Organic Chemistry 1 Important Functional Groups
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
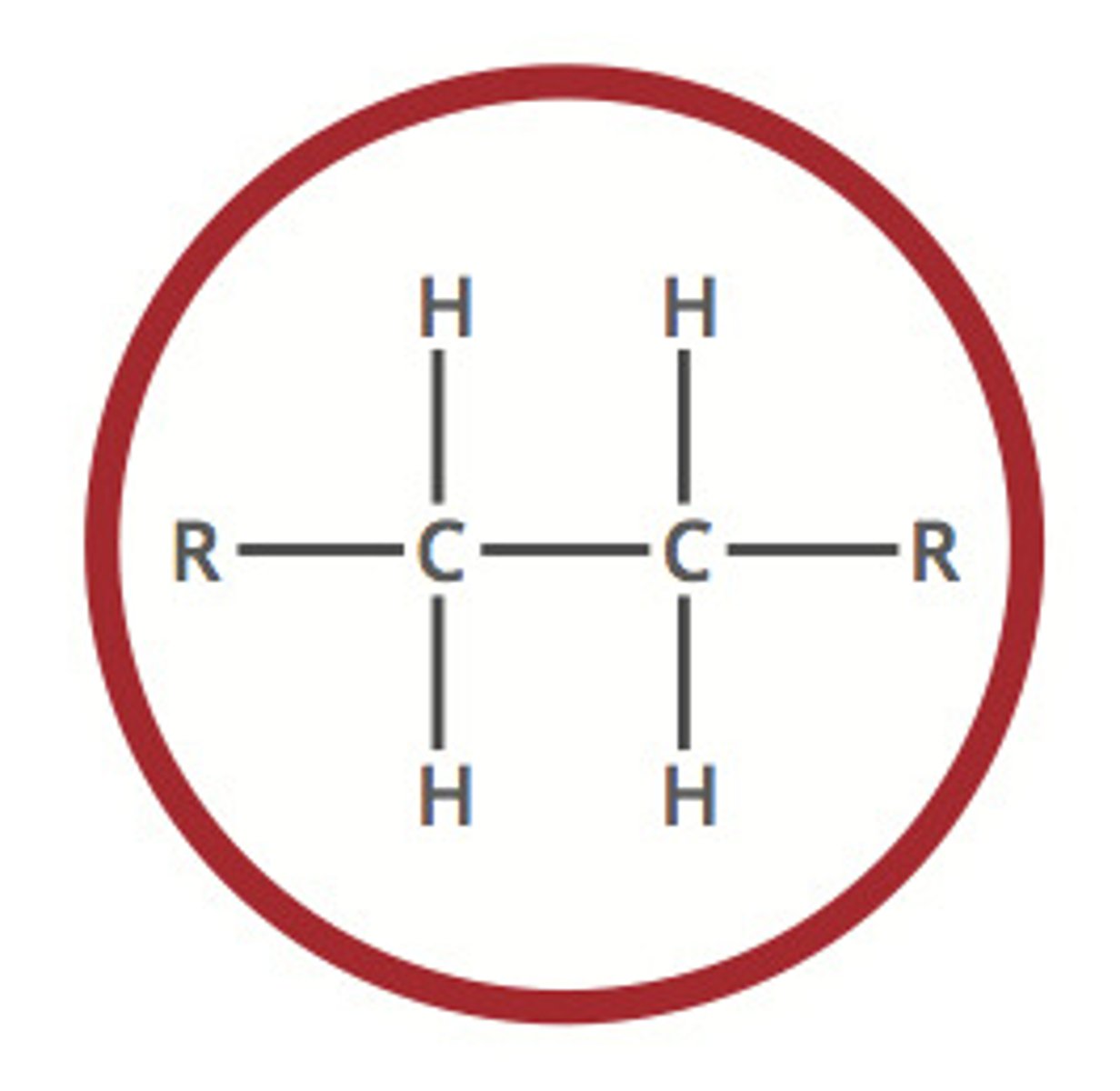
Alkane
A hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds (C-C)
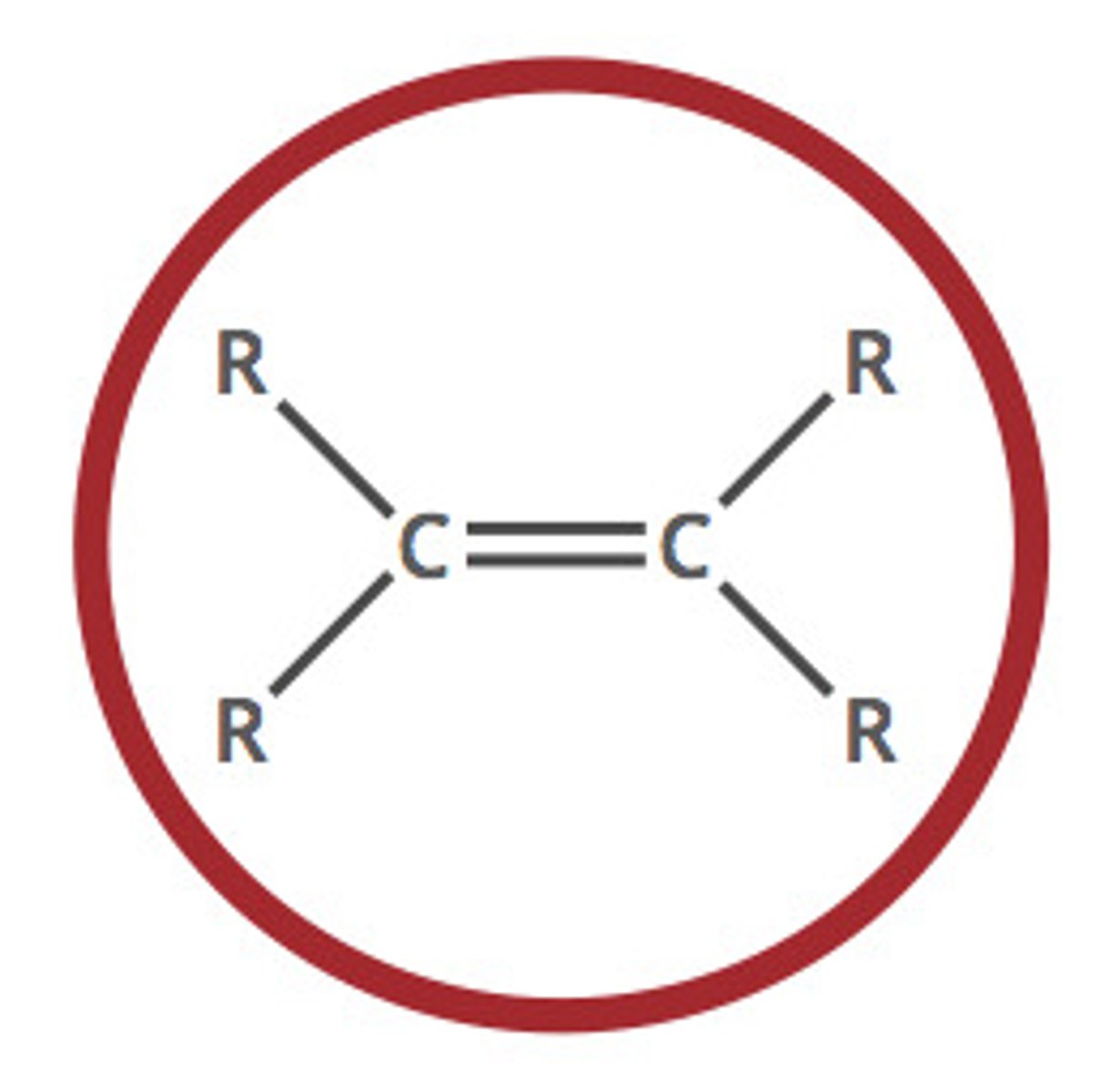
Alkene
A hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
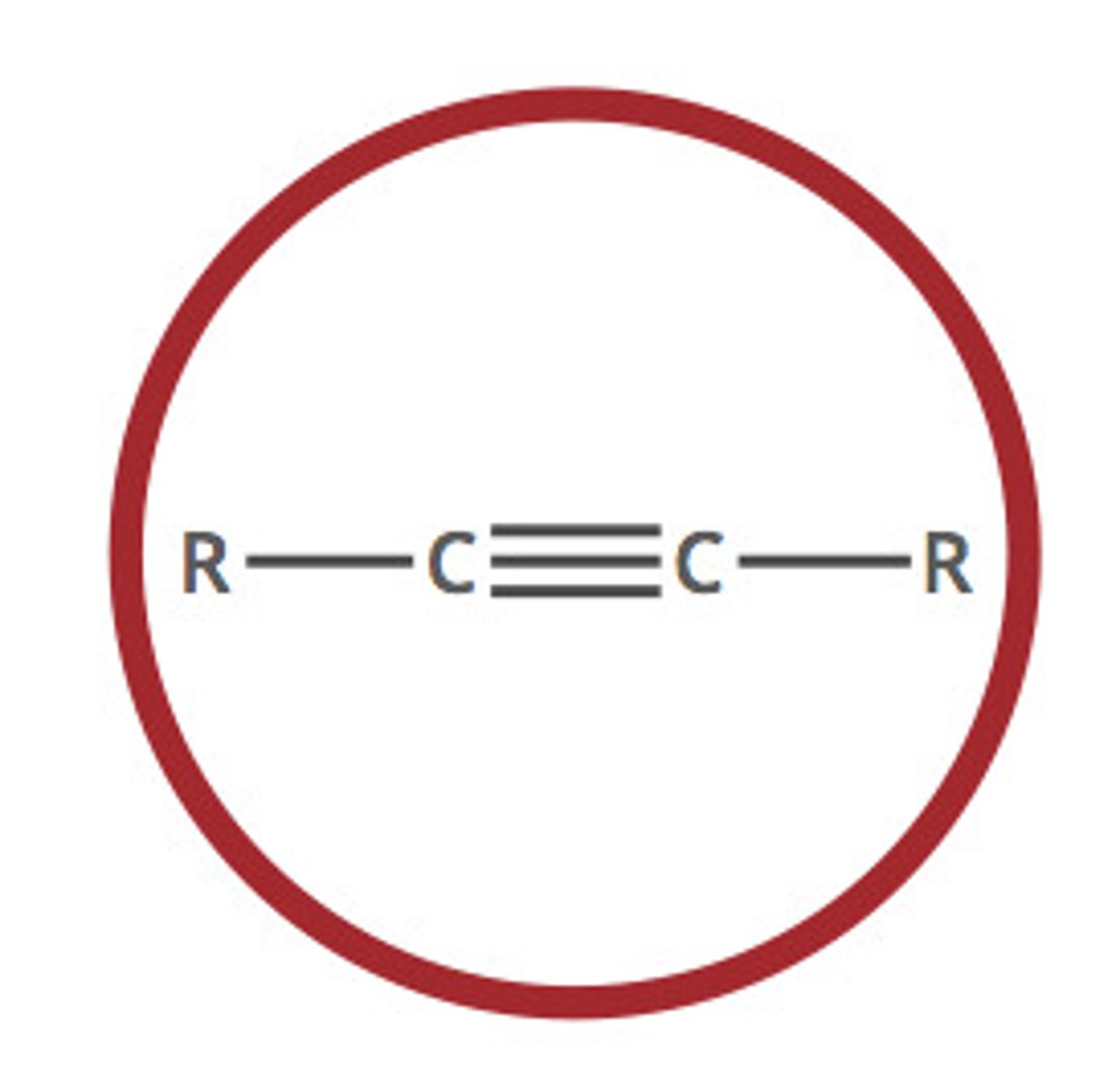
