PSY 252 Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:08 PM on 5/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
1
New cards
attitudes
A positive, negative, or mixed reaction to a person, object, or idea.
2
New cards
attitude scales
A multiple-item questionnaire designed to measure a person’s attitude toward some object.
3
New cards
bogus pipeline
A phony lie-detector device that is sometimes used to get respondents to give truthful answers to sensitive questions.
4
New cards
facial electromyograph (EMG)
An electronic instrument that records facial muscle activity associated with emotions and attitudes.
5
New cards
implicit attitudes
An attitude, such as prejudice, that one is not aware of having.
6
New cards
Implicit Association Test (IAT)
A covert measure of unconscious attitudes derived from the speed at which people respond to pairings or concepts--such as black or white with good or bad.
7
New cards
evaluative conditioning
The process by which we form an attitude toward a neutral stimulus because of its association with a positive or negation person, place, or thing.
8
New cards
theory of planned behavior
The theory that attitudes toward a specific behavior combine with subjective norms and perceived control to influence a person’s actions.
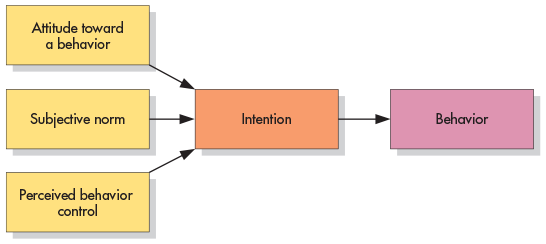
9
New cards
persuasion
The process by which attitudes are changed.
10
New cards
central route to persuasion
The process by which a person thinks carefully about a communication and is influenced by the strength of its arguments.
11
New cards
peripheral route to persuasion
The process by which a person does not think carefully about a communication and is influenced instead by superficial cues.
12
New cards
elaboration
The process of thinking about and scrutinizing the arguments contained in a persuasive communication.
13
New cards
sleeper effect
A delayed increase in the persuasive impact of a non-credible source.
14
New cards
need for cognition (NC)
A personality variable that distinguishes people on the basis of how much they enjoy effortful cognitive activities.
15
New cards
inoculation hypothesis
The idea that exposure to weak versions of a persuasive argument increases later resistance to that argument.
16
New cards
psychological reactance
The theory that people react against threats to their freedom by asserting themselves and perceiving the threatened freedom as more attractive.
17
New cards
cognitive dissonance theory
Theory holding that inconsistent cognitions arouses psychological tension that people become motivated to reduce.
18
New cards
insufficient justification
A condition in which people freely perform an attitude-discrepant behavior without receiving a large reward.
19
New cards
insufficient deterrence
A condition in which people refrain from engaging in a desirable activity, even when only mild punishment is threatened.
20
New cards
collectivism
A cultural orientation in which interdependence, cooperation, and social harmony take priority over personal goals.
21
New cards
compliance
Changes in behavior that are elicited by direct requests.
22
New cards
conformity
The tendency to change our perceptions, opinions, or behavior in ways that are consistent with social or group norms.
23
New cards
door-in-the-face technique
A two-step compliance technique in which an influencer prefaces the real request with one that is so large that it is rejected.
24
New cards
foot-in-the-door technique
A two-step compliance technique in which an influence sets the stage for the real request by first getting a person to comply with a much smaller request.
25
New cards
individualism
A cultural orientation in which independence, autonomy, and self-reliance take priority over group allegiances.
26
New cards
informational influence
Influence that produces conformity when a person believes others are correct in their judgements.
27
New cards
lowballing
A two-step compliance technique in which the influencer secures agreement with a request but then increases the size of that request by revealing hidden costs.
28
New cards
minority influence
The process by which dissenters produce change within a group.
29
New cards
normative influence
Influence that produces conformity when a person fears the negative social consequences of appearing deviant.
30
New cards
obedience
Behavior change produced by the commands of authority.
31
New cards
private conformity
The change of beliefs that occurs when a person privately accepts the position taken by others.
