Page 134 - Circuit Basics
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Page 134 - Circuit Basics Total Charge in a Circuit: Current is the rate of flow of charge. Charge (Q) in a circuit = Current (I) x Time (t). Measurements: Current in amperes (A), Charge in coulombs (C), Time in seconds (s). Potential Difference: It's the energy transferred per coulomb of charge. Energy transferred (E) = Charge (Q) x Potential Difference (V). Potential difference, also known as voltage, is measured in volts (V), and represents the energy per unit charge. The page provides formulas and examples related to charge, current, and potential difference in electrical circuits.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Circuit Basics
Charges transfer energy round a circuit — you can work out how much with a couple of equations...
Definition of Current
Current is the rate of flow of charge
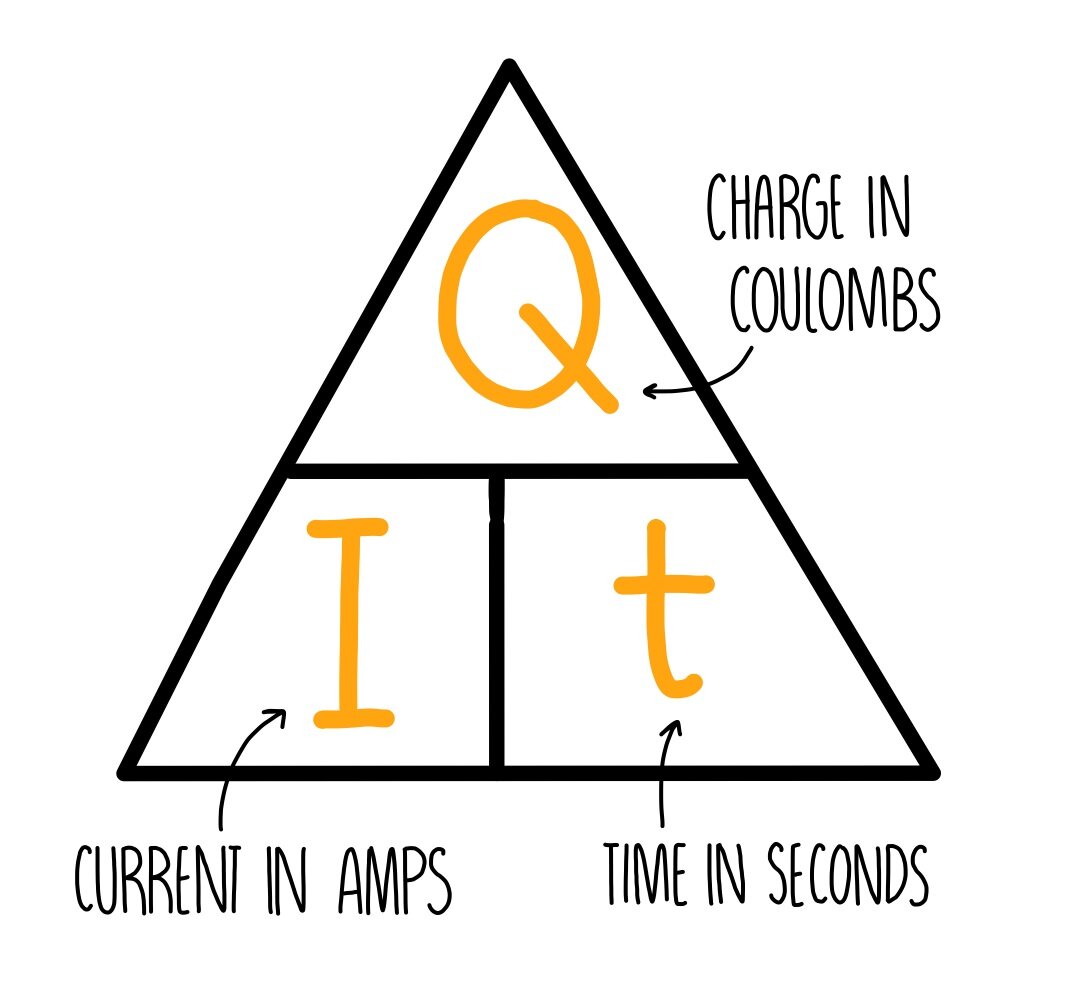
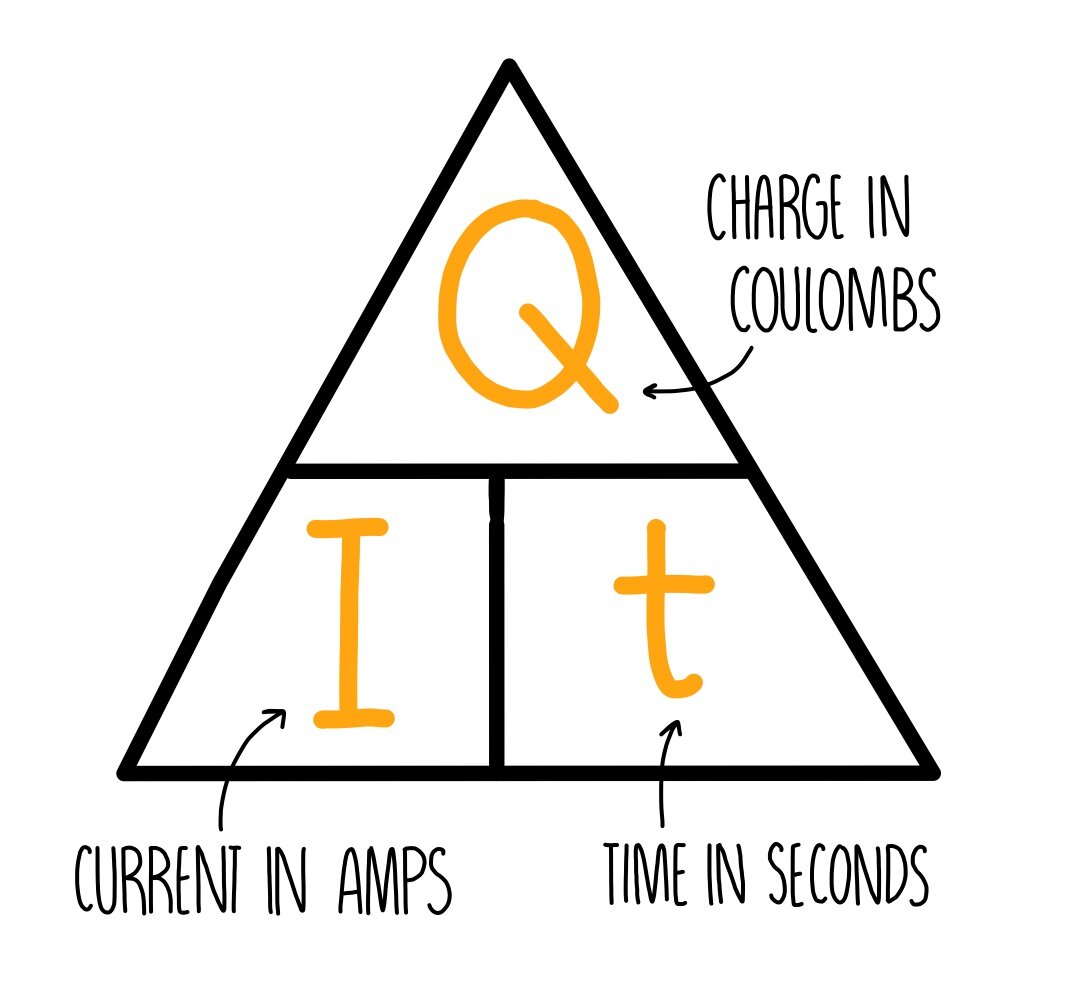
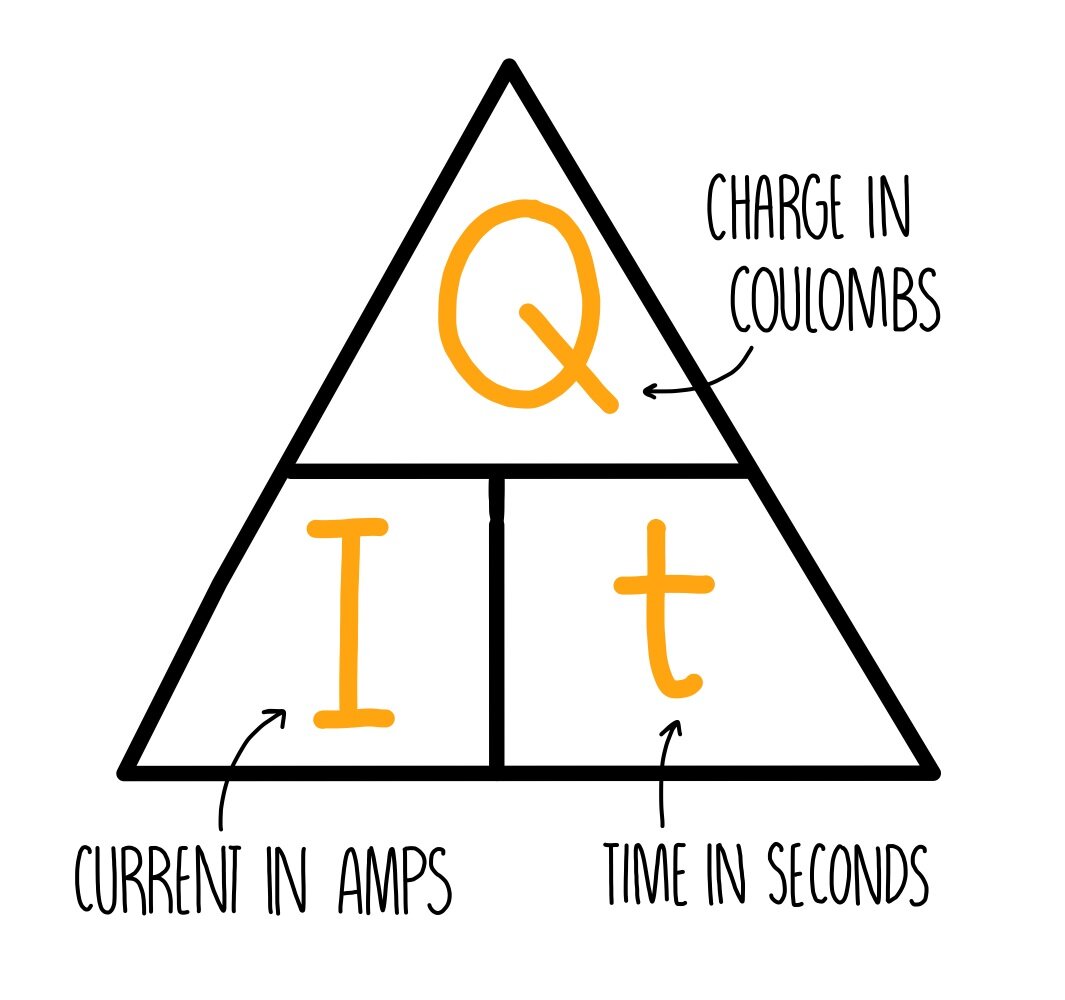
Formula for calculating charge in a circuit
Q = I × t
What is Q
Q is charge in coulombs
What is I
I is current in amperes
What is t
t is time in seconds
One more time… Formula for calculating charge in a circuit
Back: Q = I × t
Formula Triangle
Example of Charge Calculation - Battery charger example
A battery charger passes 18 000 C of charge to a battery over a period of 2.5 hours. Calculate the current flowing between the battery charger and the battery.
Convert the time into seconds.
2.5 × 60 × 60 = 9000 s
Rearrange the equation for current.
I = Q ÷ t
Substitute into the rearranged equation.
= 18 000 ÷ 9000 = 2 A
Definition of Potential Difference
Potential difference is the energy transferred per coulomb of charge that passes between two points in an electrical circuit.
Formula for calculating energy transferred
Energy transferred = charge moved × potential difference or E = Q × V
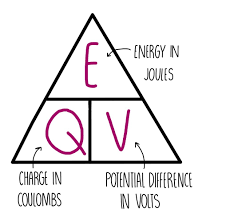
what is E
E is energy in joules,
what is Q
Q is charge in coulombs
What is V
V is potential difference in volts
Example of Energy Transfer Calculation