Alkyne
A hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond (C≡C)
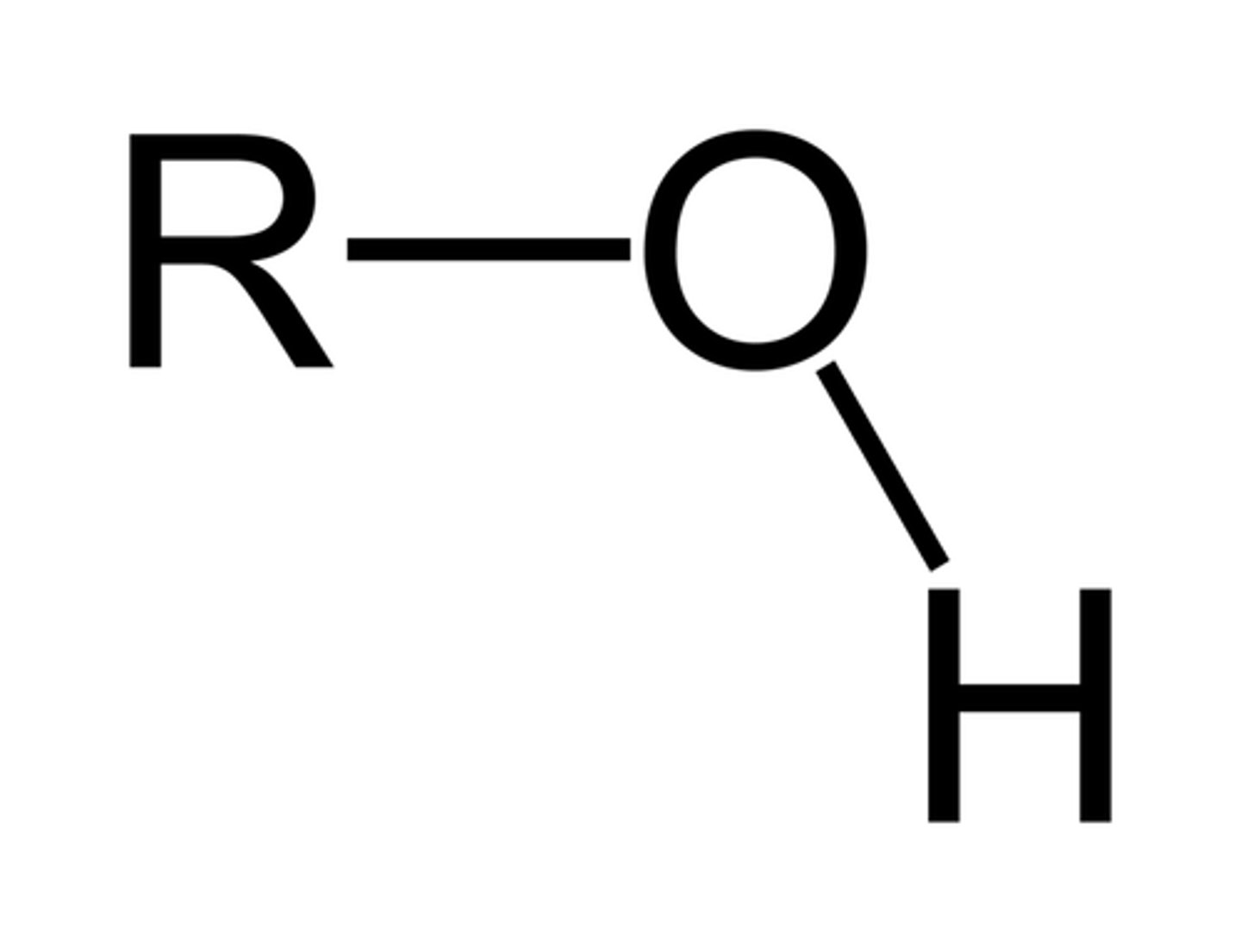
Alcohol
A hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a saturated (sp3 hybridized) carbon atom (R-OH)
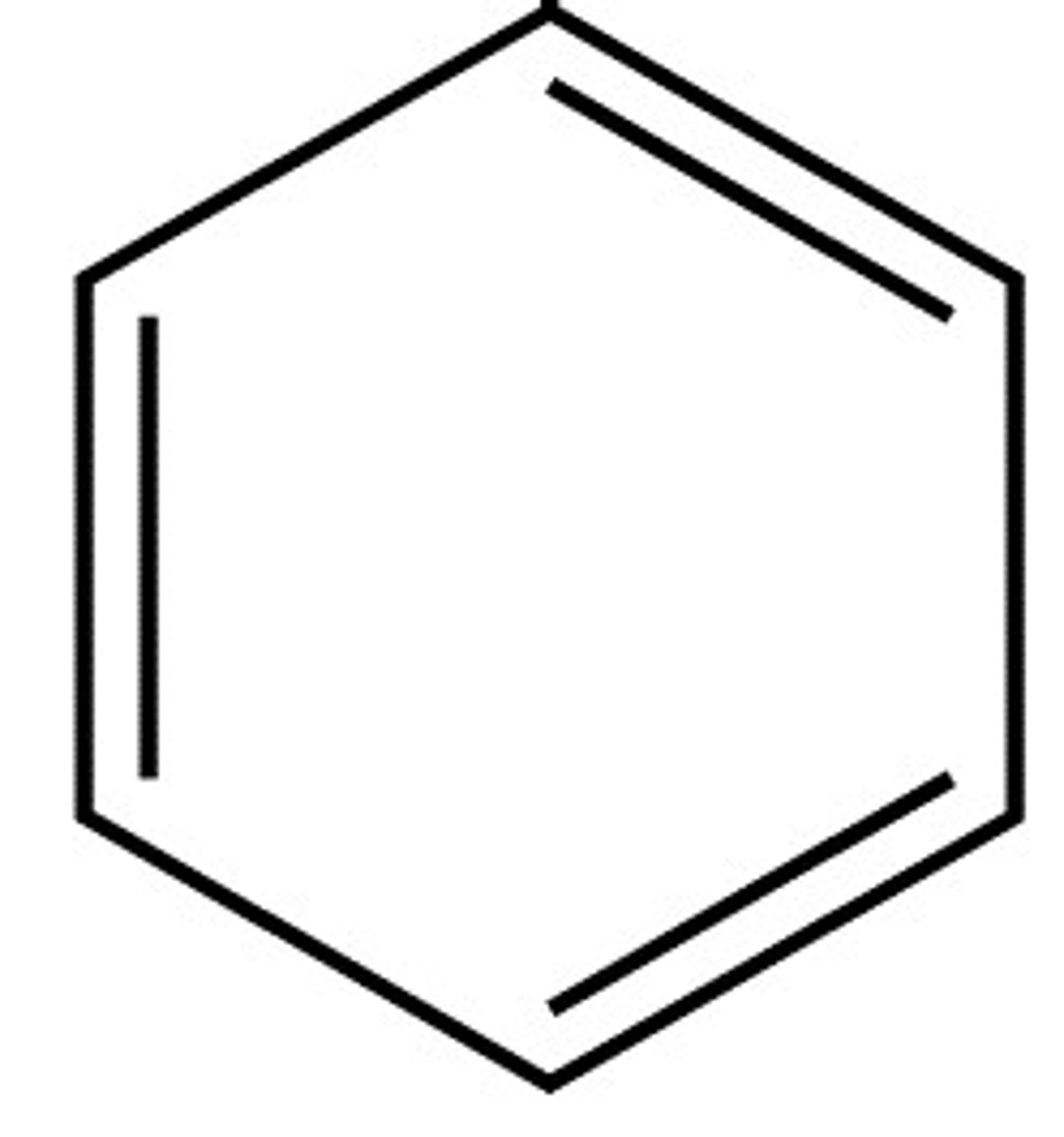
Aromatic ring
Six carbon ring with alternating double and single bonds (BENZENE)