32
New cards
public conformity
A superficial change in overt behavior without a corresponding change of opinion that is produced by real or imagined group pressure.
33
New cards
social impact theory
The theory that social influence depends on the strength, immediacy, and number of source persons relative to target persons.
34
New cards
that’s-not-all technique
A two-step compliance technique in which the influencer begins with an inflated request, then decreases its apparent size by offering a discount or bonus.
35
New cards
biased sampling
The tendency for groups to spend more time discussing shared information (information already known by all or most group members) than unshared information (information known by only one or a few group members).
36
New cards
brainstorming
A technique that attempts to increase the production of creative ideas by encouraging group members to speak freely without criticizing their own or others’ contributions.
37
New cards
collective effort model
The theory that individuals will exert effort on a collective task to the degree that they think their individual efforts will be important, relevant, and meaningful for achieving outcomes that they value.
38
New cards
collective intelligence
The general ability of a group to perform well across a wide range of different tasks.
39
New cards
deindividuation
The loss of a person’s sense of individuality and the reduction of normal constraints against deviant behavior.
40
New cards
distraction-conflict theory
A theory that the presence of other will produce social facilitation effects only when those others distract from the task and create attentional conflict.
41
New cards
evaluation apprehension theory
A theory that the presence of others will produce social facilitation effects only when those others are seen as potential evaluators.
42
New cards
group
A set of individuals who interact over time and have shared fate, goals, or identity.
43
New cards
group cohesiveness
The extent to which forces push group members closer together, such as through feelings of intimacy, unity, and commitment to group goals.
44
New cards
group polarization
The exaggeration of initial tendencies in the thinking of group members through group discussion.
45
New cards
group support systems
Specialized interactive computer programs that are used to guide group meetings, collaborative work, and decision-making processes.
46
New cards
groupthink
A group decision-making style characterized by an excessive tendency among group members to seek concurrence.
47
New cards
integrative agreement
A negotiated resolution to a conflict in which all parties obtain outcomes that are superior to what they would have obtained from an equal division of the contested resources.
48
New cards
mere presence
The proposition that the mere presence of others is sufficient to produce social facilitation effects.
49
New cards
prisoner’s dilemma
A type of dilemma in which one party must make either cooperative or competitive moves in relation to another party. The dilemma is typically designed so that the competitive move appears to be in one’s self-interest, but if both sides make this move, both suffer more than if both had cooperated.
50
New cards
process gain
The increase in group performance so that the group outperforms the individuals who make up the group.
51
New cards
process loss
The reduction in group performance due to obstacles created by group processes, such as problems of coordination and motivation.
52
New cards
resource dilemmas
Social dilemmas involving how two or more people will share a limited resource.
53
New cards
social dilemma
A situation in which a self-interested choice by everyone will crease the worst outcome for everyone.
54
New cards
social facilitation
A process whereby the presence of others enhances performance on easy tasks but impairs performance on difficult tasks.
55
New cards
social identity model of deindividuation effects (SIDE)
A model of group behavior that explains deindividuation effects as the result of a shift from personal identity to social identity.
56
New cards
social loafing
A group-produced reduction in individual output on task where contributions are pooled.
57
New cards
transactive memory
A shared system for remembering information that enables multiple people to remember information together more efficiently than they could do so alone.
58
New cards
attachment styles
The way a person typically interacts with significant others.
59
New cards
communal relationship
A relationship in which the participants expect and desire mutual responsiveness to each other’s needs.
60
New cards
companionate love
A secure, trusting, stable partnership.
61
New cards
equity theory
The theory that people are most satisfied with a relationship when the ration between benefits and contributions is similar for both partners.
62
New cards
exchange relationships
A relationship in which the participants expect and desire strict reciprocity in their interactions.
63
New cards
excitation transfer
The process whereby arousal caused by one stimulus is added to arousal from a second stimulus and the combined arousal is attributed to the second stimulus.
64
New cards
hard-to-get effect
The tendency to prefer people who are highly selective in their social choices over those who are more readily available.
