Histology of Tissues in the Oral and Nasal Cavity
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
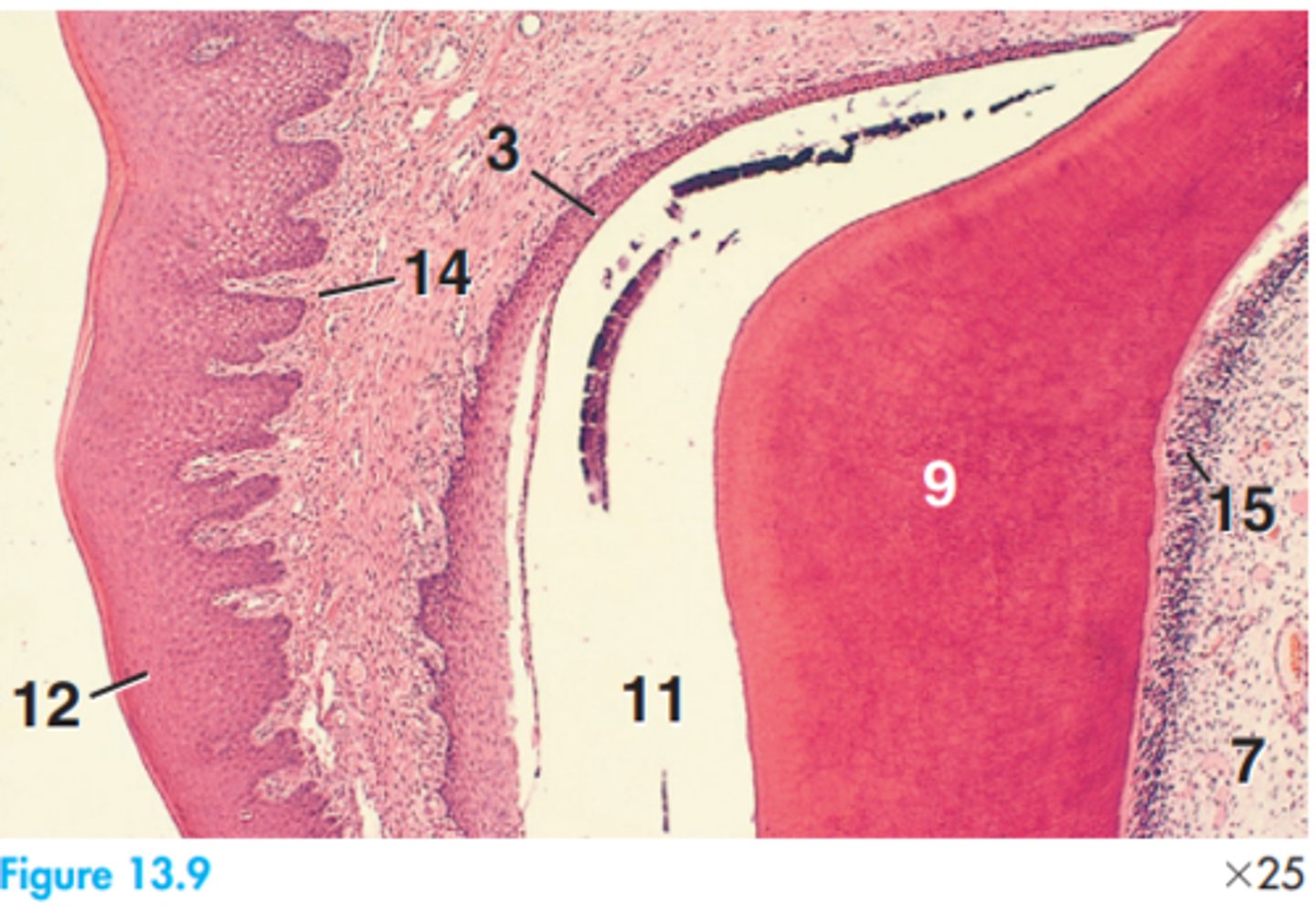
Papillae.
What are the small outgrowths of the tongue called?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
(Keratinisation depends on species)
What type of epithelium is always found in the oral cavity?
Upper surface of the tongue.
Where are papillae mainly located on the tongue?
-Filiform = thread-like projections or bear spines
-Circumvallate, fungiform = Cushion-shaped
-Foliate = successive folds
Describe the different structures of papillae
Epithelium
Where are tastebuds found in the tongue?
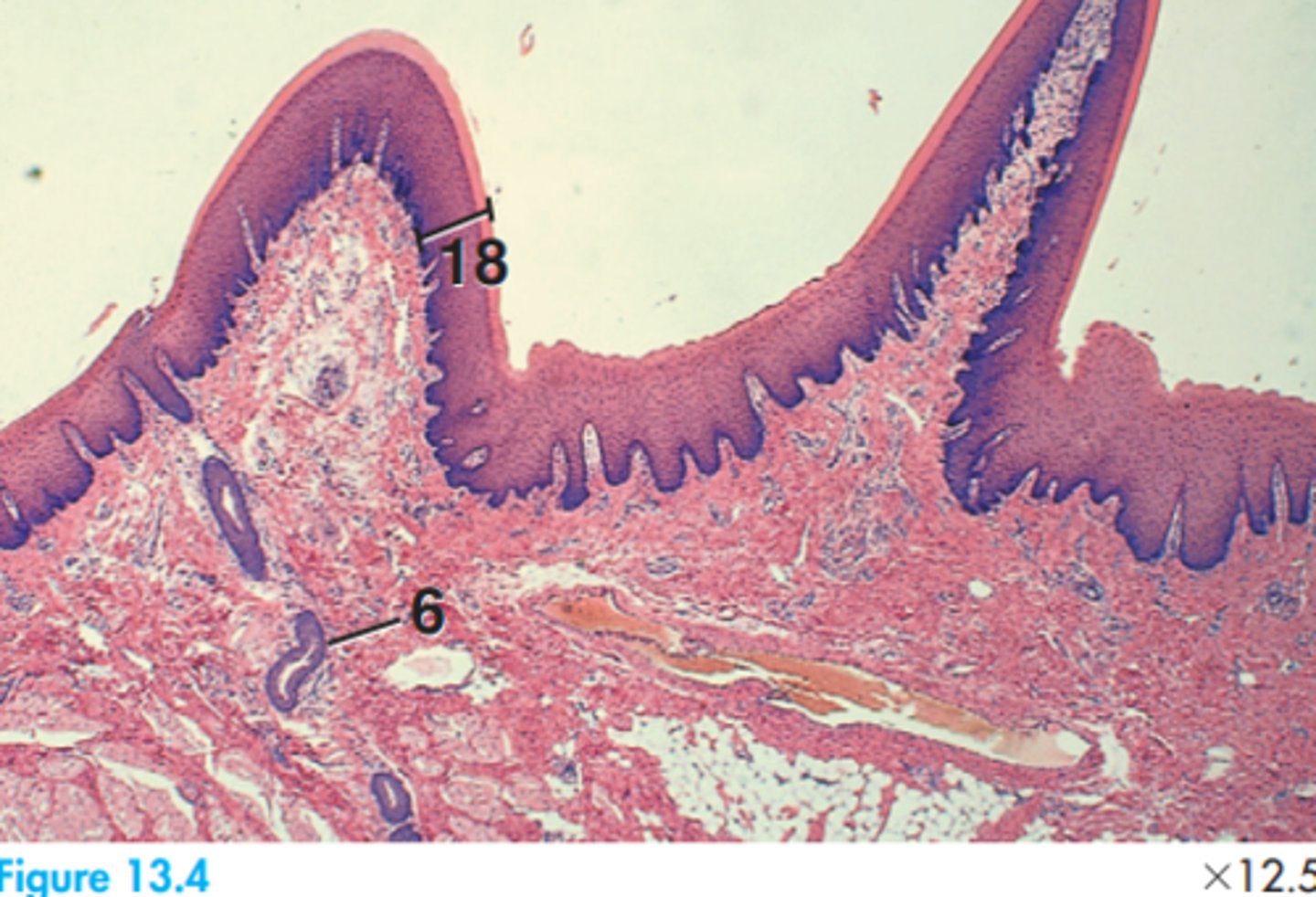
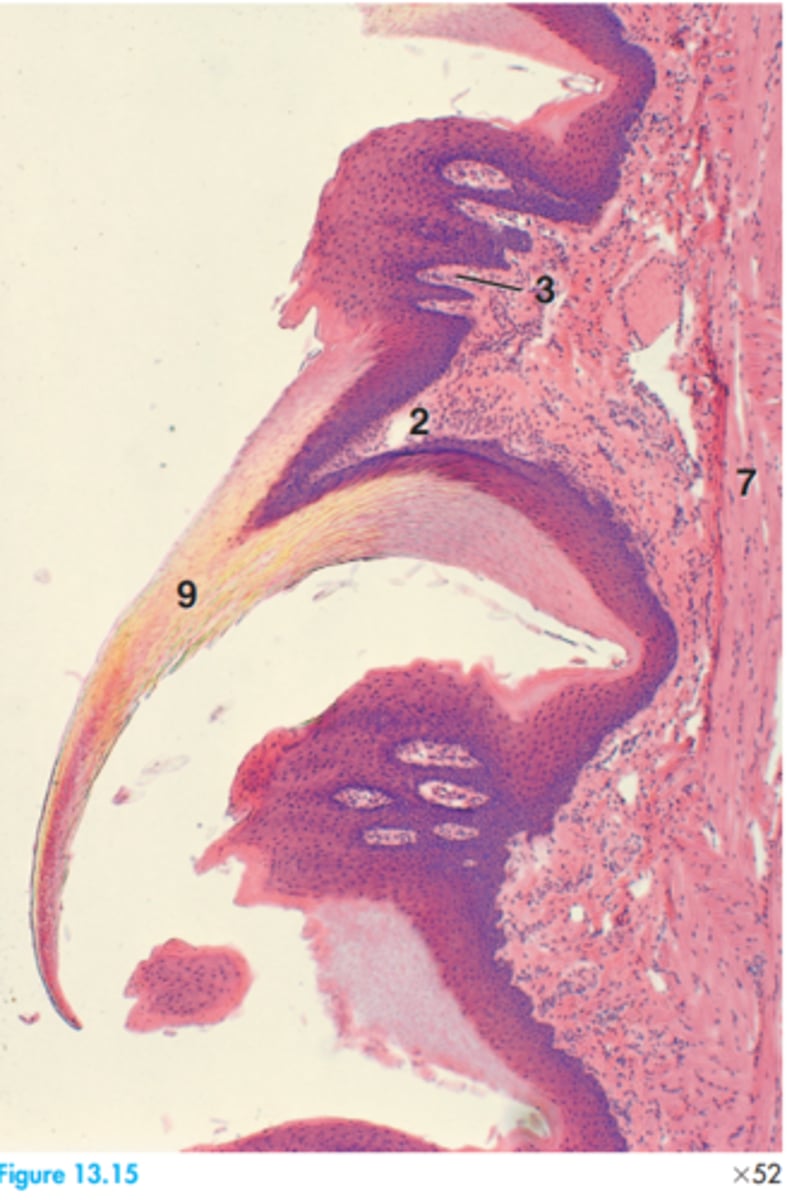
1 = Alveolar bone
4 = Dental papillae
3 = Dental lamina
5 = Dental sac
12 = Outer enamel epithelium
17 = Stellate reticulum
Label this slide of the canine developing permanent tooth
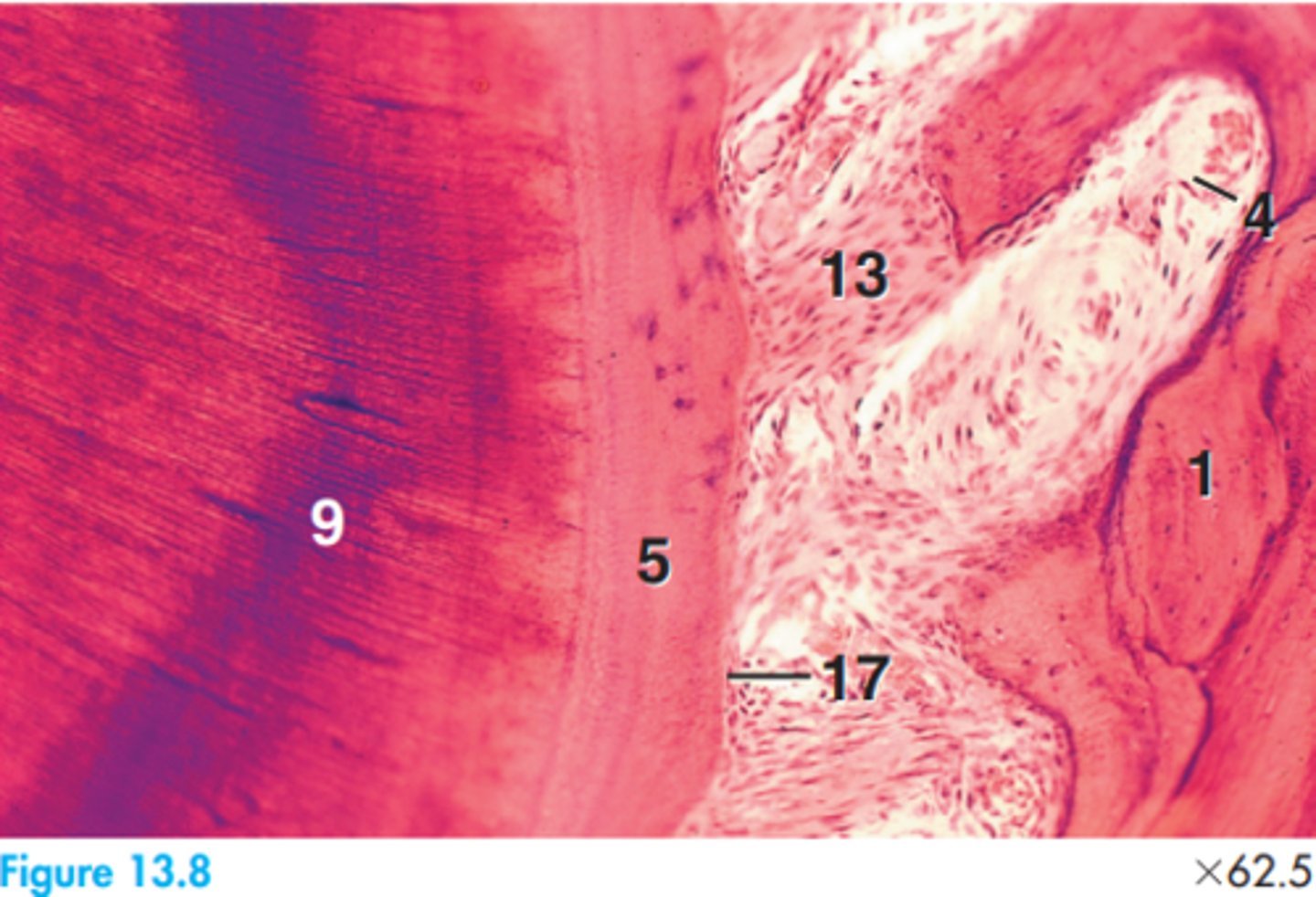
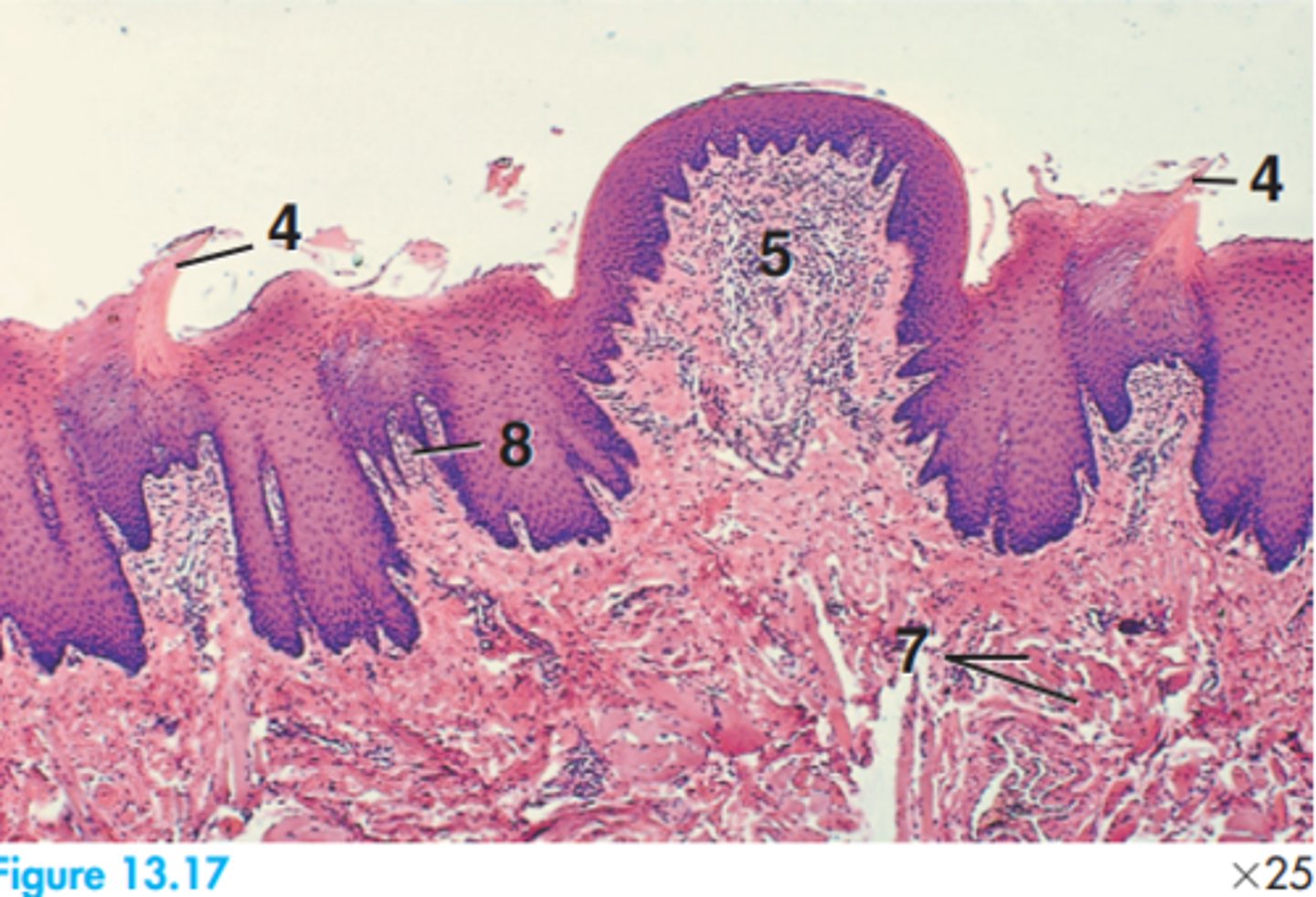
1 = Alveolar bone
4 = Blood vessel
5 = Cementum
9 = Dentin
13 = Fibre bundle
17 = Precementum
Label this canine tooth segment
Stratified squamous epithelia with mucous glands (except in carnivores where the glands are mixed).
