Week 6 more cards
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
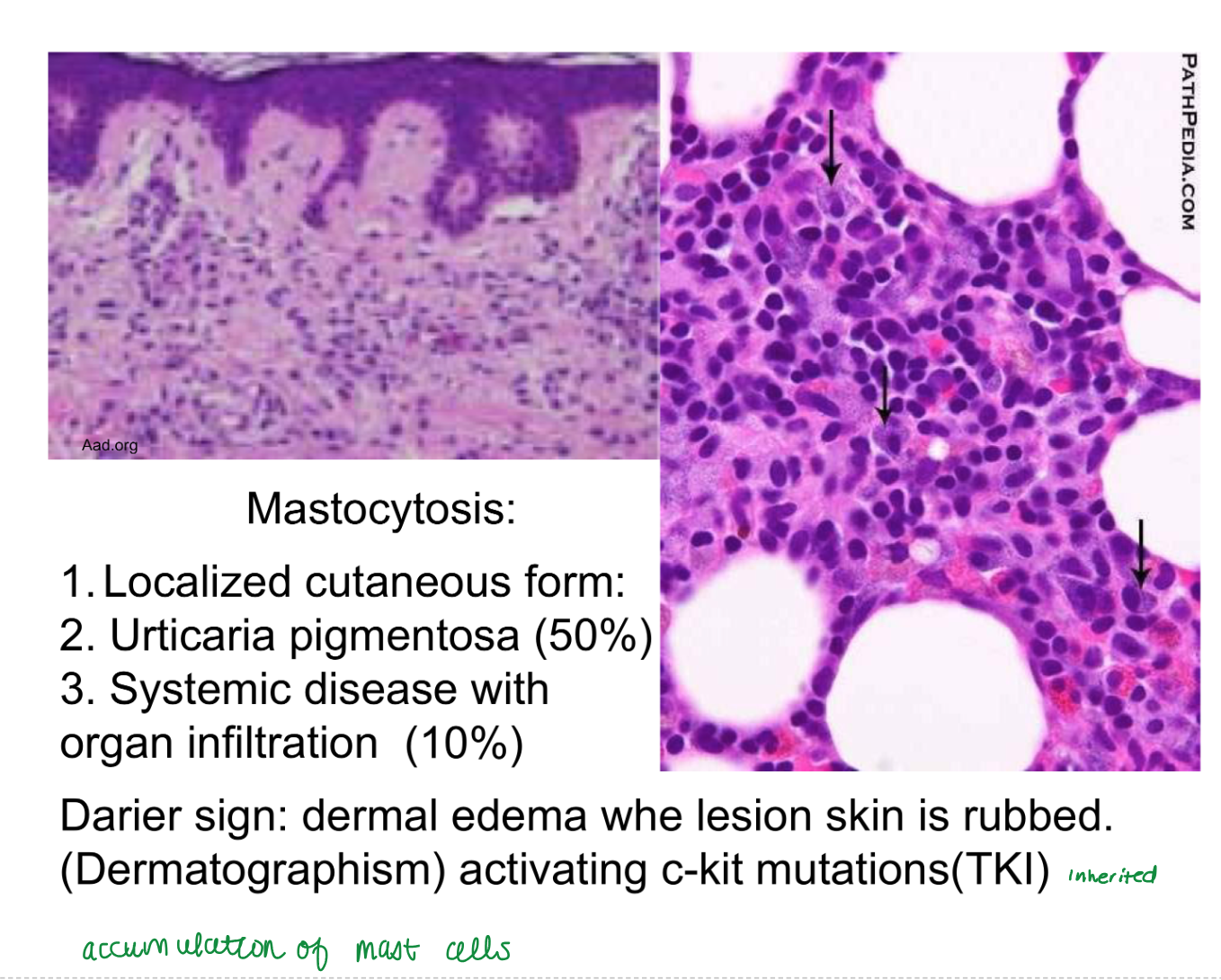
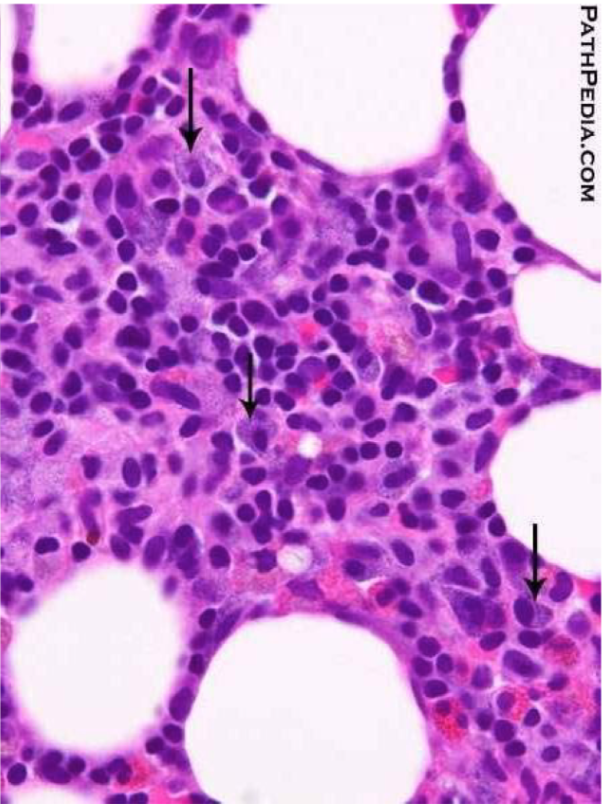
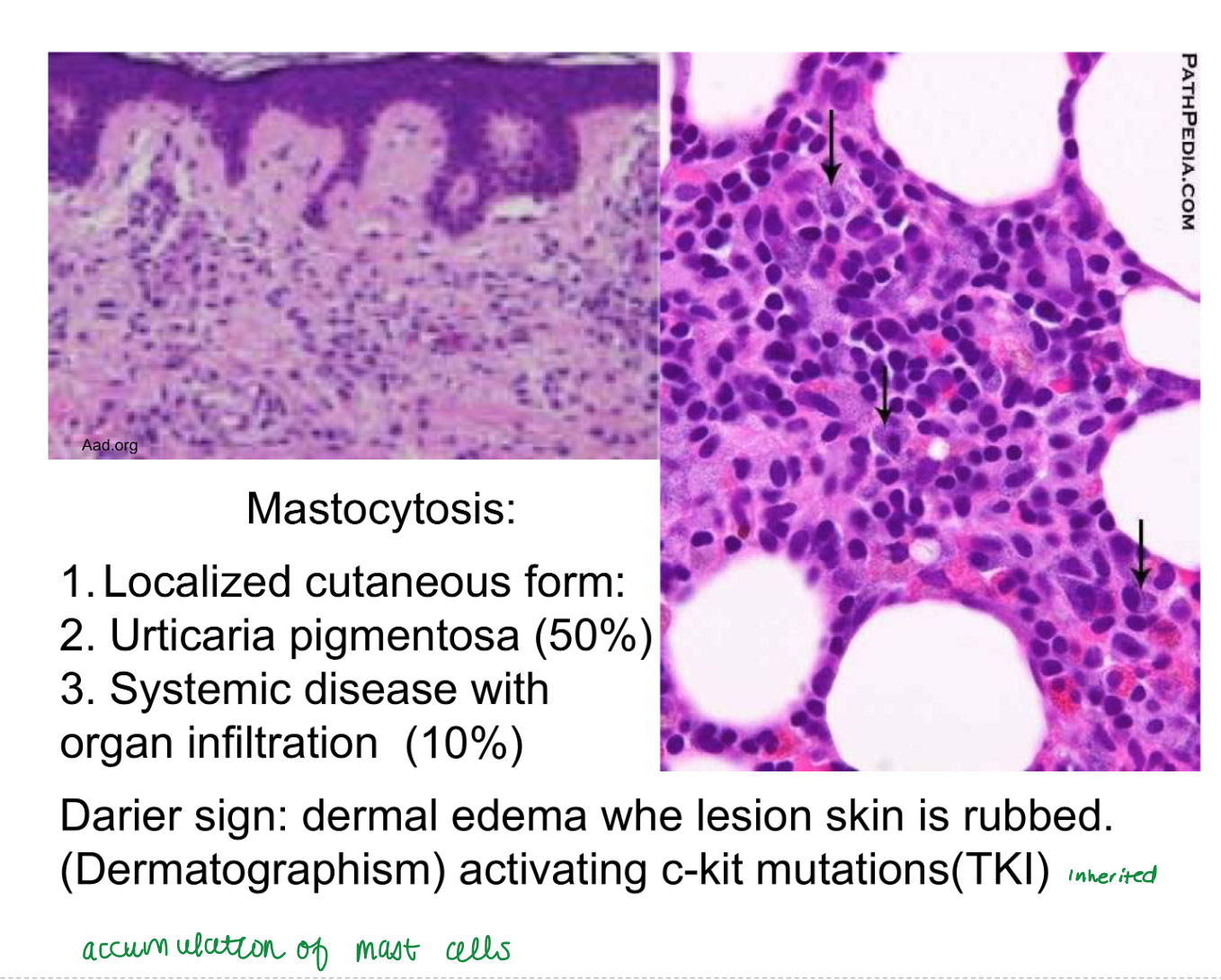
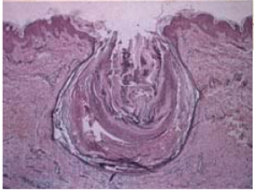
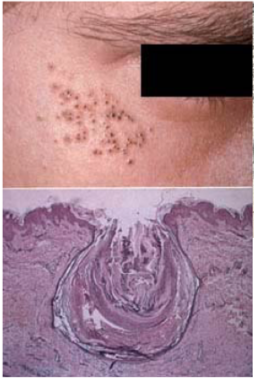
blackhead acne (open comedone)
still able to produce melanin
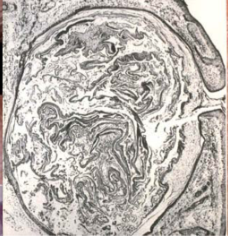
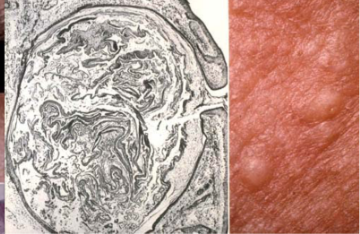
white head acne (closed comedone)
Altered follicular growth and diff
Keratin plug blocks outflow of sebum to surface
can cause
acne
Propionibacterium acnes colonization of duct → lipase converts sebum to pro-inflamm fatty acids
can cause
acne
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia from hormonal stim or steroid use
Inflammation and immune response (release of cytotoxic and chemotactic factors)
Altered follicular growth and diff can cause
acne
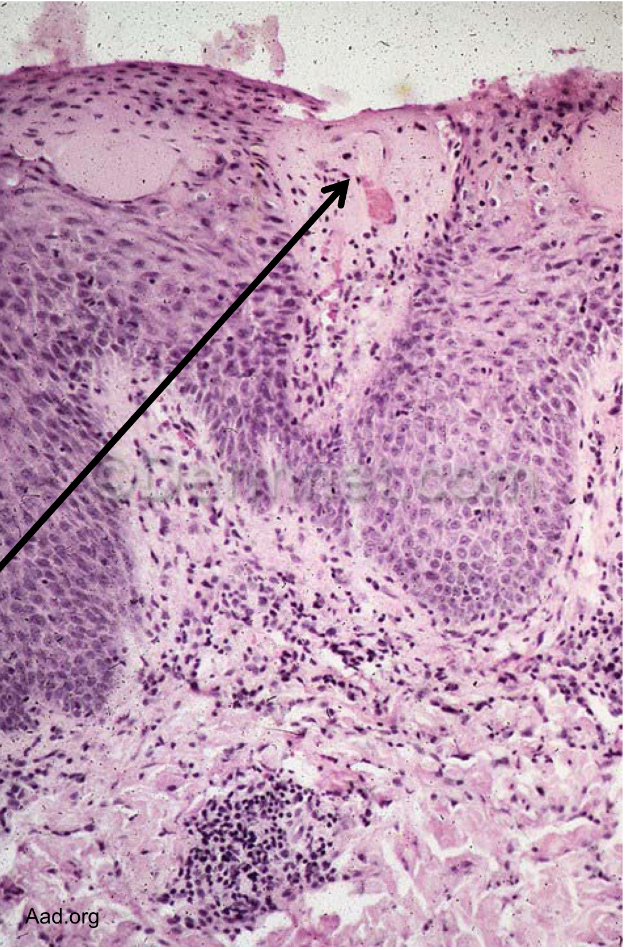
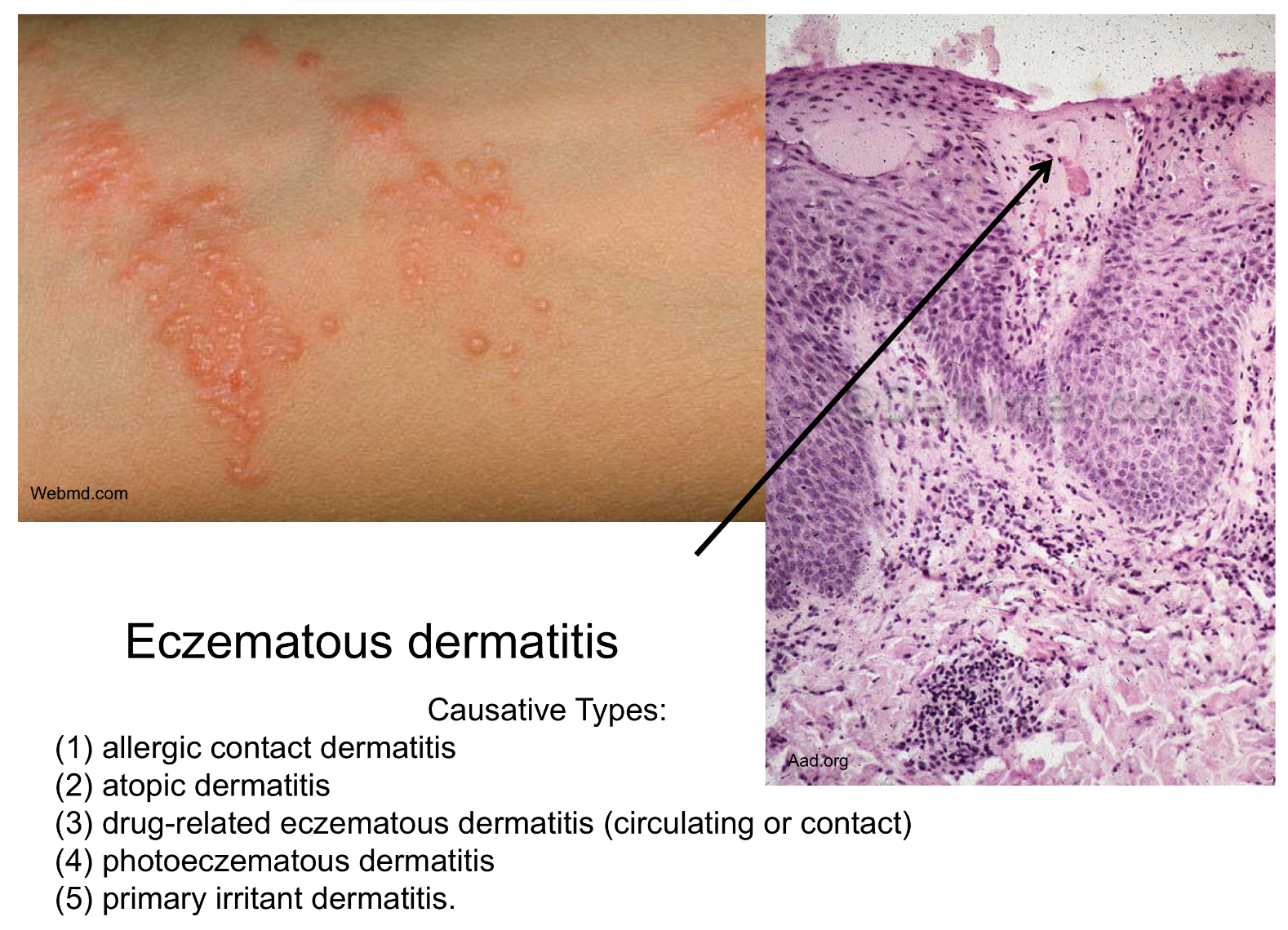
rhus dermatitis can be caused by
Can be caused by eczematous dermatitis
rhus dermatitis sensitization