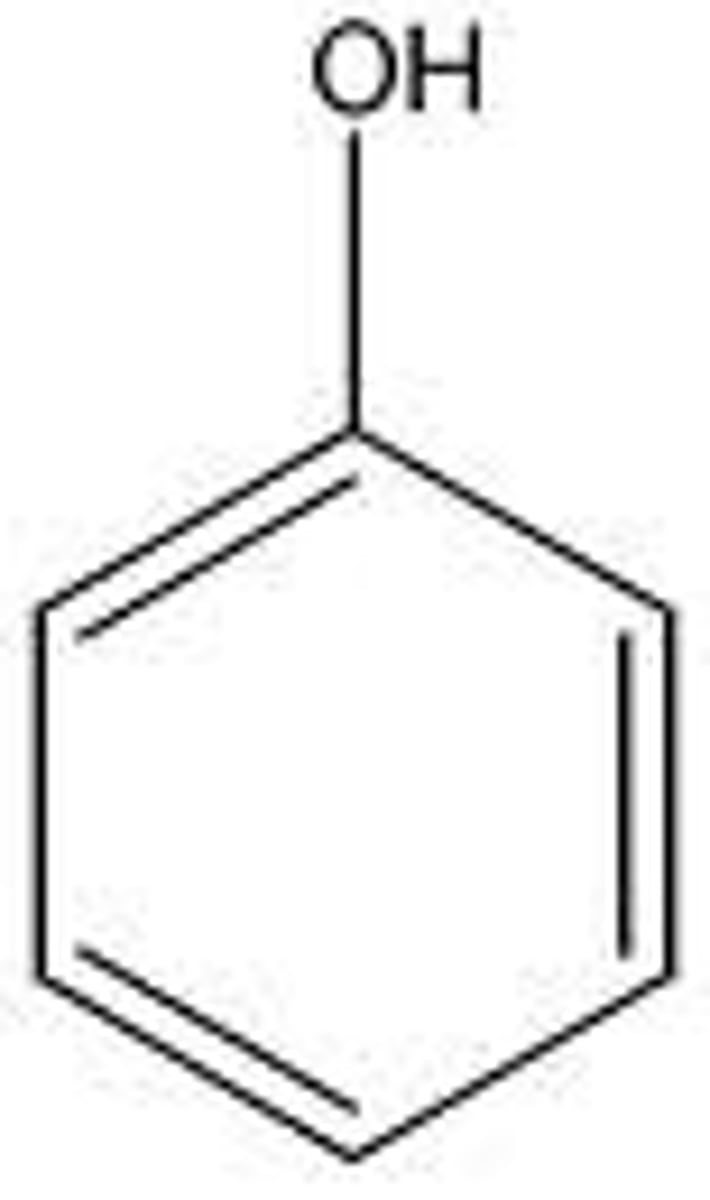
Phenol
Benzene ring with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached ("Phen"-"ol" phenyl alcohol)
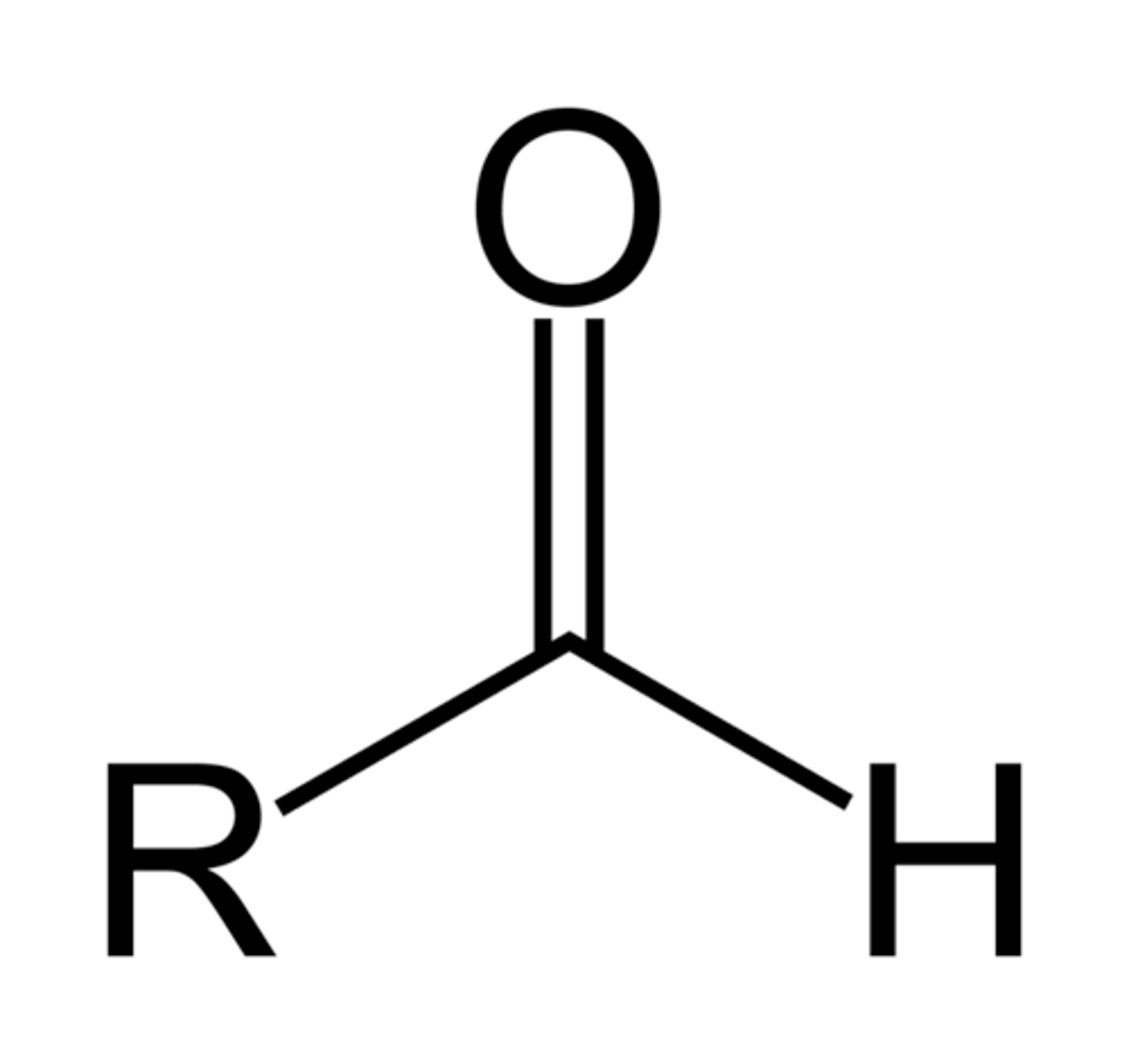
Aldehyde
A terminal functional group that contains a carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom (condensed formula: R-CHO)
