BU375: Quality Management & Productivity
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Quality
The characteristics of a product or a service that bear upon its ability to meet or exceed customer needs or expectations under a prescribed set of conditions
A product or service free of defects
Read:
Onset of the oil crisis of the 70s paved the way for the introduction of Japanese vehicles into the north American market and the eventual new age of quality
It was soon realized by some, that quality could be considered less as a cost and more as a means of reducing pre-sale and post-sale expenses
Pre-Industrial Revolution (Quality control management)
Marked by craftsmen who were responsible for the entire manufacturing process and therefore had an inherent interest in producing quality goods that would be directly associated with them personally.
Industrial Revolution (Quality control management)
This period was marked by the Division of Labour whereby workers focused on smaller portions of the mfg process and as a result were distanced from the final product.
Quality Control became more the responsibility of shop floor supervisors and quality control inspectors
1950s (Quality control management)
This period saw the rise of the term quality assurance. Workers were once again encouraged to take responsibility for product quality
Quality Assurance
Providing confidence that a products quality will be good by preventing defects before they occur
Late 1980s (Quality control management)
ISO 9000 was introduced as a quality management system which began to be accepted on an international basis
TQM (Total Quality Management)
An approach to quality management that involves everyone in an organization in the management of quality and in ongoing efforts to continually improve quality and customer satisfaction.
Focused on customer satisfaction
Instituted as a plant-wide process that involved all levels of workers and management
Led to the concept of continuous process improvement
Continuous Improvement – Never-ending improvements to key processes as part of Total Quality Management
The quality standard is “no defects”
Management must provide genuine leadership
1980s (TQM)
TQM began to be accepted as a strategic management approach that replaced the earlier themes of quality control and quality assurance
Key Steps to Total Quality Management (TQM)
Focus on Customer satisfaction
Determine what customers want
Design a product that meets or exceeds customer wants
Design processes that facilitate the production of the properly designed product
Instituted as a plant-wide process that involved all levels of works and management
Management must provide genuine leadership
Continuous Improvement
Never ending improvements to key processes as part of TQM
The quality standard is ‘no defects’
Keep records of performance to ensure continuous improvements
Extend these concepts to suppliers
Present Day (History and Evolution of Present Day Quality Control Management)
We are seeing the rise of a new problem solving and process improvement system known as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma
A project-oriented methodology that helps businesses improve their processes. An increase in performance through a decrease in process variation leads to a reduction in defects and an increase in quality and an increase in profitability.
“All quality improvement occurs on a project-by-project” basis with elements of kaizen-type employee involvement.
Dimensions of Quality (Definition)
Made up of the aspects of quality that may affect a wide range of customers depending upon their individual tastes and perspectives
In other words, quality may mean different things to different people
Dimensions of Quality of Manufactured Goods (8)
Performance
Basic characteristics or functions of a good
Aesthetics
Appearance, feel, smell, taste
Special Features
Something extra that differentiates the product from the basic item
Safety
Assurance that a customer will not be harmed from the use of the product
Reliability
Probability that a product will operate properly for a prescribed period of time
Durability
How long a product will ‘last’ before it needs to be replaced
Conformance
How well the product meets some pre-established set of standards (or expectations)
Serviceability
Ease with which a product can be serviced or repaired
Dimensions of Quality of Services (6)
Time and Timeliness
How long must a customer wait for a service?
Is it completed on time?
Consistency
Is same level of service provided to each customer each time?
Courtesy
How are customers treated by employees?
Accessibility and Convenience
How easy is it to obtain the service?
Accuracy
Is service performed right every time?
Responsiveness
How well does company (organization) react to unusual situations?