Sensitization: Ag taken up by dendritic Langerhans cells → lymph → naive CD4 T cell → effector and memory cells → Ab pdn w/ B cells
rhus dermatitis re exp
Re-exp: memory T migrate to affected skin sites → extravasate into tissues → release cytokines and chemokines that activate immune response
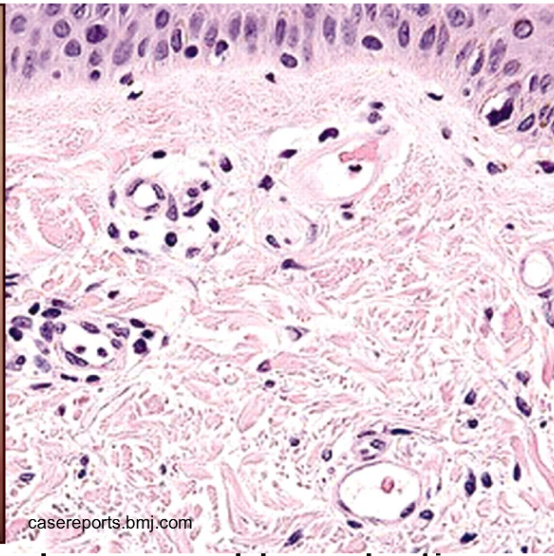
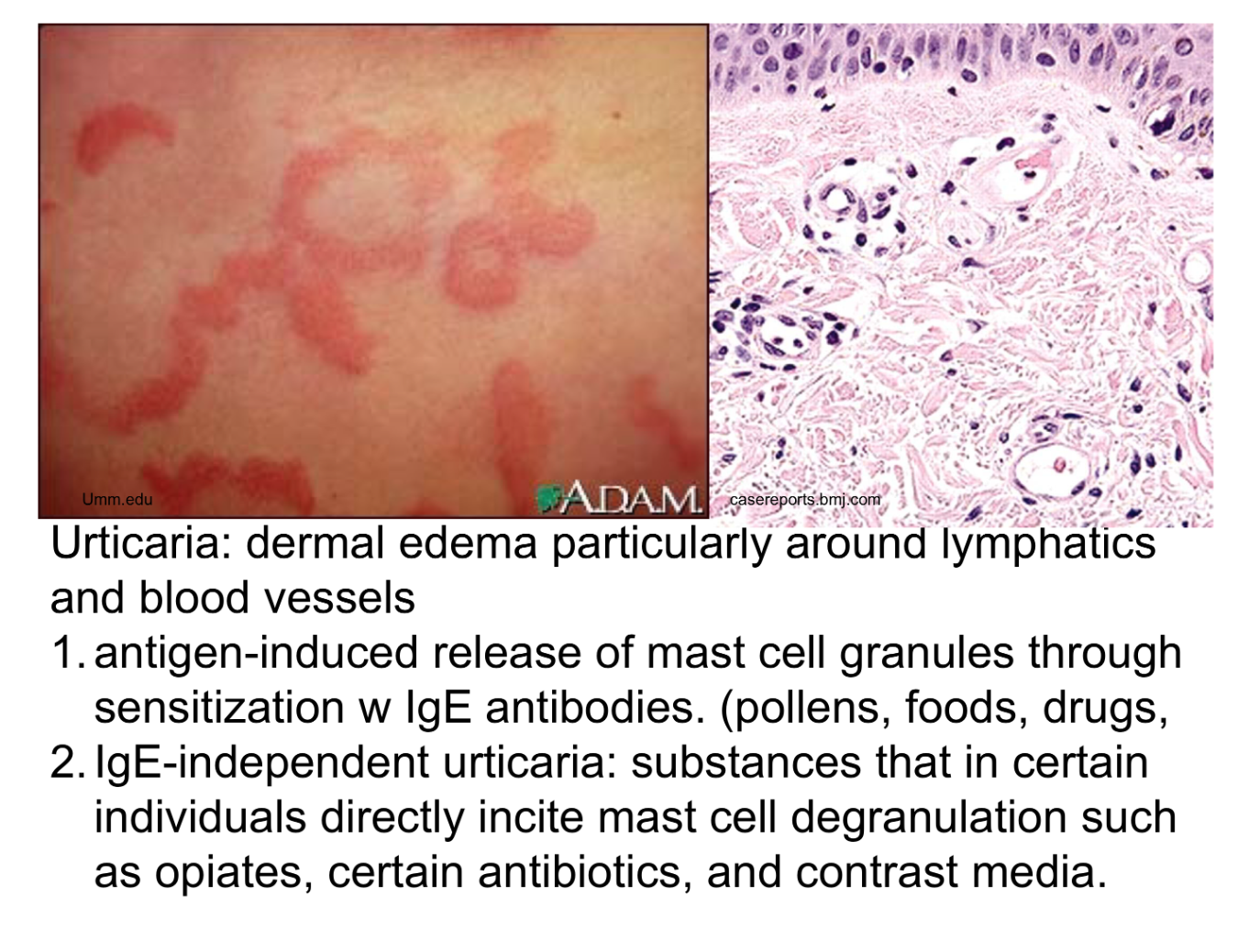
Urticaria causes
Ag- induced release of mast cell granules (IgE Ab)
IgE- induced
complement mediated
pollen drugs foods causing urticaria
Ag-induced release of mast cell granules (IgE Ab) ie pollen, foods, drugs
IgE-ind urticaria
substances in certain ind directly incite mast cell degranulation (ie opiates, ABx, contrast media)
Complement - mediated uricaria
hereditary angioedema, inherited def of C1 inh → uncontrolled act of complement
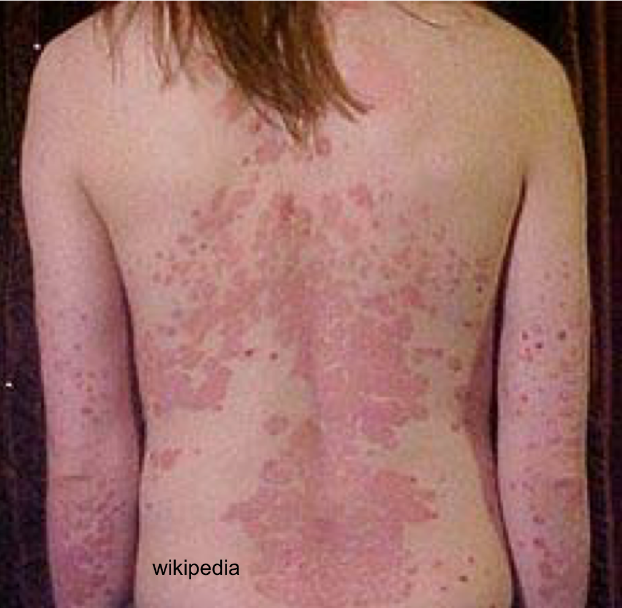
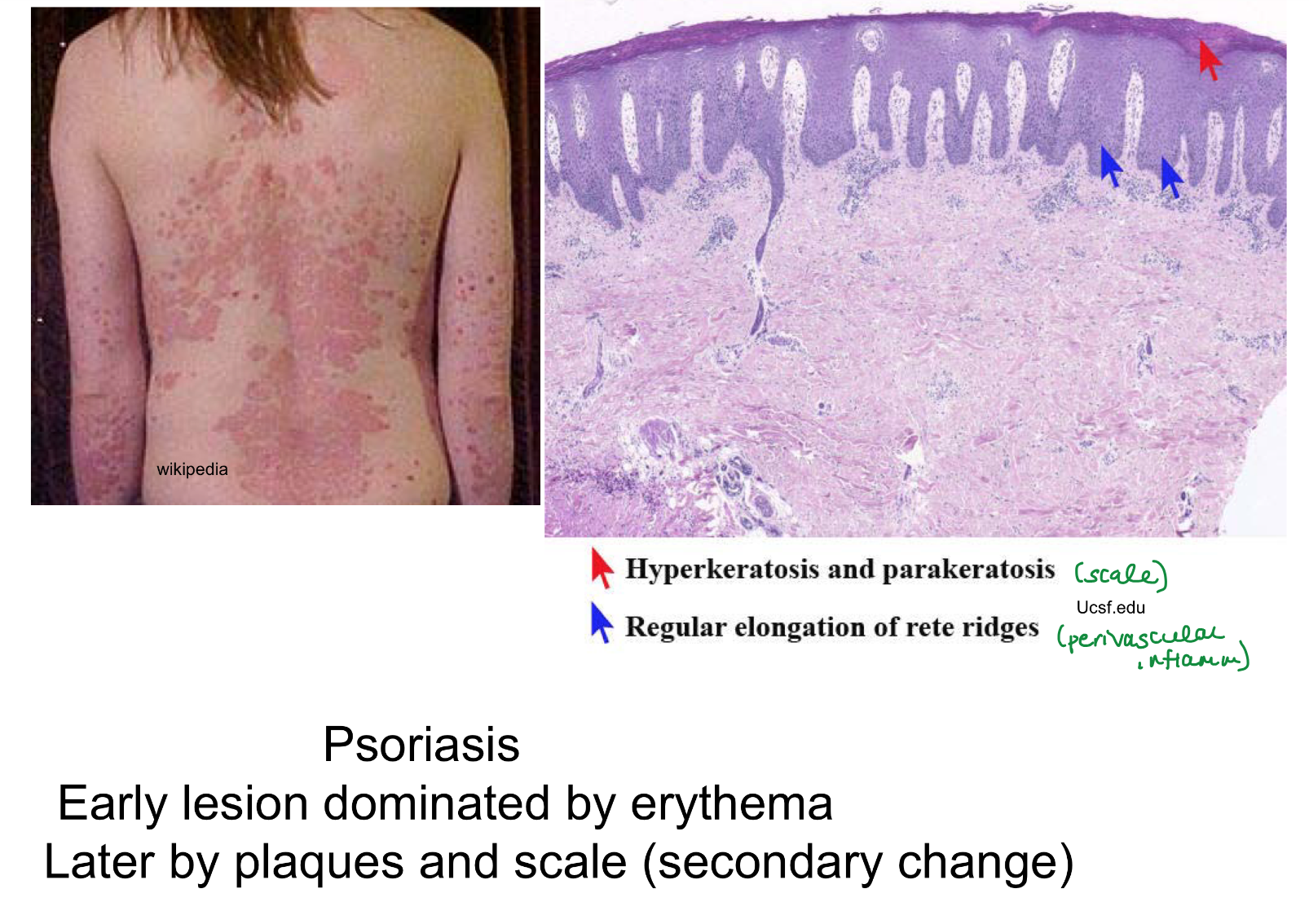
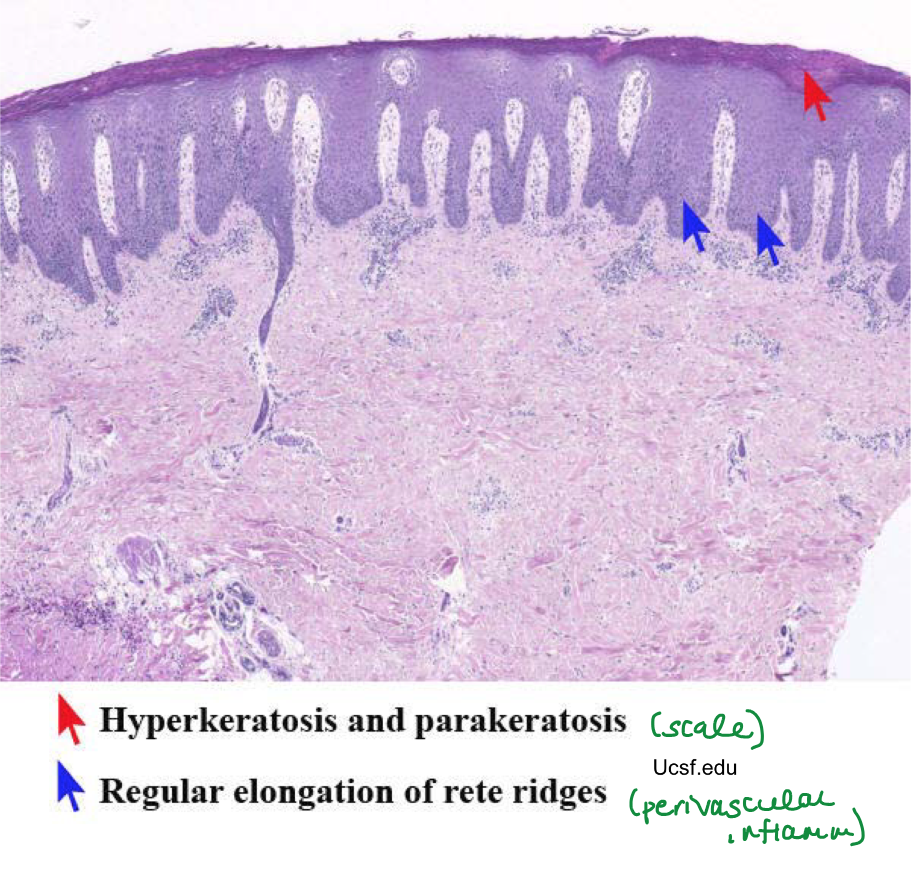
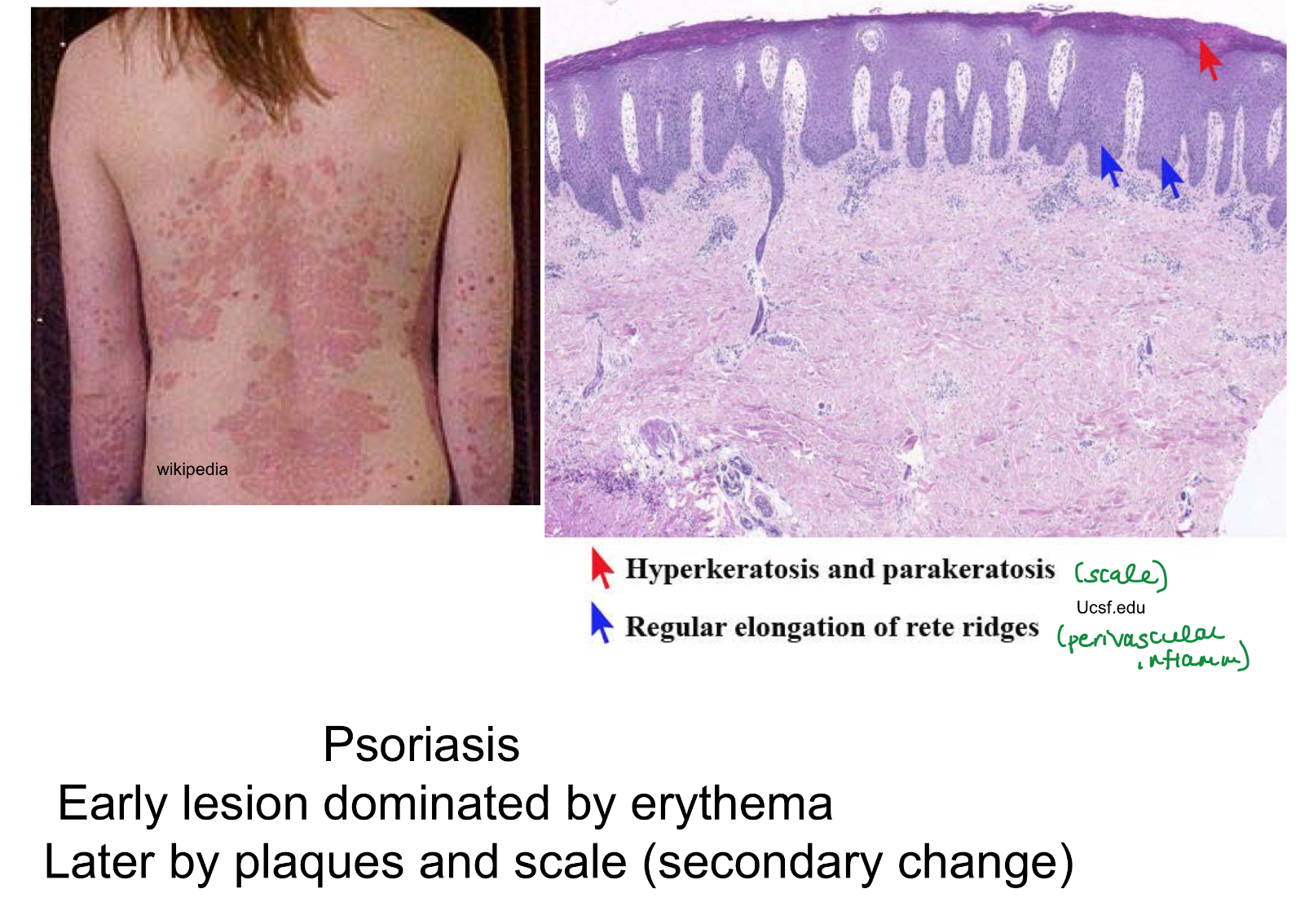
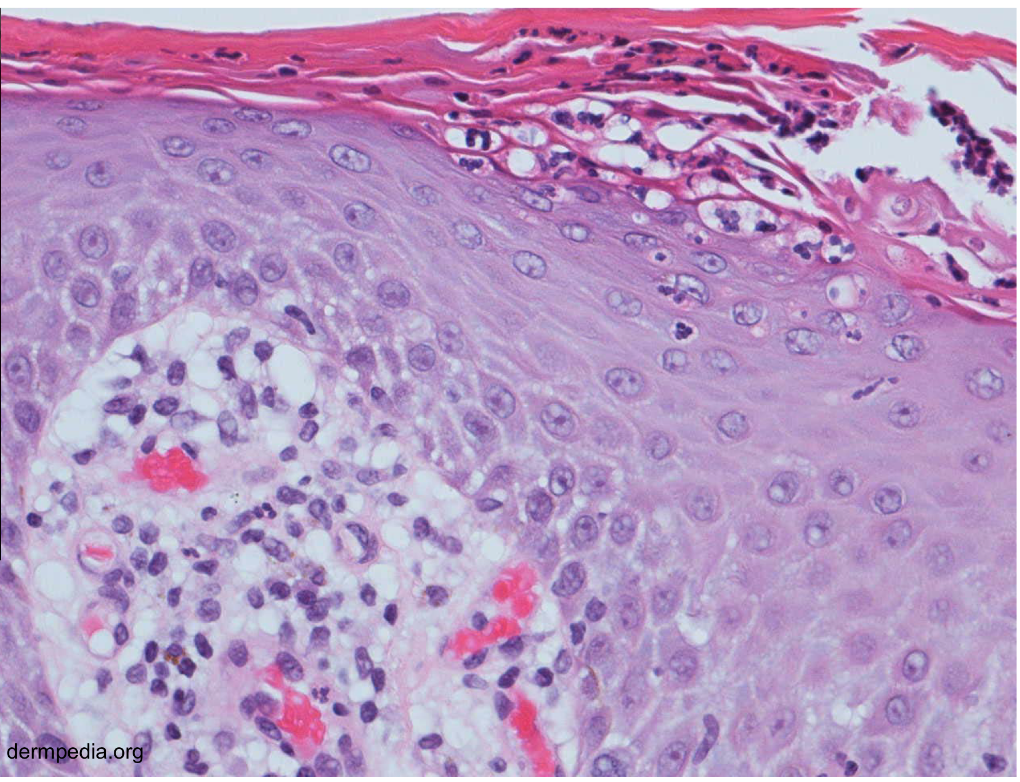
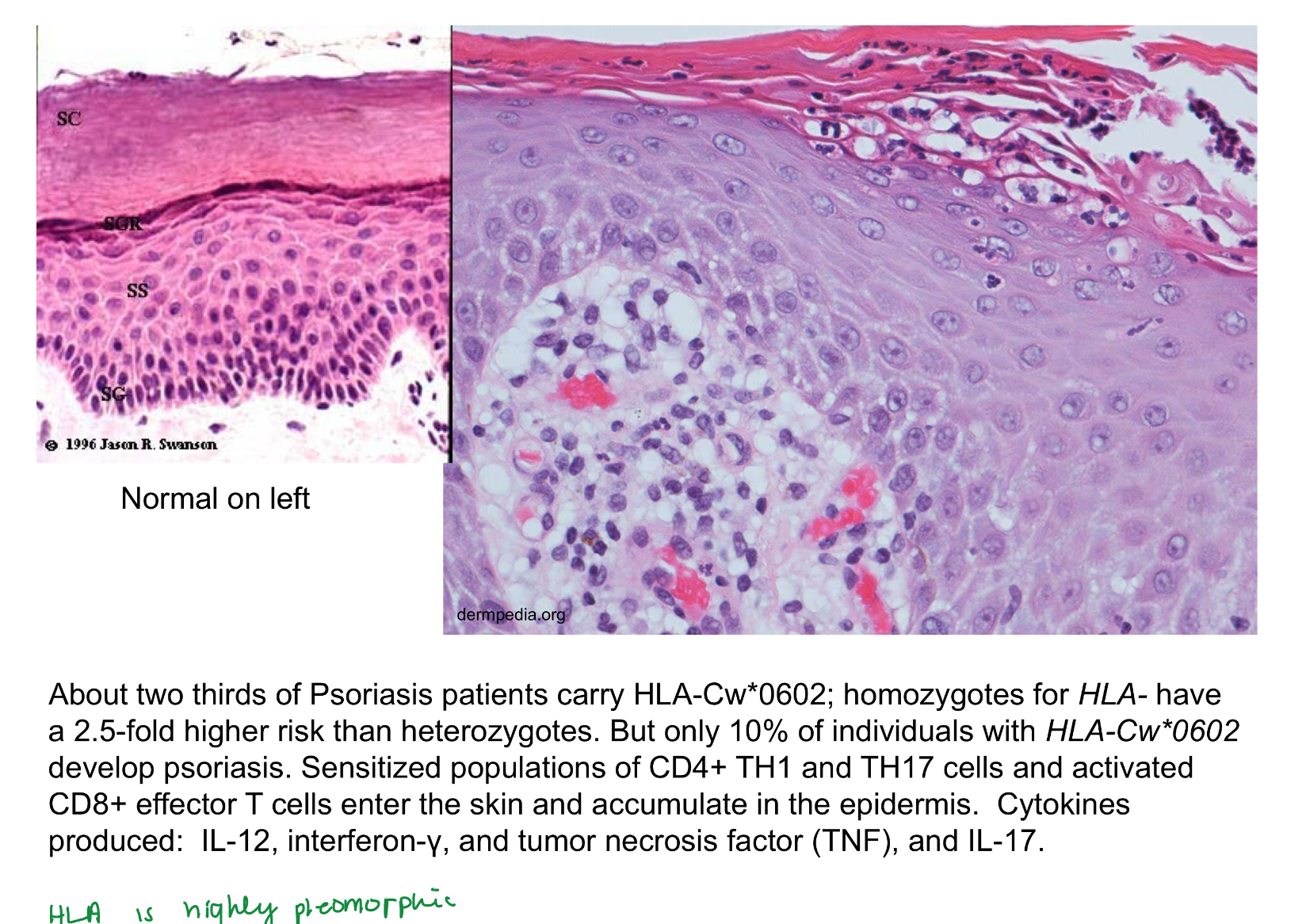
early psoriasis dominated by
erythematous lesions