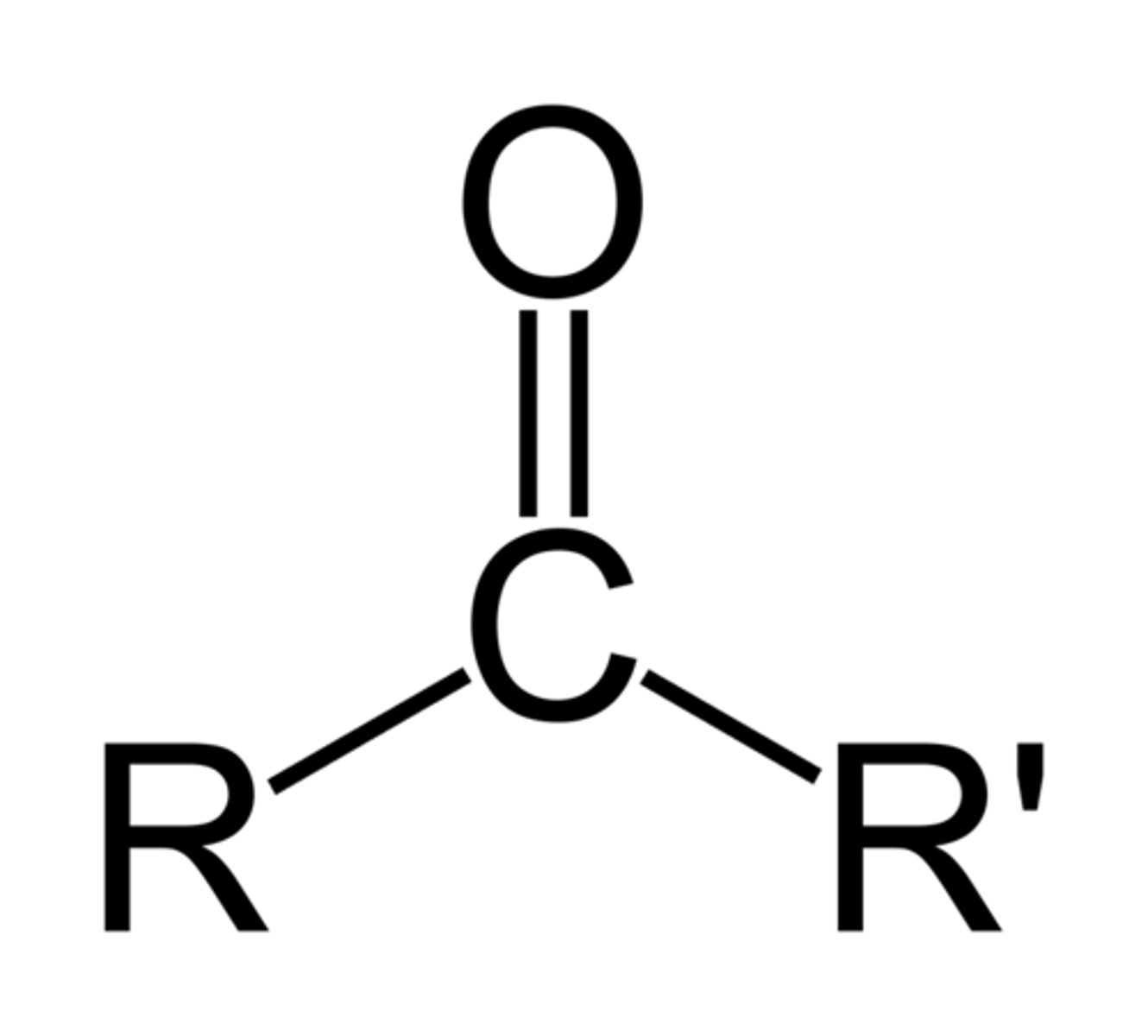
Ketone
A non-terminal functional group in which the carbonyl group is bonded to two other carbons or alkyl chains (condensed formula: RCOR')
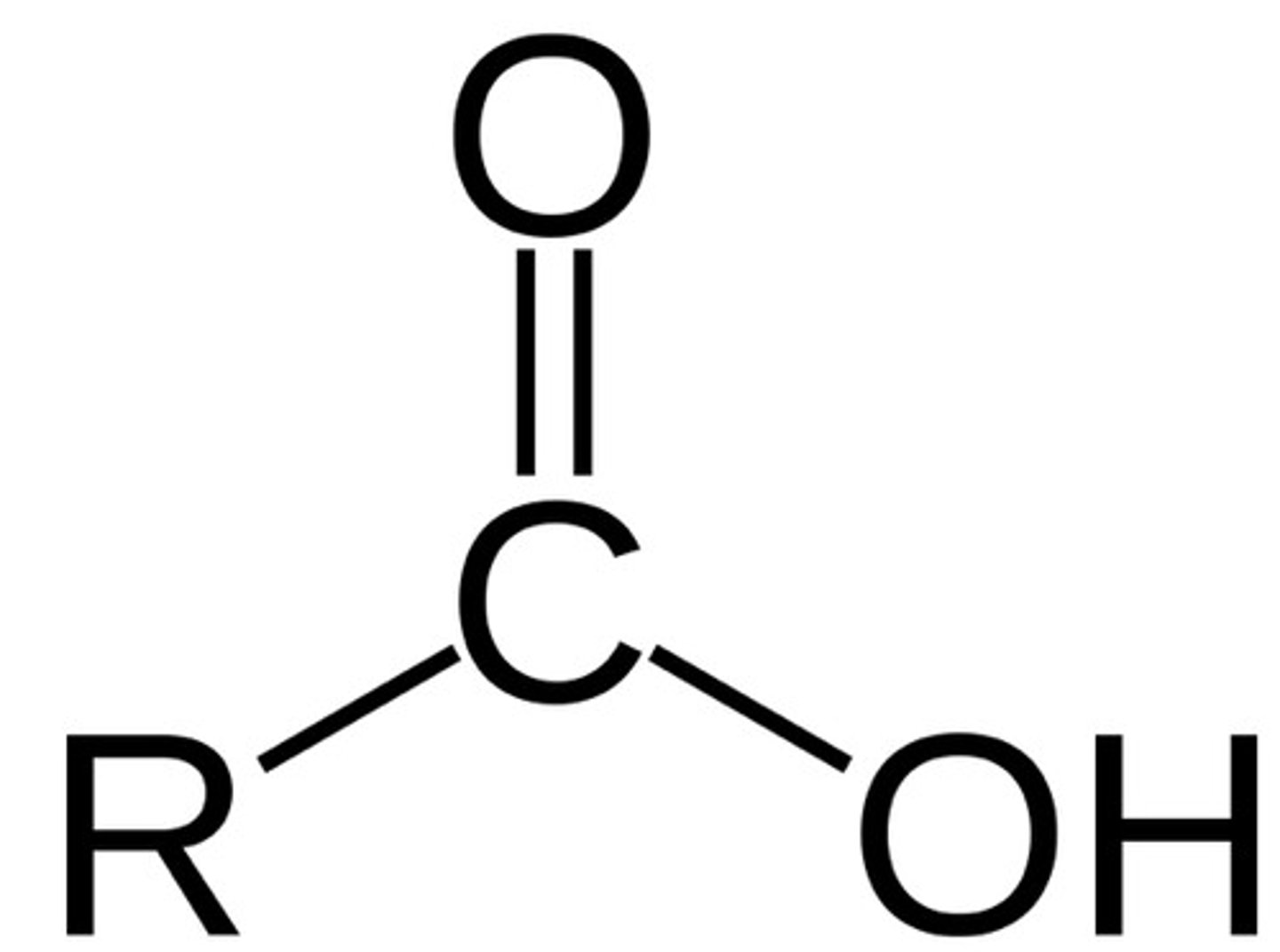
carboxylic acid
A terminal functional group in which the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH) (condensed formula: R-COOH)