What epithelium lines the oropharynx?
-External muscularis layer (skeletal muscle)
--Surrounded by adventitia
Describe the structural layers of the oropharynx
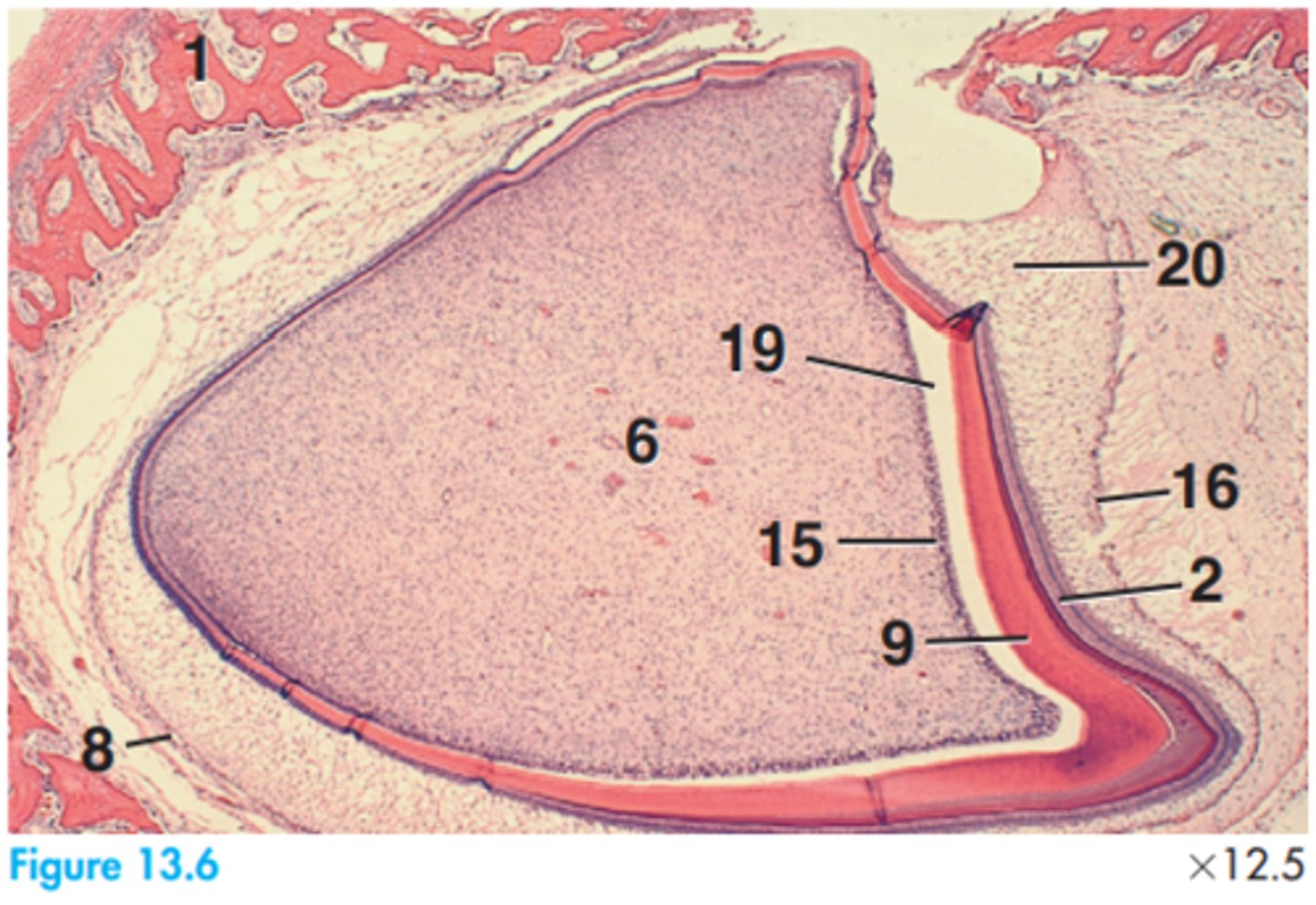
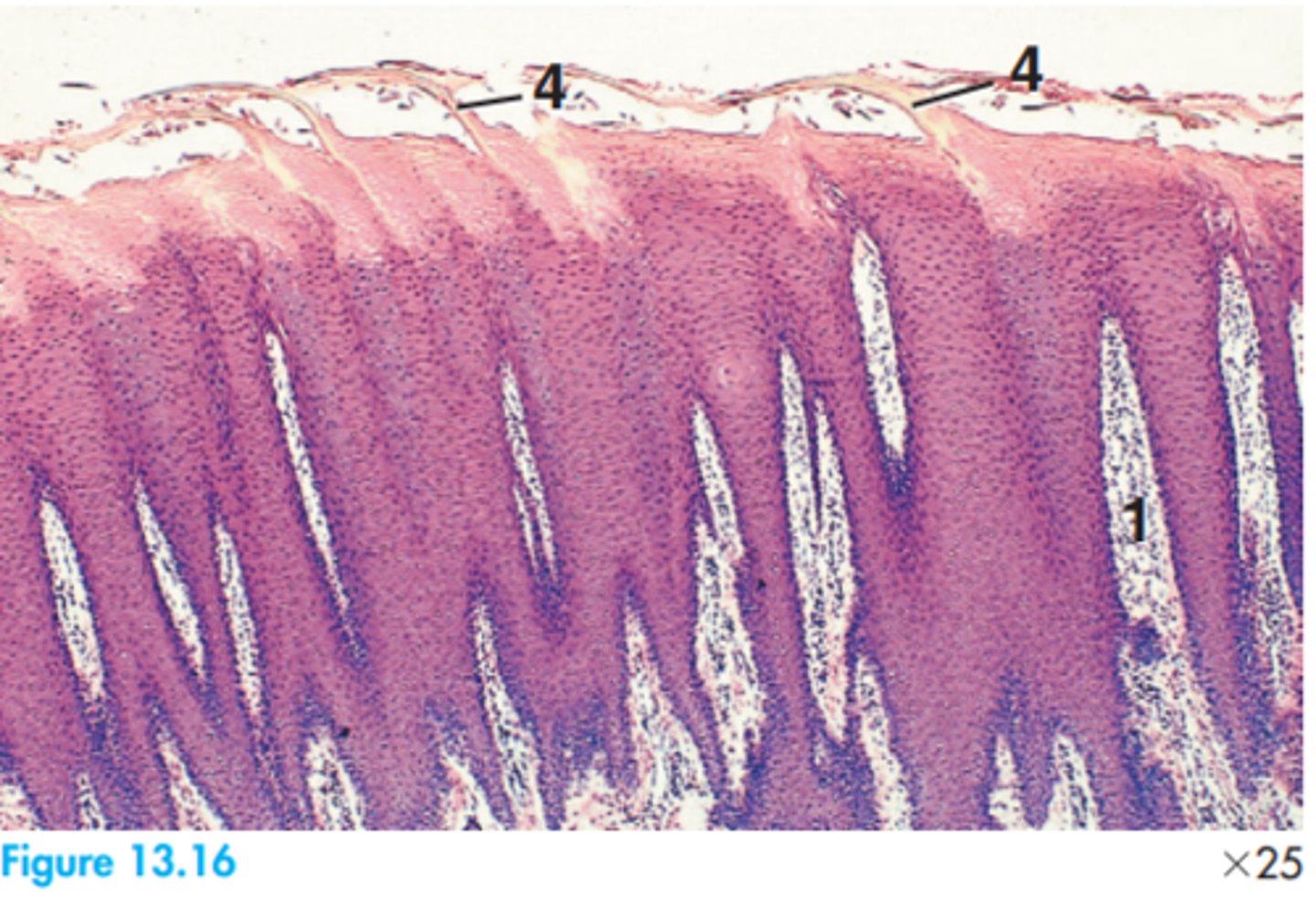
2 = Ameloblasts
6 = Dental papillae
8 = Dental sac
9 = Dentine
15 = Odontoblasts
16 = Outer enamel epithelium
19 = Space artifact
20 = Stellate reticulum
Label this slide of the developing permanent tooth of a dog
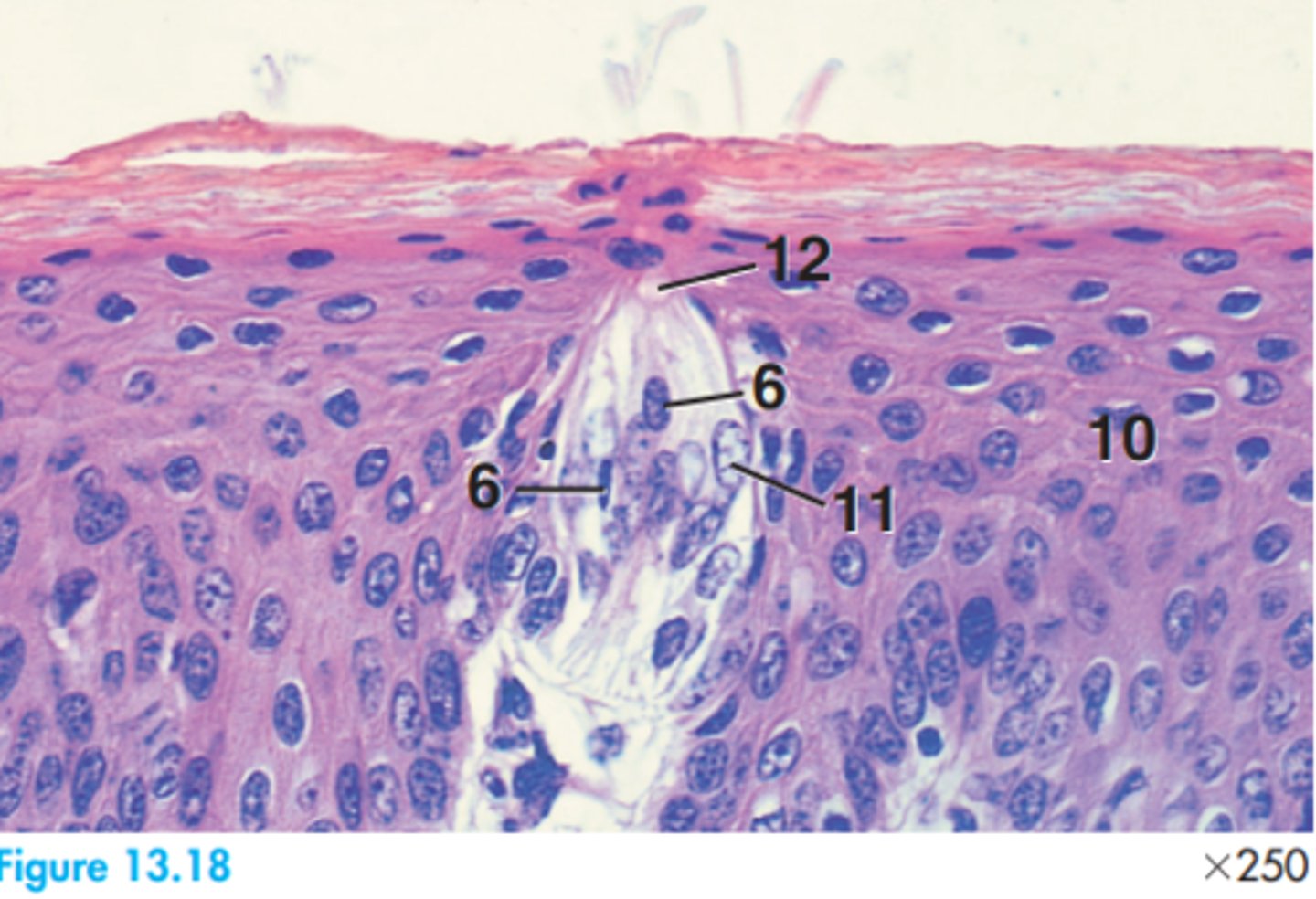
2 = Ameloblasts
6 = Dental papilla
9 = Dentine
10 = Enamel
15 = Odontoblasts
18 = Precementum
19 = Space artifact
Label this slide of the dentioenamel junction of a developing permanent tooth in a dog
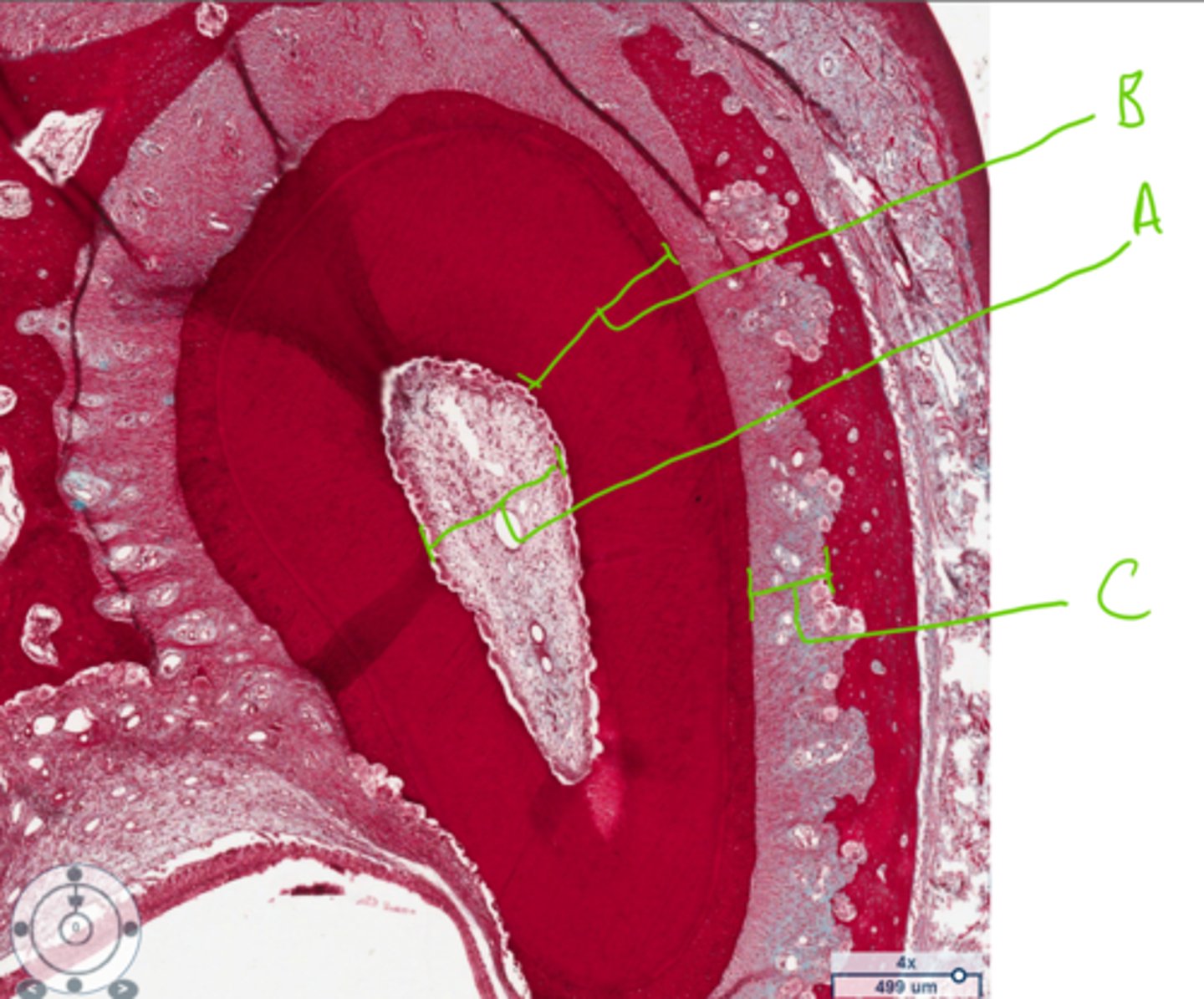
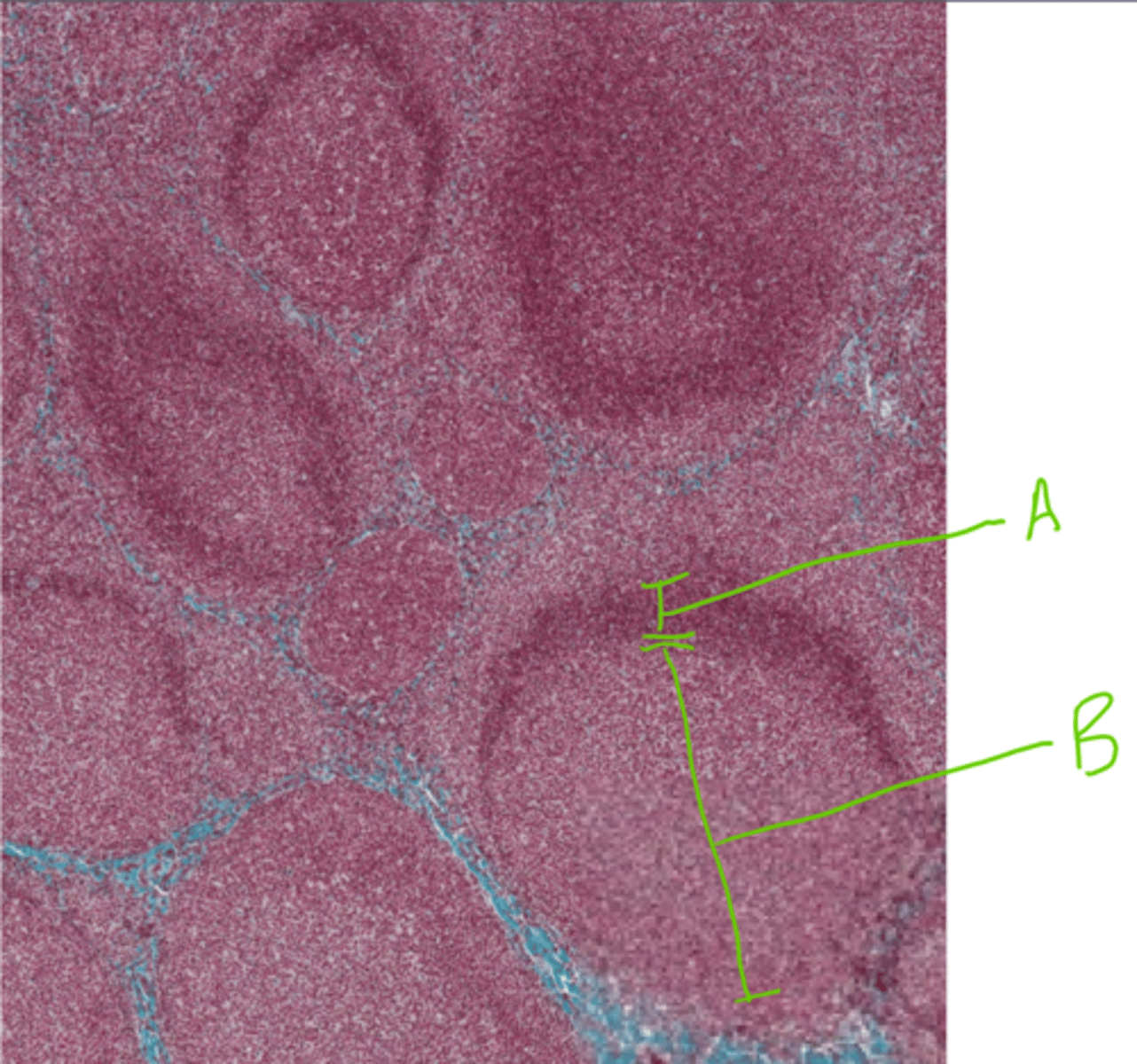
A = Osteon
B = Odontoblasts
What are these structures found in the tooth?
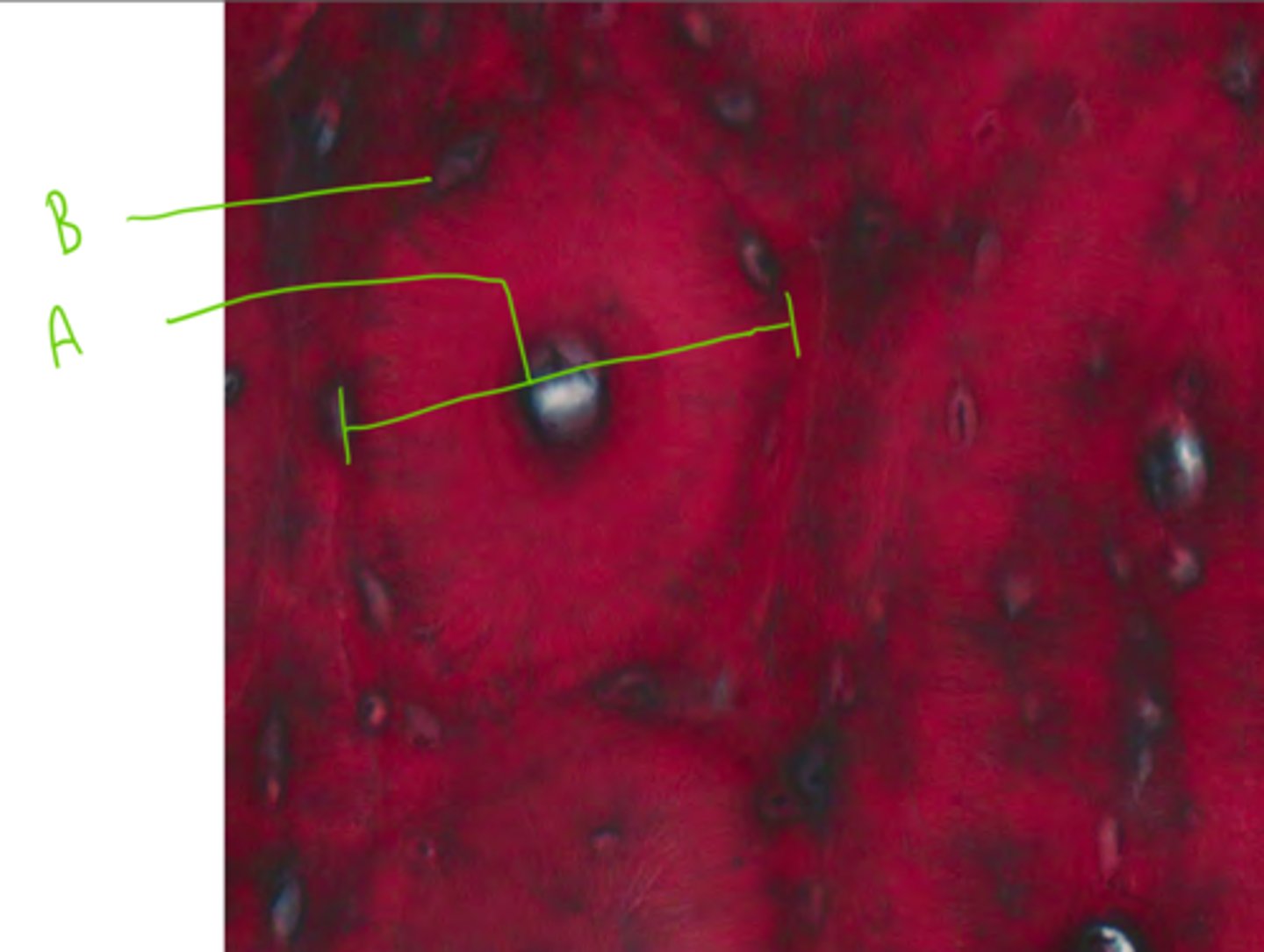
A = Rete pegs
B = Stratified squamous epithelium
C = Lamina propria