secondary phase of psoriasis dominated by
plaques and scales
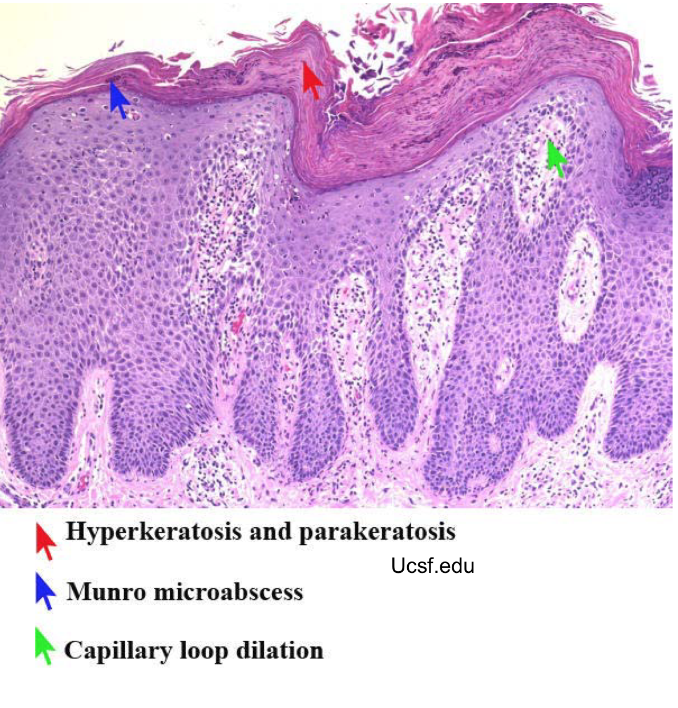
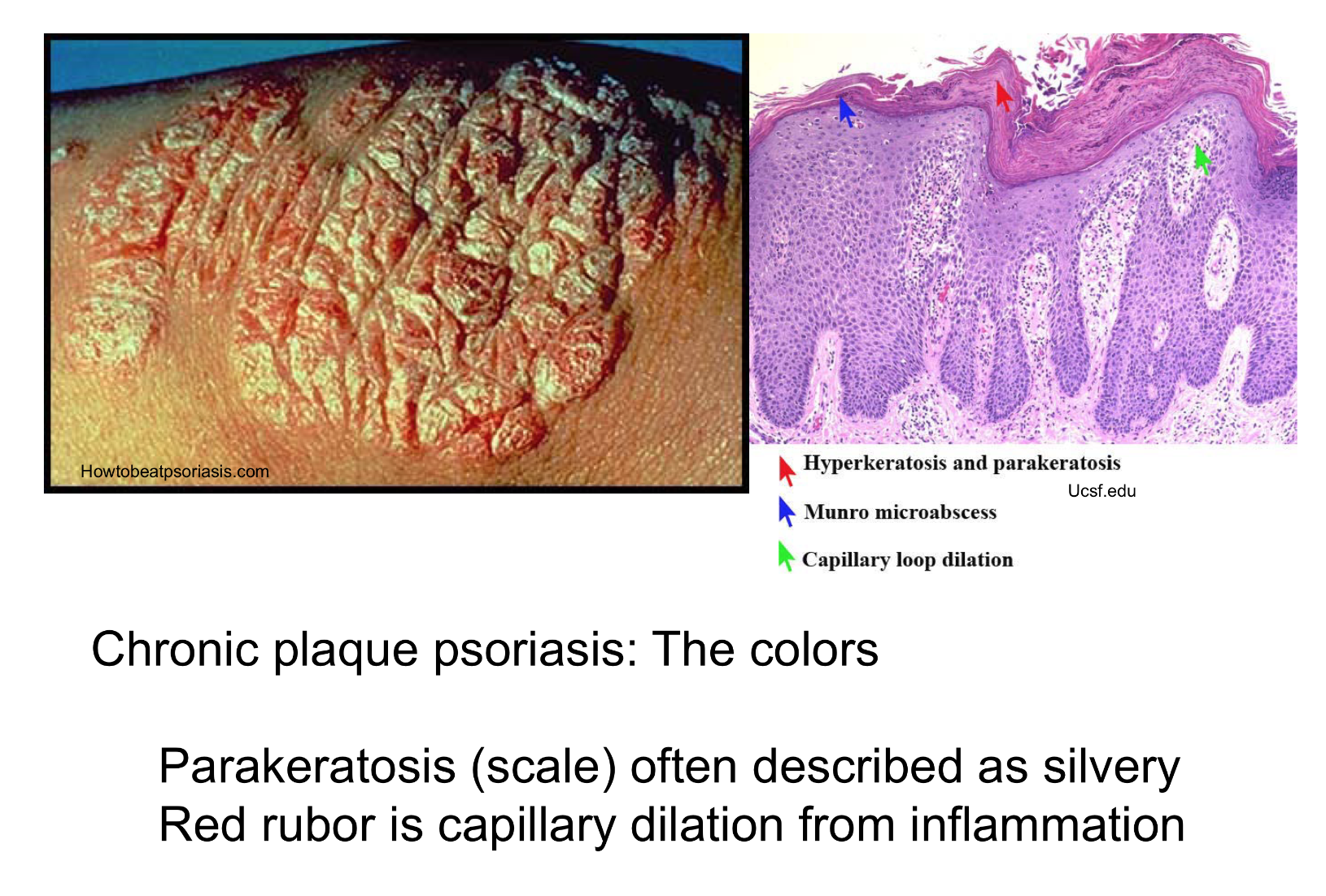
colors of psoriasis
Red- capillary dilation from inflammation
Silver- parakeratosis scale
what mutation can contribute to psoriasis risk
HLA-Cw*0602 can contribute to risk
psoriasis inflammatory response
CD4 TH1 and TH17, activated CD8 effector T → IL12, IFNy, TNF, IL17
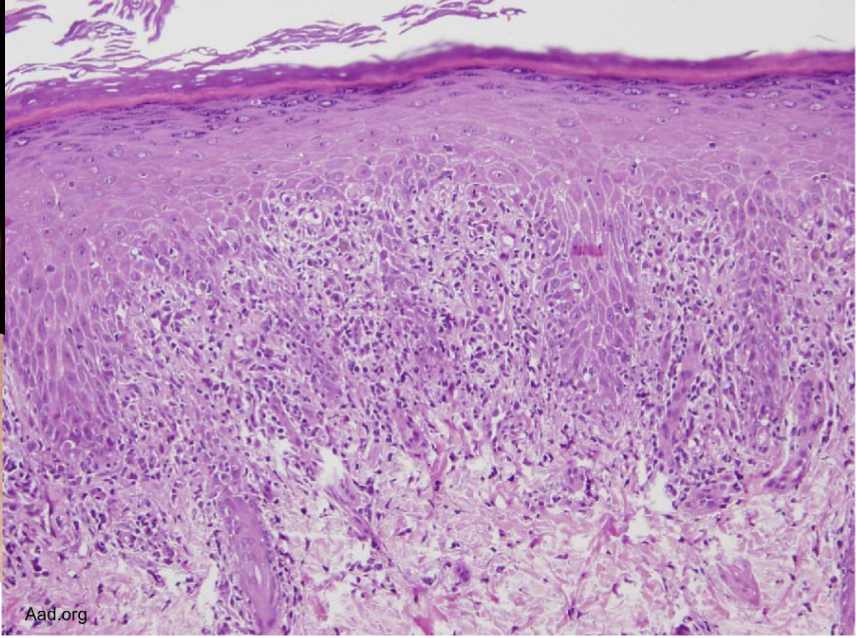
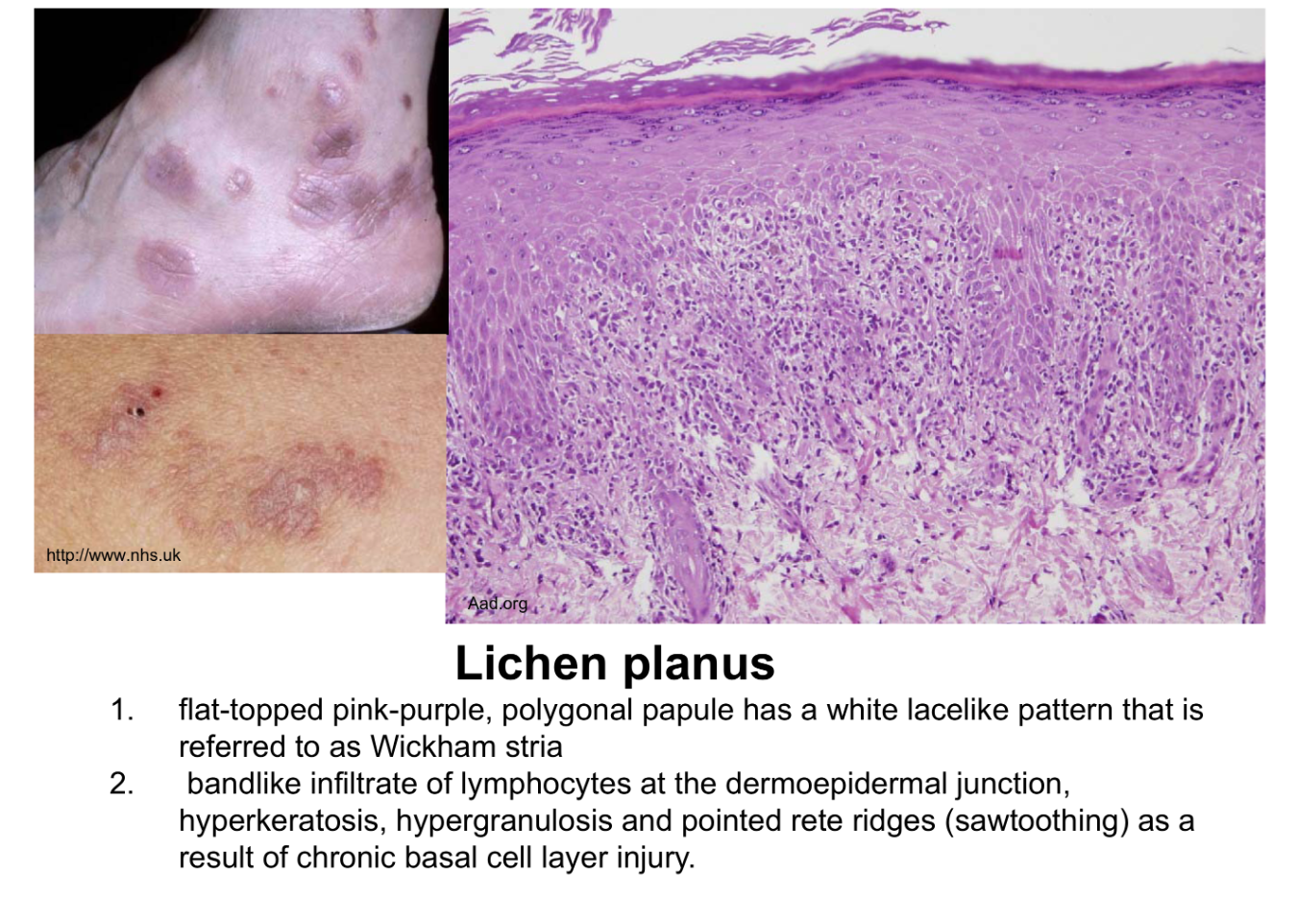
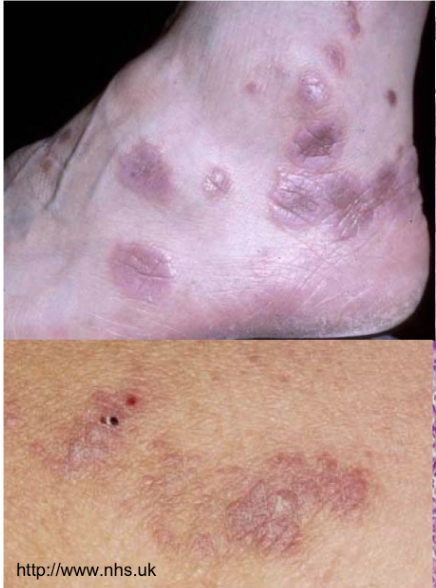
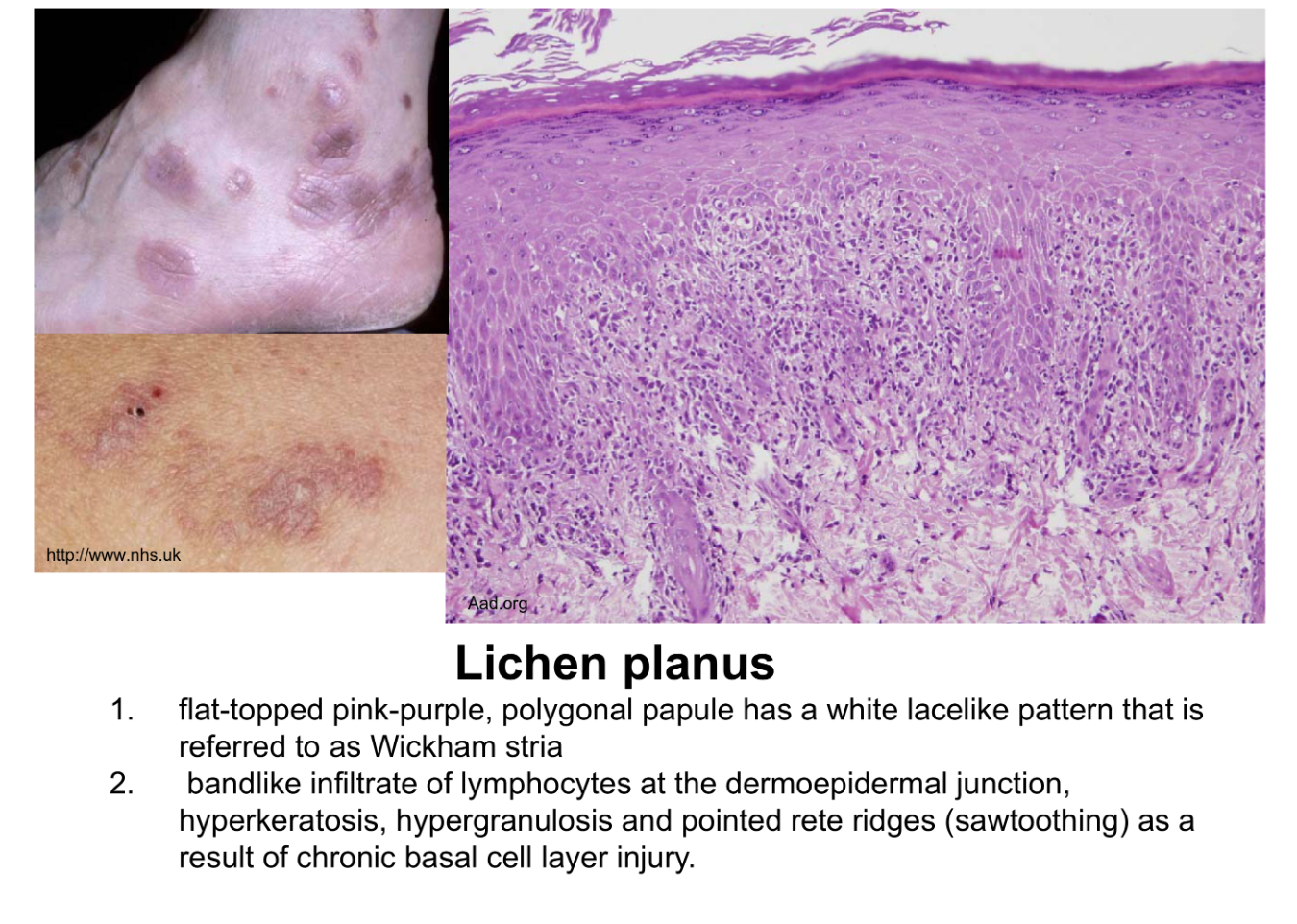
Bandlike infiltrate of lymphocytes @ dermoepidermal junction
Hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, sawtoothing (result of chronic basal cell layer injury)
lichen planus
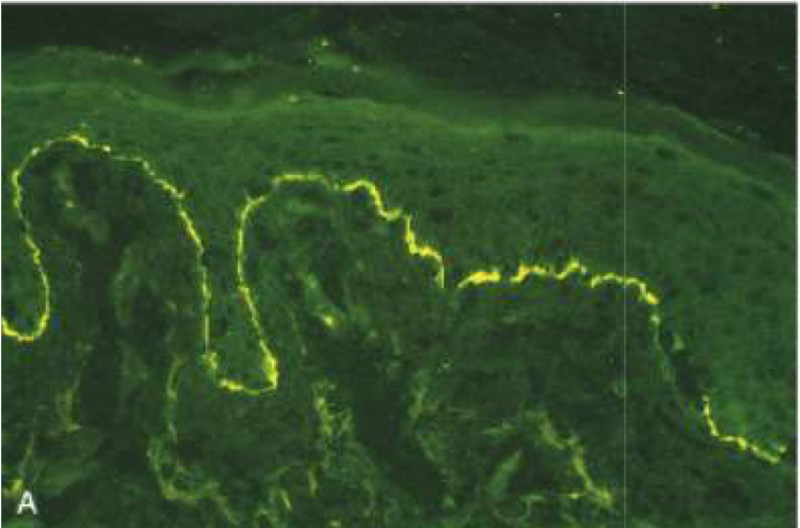
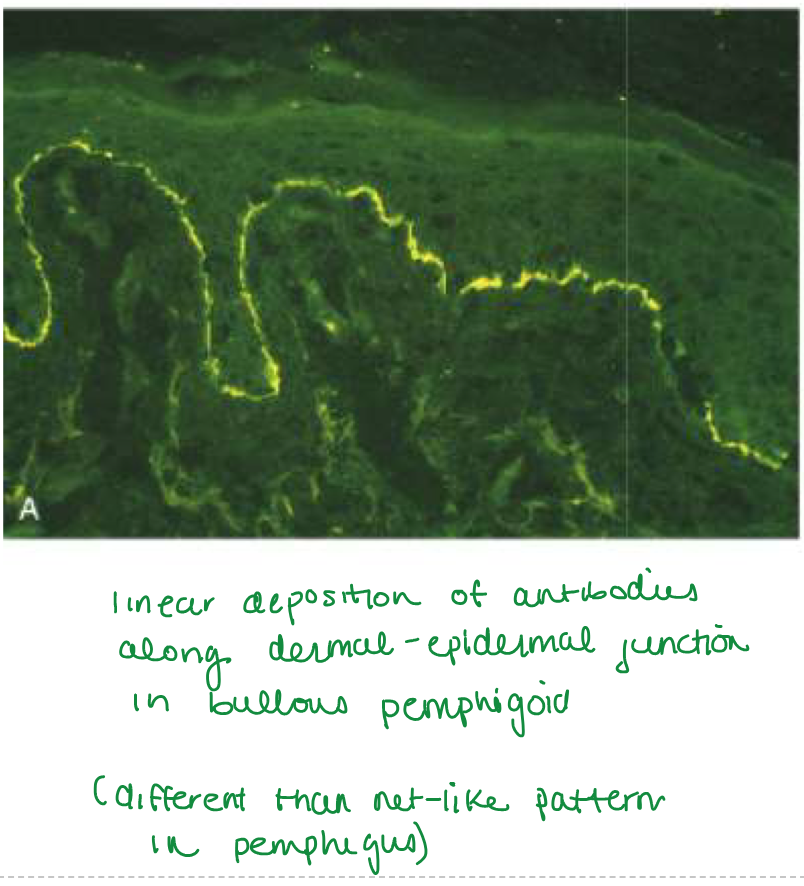
Linear pattern at dermoepidermal junction
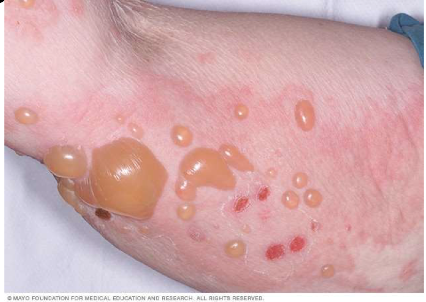
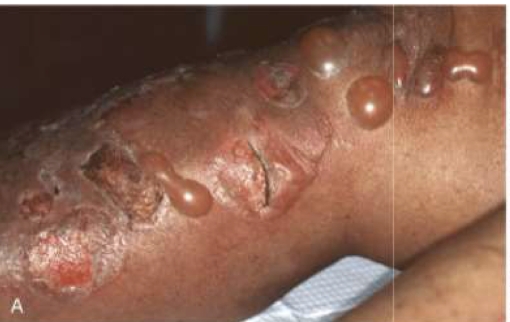
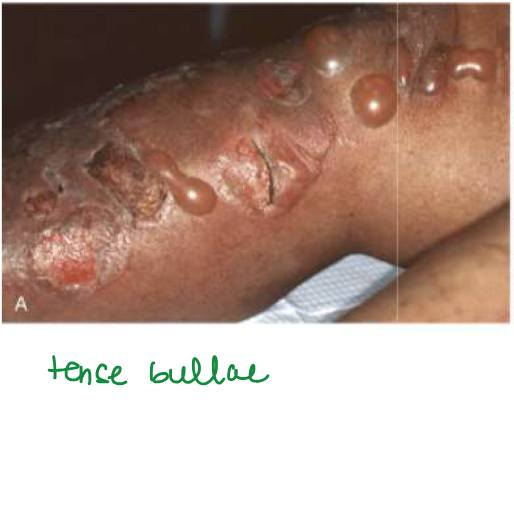
Bullous pemphigoid
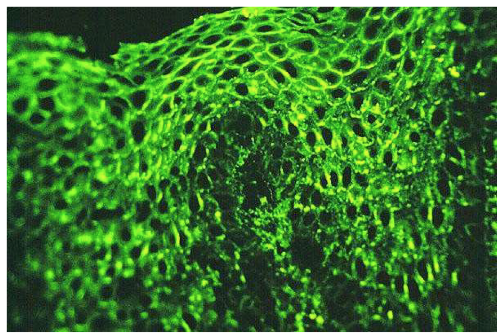
