
cholesterol: what is it a type of and what is its function
type of steroid; essential in cell membrane
what does cholesterol enable animal cells to do? (3)
not need a cell wall, be able to change shape, move freely
saturated fats
no double bonds and solid at room temp
unsaturated fats
double bonds, kinking the molecule, and liquid at room temp
triglyceride function
store long term energy by getting stored in fat cells as lipids
What make up triglycerides?
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
3 examples of lipids
triglycerides, cholesterol, testoterone
function of phospholipids and cholesterol
membrane structure
function of triglycerides
long term energy storage
function of testosterone and estrogen
hormones / messengers
Identify:

lipid
3 examples of saturated fats
butter
cheese
whole milk
3 examples of unsaturated fats
olive, vegetable, or avocado oil
nuts, seeds
fish
peanut butter
What is phosphorus in? (3)
ATP, nucleic acids, and phospholipids
is dehydration synthesis endergonic or exergonic?
endergonic — absorbs energy
What is glucose and what does it power?
a six carbon simple sugar powering the synthesis of ATP during cellular respiration
Differences in saturation determine ___
__ determine the differences between fats and oils
what does the structure of phospholipids give them?
polar/hydrophilic regions and nonpolar/hydrophobic regions
monomers of proteins and what they are joined by
amino acids — joined by peptide bonds
polymers of proteins
polypeptides
what are proteins main function?
building blocks for living tissue
examples of proteins (5)
lactase (enzyme)
hemoglobin
insulin
keratin
myoglobin (muscles)
denatured
heat causes it to lose its shape and its functionality
can proteins be denatured?
yes
how many known amino acids
20
primary structure of proteins
way amino acids are put together
secondary
first way proteins fold: alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
tertiary
interactions between side chains (folding of a protein relating to hydrogen bonding between side chains)
quaternary
interactions between polypeptide chains
identify
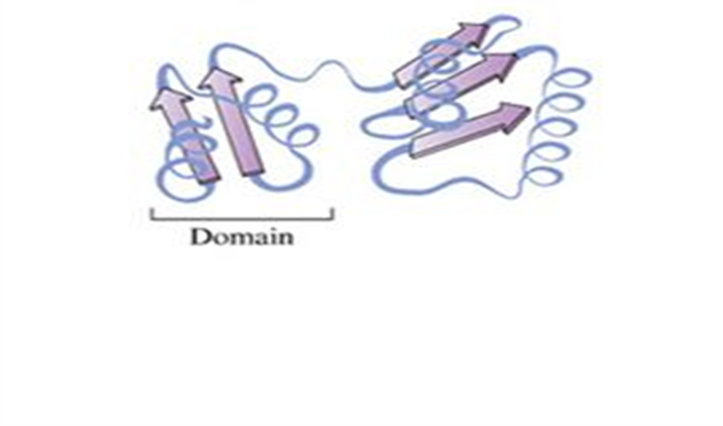
tertiary structure
identify:
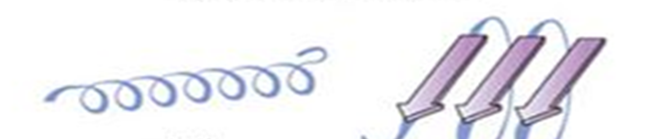
secondary
identify
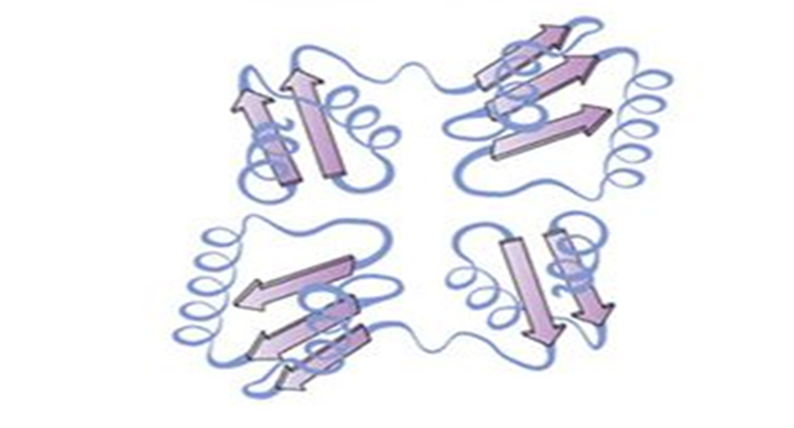
quaternary
identify

primary
What two functional groups are the peptide bonds between?
carboxyl and amino groups
what are antibodies? hair? nails?
proteins
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide
what does each nucleotide contain? (3)
sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
what 2 sugars are there for NAs?
ribose and deoxyribose
how is the phosphate bonded in nucleic acid?
covalently to the sugar
how is the nitrogen base bonded in nucleic acid?
hydrogen bonded together
identify
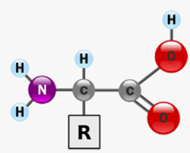
protein
identify
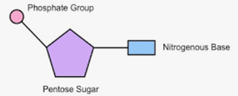
nucleic acid
structure of amino acids
Central carbon, hydrogen atom, amine group, carboxyl group, variable side chain
Are proteins directional? what do they have? (2)
yes — have an amino terminus and a carboxyl terminus
is DNA’s complementary strands antiparallel?
yes
function of hemoglobin
carrier
function of keratin
structural support
function of lactase
enzymes
function of myosin
movement
function of insulin
hormones/messengers
3 examples of Nucleic acids
DNA, RNA, ATP
function of DNA
info storage
function of Rna
info transmission
function of ATP
energy storage
protein elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur
Nucleic acid elements
CHO, Nitrogen, phosphorus