Label this slide from a dog permanent tooth
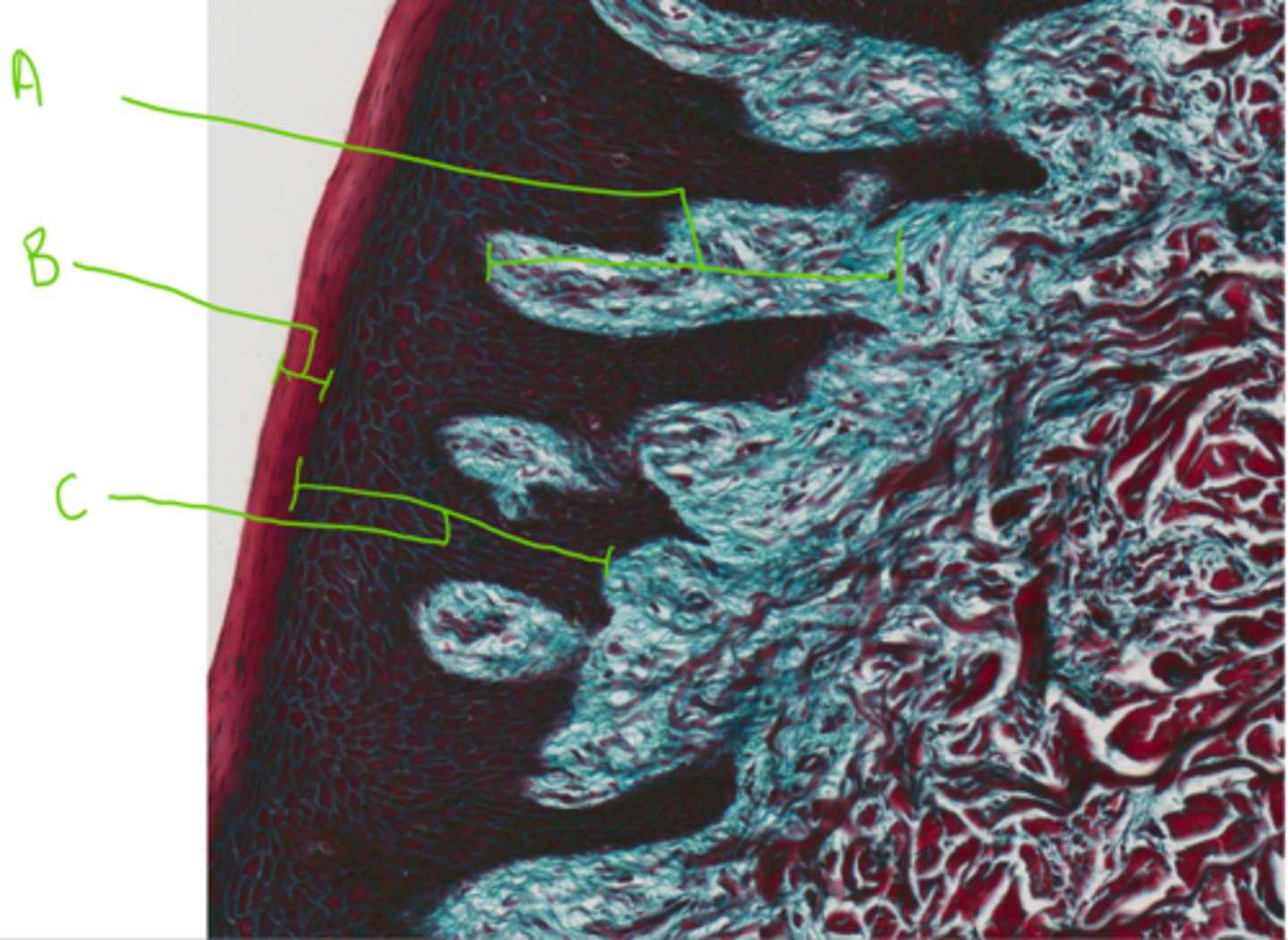
A = Arteriole
B = Lymph duct
C = Venule
D = Nerves
Label this slide of a dog permanent tooth
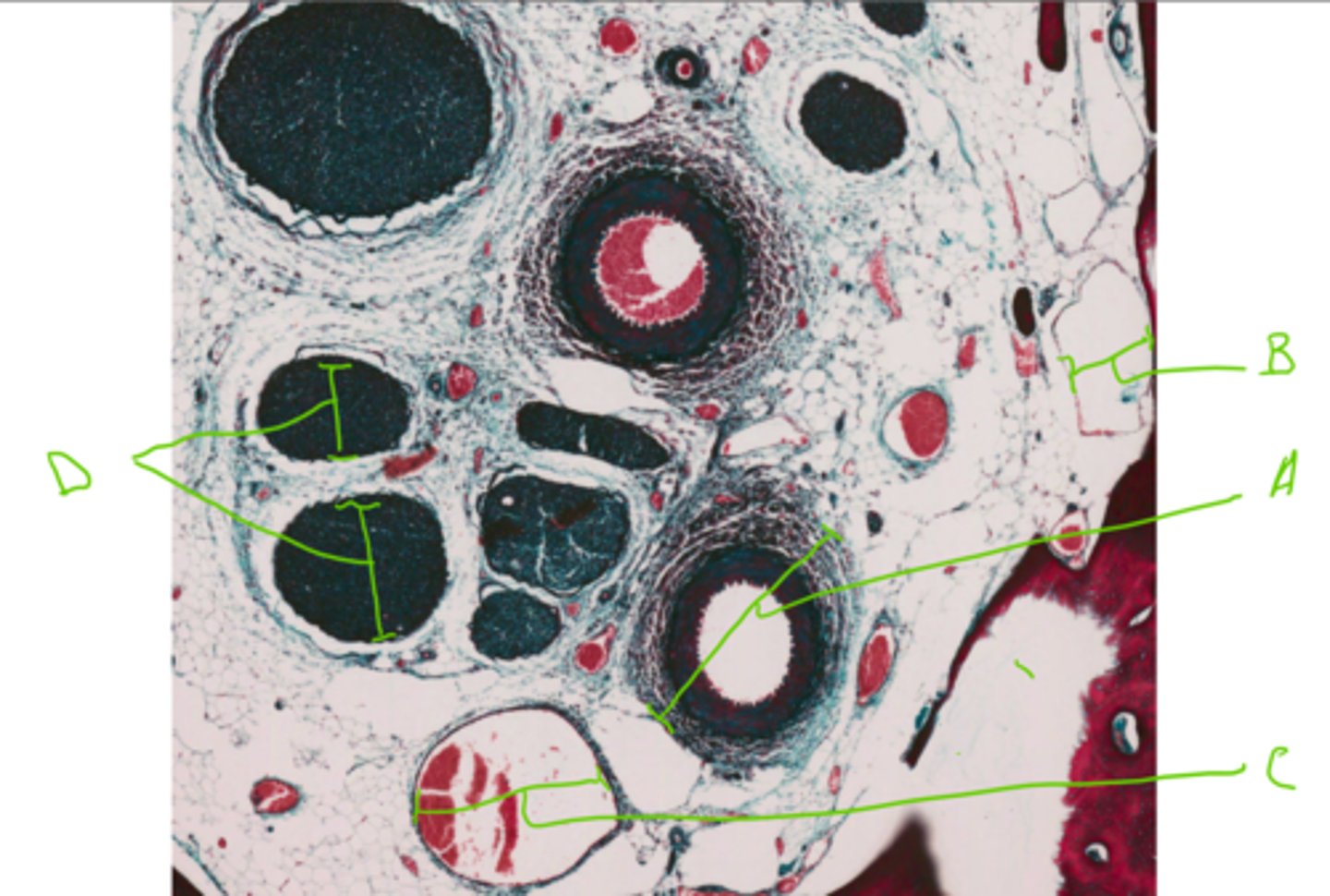
3 = Attachment epithelium
7 = Dental pulp
9 = Dentine
11 = Enamel space
12 = Free gingiva epithelium
14 = Lamina propria
15 = Odontoblasts
Label this slide from an upper deciduous tooth of a dog
-Collagen fibres
-Blood vessels
-Lymph vessels
-Nerves
-Mostly fibroblast cells
Describe the histological structure of the periodontal ligament
2 = Caudal connective tissue of papilla
3 = Rostral connective tissue of papilla
7 = Skeletal muscle
9 = Spine
Label this feline tongue
-Skeletal muscle
-Lingual glands
-Stratified squamous epithelium
What tissue layers are in the tongue?
1 = Connective tissue of papillae
4 = Projection of fuliform papilla
Label this horse tongue
6 = Nucleus of sensory cell
10 = Stratum spinosum