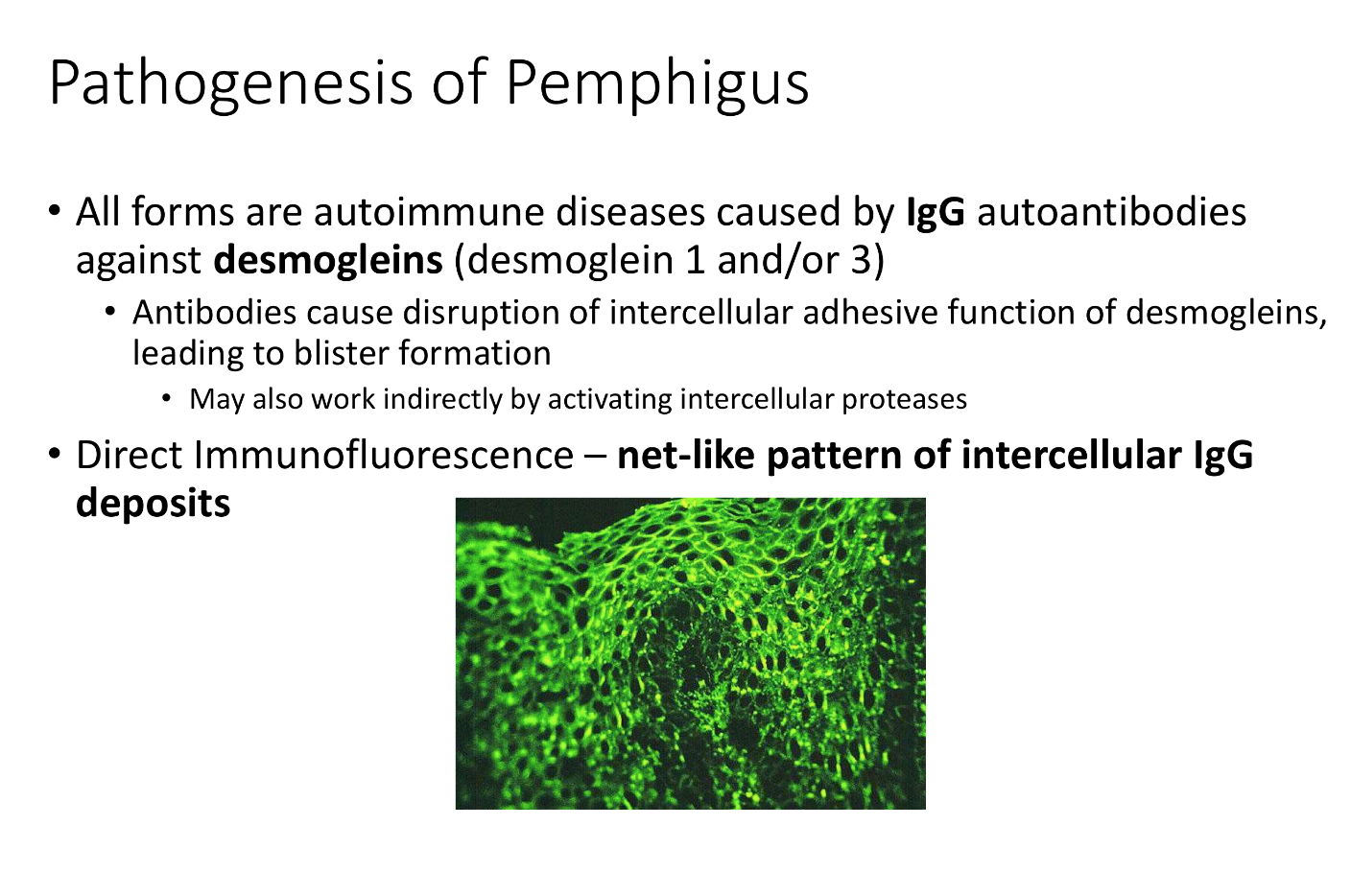
NET-LIKE PATTERN OF INTERCELLULAR IgG deposits
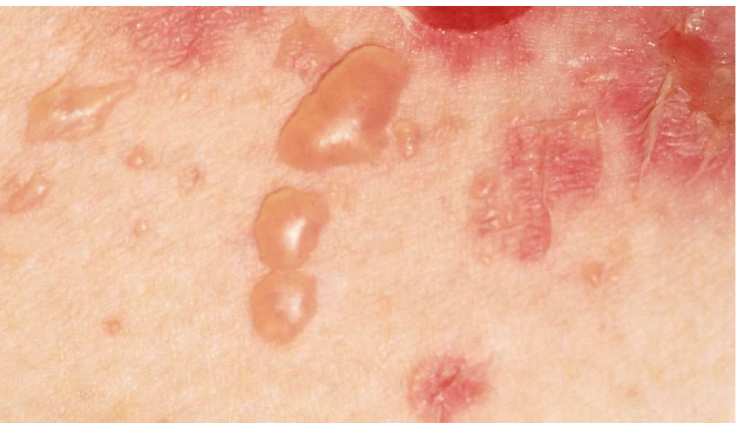
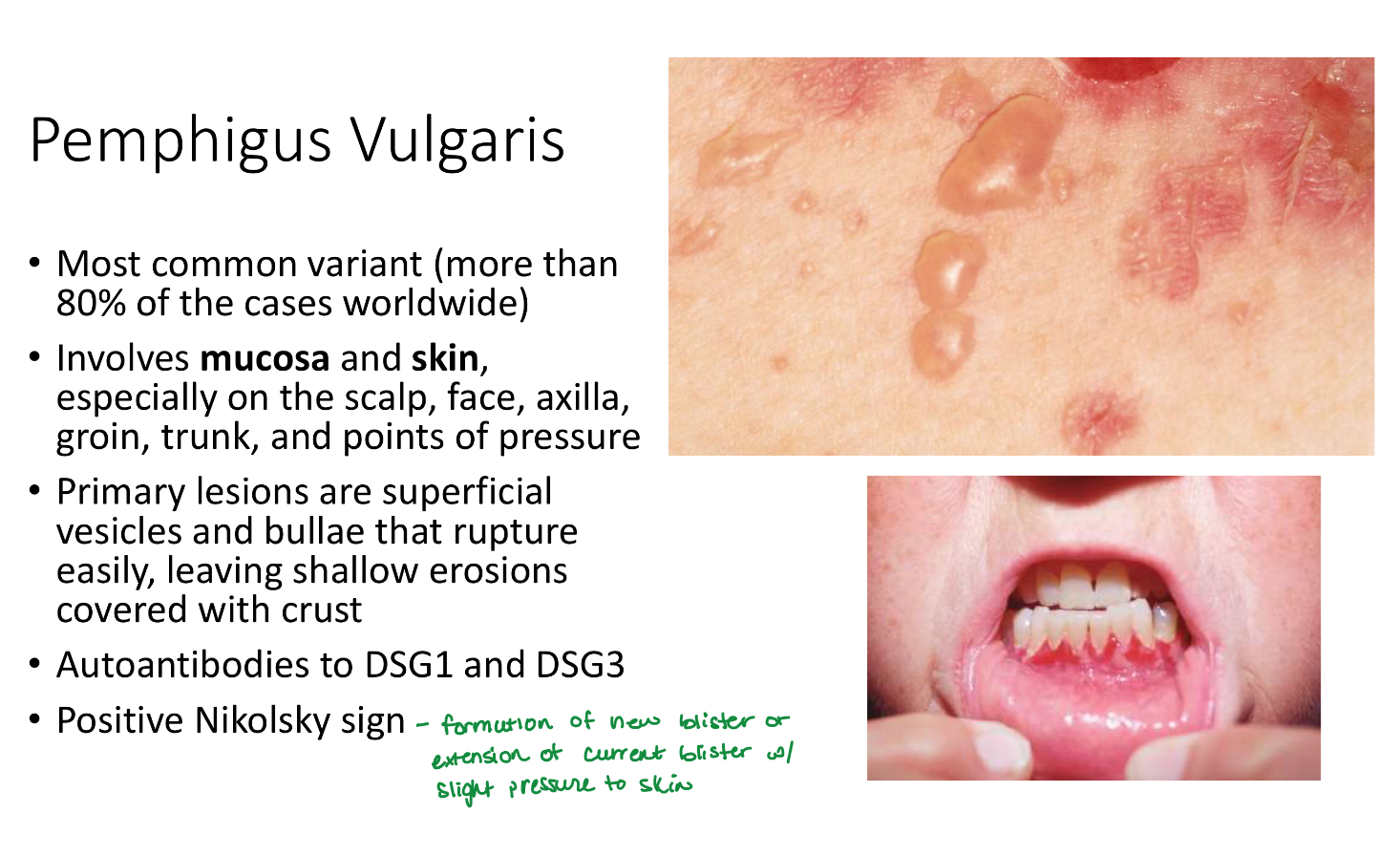
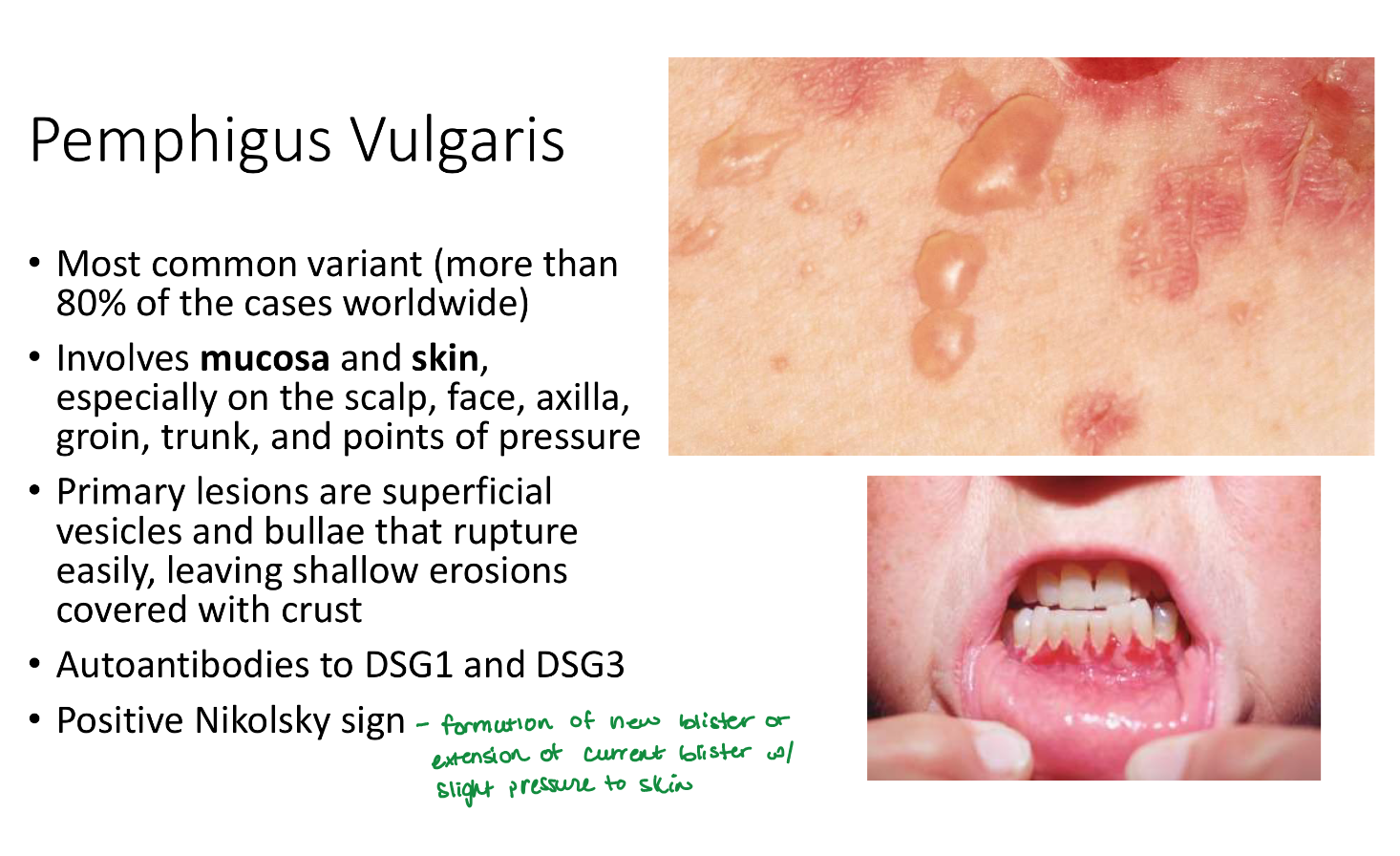
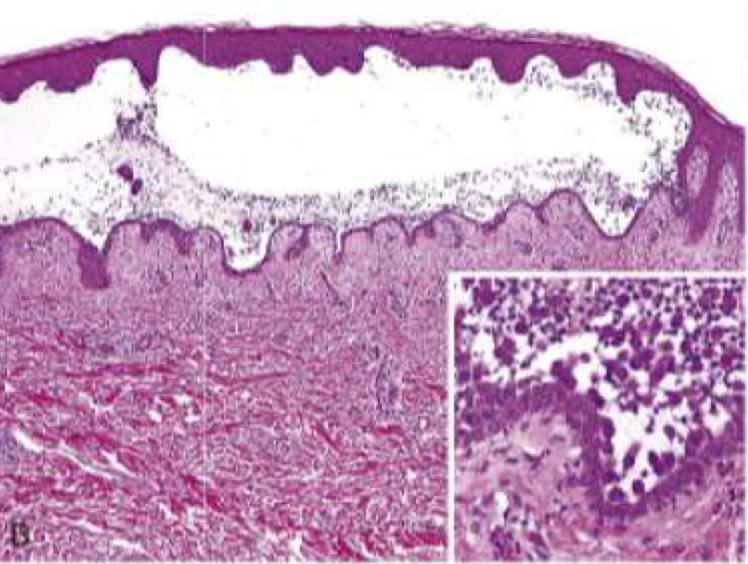
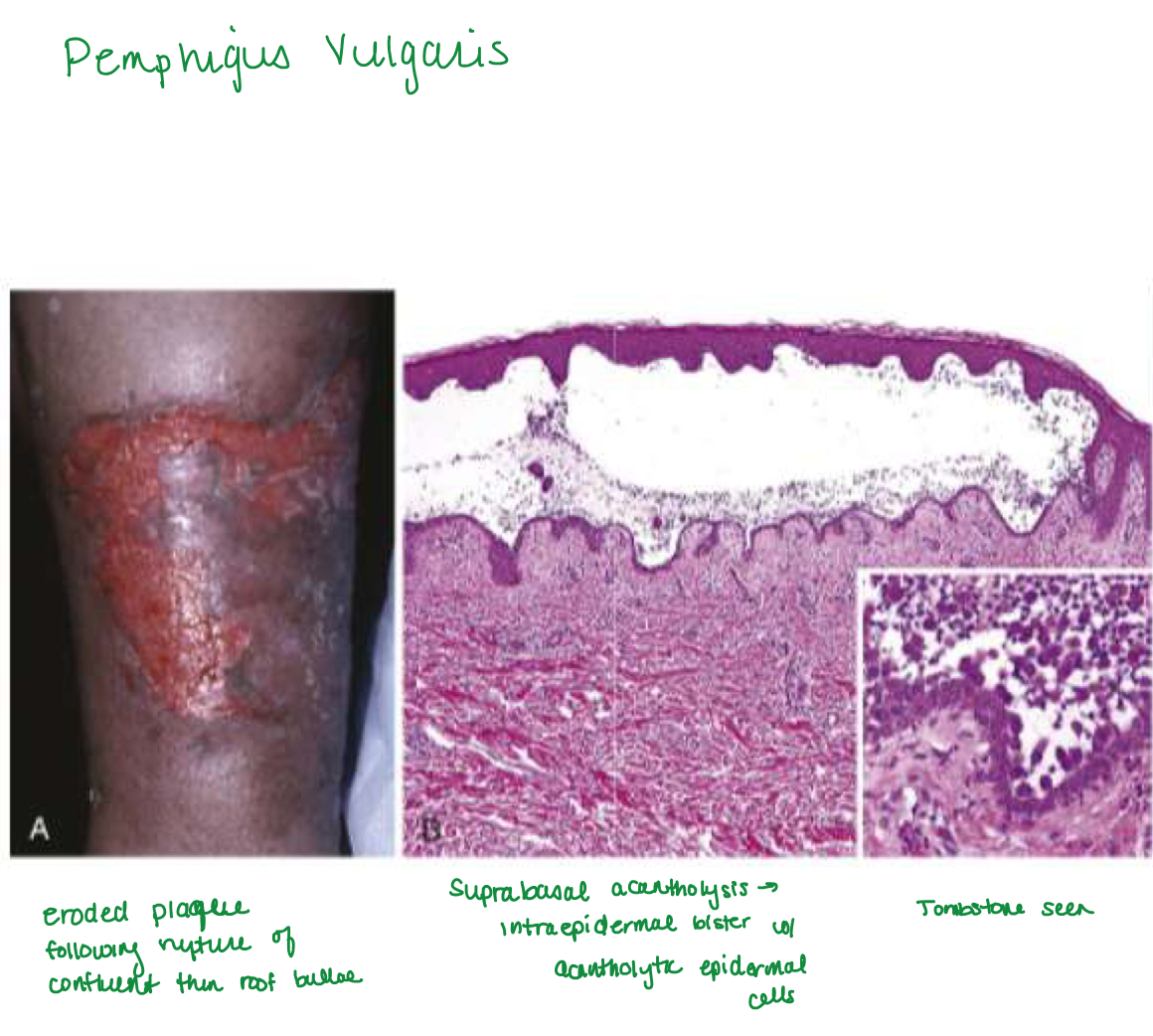
Pemphigus vulgaris
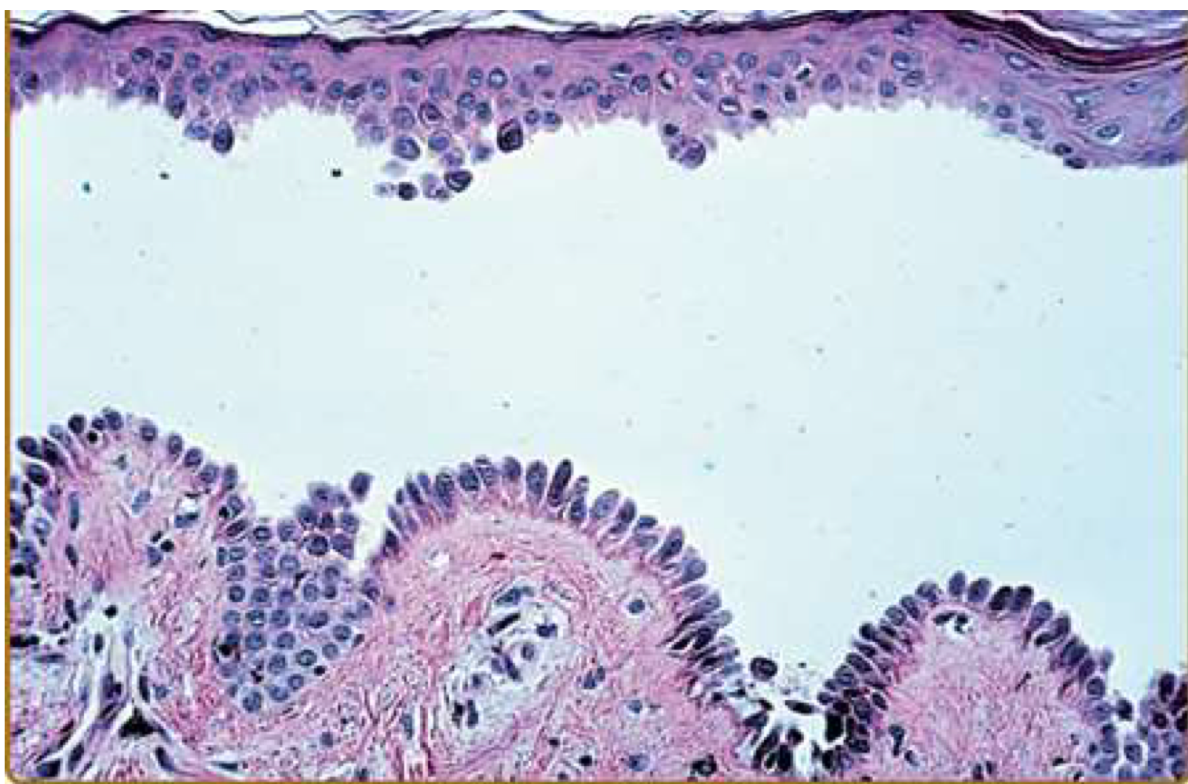
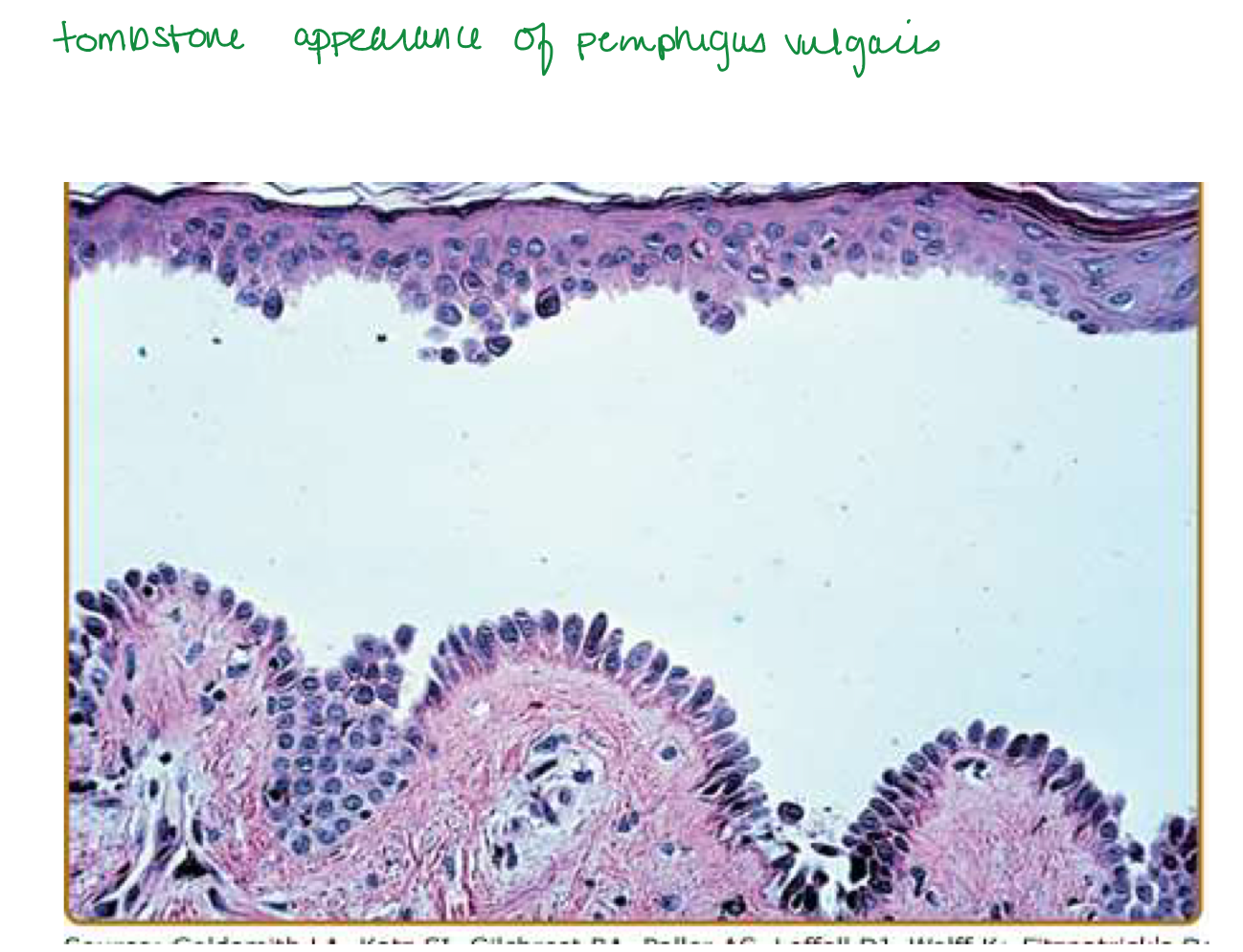
tombstone basale layer
Pemphigus vulgaris
Supepidermal, NONACANTHOLYTIC BLISTERS
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullae usually < 2cm
Usually heal w/o scarring, unless secondarily infected
Bullous pemphigoid
SUBEPIDERMAL blisters
Inner aspects of thighs, flexor surfaces of forearms, axillae, groin, lower abdomen
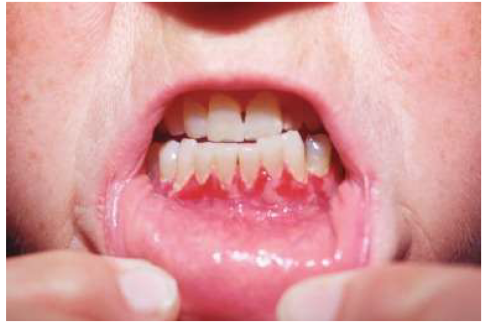
Oral (sometimes, would be after cutaneous lesions)
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid involves what type of Ab
IgG
auto IgG Ab to BP Ag 230 (BPAG1) and BP Ag 180 (BPAG2
BPAG2 can activate
complement → more inflammation
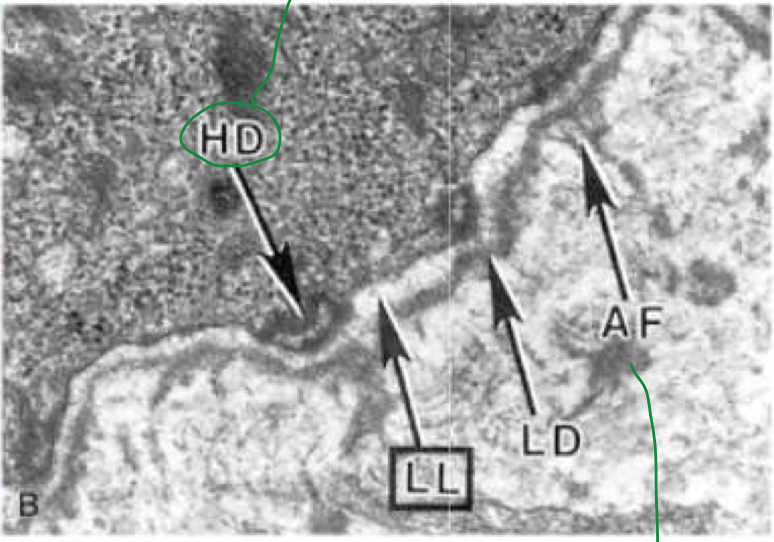
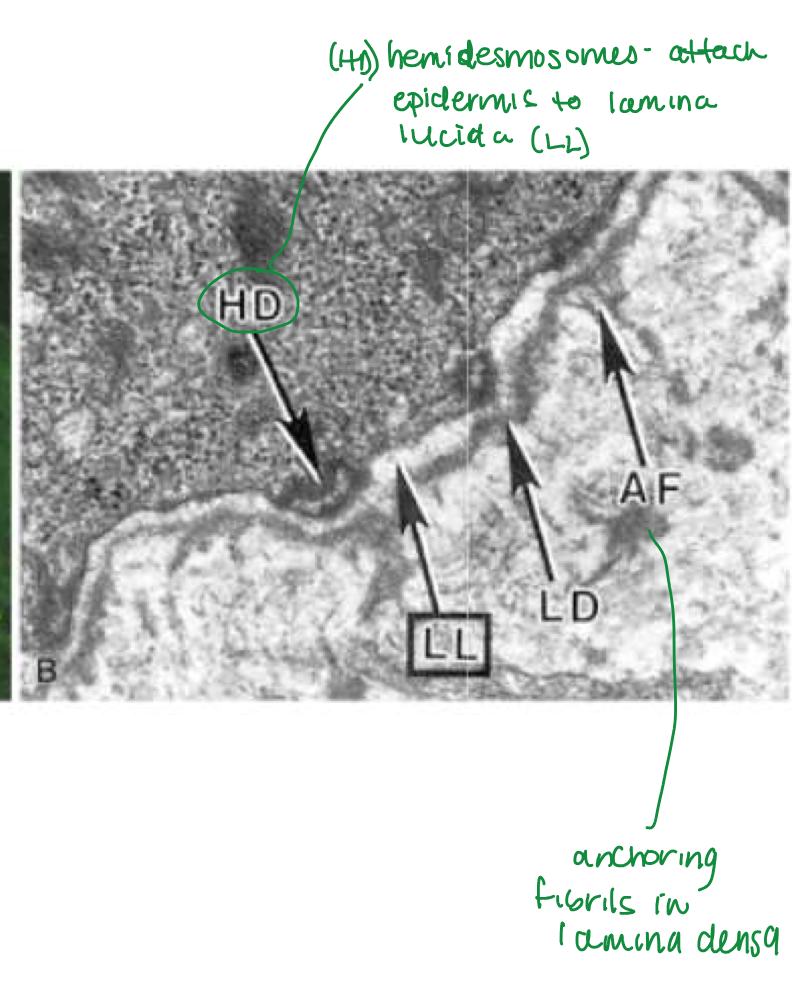