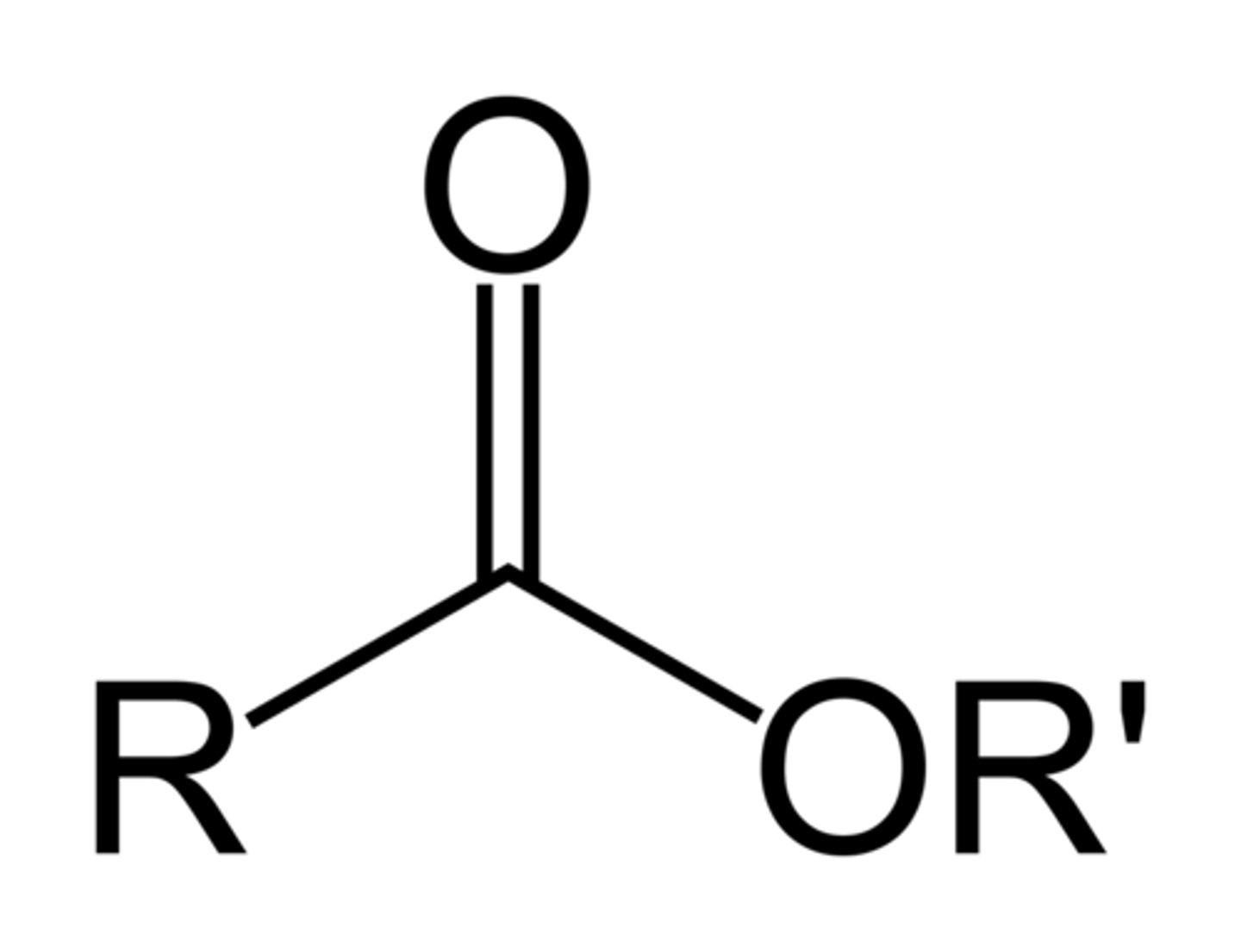
Ester
A carbonyl group bonded to an alkoxy group (R-O) think carbonyl ether (condensed formula: R-COOR)
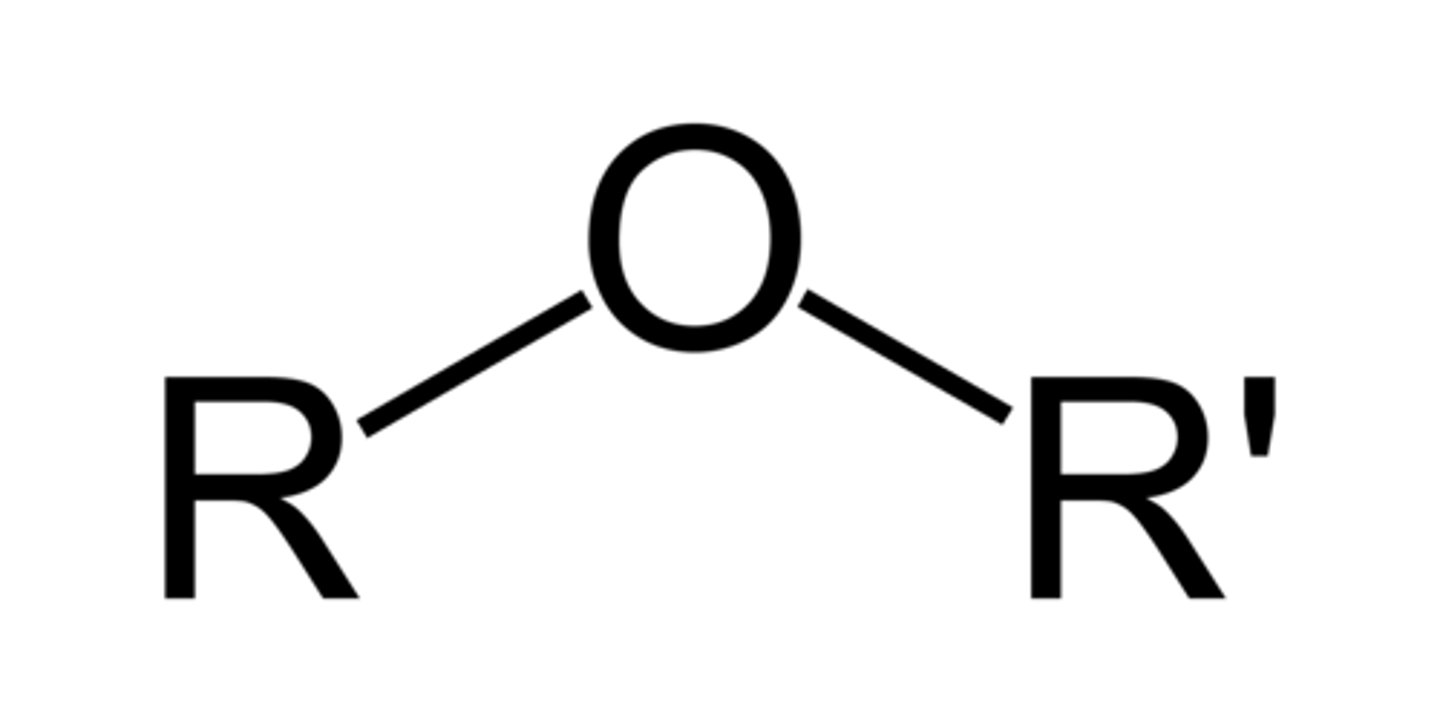
Ether
An oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl chains easiest way to remember R-O-R
Amine