11 = Supporting cell (spore)
12 = Taste pore
Label this section of a taste bud from a horse
4 = Projection of filiform papilla
5 = Core of fungiform papilla
7 = Skeletal muscle
8 = Small papilla
Label this goat tongue
Circumvallate papilla
1 = Core of connective tissue
2 = Connective tissue
3 = Duct
4 = Lingual salivary gland
5 = Stratified squamous epithelium
6 = Taste buds
Label this goat tongue stating what papilla type it has
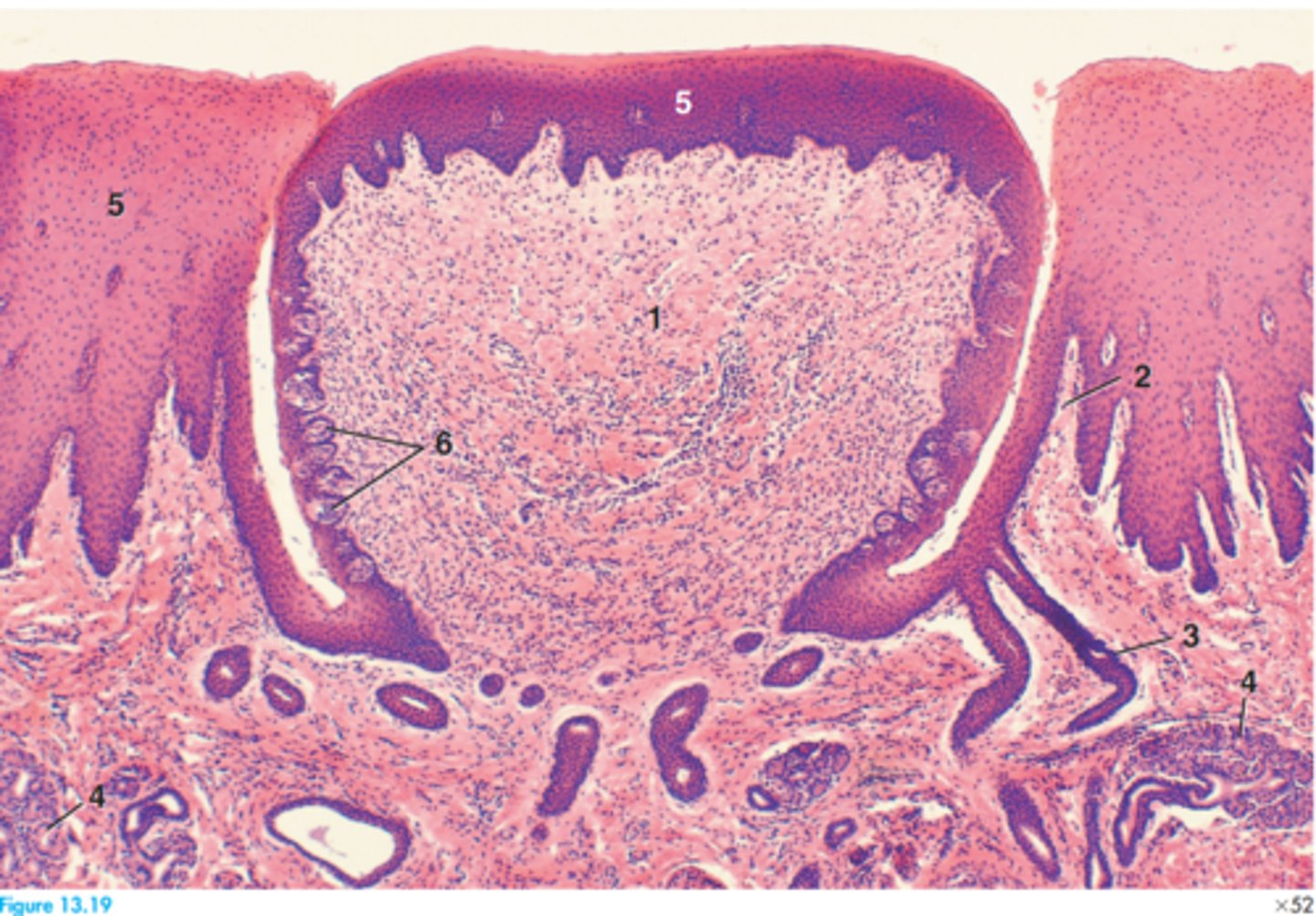
3 = Epithelium of filiform papilla
9 = Longitudinal skeletal muscle
10 = Transverse skeletal muscle
11 = Vertical skeletal muscle
Label this feline tongue
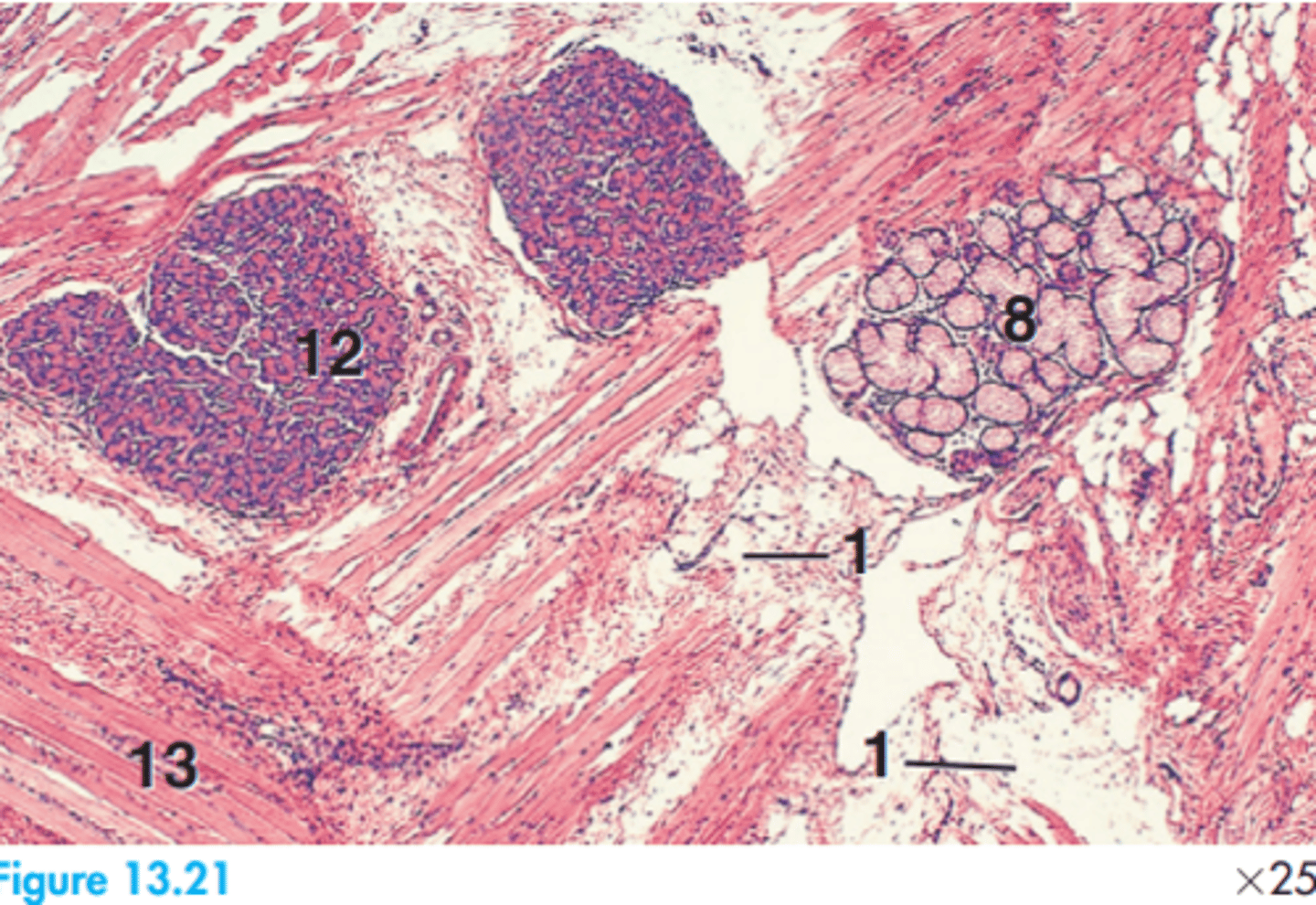
1 = Adipose tissue
8 = Mucous glands
12 = Serous gland
13 = Skeletal muscle
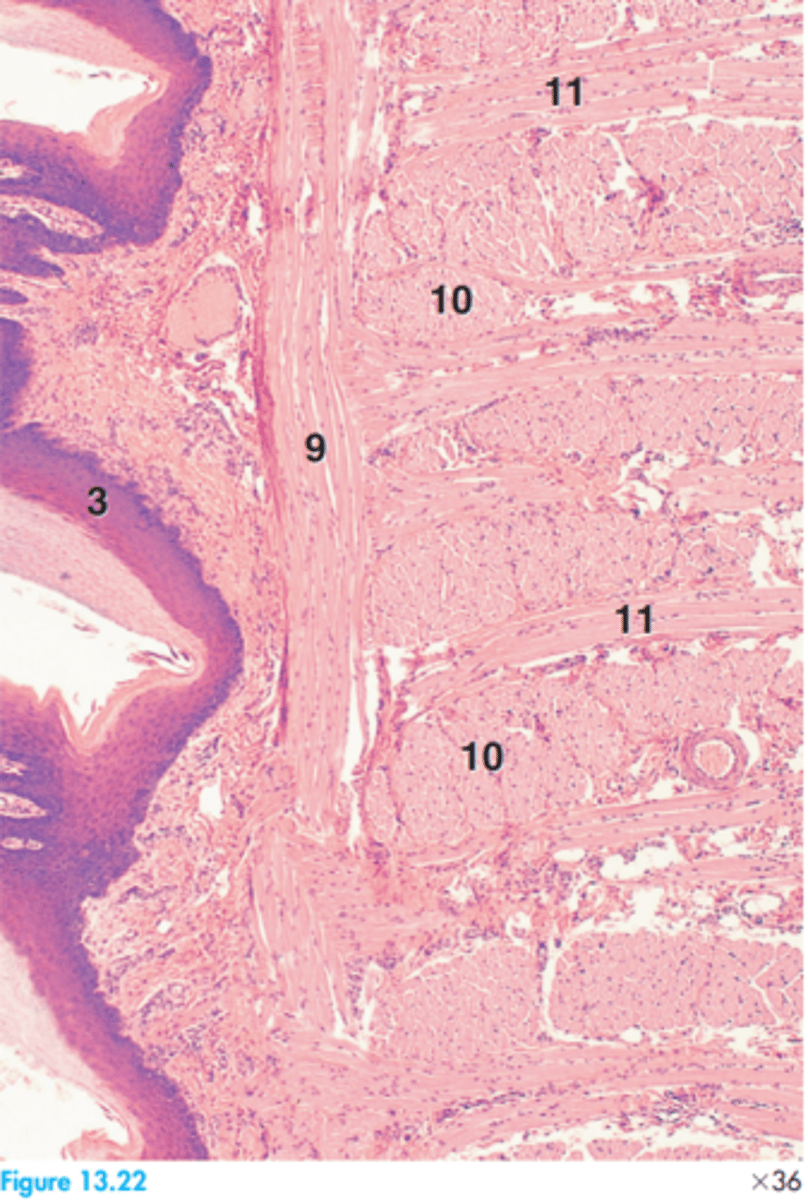
Label this tissue segment of a horse
-Serous nature
-Compound serous gland
What is the secretory nature of the lingual glands? What type of gland are the lingual glands?
