2.1.2 Inflation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Spec points

Define inflation?
inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy
it leads to a decrease in the purchasing power of money
What percentage does the UK aim to keep its inflation at? (a Macro objective)
2%
What does inflation at 2% mean?
That the general price level have increased by 2% form one year to the next
Define -”an increase in the general price level”
A decrease in the value of money
What are the 2 products which tend to make inflation high?
Air fairs and Tobacco
Define Deflation
Deflation is the opposite of inflation, characterized by a sustained decrease in the general price level.
it increases the purchasing power of money but can discourage spending and investment
Define disinflation
Disinflation occurs when the rate of inflation declines but remains positive.
Prices are still rising, but at a slower rate than before.
What is an index number?
A figure reflecting price or quantity compared with a base value.
What is a weighted index?
A weighted index in an average index made up of combination of other indicie
Define the Consumer Prices Index (CPI)
it is a widely used measure of inflation in the UK
it tracks changes in the prices of a basket of goods and services purchased by an average household
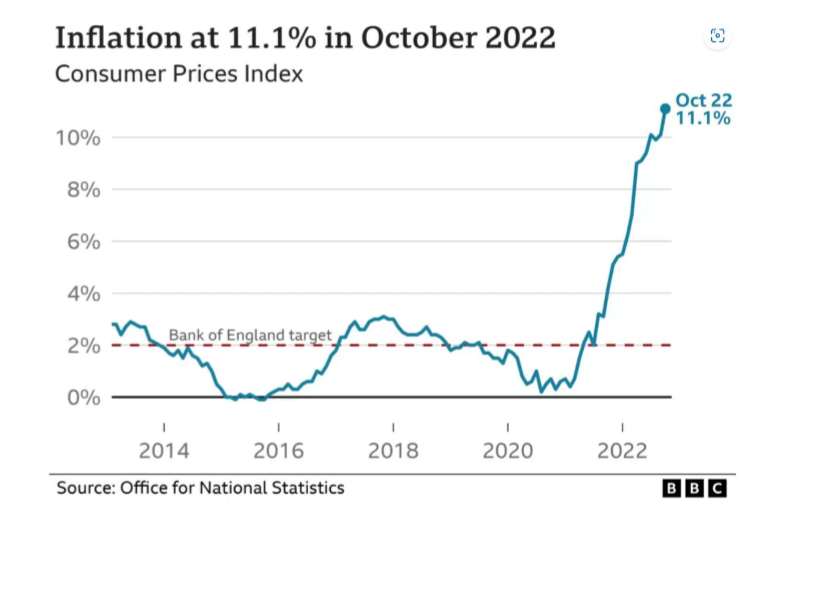
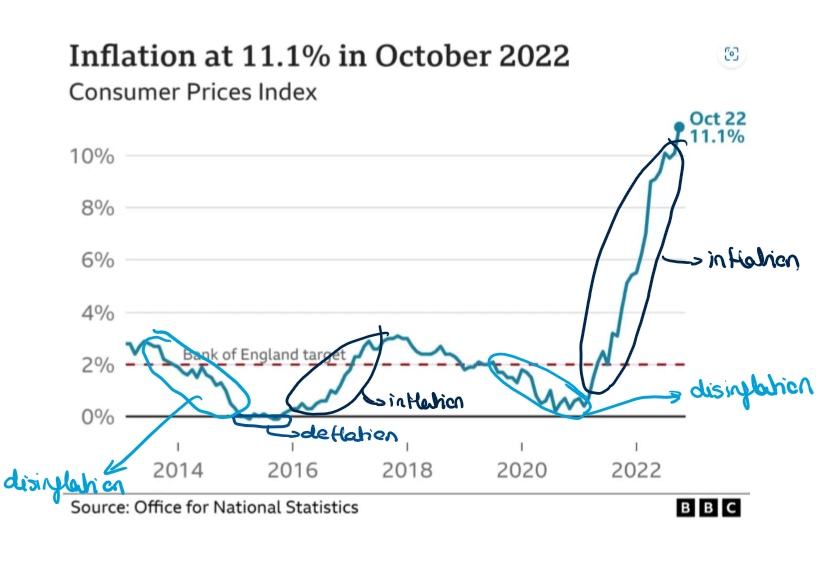
On the diagram below circle the areas whihc show all the different types of inflation (deflation, disinflation and inflation)
What is the formula for calculating CPI inflation?
CPI Inflation Rate = [(Current CPI - Previous CPI) / Previous CPI] x 100
Give 2 limitations of CPI in measuring inflation
Substitution Bias
Quality changes
Explain how substitution bias is a limitation of using CPI to measure inflation
CPI measures constant consumption patterns, whereas consumers often adjust their purchases in response to changing prices
This can lead to an overestimation of inflation.
Explain how quality changes is a limitation of using CPI to measure inflation
CPI may not adequately account for improvements in goods and services overtime.
This can result in an overestimation of prices increases
Give another alternative measure of inflation
Retail Prices Index (RPI)
What is Retail Prices Index?
RPI is another measure of inflation in the UK that includes a broader range of expenditures than CPI.
It is used for various purposes, including index- linked bonds and some pension calculations
Outline how Retail Prices Index differs from Consumer Prices Index
RPI tends to produce a higher inflation rate than CPI because it includes housing costs and uses a different formula
How else can inflation be measured? (explain the process)
Decide on products to include - living costs and food survey
Give each product a weighting (how much of peoples sending it accounts for)
Find out the current prices
Wait a month
Find out the new prices
Calculate percentage price changes
Change weightings by percentage price changes
Add them all up
Compare with previous to see rise/ fall in price level
Recap: What does this represent:
CPI increases from 4% to 6%
CPI falls from 4% to 2%
CPI falls from 2% to -1%
What are the 2 steps for calculating CPI?
Inflation
Disinflation
Deflation
First carry out research into typical spending habits. Next create the basket of goods. Then give each category a weighting
Give 3 causes of inflation
Demand-Pull inflation
Cost-Push inflation
Growth of the Money Supply
Explain Demand-Pull inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, leading to upward pressure on prices
Factors like increased consumer spending, business investment, or government expenditure can contribute to demand-pull inflation
Give an examples of demand-pull inflation
An economic boom that stimulates consumer spending and business investment may result in demand-pull inflation
Explain Cost-Push inflation
Cost-push inflation arises when production costs increase, causing firms to raise prices to maintain profitability.
Factors like rising raw material prices, higher wages, or supply chain disruptions can lead to cost-push inflation
Give an examples of cost-push inflation
A spike in oil prices can trigger cost-push inflation as it raises the costs of production for many goods and services.
Explain growth of the Money Supply
An increase in the money supply, not matched by an increase in economic output, can lead to excess demand for goods and services and result in inflation
Give an example of Growth of Money Supply
Central banks printing excessive amounts of money can contribute to inflationary pressures.
What are the 4 things inflation effects?
Consumers
Firms
Government
Workers
How does inflation effect consumers?
inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, reducing the real value of savings.
fixed- income earners may experience reduced real incomes
people on fixed pensions may find it more challenging to maintain their standard of living
How does inflation effect firms?
Firms may face rising production costs, reducing profit margins
They may adjust prices upwards to maintain profitability
How does inflation effect the government?
inflation can increase the cost of servicing government debt, diverting resources from other public spending priorities
tax brackets may not be adjusted for inflation, resulting in “bracket creep” and higher tax burdens
How does inflation effect workers?
While workers may see nominal wage increases, their real wages may decline due to inflation
Labour unions may negotiate for higher wages to keep pace with rising prices.