A basic Nitrogen atom with a lone pair (Can be bonded to alkyl chains or hydrogens)
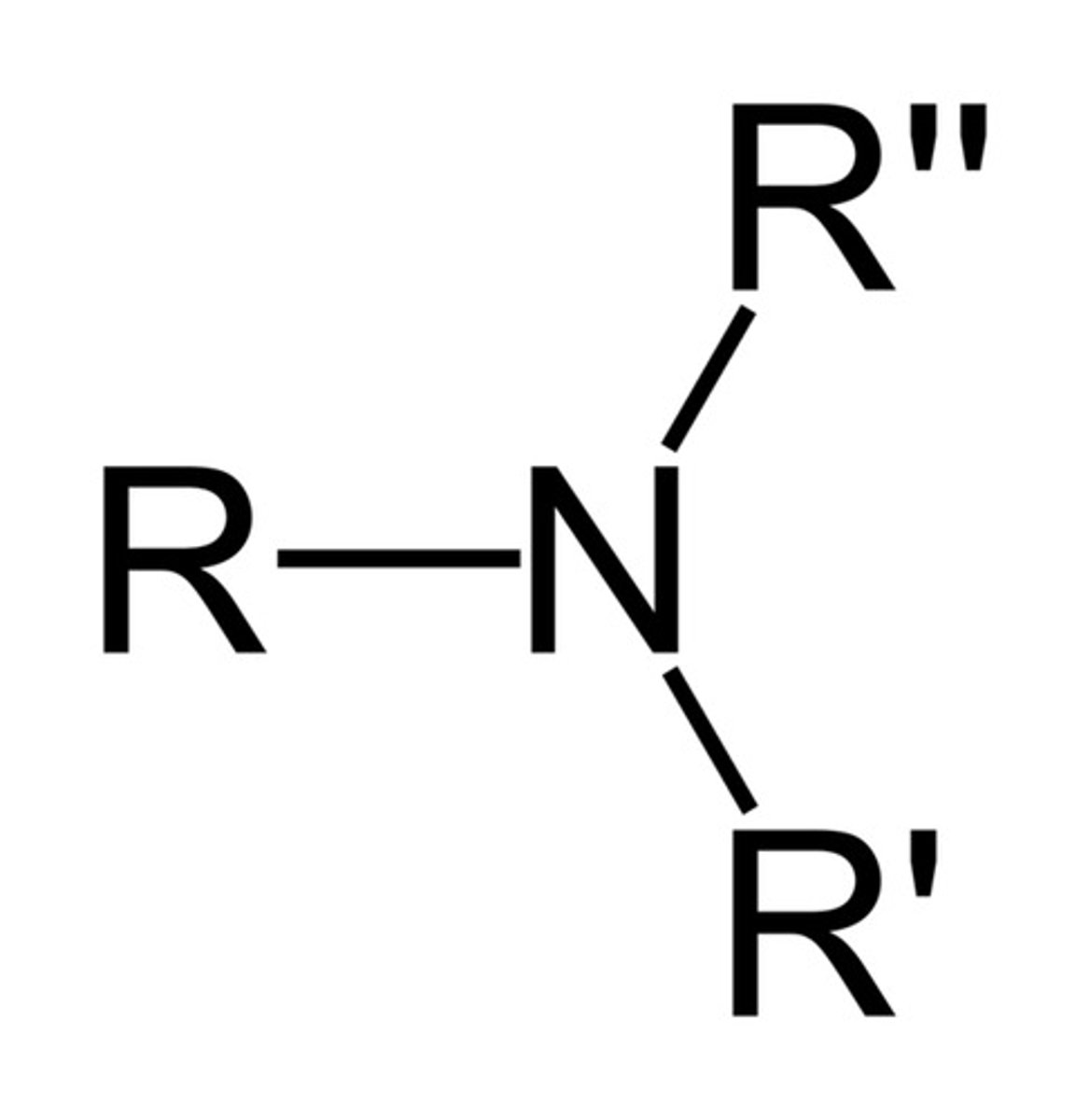
Amide
A functional group containing a carbonyl group bonded to a Nitrogen atom (the nitrogen can be substituted as well)
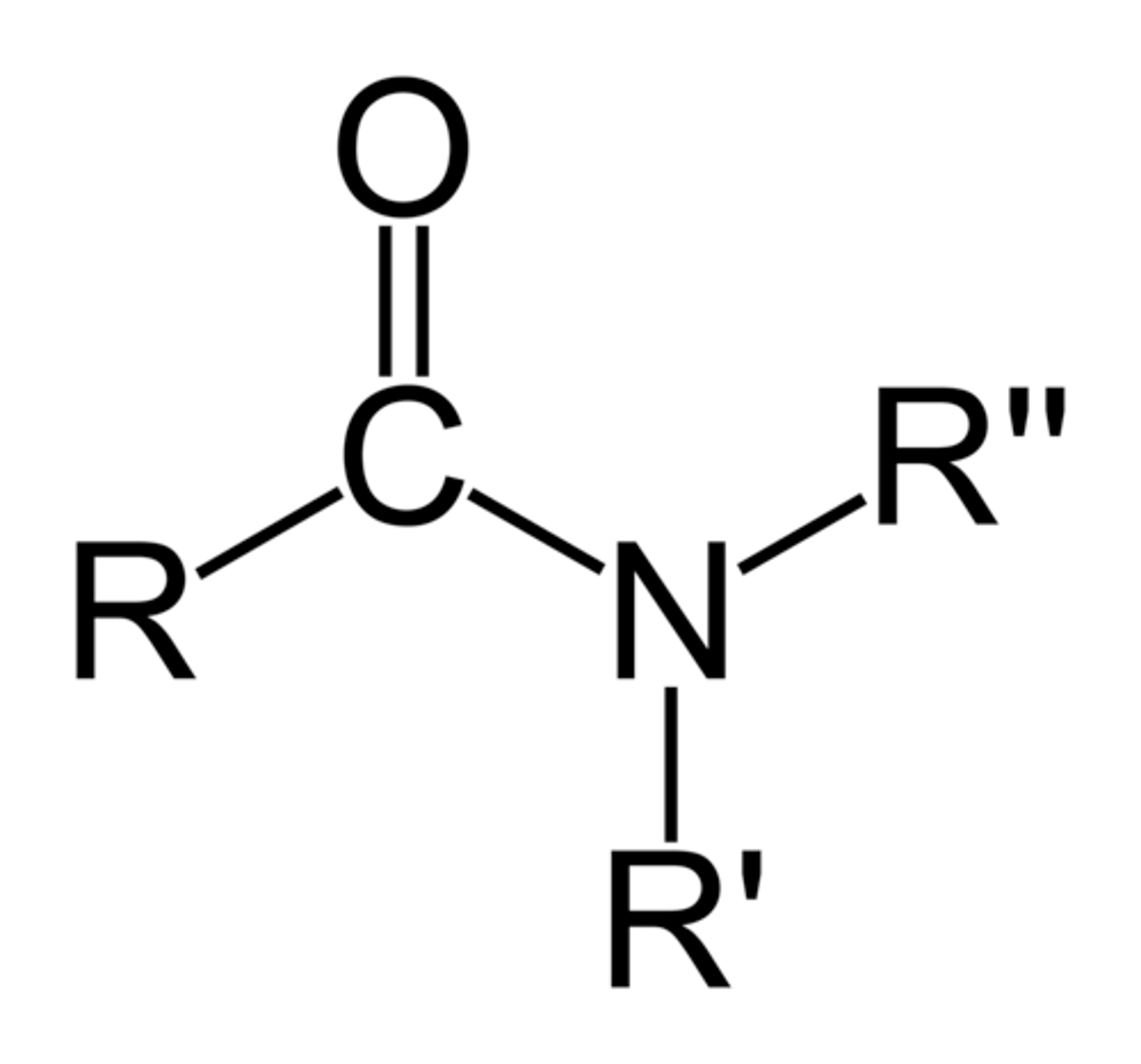
Alkyl halide
An alkane in which one of the hydrogens has been replaced by