hemidesmosomes are needed for
adherence of basal keratinocytes to basement mem
HEMIDESMOSOMES connect
basal epidermal layer w/ underlying membrane
Dissolution of intercellular attachments w/i epidermis and mucosal epithelium
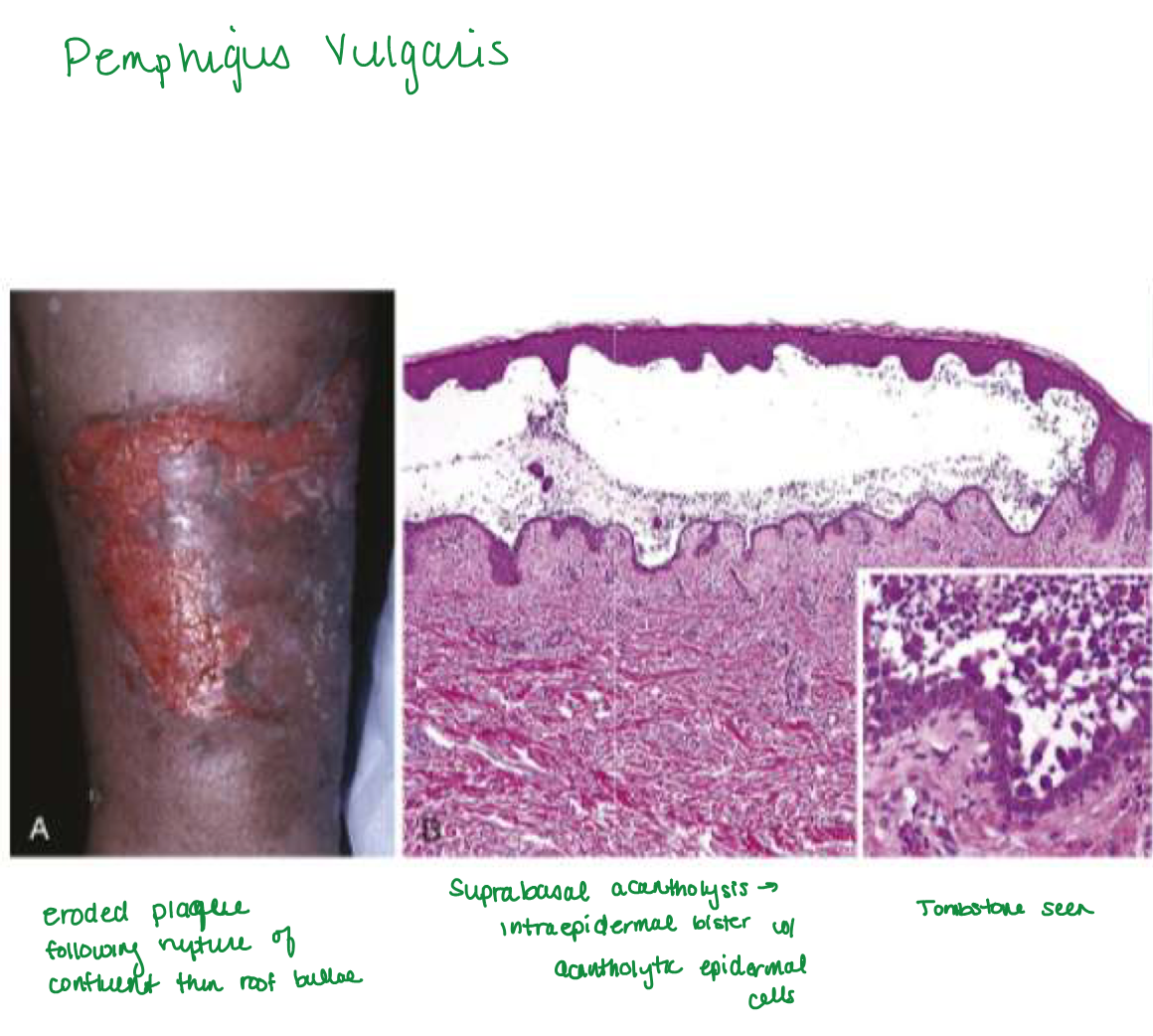
Pemphigus vulgaris
Acantholysis
dissolution of intercellular bridges that connect squamous epithelial cells → rounded, dissociated cells
Pemphigus vulgaris
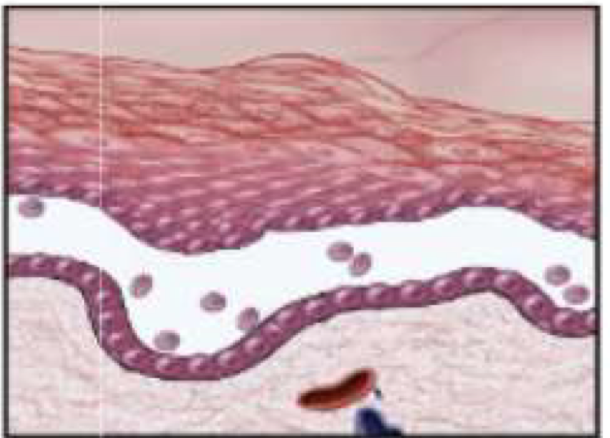
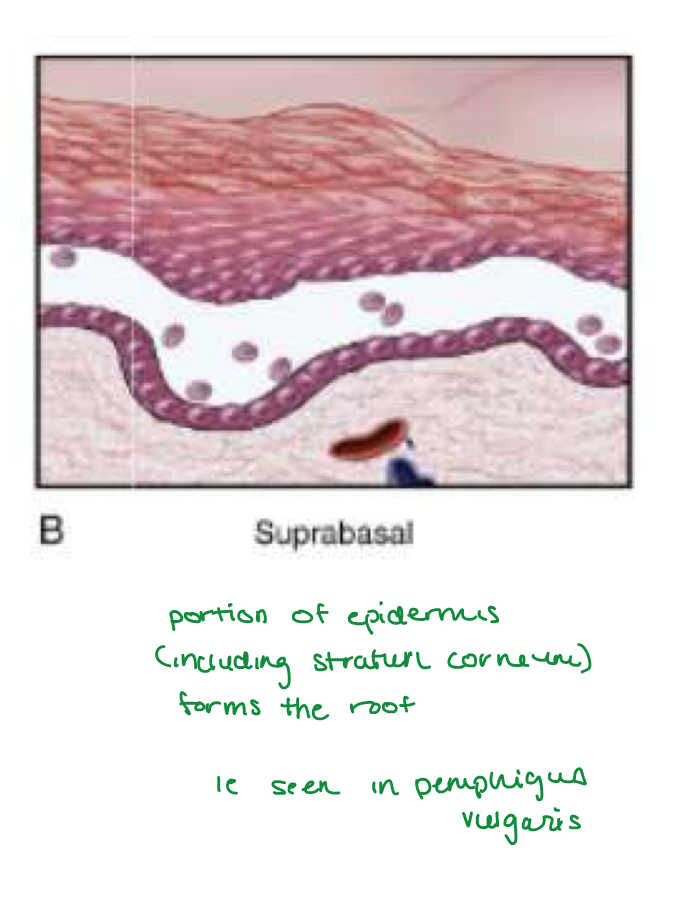
Suprabasal acantholytic blister histology
row of tombstones, intact basal cells at base of blister
pemphigus vulgaris
Rupture easily → shallow erosions covered w/ crust
pemphigus vulgaris
positive nikolsky sign
(formation of new blister or extension of current blister w/ slight pressure to skin)
Pemphigus vulgaris
Portion of epidermis (including stratum corneum) forms the roof of bullae
pemphigus vulgaris
(Dsg1 and Dsg3), parts of
desmosome
pemphigus vulgaris
DESMOSOMES adhesion between
epidermal cells
pemphigus vulgaris
Dsg1: higher exp in
more superficial epidermis (ie stratum corneum)