65
New cards
Intimate relationships
A close relationship between two adults involving emotional attachment, fulfillment of psychological needs, or interdependence.
66
New cards
lonliness
A feeling of deprivation about existing social relations.
67
New cards
matching hypothesis
The proposition that people are attracted to other who are similar in physical attractiveness.
68
New cards
mere exposure effect
The phenomenon whereby the more often people are exposed to a stimulus, the more positively they evaluate that stimulus.
69
New cards
need for affiliation
The desire to establish and maintain many rewarding interpersonal relationships.
70
New cards
passionate love
Romantic love characterized by high arousal, intense attraction, and fear of rejection.
71
New cards
reciprocity
A mutual exchange between what we give and receive--for example, liking those who like us.
72
New cards
self-disclosure
Revelations about the self that a person makes to others.
73
New cards
social exchange theory
A perspective that views people as motivated to maximize benefits and minimize costs in their relationships with others.
74
New cards
triangular theory of love
A theory proposing that love has three basic components--intimacy, passion, and commitment--that can be combined to produce eight subtypes.
75
New cards
what-is-beautiful-is-good stereotype
The belief that physically attractive individuals also possess desirable personality characteristics.
76
New cards
altruistic
Motivated by the desire to improve another’s welfare.
77
New cards
audience inhibition
Reluctance to help for fear of making a bad impression on observers.
78
New cards
bystander effect
The effect whereby the presence of others inhibits helping.
79
New cards
diffusion of responsibility
The belief that others will or should take the responsibility for providing assistance to a person in need.
80
New cards
egoistic
Motivated by the desire to improve one’s own welfare.
81
New cards
empathy
Understanding or vicariously experiencing another individual’s perspective and feeling sympathy and compassion for that individual.
82
New cards
empathy-altruism hypothesis
The proposition that empathic concern for a person in need produces an altruistic motive for helping.
83
New cards
identity fusion
A strong sense of “oneness” and shared identity with a group and its individual members.
84
New cards
kin selection
Preferential helping of genetic relatives which results in the greater likelihood that genes held in common will survive.
85
New cards
negative state relief model
The proposition that people help others in order to counteract their own feelings of sadness.
86
New cards
pluralistic ignorance
The state in which people in a group mistakenly think that their own individual thoughts, feelings, or behaviors are different from those of the others in the group.
87
New cards
prosocial behaviors
Actions intended to benefit others.
88
New cards
reciprocal altruism
Altruism that involves an individual helping another (despite some immediate risk or cost) and becoming more likely to receive help from the other in return.
89
New cards
reluctant altruism
Altruistic kinds of behavior that result from pressure from peers or other sources of direct social influence.
90
New cards
aggression
Behavior intended to harm another individual.
91
New cards
catharsis
A reduction of the motive to aggress that is said to result from any imagined, observed, or actual act of aggression.
92
New cards
corporal punishment
Physical force (such as spanking or hitting) intended to cause a child pain--but not injury--for the purpose of controlling or correcting the child’s behavior.
93
New cards
culture of honor
A culture that emphasizes honor and social status, particularly for males, and the role of aggression in protecting that honor.
94
New cards
cycle of violence
The transmission of domestic violence across generations.
95
New cards
Dark Triad
A set of three traits that are associated with higher levels of aggressiveness: Machiavellianism, psychopathy, and narcissism.
96
New cards
displacement
Aggressing against a substitute target because aggressive acts against the source of the frustration are inhibited by fear or lack of access.
97
New cards
executive functioning
The cognitive abilities and precesses that allow humans to plan or inhibit their actions.
98
New cards
frustration-aggression hypothesis
The idea that (1) frustration always elicits the motive to aggress and that (2) all aggression is caused by frustration.
99
New cards
hostile attribution bias
The tendency to perceive hostile intent in others.
100
New cards
proactive aggression
Aggressive behavior whereby harm is inflicted as a means to a desired end (also called instrumental aggression).