Histology of Large Intestine
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What does the large intestine consist of?
Cecum
Colon
Rectum
Anal canal
Characteristics of large intestine
Villi?
Shape
Type of glands
Goblet cells?
Panneth cells?
Lymphatic nodules
Compare surface of tunica mucosa to TM in small intestine
Why is mucosa layer is thicker?
Villi: Absent
Shape: Less coiled
Type of glands: Simple tubular intestinal glands
Goblet cells: Lots
Panneth cells: Absent
Lymphatic nodules: Increased number
Surface of tunica mucosa compared to it in SI: More uniform and flatter
Mucosa layer is thicker because: Increase length of intestinal glands
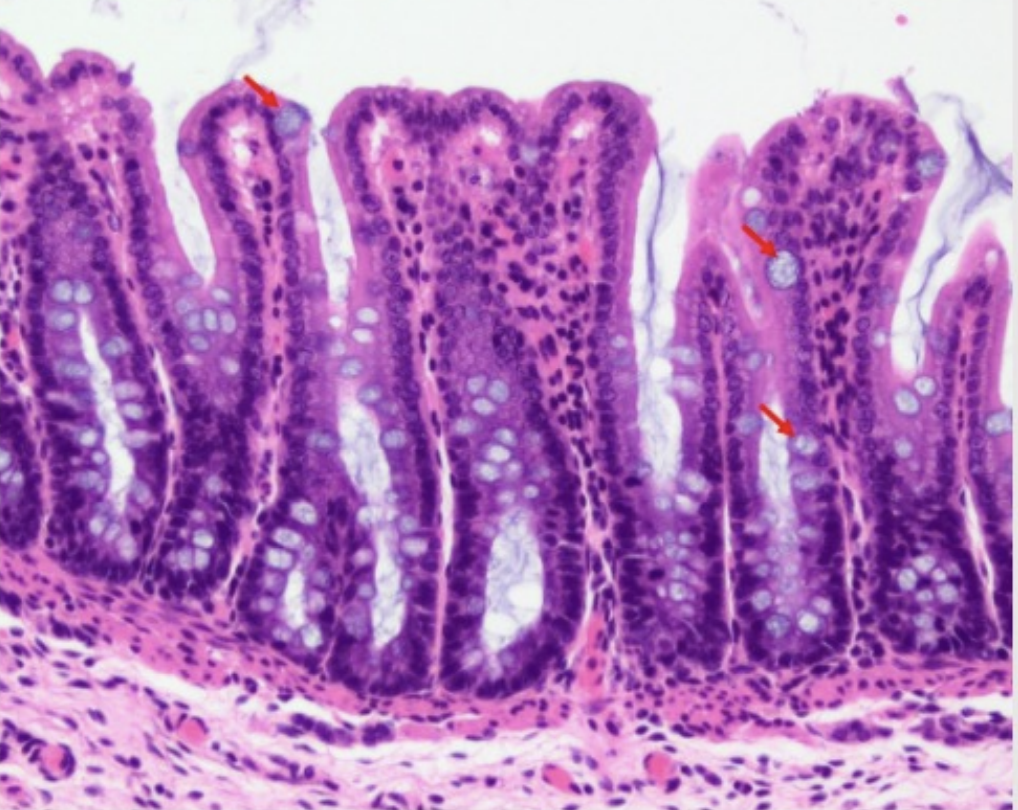
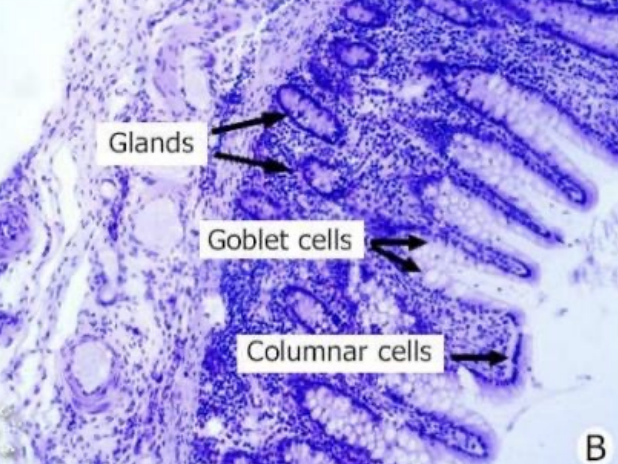
Histology of Large Intestine: Tunica Mucosa
Epithelium
Type of glands
Type of lining
Type of cells
Lamina propria
Consist of
Muscularis mucosae
Location
Function
Epithelium:
Type of glands: Straight tubular glands
Type of lining: Absorptive columnar cells
Type of cells:
Goblet cells
Stem cells
Lymphocytes
Lamina propria:
Consist of:
Loose CT
Blood and lymphatic vessels
Collagen
Lymphocytes
Plasma cells
Muscularis mucosae:
Location: Beneath base of the crypts
Function: Undergoes rhythmic contractions
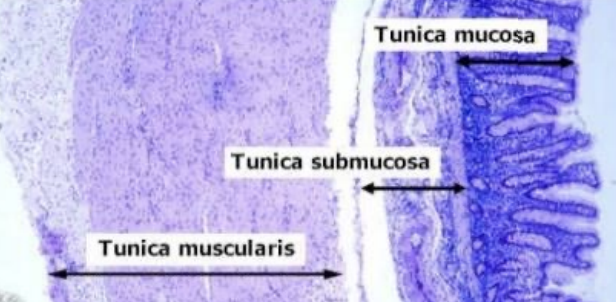
Histology of Large Intestine: Submucosa