Always simple cuboidal (except in reproductive system).
What type of epithelium lines glandular ducts?
Butterfly (:
What does a cross-section of a tongue typically look like?
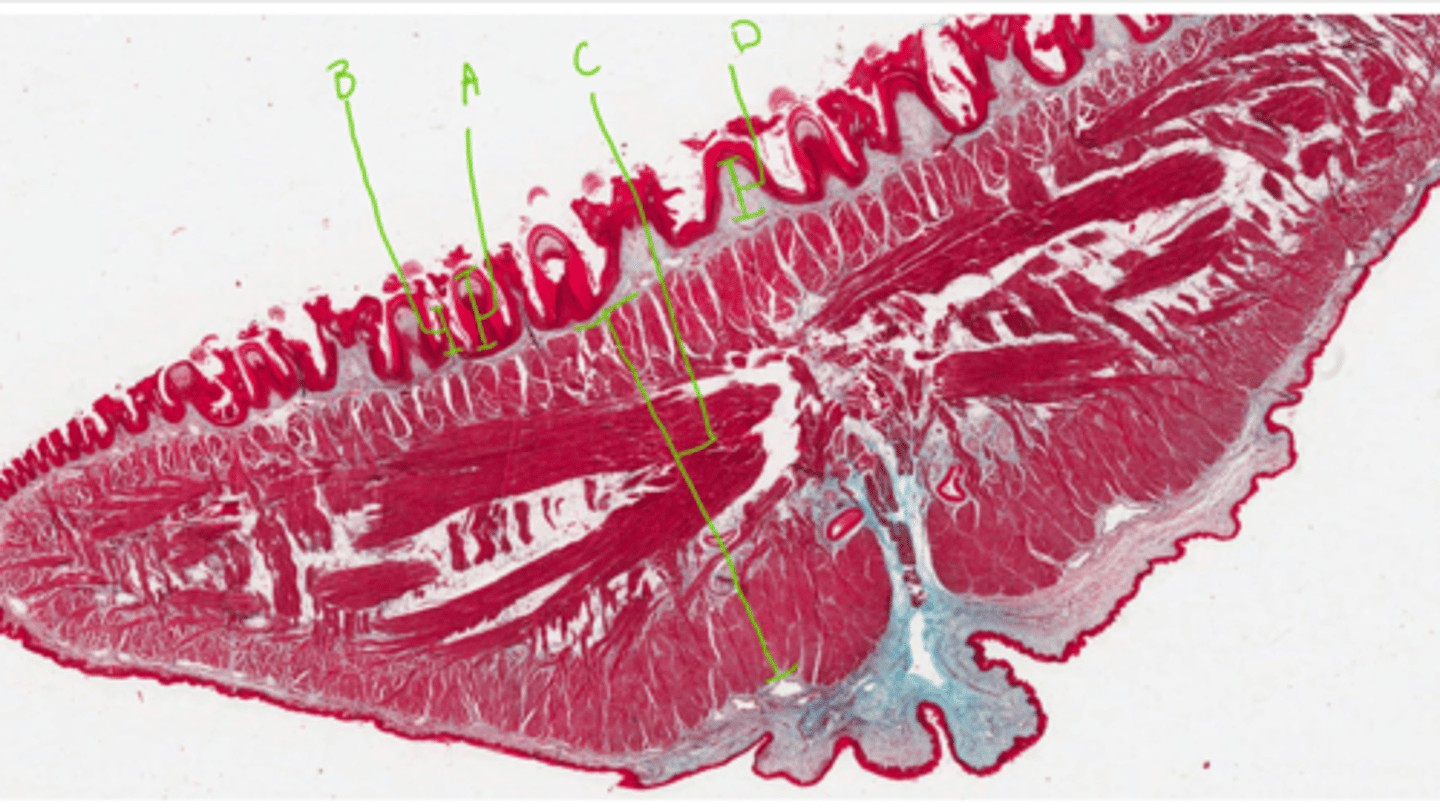
A = Filiform papillae (large keratinisation, especially in caudal)
B = Foliform papilla
C = Skeletal muscle fibres running in many directions
D = Dense irregular connective tissue
Label this feline tongue
A = Nerve
B = Artery
Label this segment from the feline tongue
Dorsal.
Is the surface with papillae of the tongue on dorsal or ventral?
No.
Does the ventral aspect of the tongue have papillae?
-Keratinised on both
-Thinner on ventral aspect
Describe the epithelial lining of the dorsal and ventral aspects of the tongue
Lingual frenulum.
What connective tissue structure holds the tongue to the mouth ventrally?
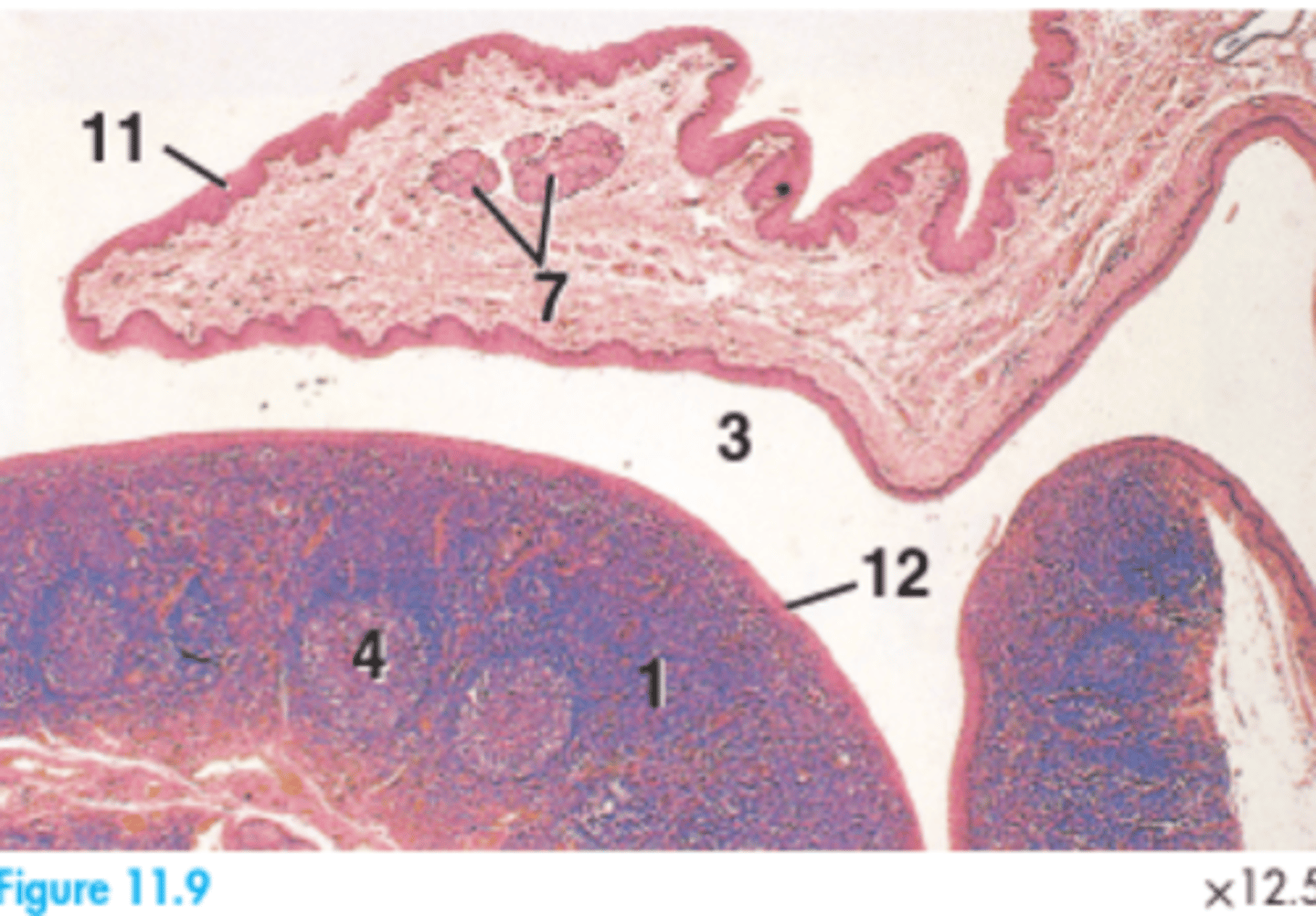
1 = Diffuse lymphatic tissue
3 = Fossa semilunar fold
4 = Lymphatic nodule
7 = Salivary glands
11 = Stratified squamous epithelium of semilunar fold