why you see subcorneal blister in pemphigus foliaceus (Dsg1 only) and lower in pemphigus vulgaris (Dsg1 and Dg3)
Dsg3: higher exp in
deeper epidermis (ie basal lamina)
pemphigus vulgaris
Benign but can be fatal w/o tx
pemphigus vulgaris
endemic to brazil
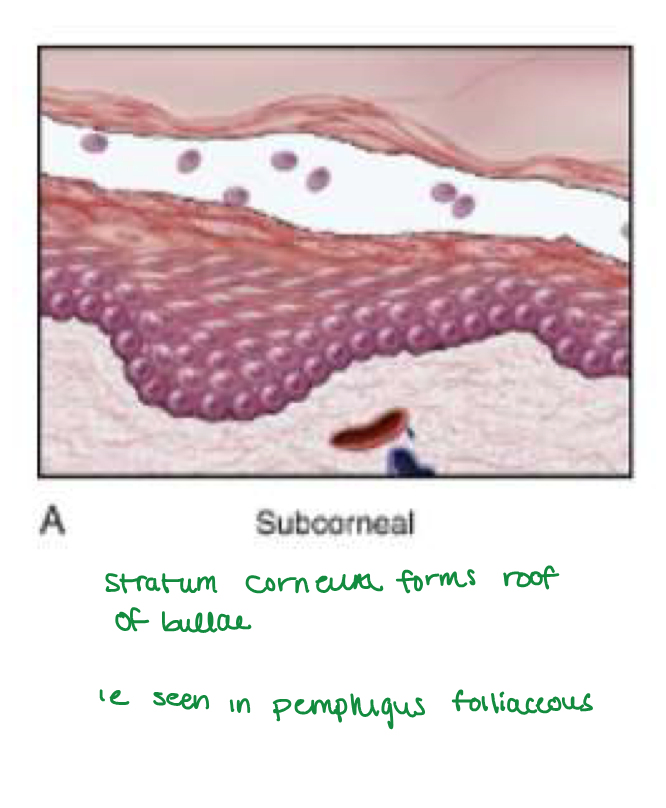
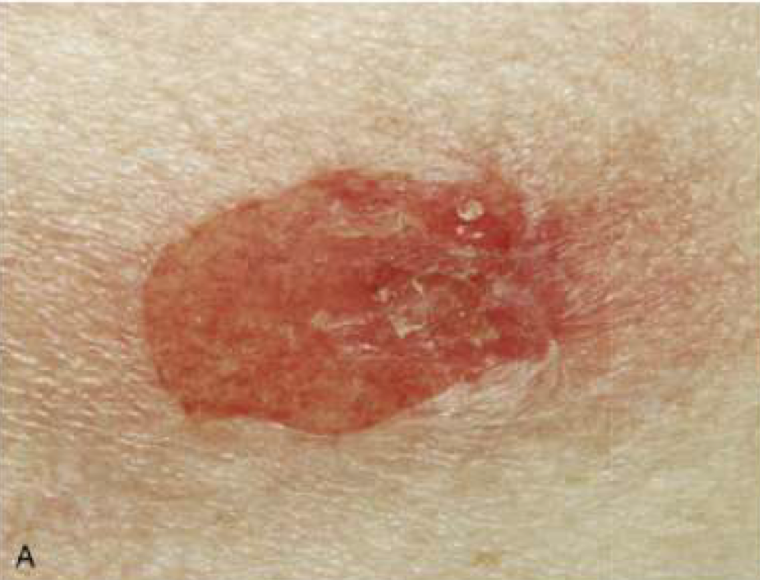
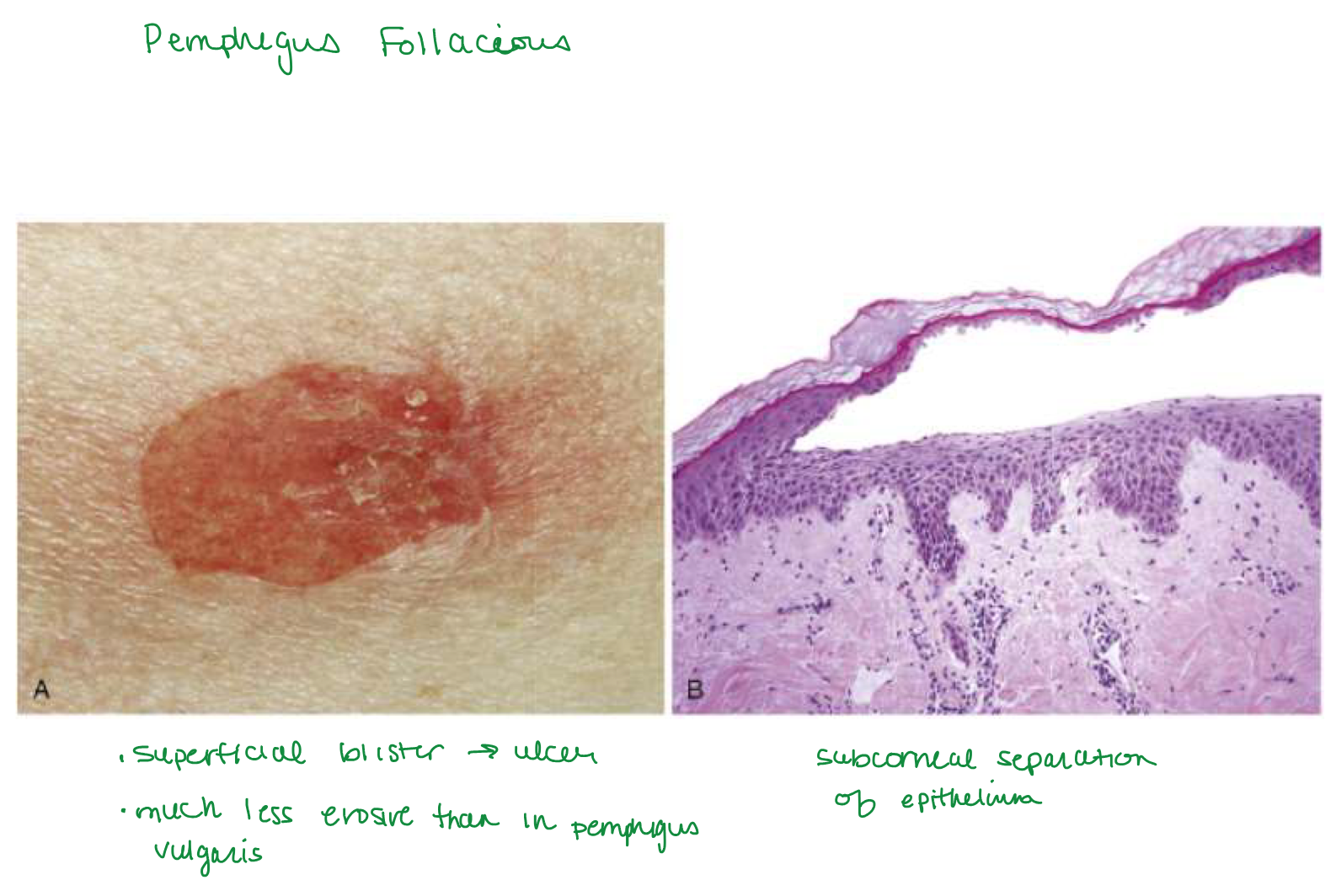
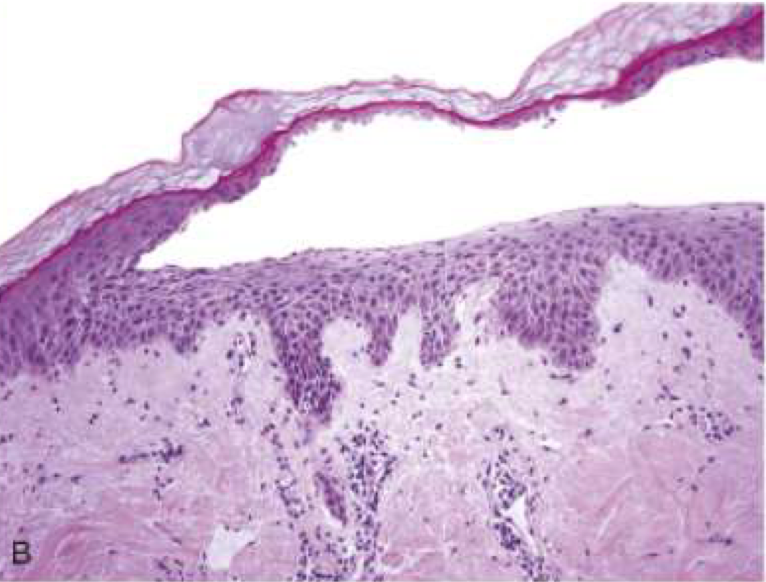
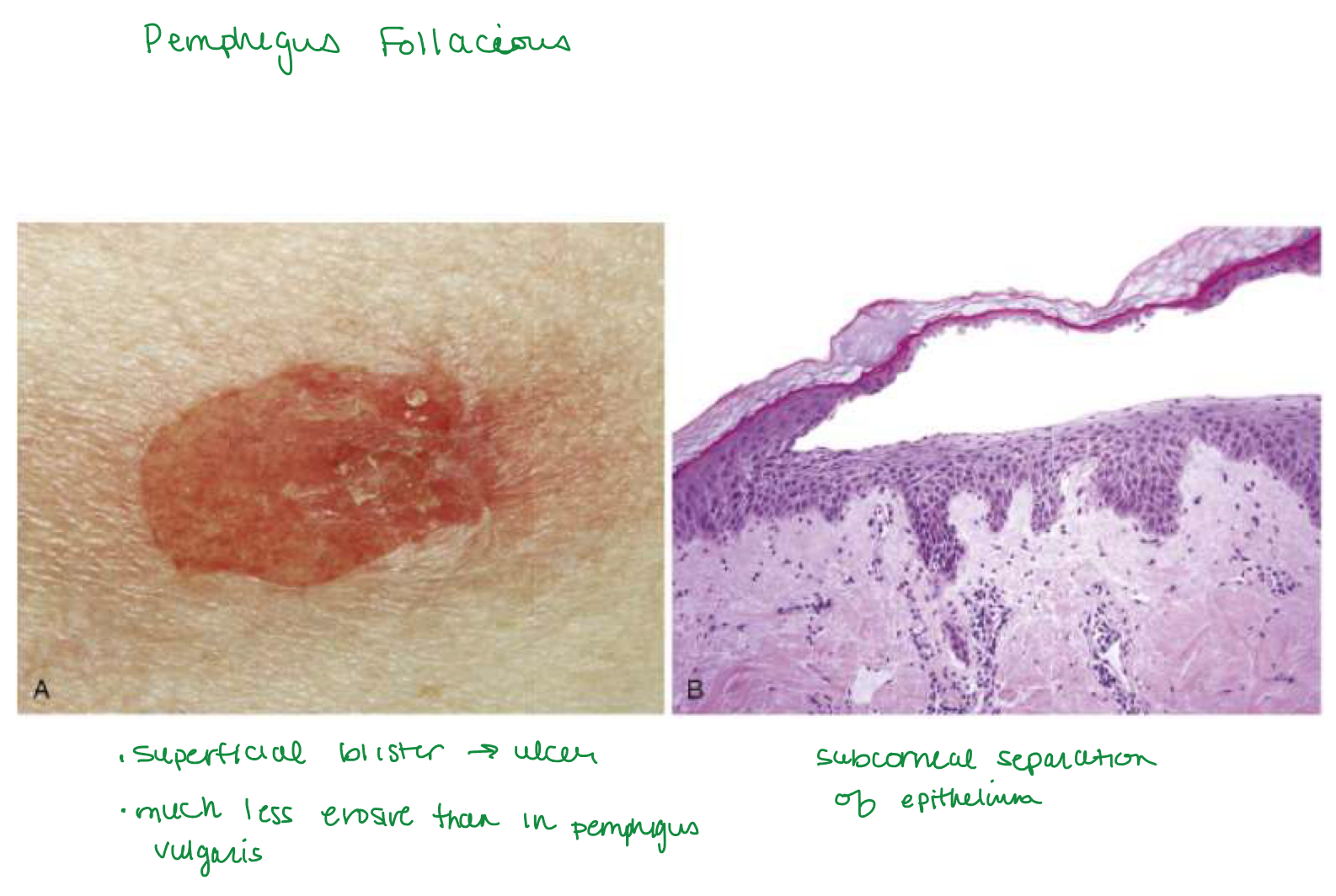
Pemphigus foliaceus
Pemphigus foliaceus blister location
Superficial subcorneal blisters in STRATUM GRANULOSUM (stratum corneum forms roof of bullae)
Superficial subcorneal blisters in STRATUM GRANULOSUM (stratum corneum forms roof of bullae)
pemphigus foliaceus
pemphigus foliaceus Ab type
Auto IgG Ab just against Dsg1 → more superficial subcorneal blisters
pemphigus foliaceus affects
DESMOSOMES (adhesion between epidermal cells)
Large, wart like vegetating plaques
Studded w/ pustules
on Groin, axillae, flexural surfaces
Pemphigus vegetans
Localized version of pemphigus foliaceus
Malar region
Pemphigus erythematous