Describe
Typical
Glands extend to submocosa
Histology of Large Intestine: Tunica Muscularis #ffb300
2 layers
What separates the second layer
Function
2 layers:
Inner circular
Outer longitudinal
Separates second layer: 3 longitudinal bands of taenia coli (smooth muscle)
Function: Movement of more solid waste to rectum (aid in contraction)
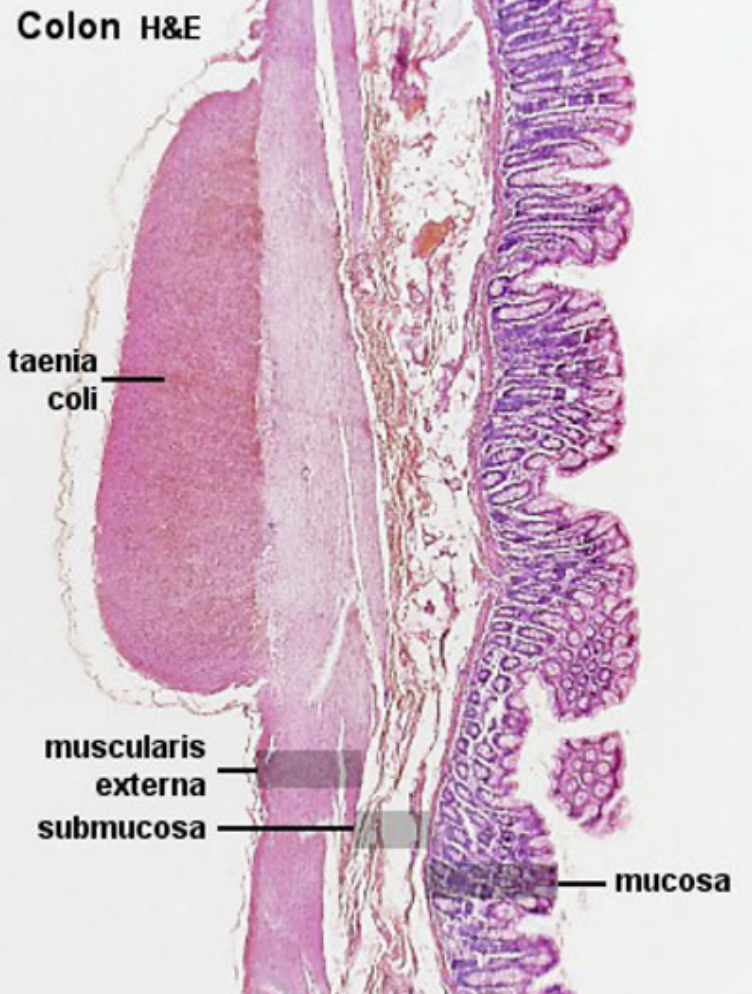
Histology of Large Intestine: Tunica Serosa
Describe
Typical
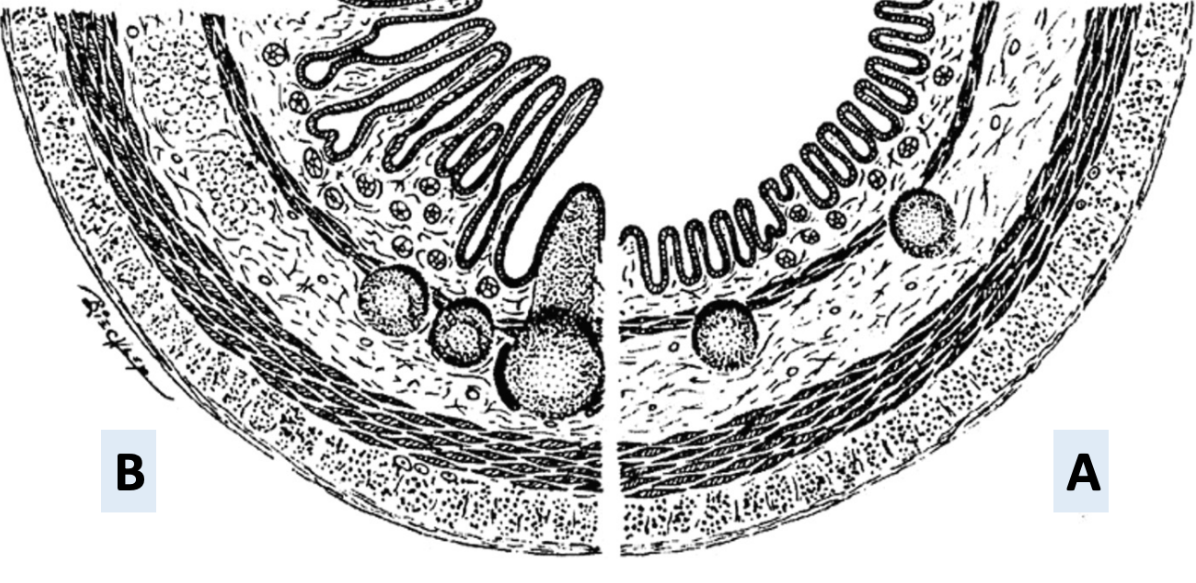
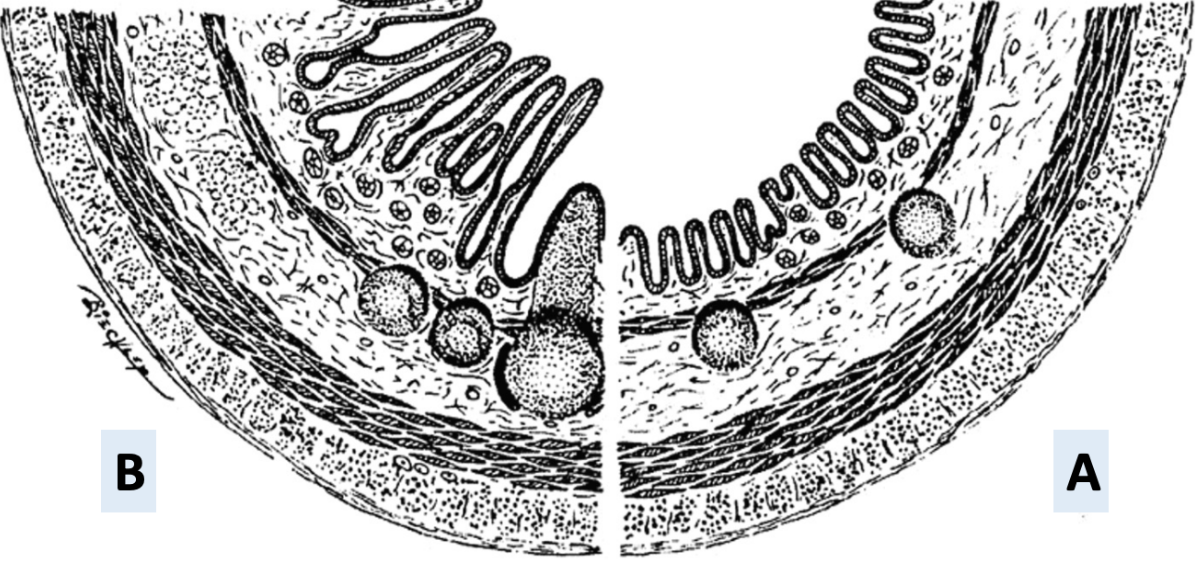
Between A and B which small intestine and large intestine?
Small intestine: B
Large intestine: A
Because: Tunica mucosa is more uniform and flat