12 = Stratified squamous epithelium of tonsil
Label this canine palatine tonsil
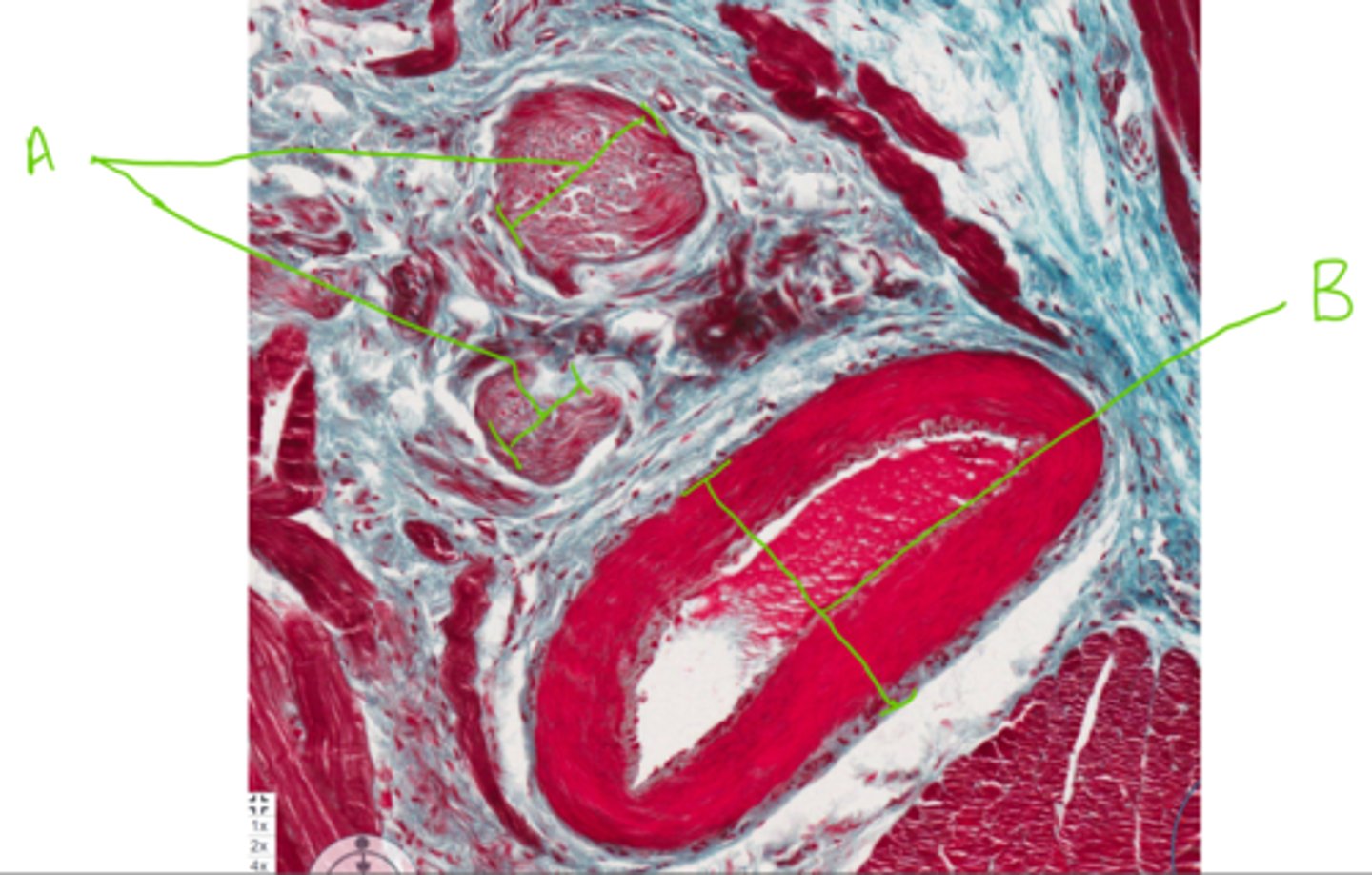
A = Lingual frenulum
B = Dense irregular connective tissue
Label this section of the tongue
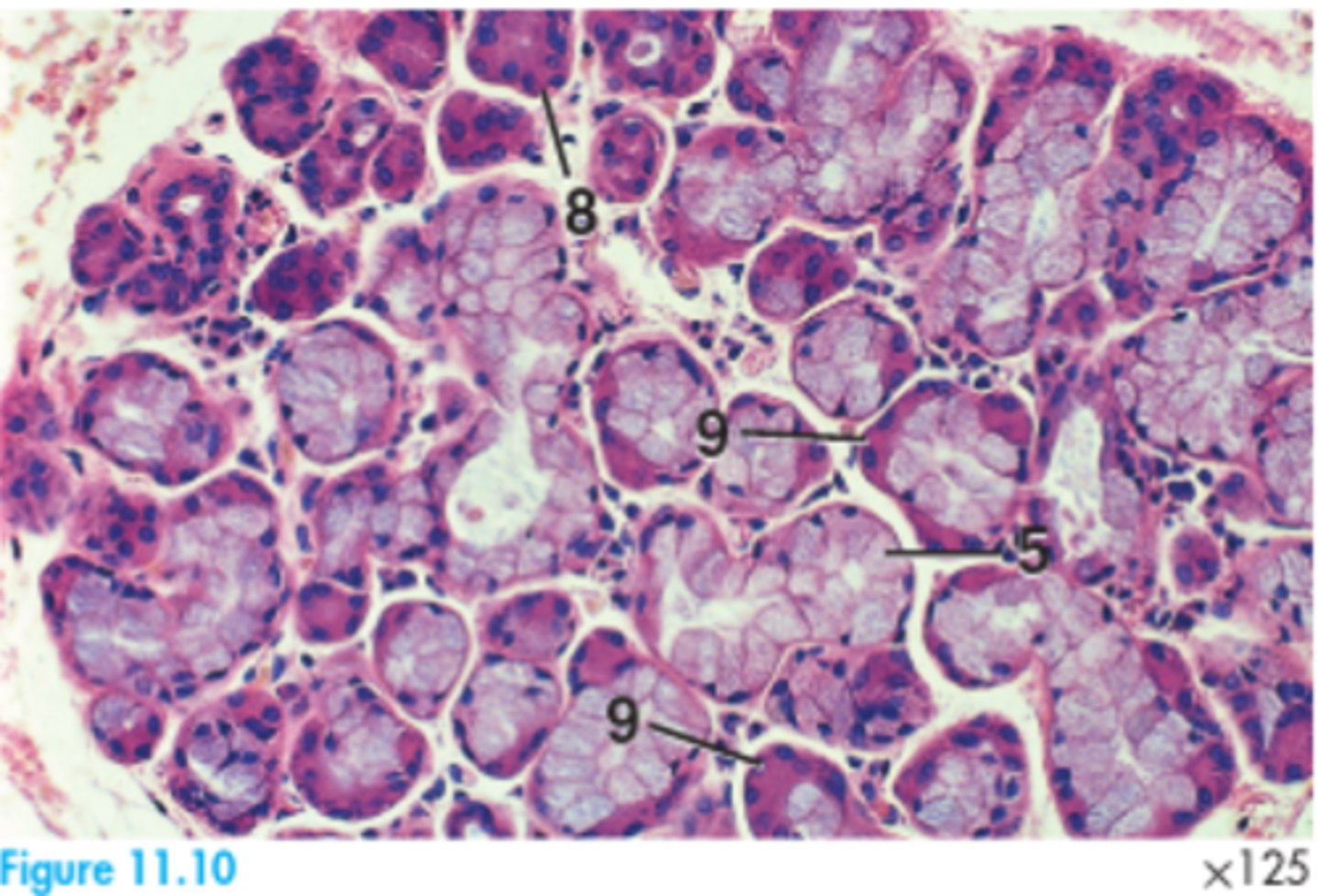
5 = Mucous acinar gland
8 = Serous acinar gland
9 = Serous demilune
Label this section of a canine palatine tonsil
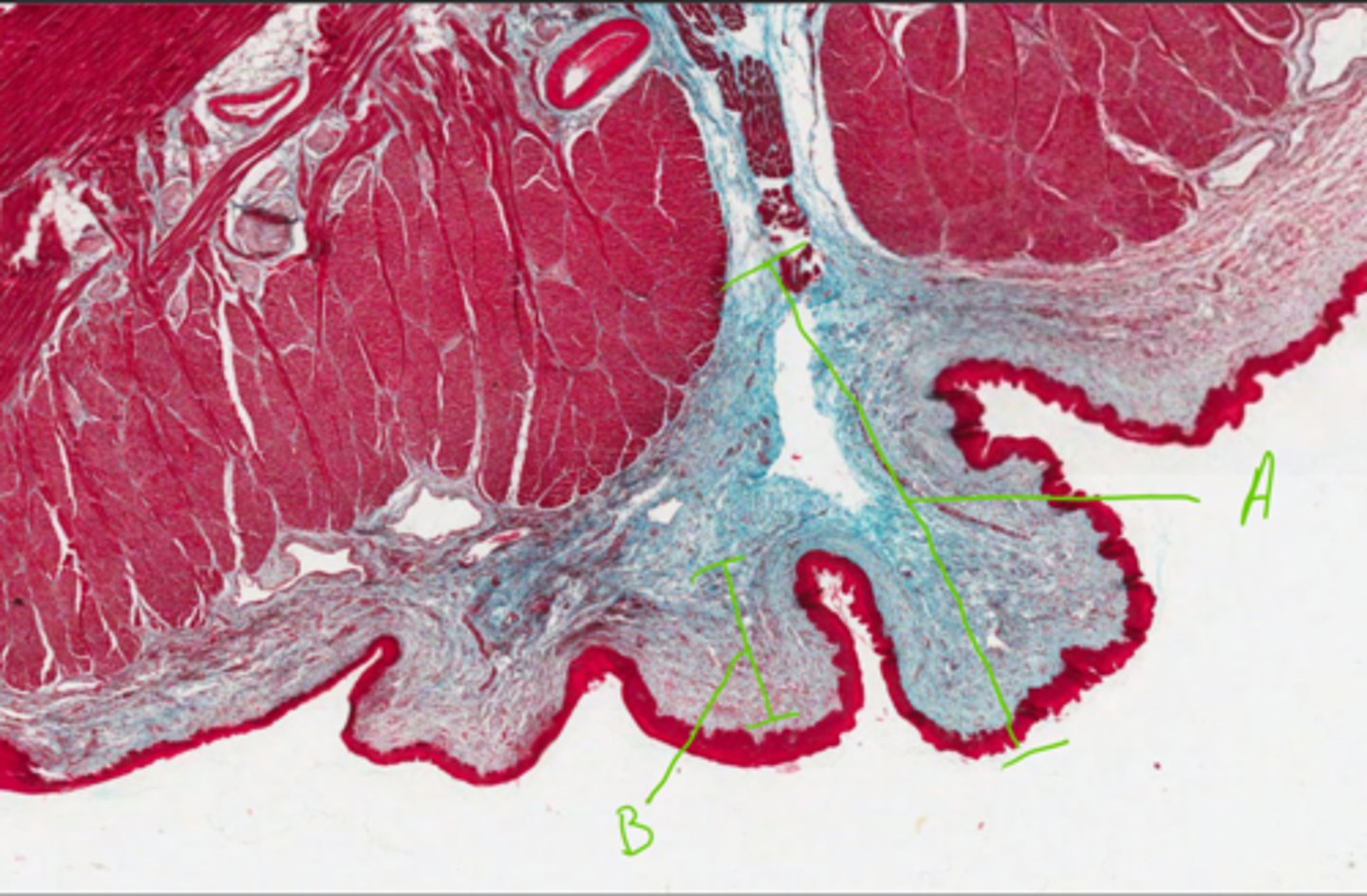
3 = Crypt
5 = Diffuse lymphatic tissue
7 = Lymphatic nodule
11 = Subscapular sinus
Label this equid palatine tonsil
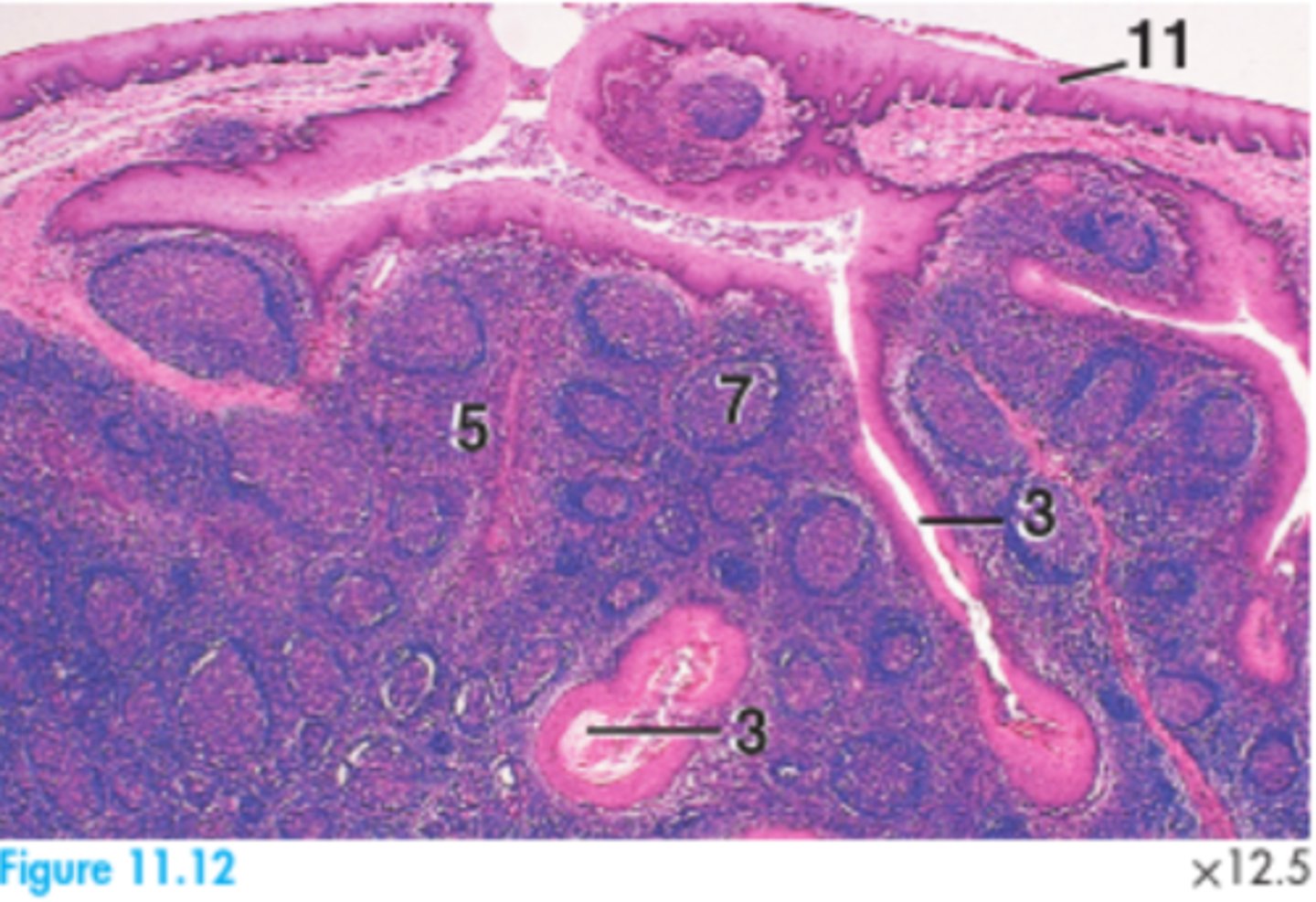
Base of the tongue and the dorsal aspect of the soft palate.
What is the anatomical location of the palatine tonsil?
Secondary lymphoid organ.
What type of structure is the palatine tonsil?
A = Mantle
B = Germinal centre
Label this section from the palatine tonsil
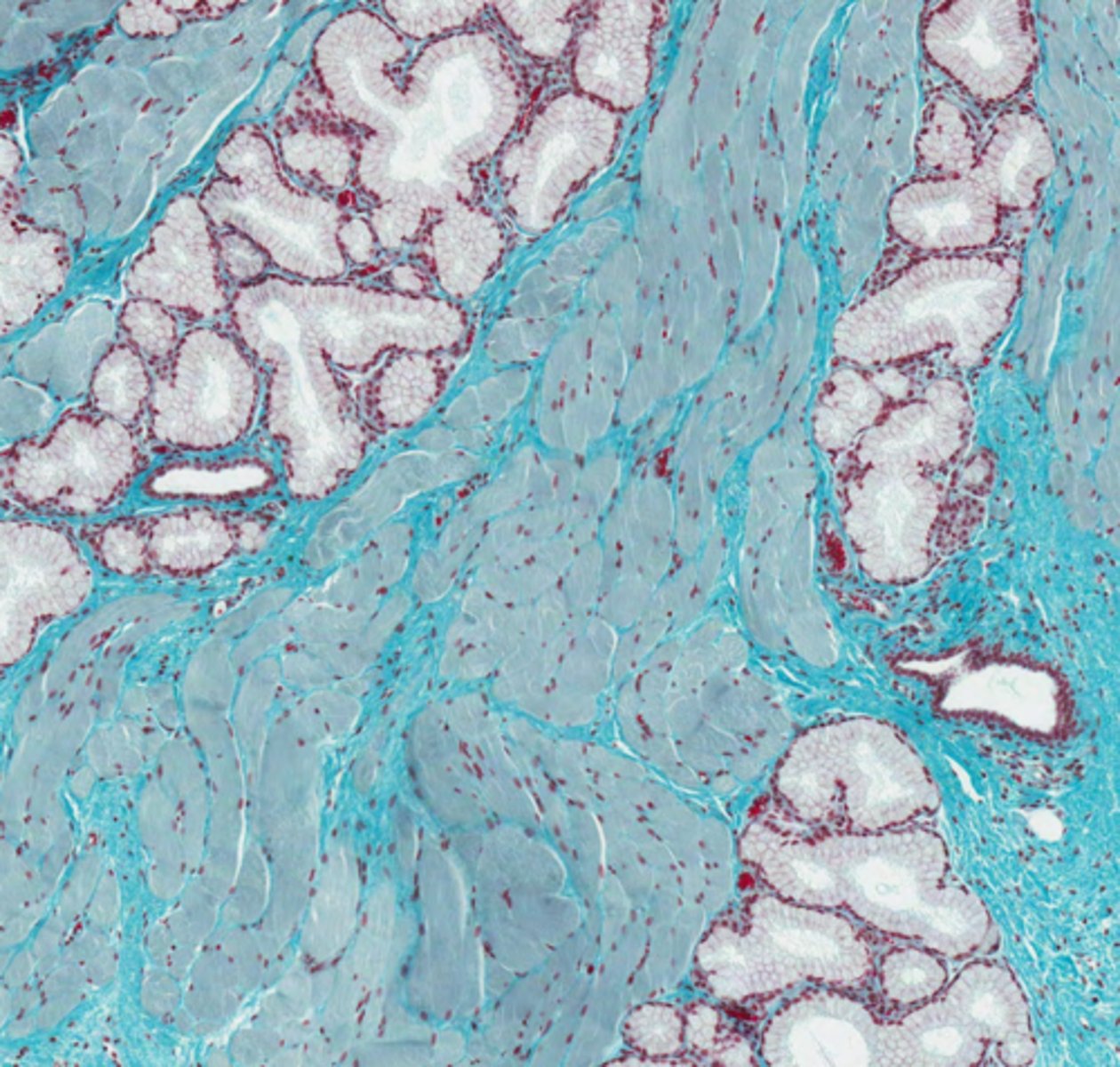
Compound tubular mucous secretory glands. Skeletal muscle surrounds them.
What glands are shown here? What is their shape? What tissue surrounds the glands?