Name the 6 Quality Gurus mentioned in class:
Walter Shewhart
W. Edwards Deming
Joseph M. Juran
Armand V. Feigenbaum
Philip Crosby
Kaoru Ishikawa
Walter Shewhart (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
In 1920s, developed control charts
Introduced term “quality assurance”
W. Edward Deming (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
Developed courses during WW II to teach statistical quality-control techniques to engineers and executives of military suppliers
After war, he began teaching statistical quality control to Japanese companies
Joseph M. Juran (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
Followed Deming to Japan in 1954
Focused on strategic quality planning
Quality improvement achieved by focusing on projects to solve problems and securing breakthrough solutions
Armand V. Feigenbaum (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
In 1951, introduced concepts of total quality control and continuous quality improvement
Philip Crosby (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
In 1979, emphasized that costs of poor quality far outweigh cost of preventing poor quality
In 1984, defined absolutes of quality management—conformance to requirements, and “zero defects”
Kaoru Ishikawa (Evolution of Quality Management: Quality Gurus)
Promoted use of quality circles
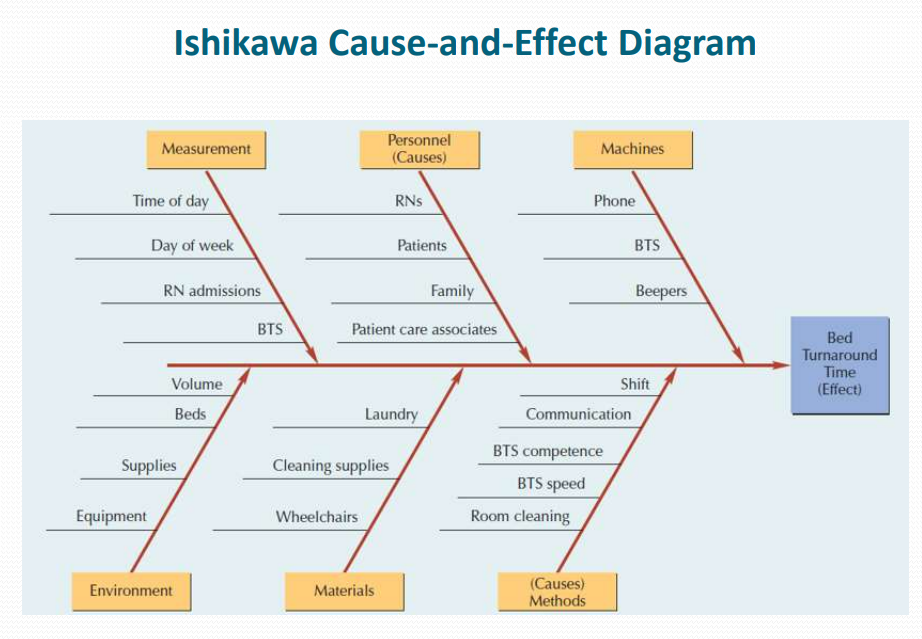
Developed “fishbone” diagram
Emphasized importance of internal customer
Deming’s 14 Points
Create constancy of purpose
Adopt a philosophy of prevention of poor quality
Cease mass inspection
Select a few suppliers based upon quality
Constantly improve system and workers
Institute vigorous training and education programs (worker training)
Institute leadership among supervisors
Eliminate fear among employees
Eliminate barriers between departments
Eliminate slogans
Eliminate numerical quotas
Enhance worker pride
Institute vigorous education and training programmes
Develop a commitment from top management to quality
List 7 Quality Tools
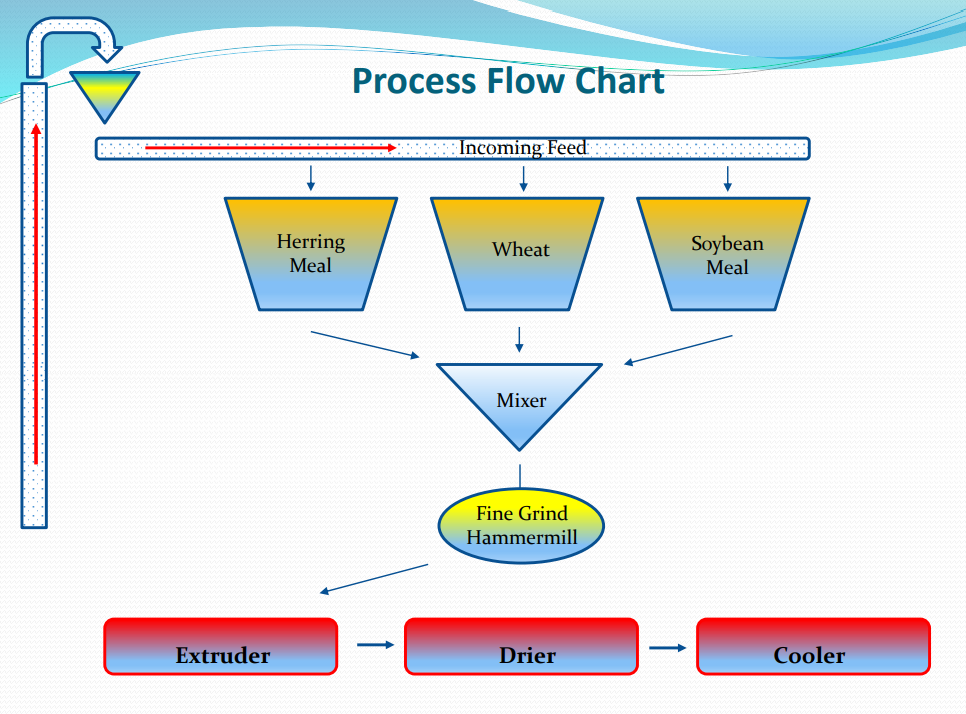
Process Flow Chart*
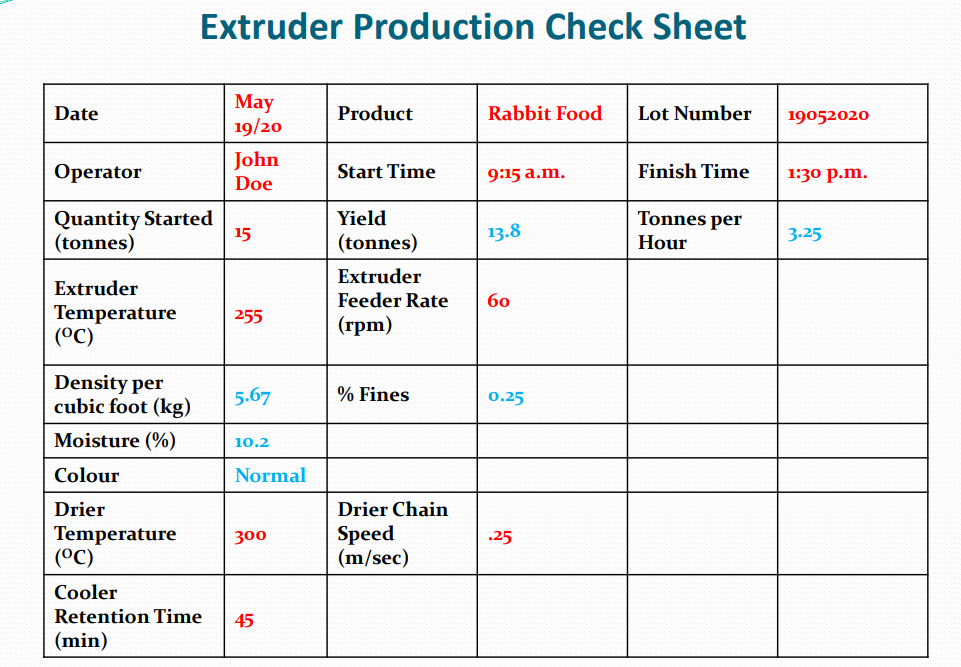
(Extruder Production) Check Sheet*
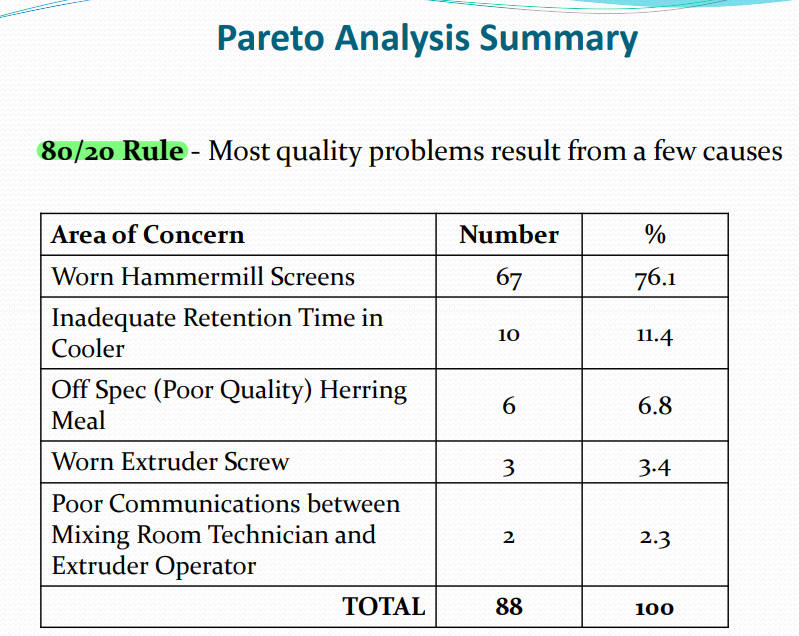
Pareto Analysis*
(Ishikawa) Cause-and-Effect Diagram*
Histogram
Scatter Diagram
Statistical Process - Control Chart
Process Flow Chart (Picture)
(Extruder Production) Check Sheet*
Pareto Analysis*
(Ishikawa) Cause-and-Effect Diagram*
LO 20/41