a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I)
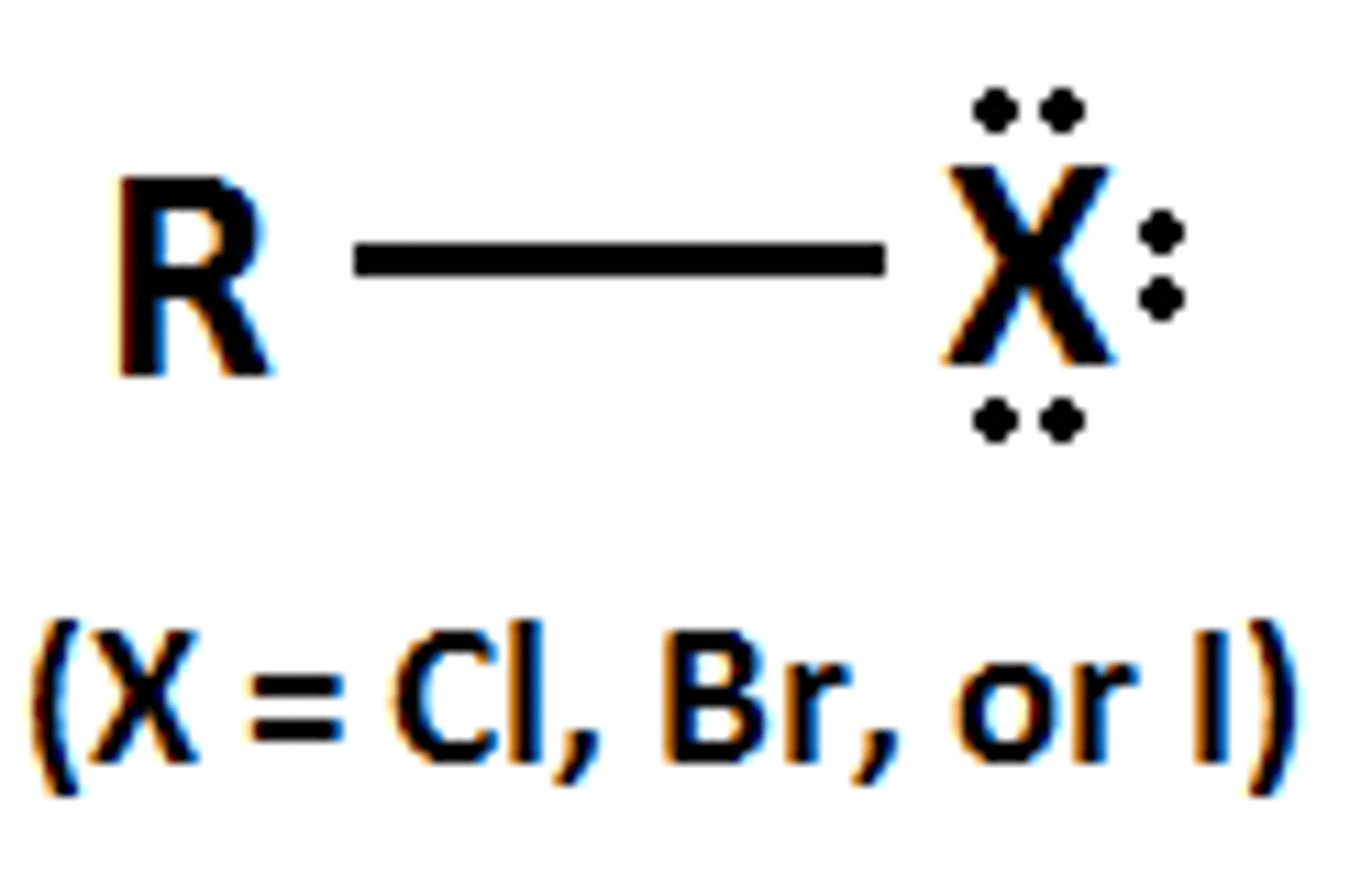
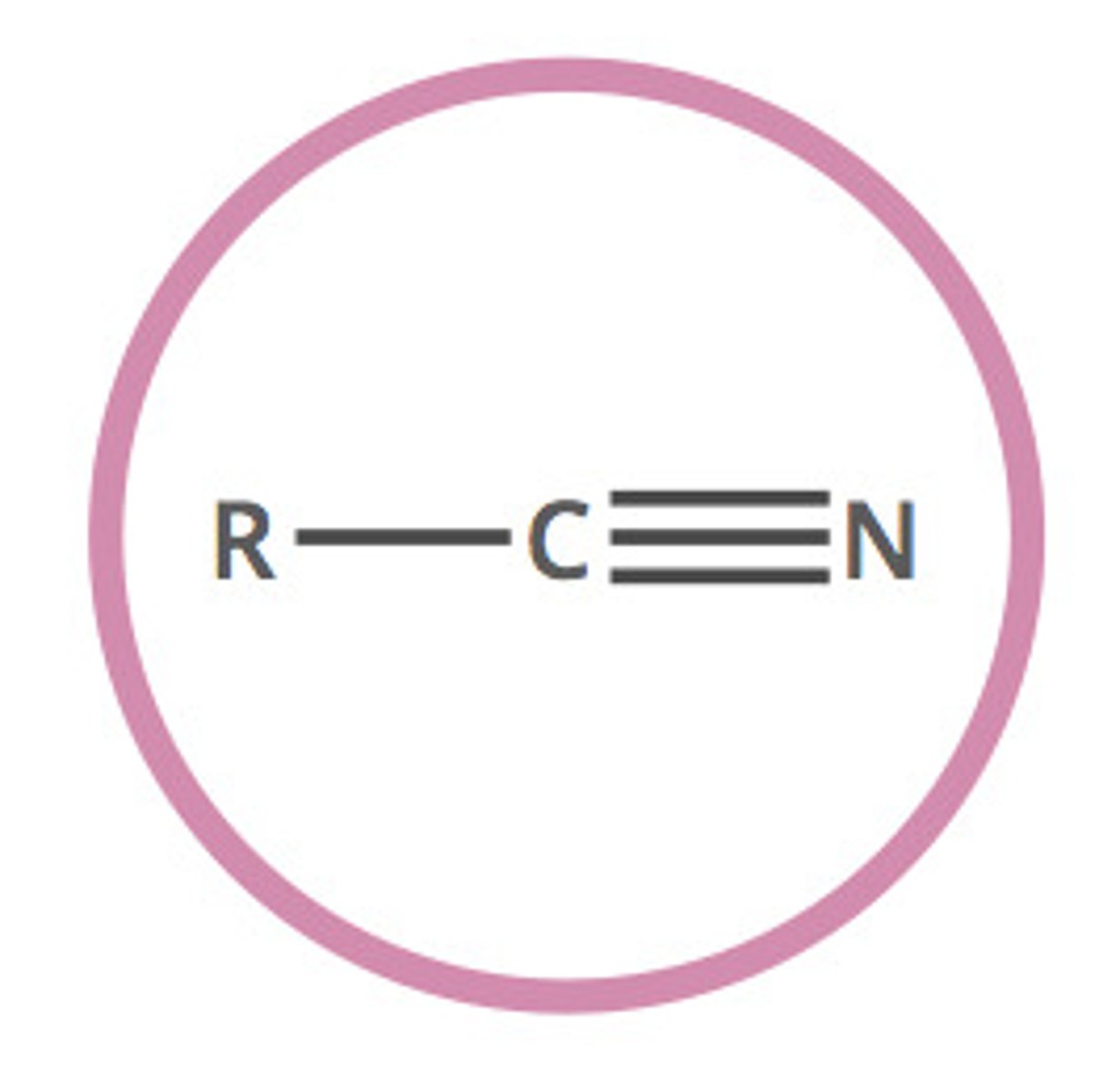
Nitrile
A functional group containing a Carbon-Nitrogen triple bond (condensed formula: R-CN)
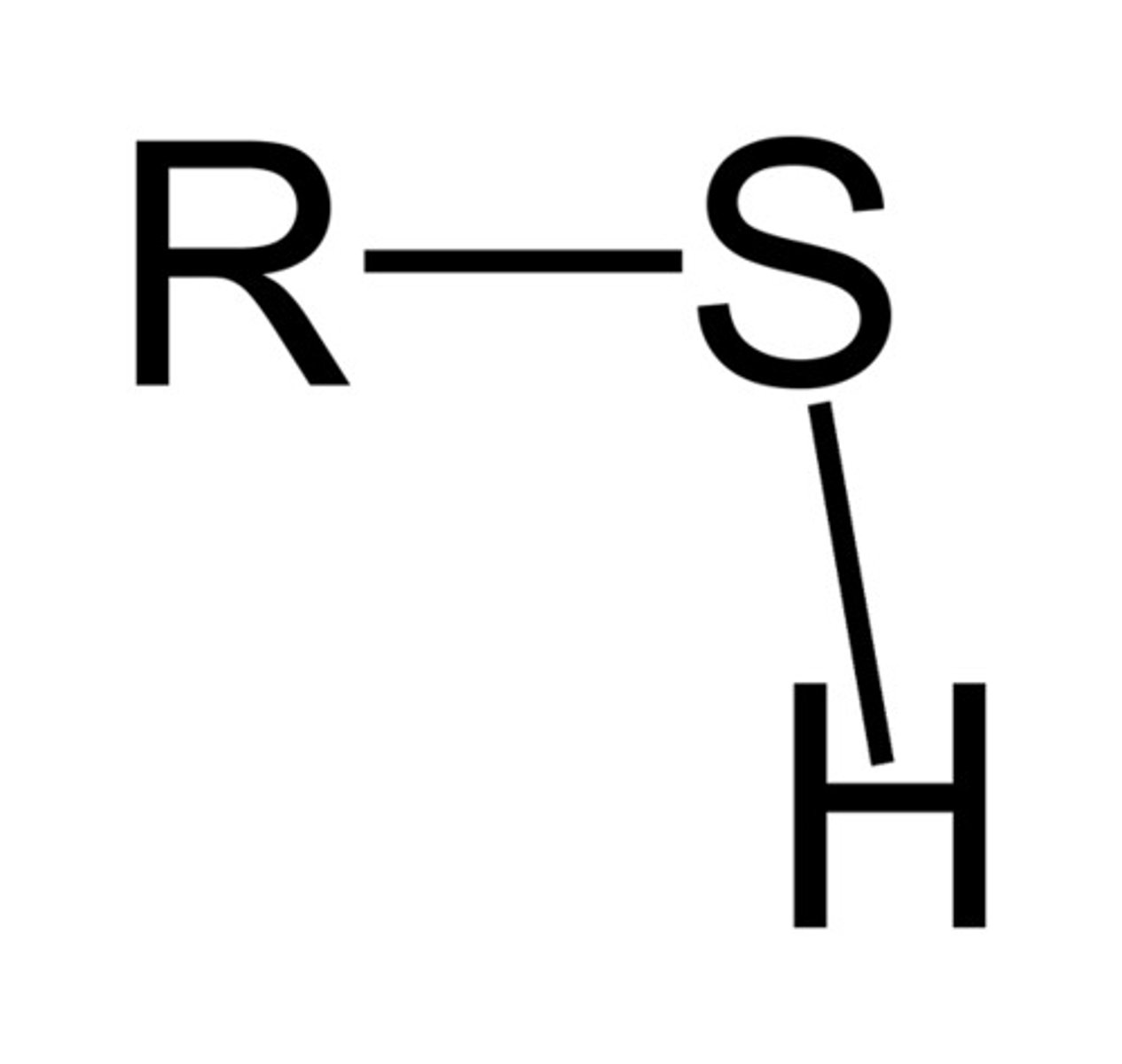
Thiol
A functional group containing a sulfur bonded to a hydrogen atom.