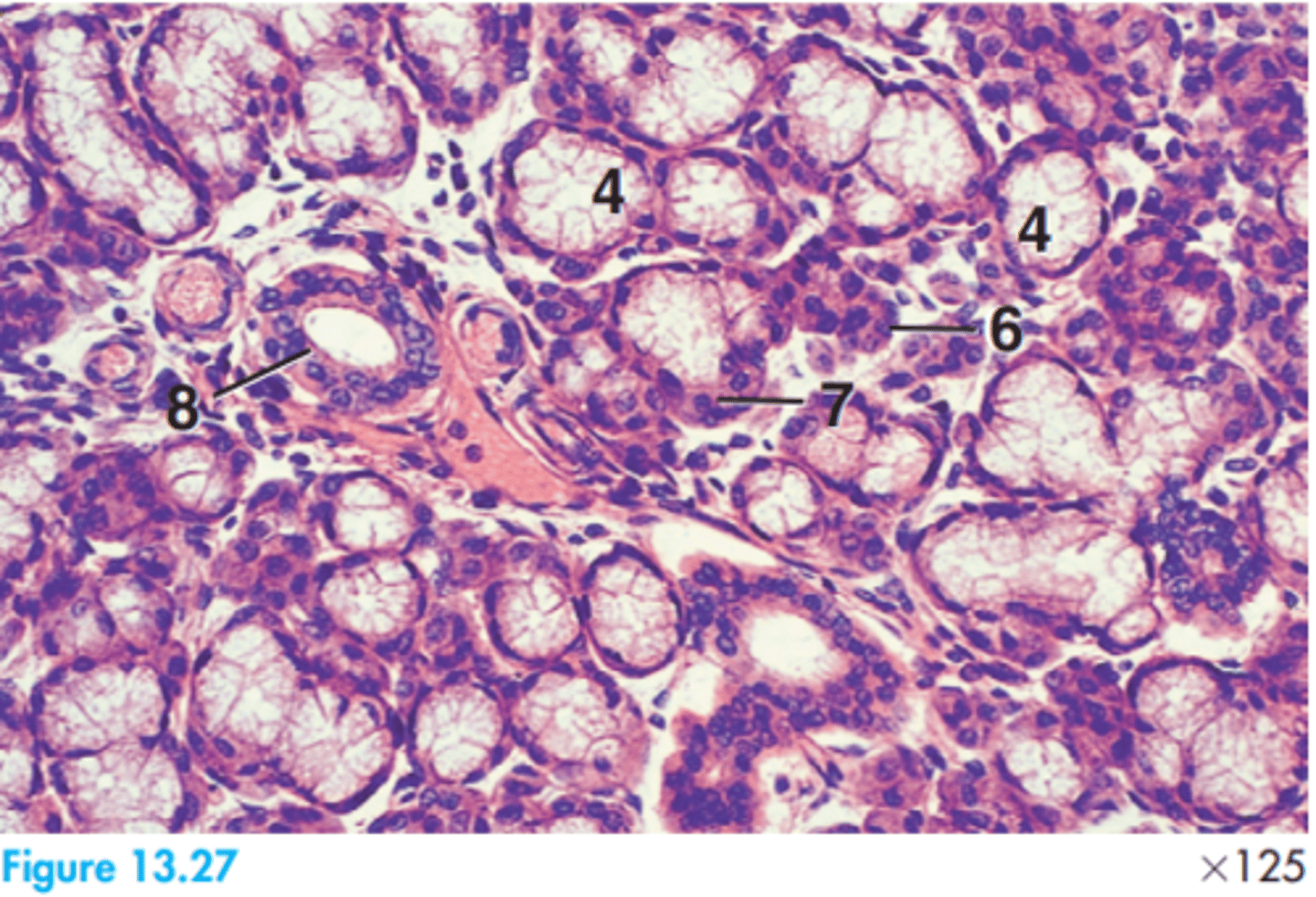
4 = Mucous acinus
6 = Serous acinus
7 = Serous demilune
8 = Striated duct
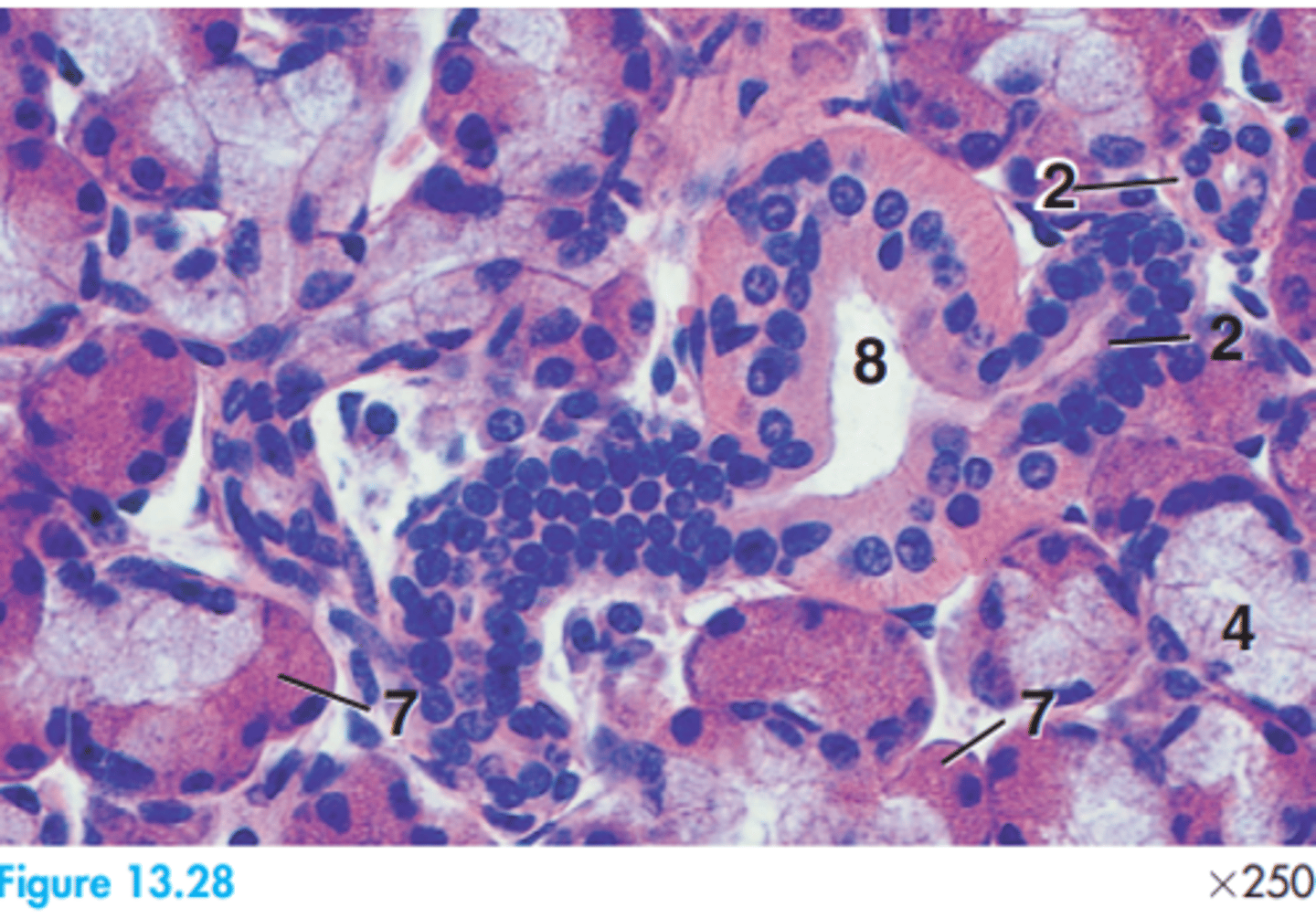
Glands are mixed compound.
Label this dog submandibular gland
2 = Intercalated duct
4 = Mucous acinus
7 = Serous demilune
8 = Striated duct
Label this sheep submandibular gland
3 = Interlobar connective tissue
6 = Serous acinus
8 = Striated duct
Label this dog parotid gland
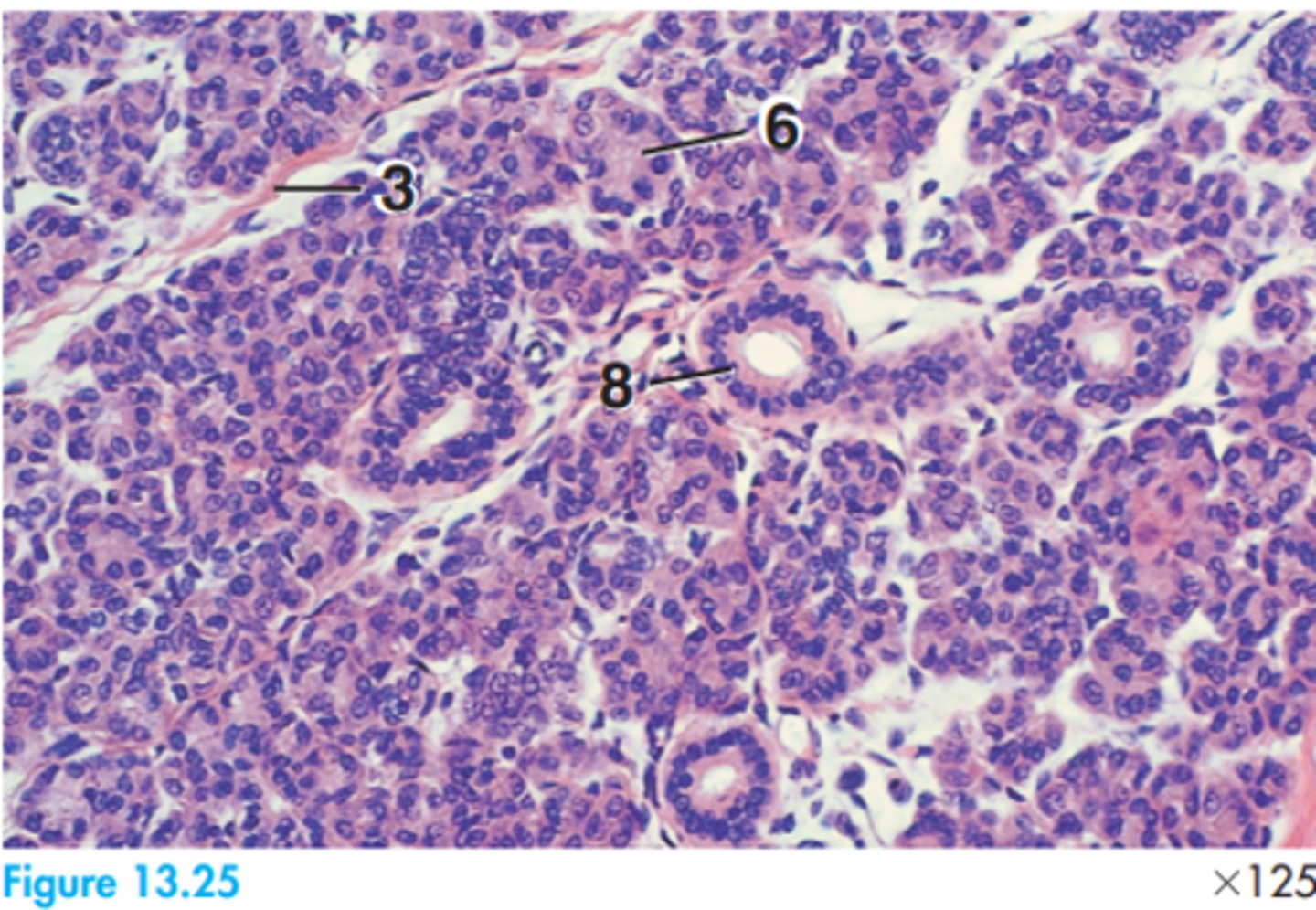
Serous secretory in nature.
What is the primary secretion nature of the parotid gland?
2 = Bone
5 = Cavernous vein
7 = Nasal cavity
9 = Pseudostratified
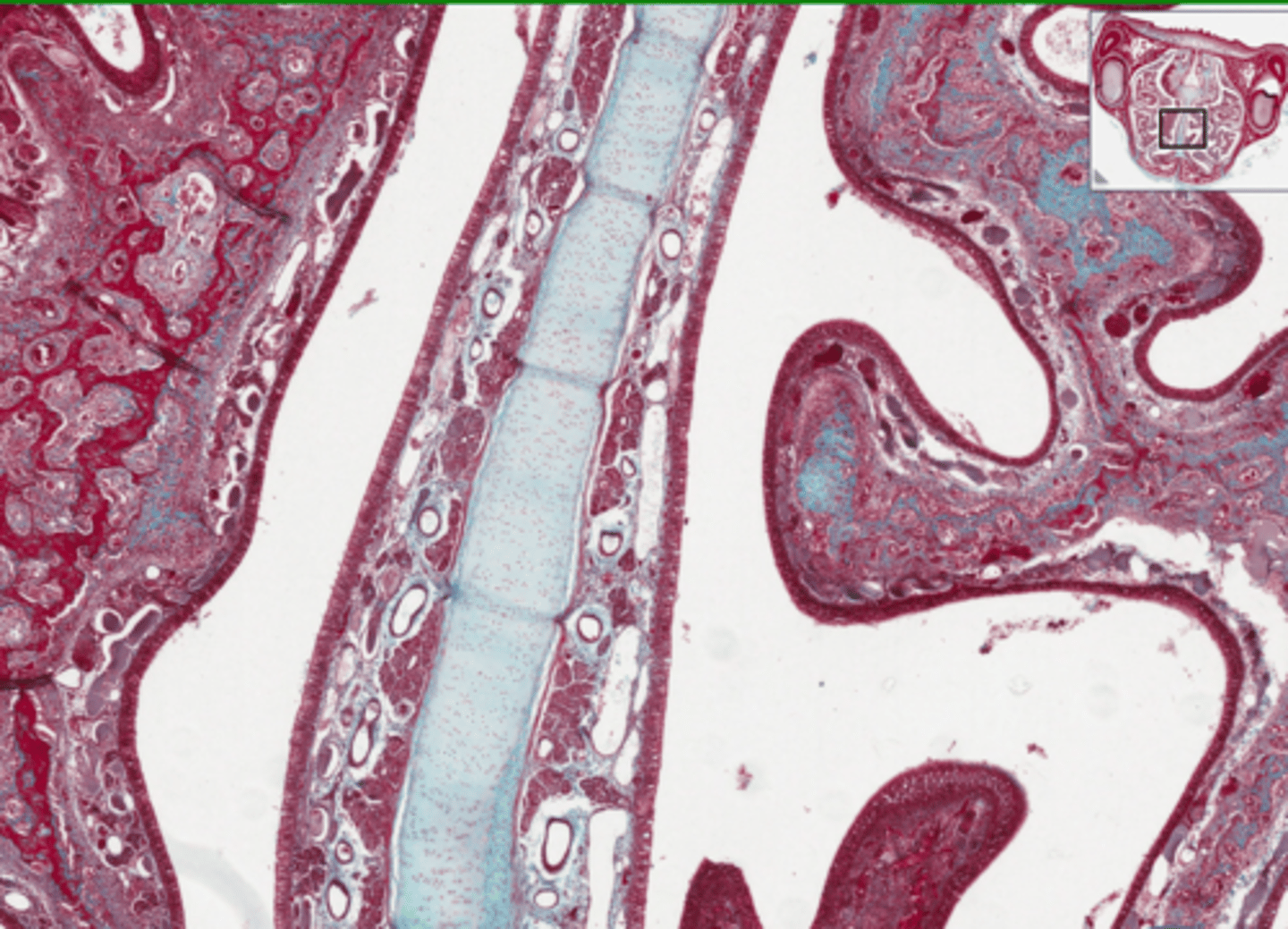
Label this portion of the dog nasal concha
A = Bony septum
B = Nasal conchae
Hyaline cartilage.