Assoc w/ various malignancies, non-Hodgkins lymphoma
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Males
3rd and 4th decades of life
Celiac disease
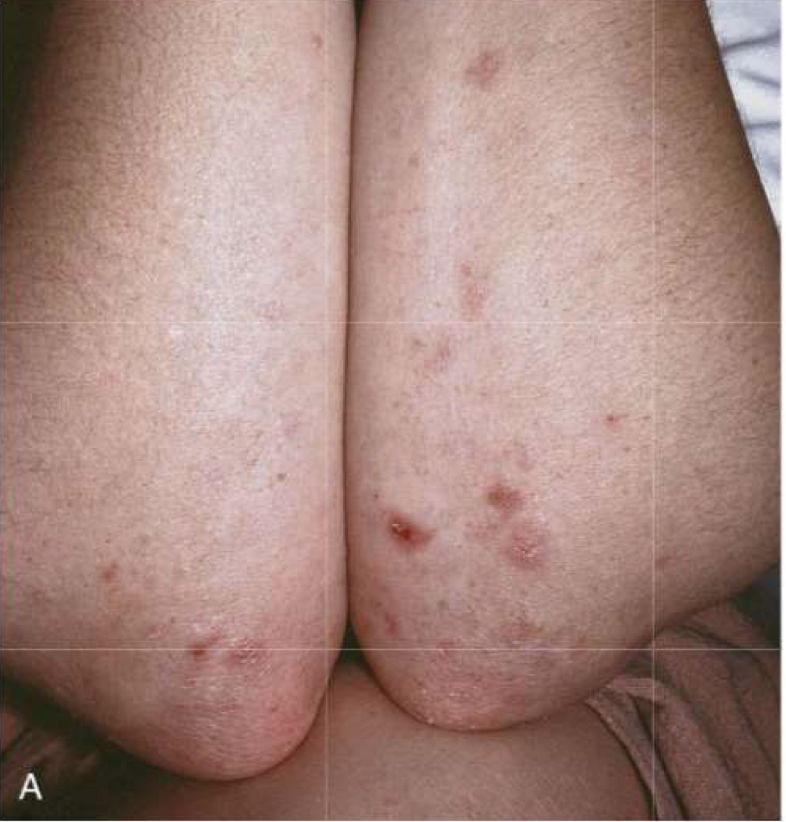
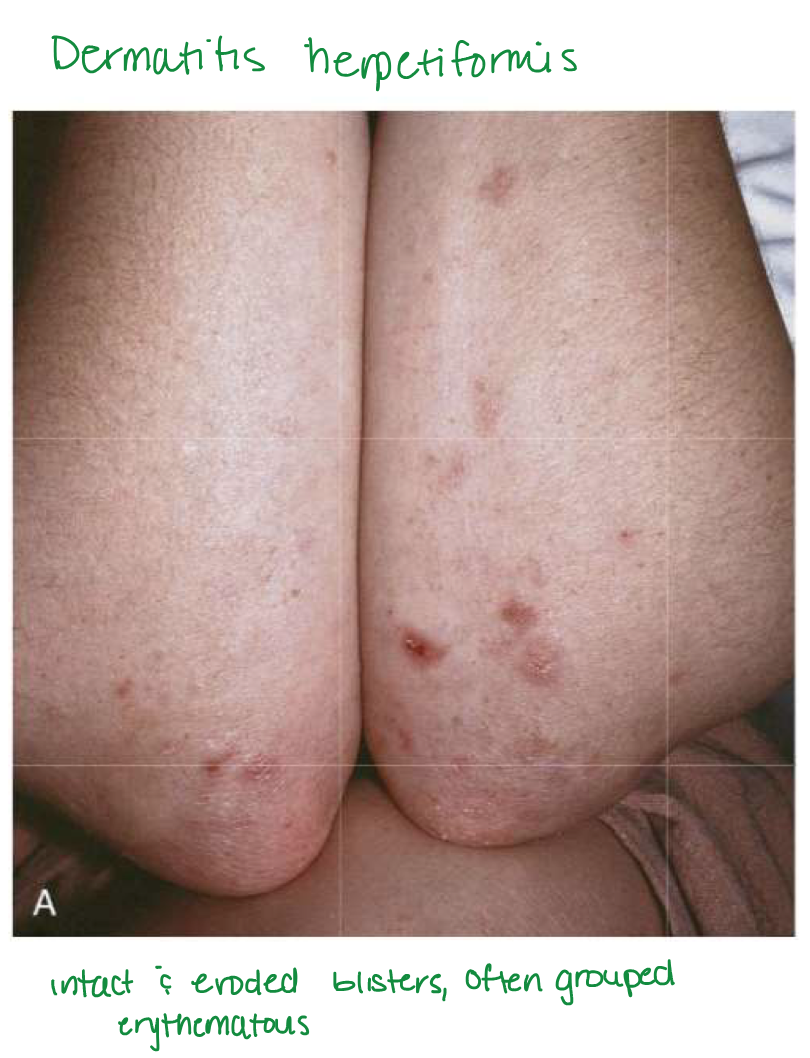
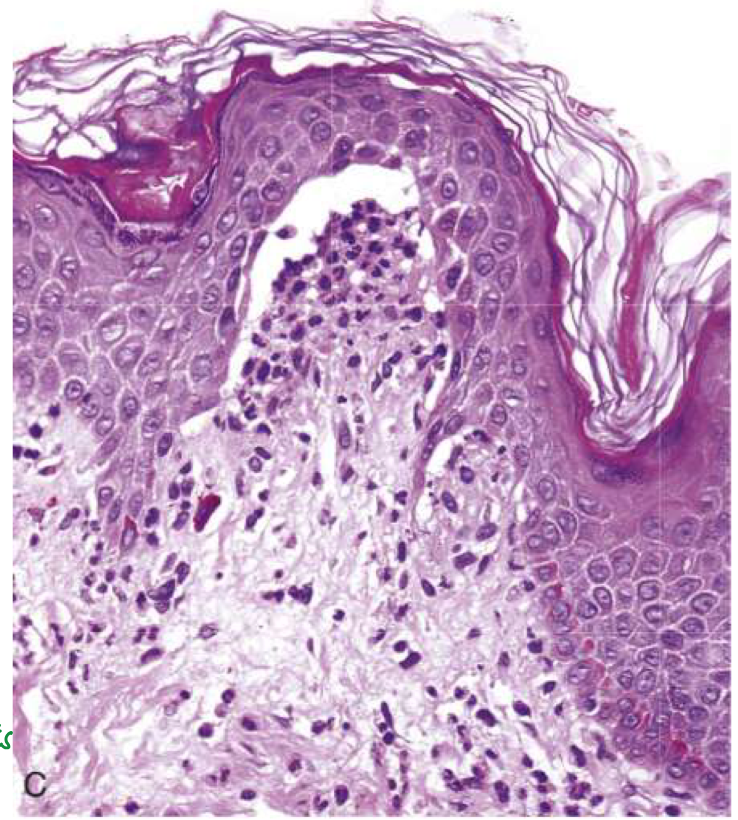
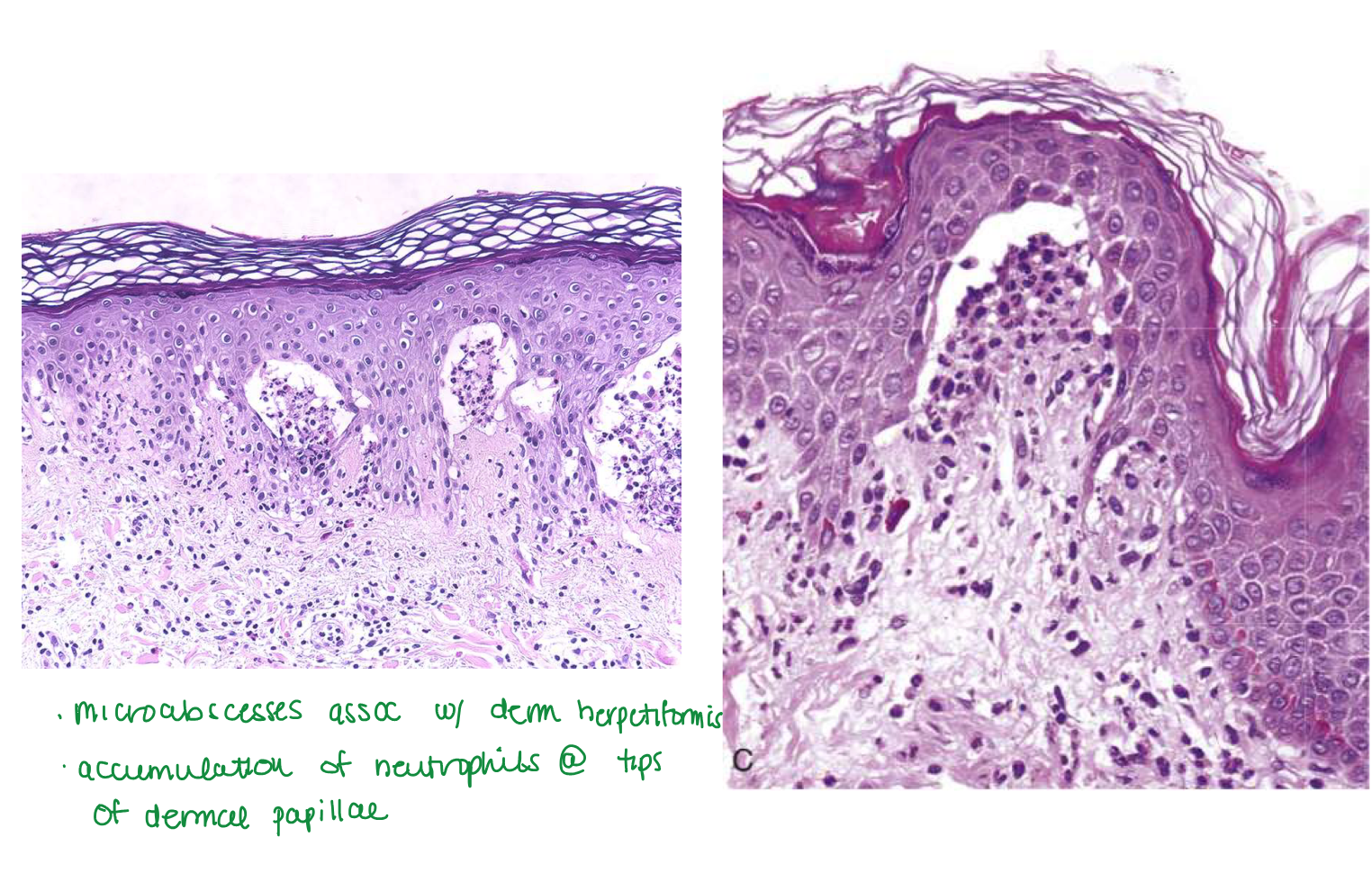
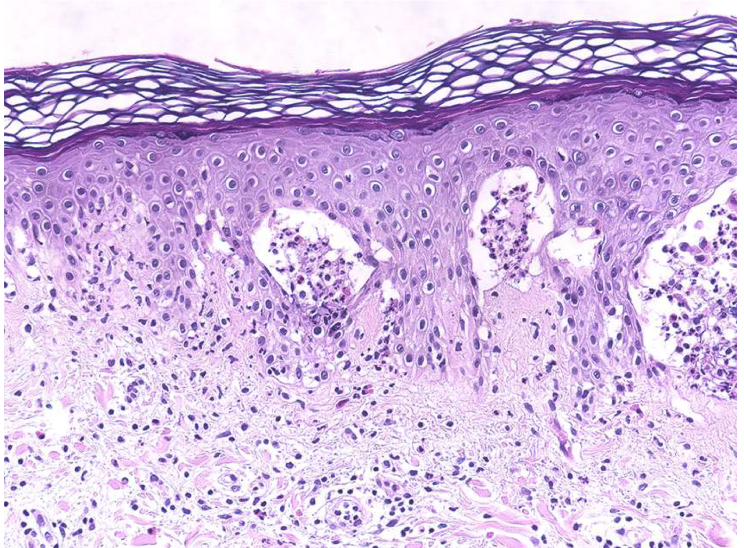
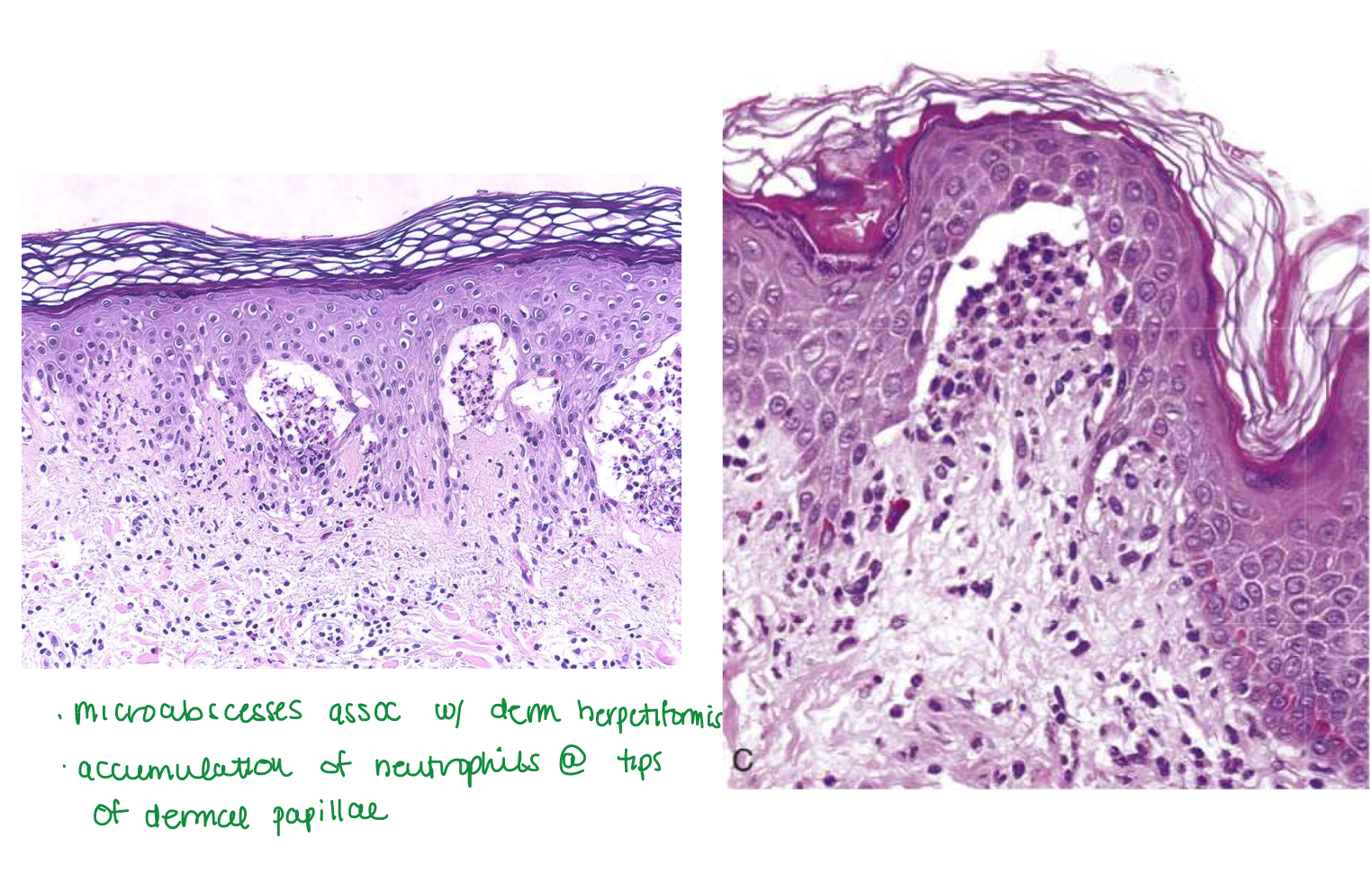
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis
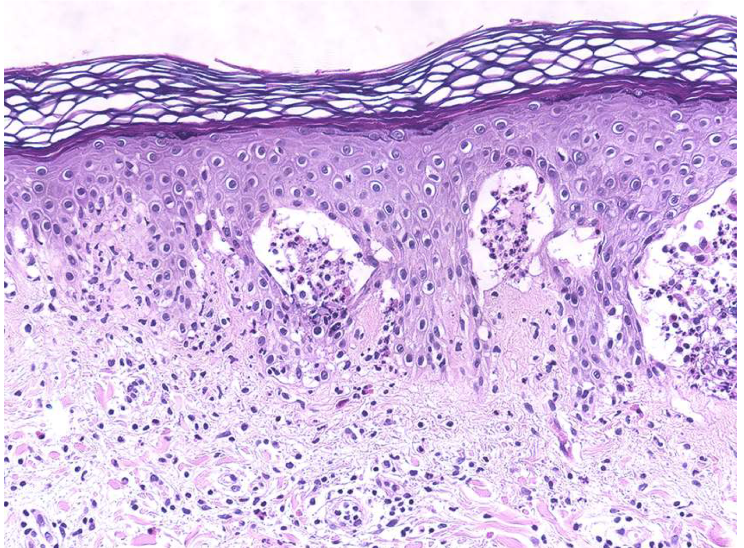
Urticaria and grouped vesicles
Bilateral, symmetric, grouped
Erythematous
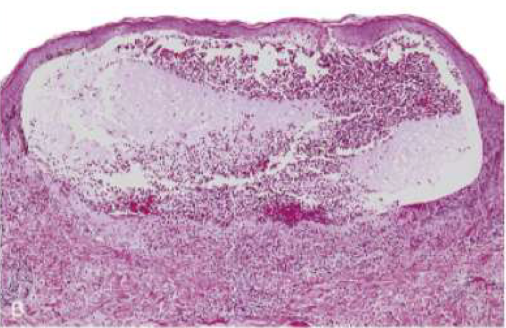
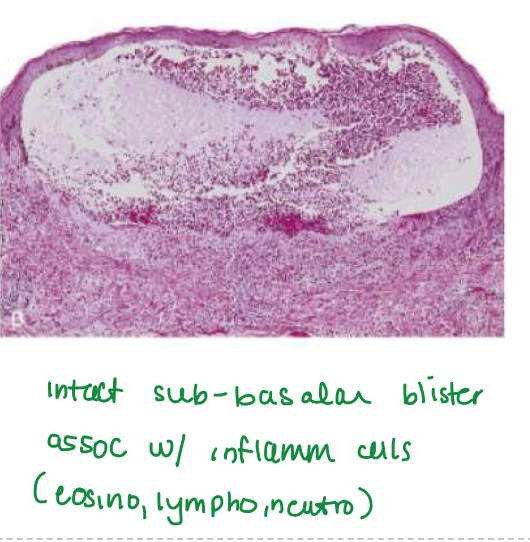
Dermatitis herpetiformis blisters
Subepidermal blisters
Dermatitis herpetiformis antibody
IgA auto Ab to fibrils that anchor hemidesmosomes to dermis
Dermatitis herpetiformis antibody anchors to
fibrils
reticulin (tethers epidermal basement mem to superficial dermis) —> blisters
reticulin
tethers epidermal basement mem to superficial dermis
targeted in dermatitis herpetiformis
In dermatitis herpetiformis, _____ accumulate at _____