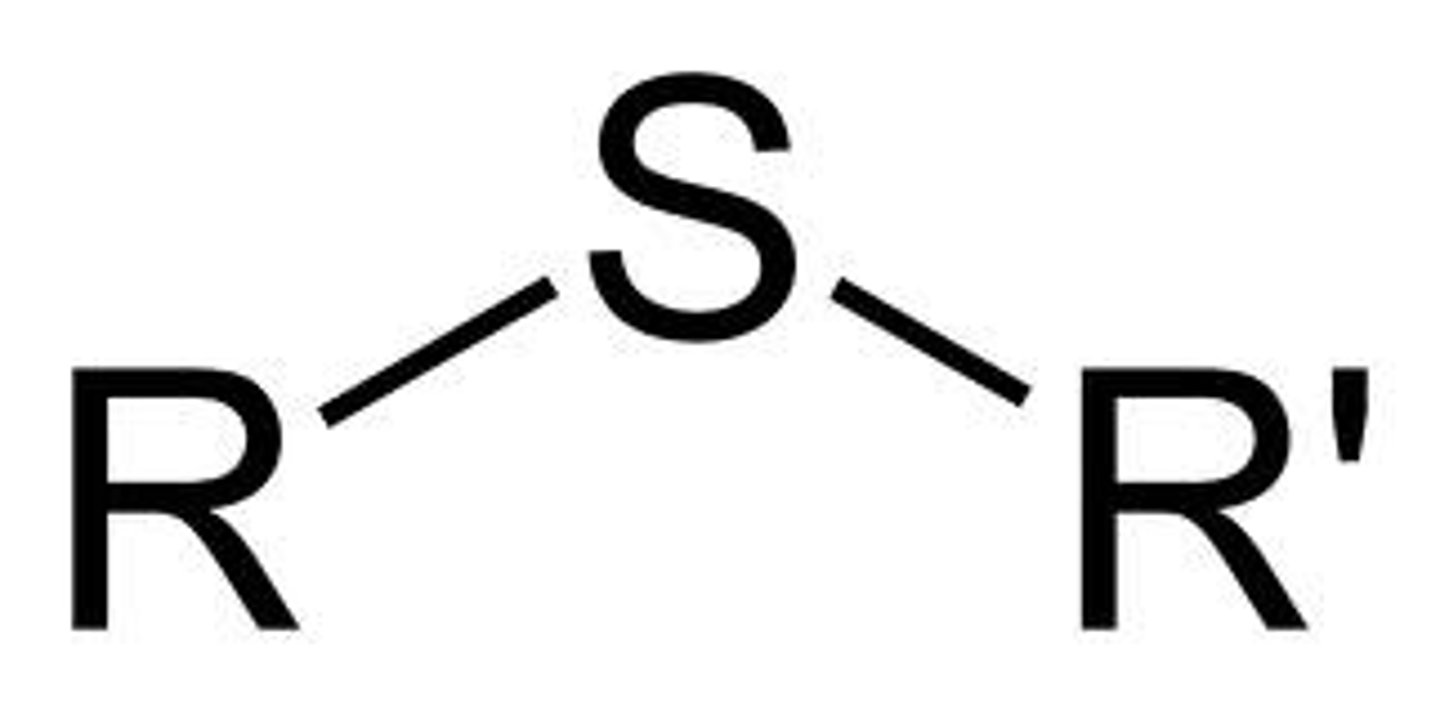
Sulfide
A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to two carbon atoms. Very similar to an ether except the oxygen is replaced by a sulfur.
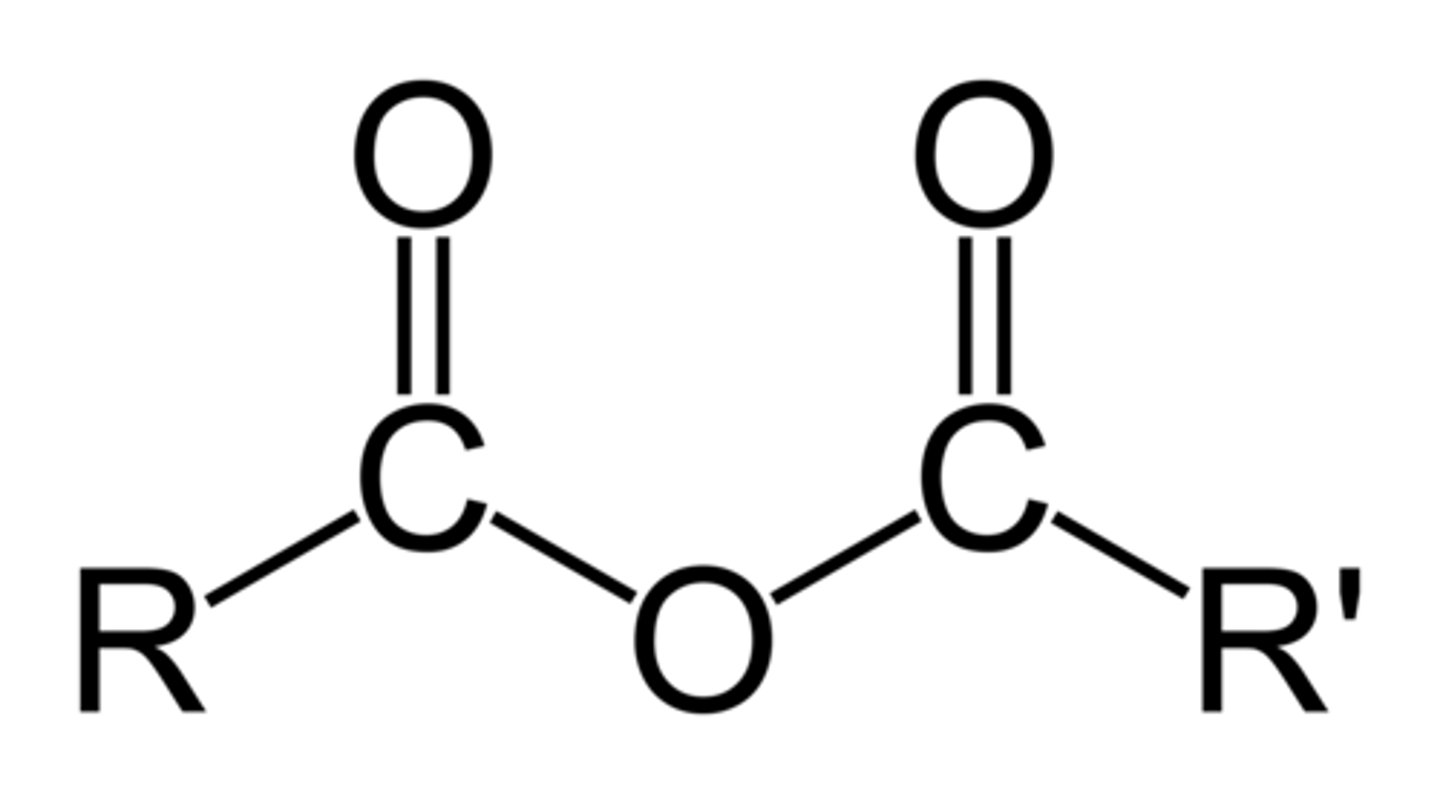
Anhydride
A functional group containing two carbonyls separated by an oxygen atom (RCOOCOR); often the condensation dimer of a carboxylic acid.