What connective tissue is likely to be found in the septum of the nose?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
What type of epithelium lines the respiratory system? (And hence the nasal cavity)
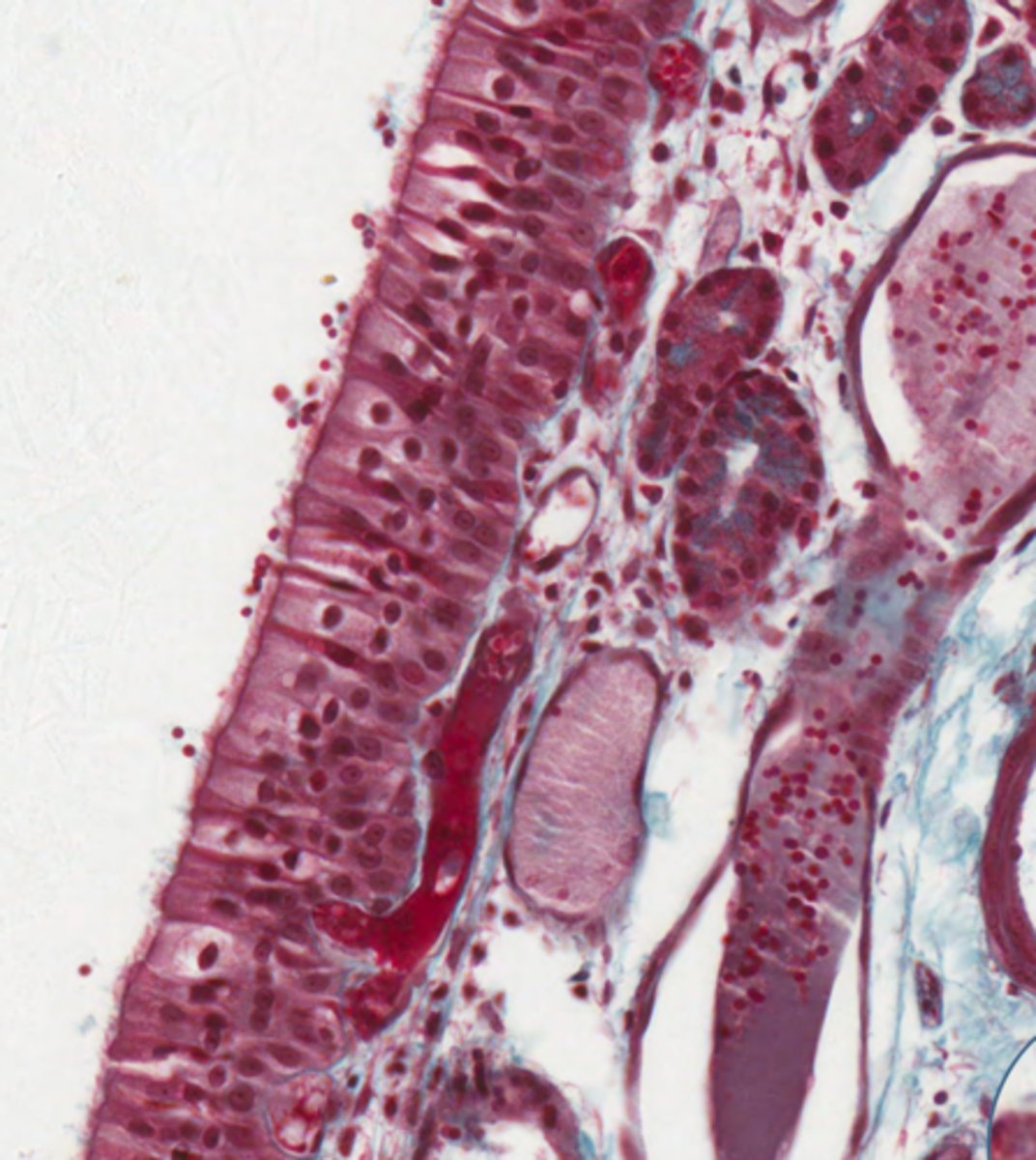
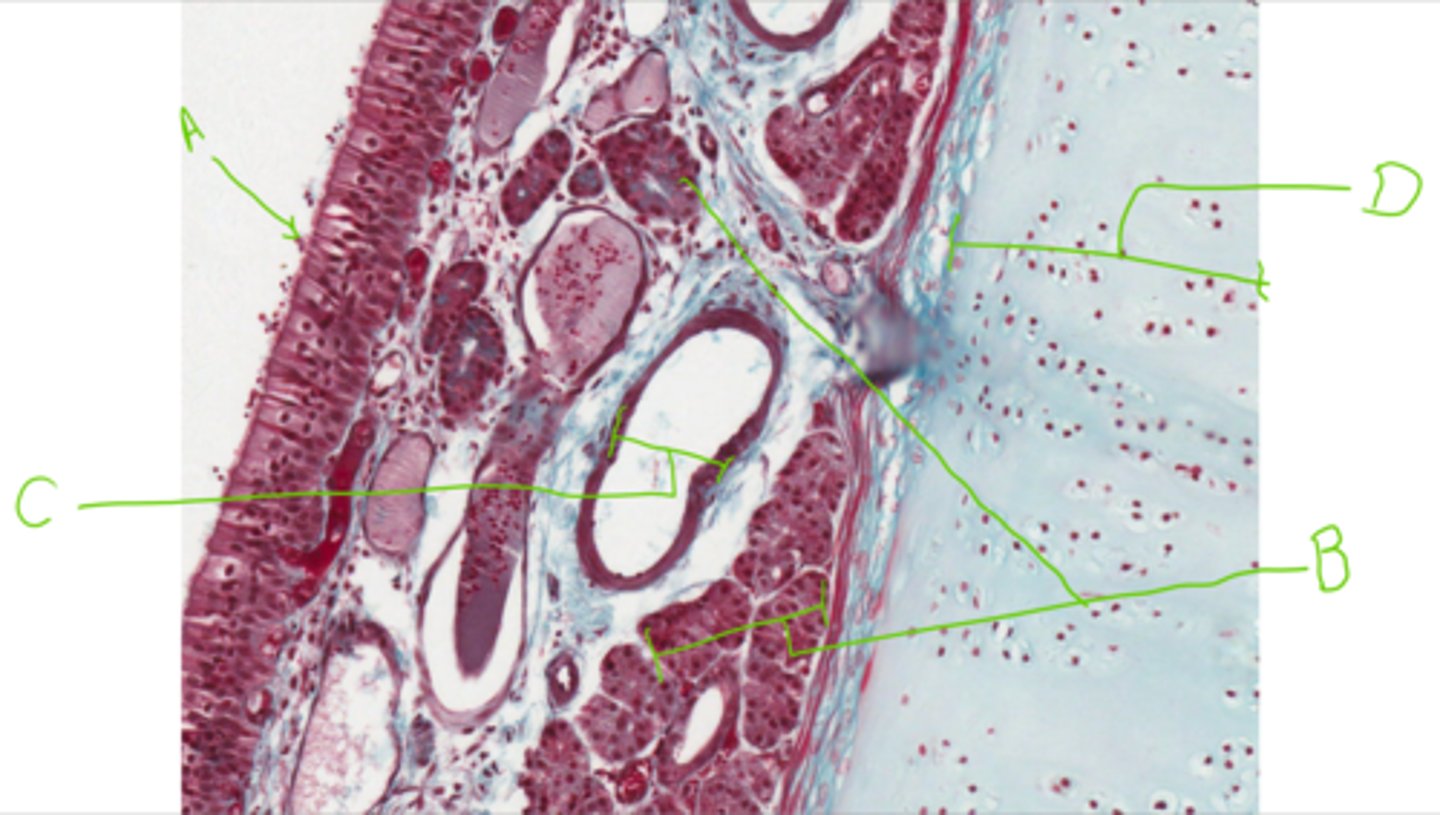
A = Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithleium
B = Simple tubular mucous glands
C = Blood vessel
D = Hyaline cartilage
Label this section from the nasal cavity
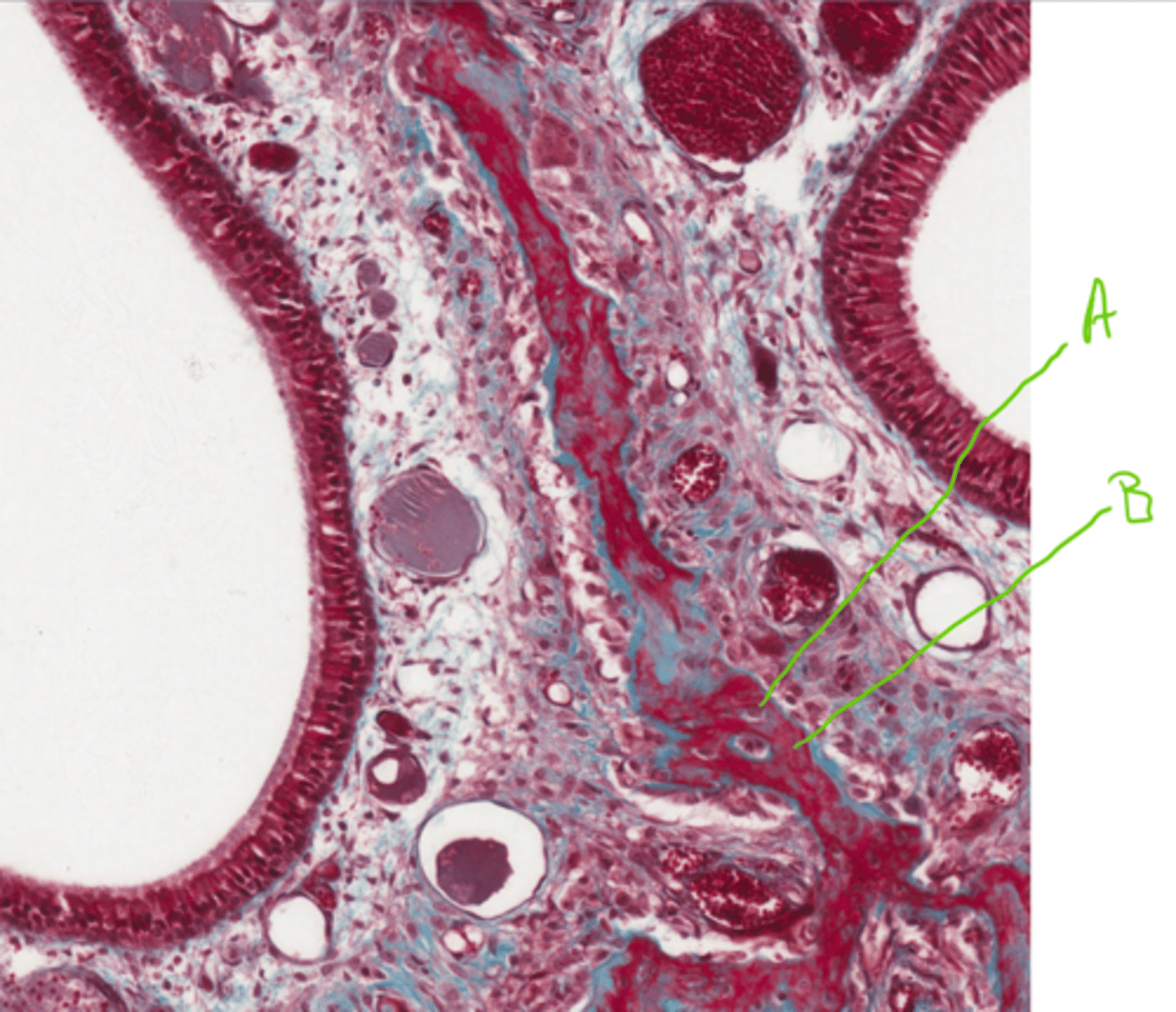
A = Mesenchyme cells
B = Bone matrix (uncalcified)
Label this section of a nasal conchae
Woven bone.
What type of bone is found in the nasal conchae?
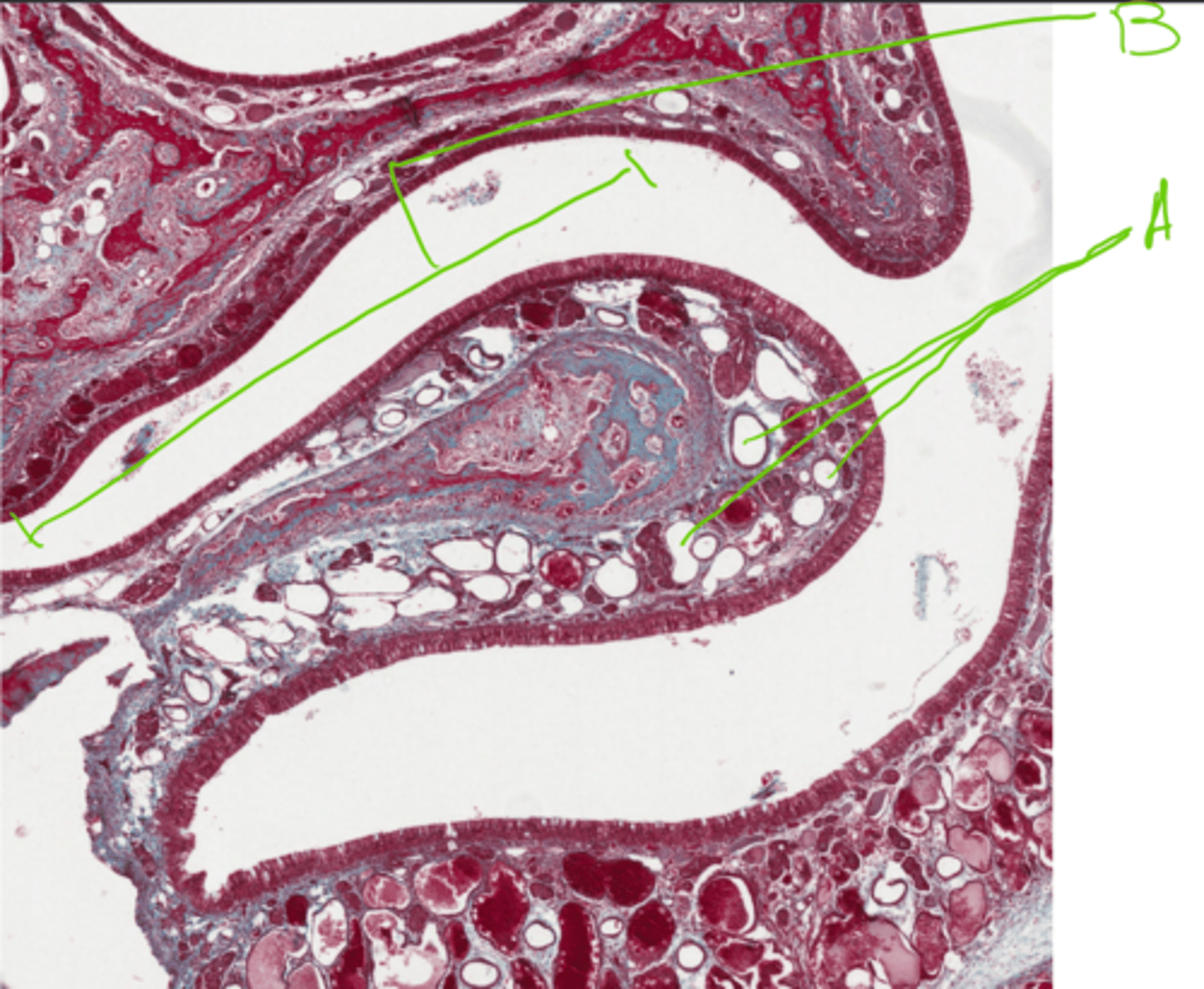
A = Blood vessels
B = Nasal concha
Label this section of the nasal cavity
A = Pulp (in pulp cavity)
B = Dentine
C = Cementum
Label this section from the nasal cavity