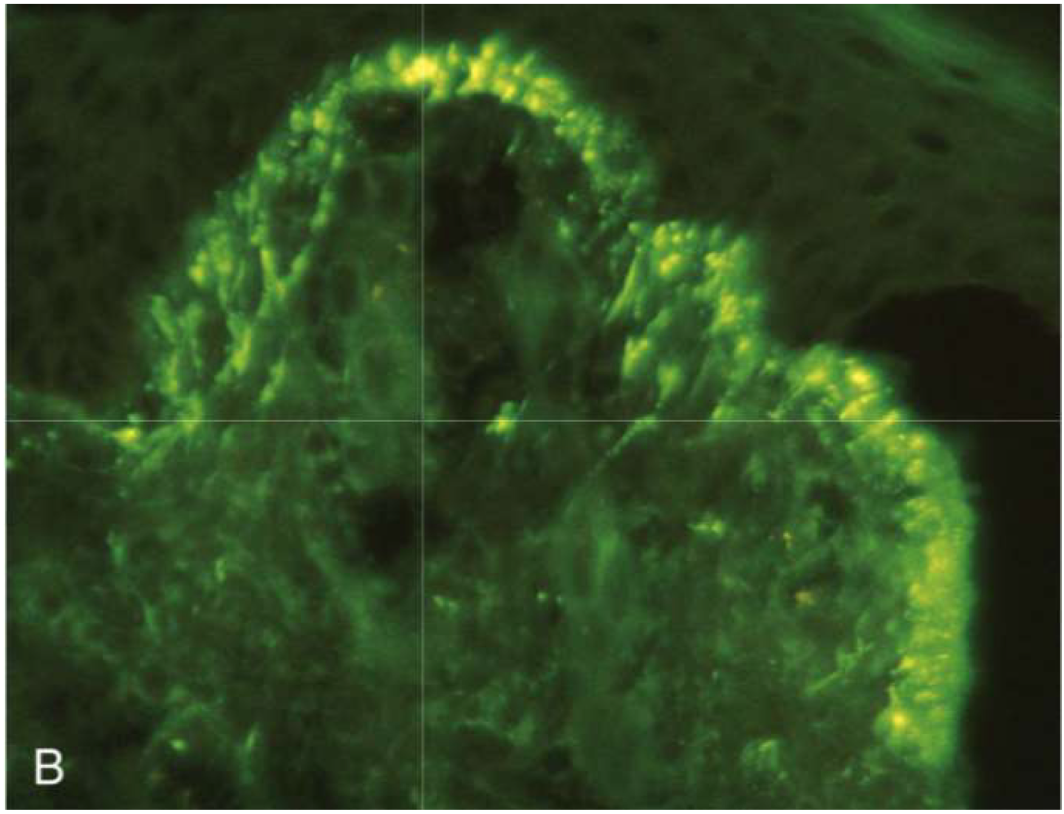
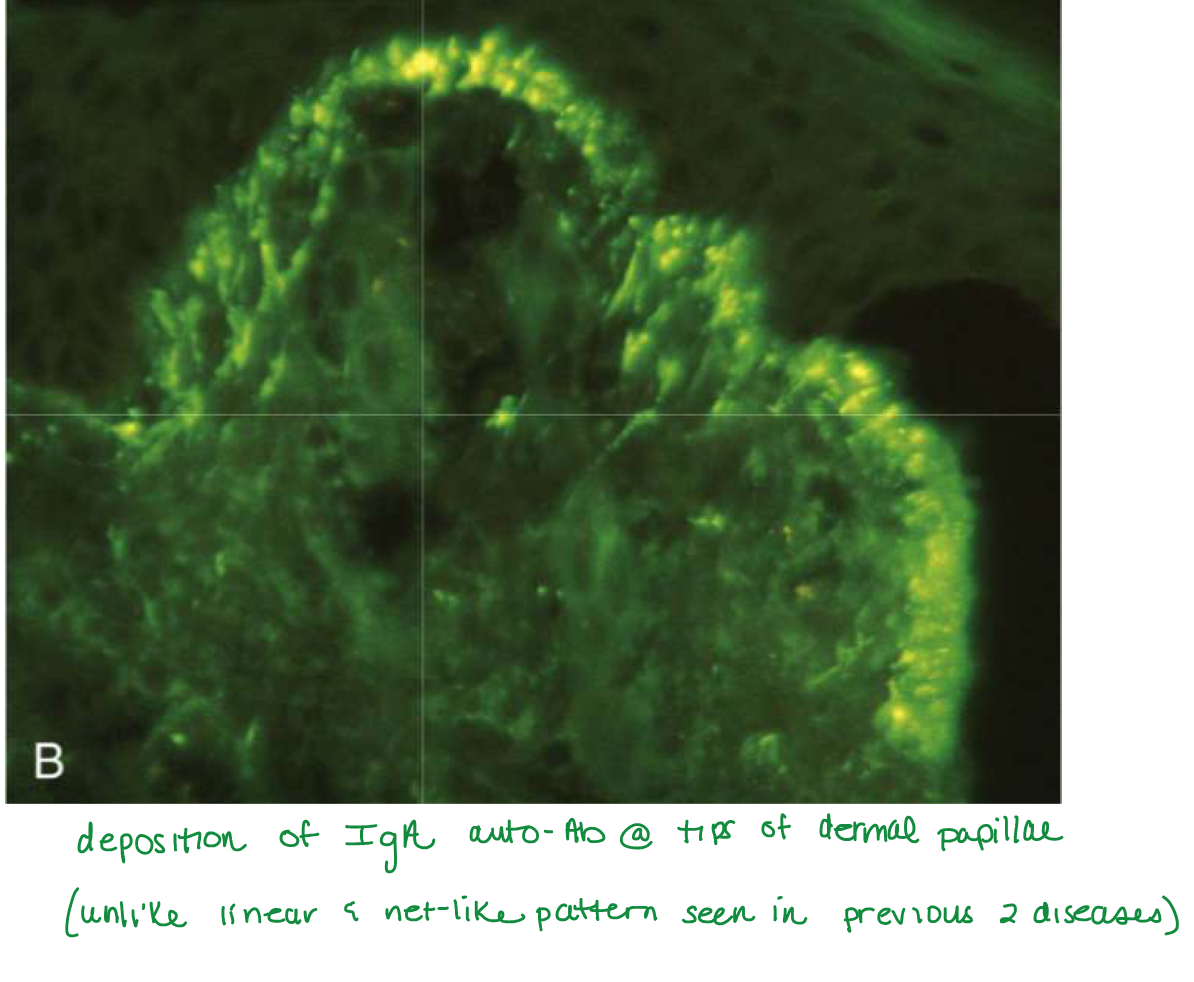
Fibrin and neutrophils accumulate at tips of dermal papillae
Fibrin and neutrophils accumulate at tips of dermal papillae —>
→ small microabscesses → subepidermal blisters
dermatitis herpetiformis
tx for dermatitis herpetiformis
GF diet
Non-inflammatory blister disorders:
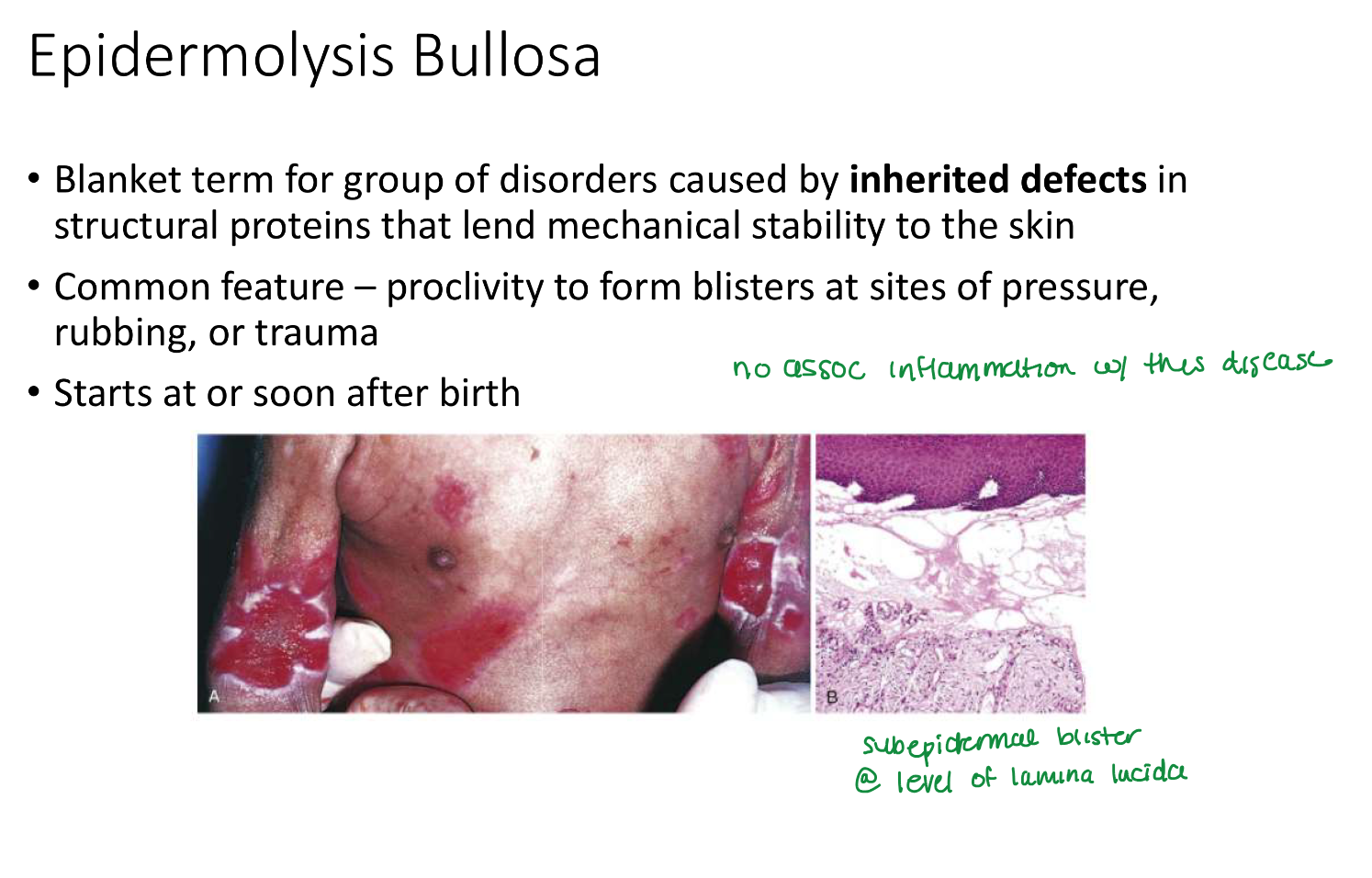
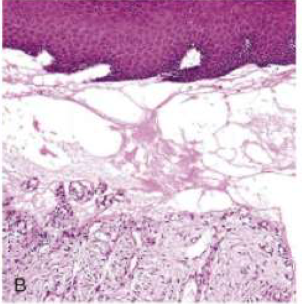
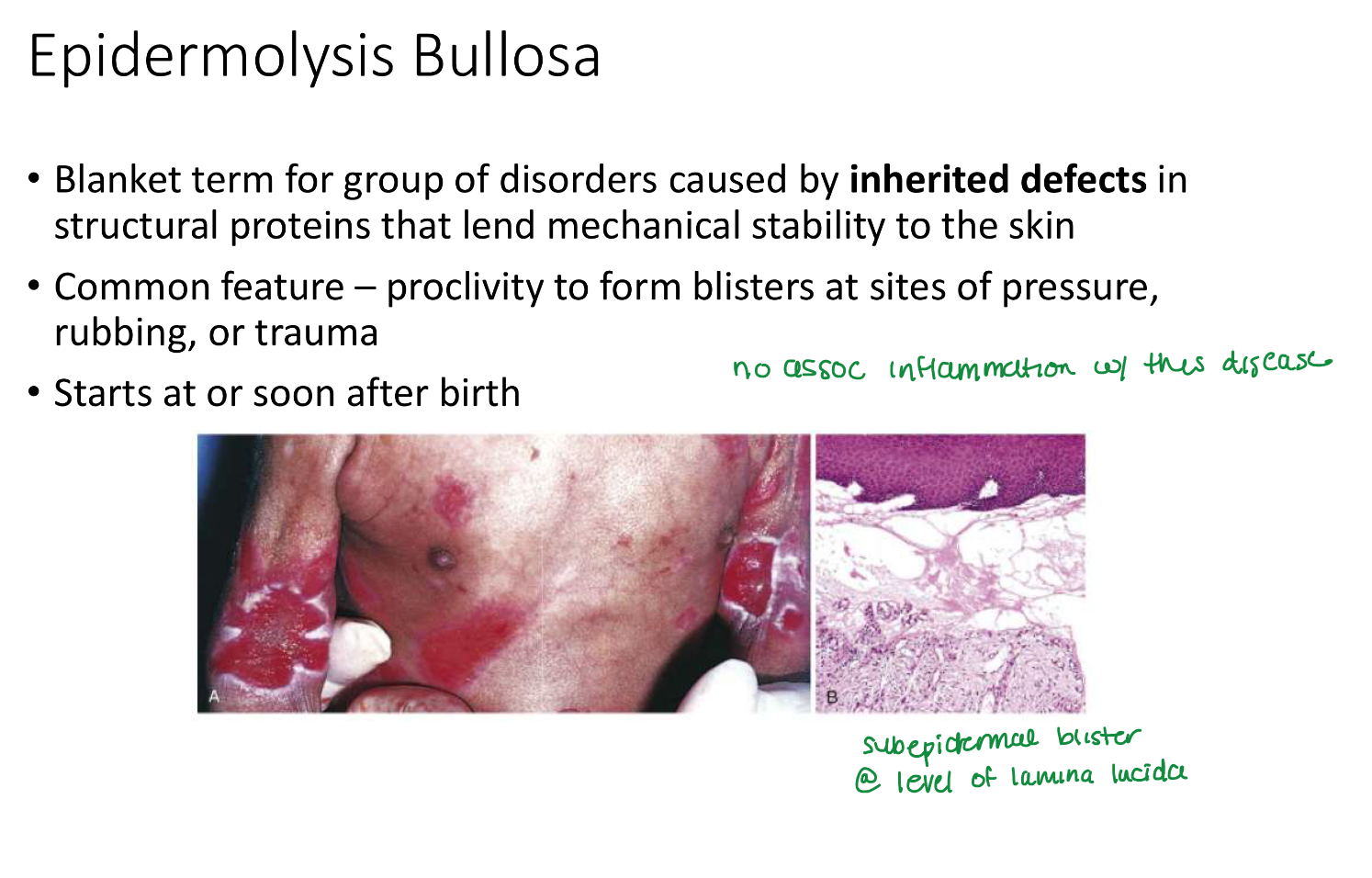
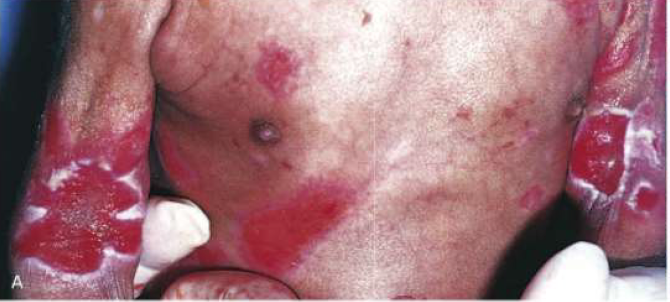
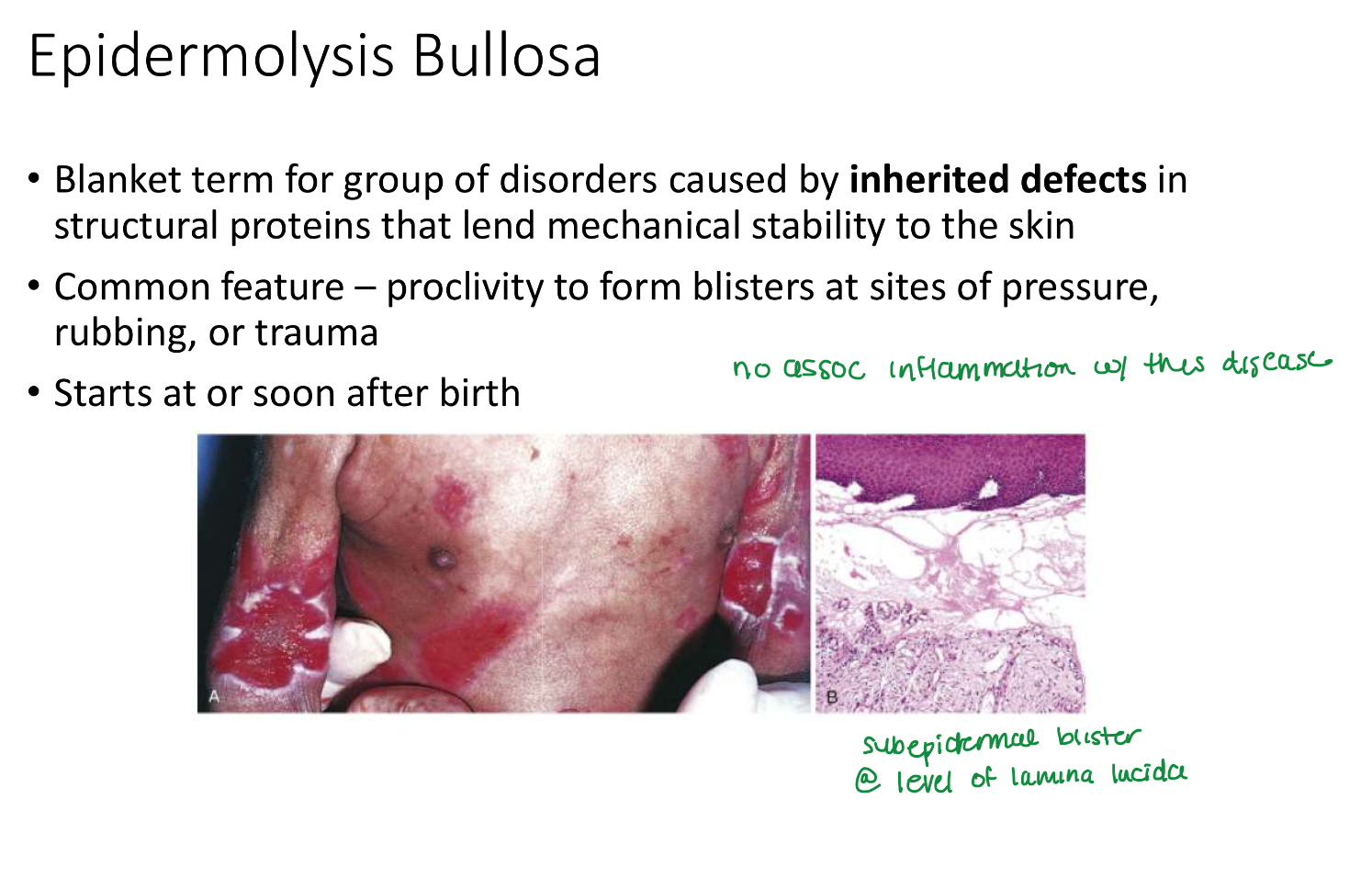
Epidermolysis Bullosa
Porphyria
Epidermolysis Bullosa starts
soon or after birth
Epidermolysis Bullosa location
Sites of pressure, rubbing, trauma
in epidermolysis bullosa, _____ in struc proteins →
inherited defects in struc proteins —>
mechanical instability of skin
porphyria exacerbated by
sunlight
Urticarial and vesicles assoc w/ scarring exacerbated by exposure to sunlight
porphyria
Subepidermal, adjacent dermis contains vessels w/ walls that are thickened by glassy deposits of serum proteins (ie immunoglobulins)
porphyria