Metal AFO LLO2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
How do we measure toe in/out? Why?
Use the medial border of the foot for easier fabrication
How do you measure tibial torsion?
Measure height of malleoli to the floor with patient HORIZONTAL to the ground/schema.
Tibial torsion
Twist of the tibia - changes as we grow and mature
Toe out
Medial border relative to the line of progression - assuming knee is directed toward the line of progression
Are tibial torsion and toe out the same thing?
No - but tibial torsion can influence toe out
Excessive pressure and relative motion between the limb and the orthosis ______ with the degree and direction of the misalignment
increase
Relative motion is also controlled by the amount of ______ between the limb and orthosis as well as the effectiveness of the strap and shoe closures
friction
The ________ _________ will change the motion of the AFO with respect to the limb.
ankle angle
What anatomical landmarks would help you find the most accurate approximation of the anatomical knee joint center?
Medial tibial plateau and adductor tubercle of the femur
In a metal and leather AFO Schema, why is 9mm added to the medial malleolus clearance and 8 mm added to the lateral malleolus clearance?
To provide room for the mechanical ankle joint and slight coronal ankle motion
What anatomical landmark is used to determine the location of the mechanical ankle axis?
Distal tip of the medial malleolus
If the mid sagittal line intersects a point 1.5cm medial to the knee before it intersects a point 3cm medial to the ankle, then the knee position would be described as
Genu Valgum
T/F: Tibial torsion and Toe Out Angle are the same thing.
FALSE
The tibialis posterior muscle contributes to which motion(s)
Plantarflexion and inversion
T/F: When obtaining a tracing for a metal AFO it is important to trace along the medial lateral sides of the knee
TRUE
In the coronal plane, forefoot posture (Varus/Neutral/Valgus) is measured between the plantar surface of the metatarsal heads and ________________
A line perpendicular to the longitudinal bisection of the calcaneus
When obtaining a tracing of a patient's leg for a metal AFO - which of the following landmarks is not necessary?
A. greater trochanter
B. medial malleolus
C. Neck of the fibula
D. Arch of the Perineum
A. greater trochanter
When tracing a patients leg to make a schema, a bolster is placed behind the patients knee to
Prevent the calf musculature from splaying
Name the different directions of misalignment that can occur in an AFO
Anterior
Posterior
Distal
Proximal
How does a mechanical joint axis become too DISTAL
If the stirrup is too short
If the mechanical joint axis is too distal, what does that result in?
“pulling the foot down” into the shoe
Calf band sliding up in the leg
Is the mechanical joint axis preferred to more proximal or distal?
Distal - as it causes the least amount of issues
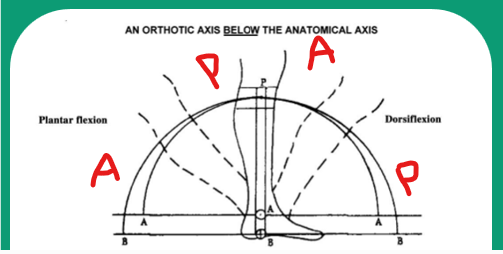
If the mechanical joint axis is distal relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient dorsiflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band moves ANTERIOR and PROXIMAL relative to the leg and resultant pressure is on the POSTERIOR aspect of the leg
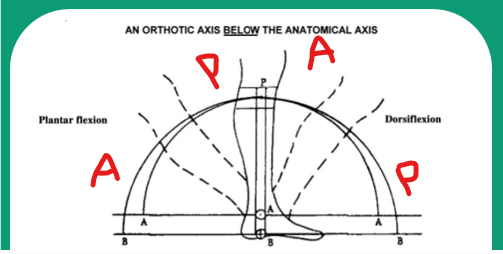
If the mechanical joint axis is distal relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient plantarflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band moves POSTERIOR and PROXIMAL relative to the leg and resultant pressure is on the ANTERIOR aspect of the leg
How does a mechanical joint axis become too proximal?
When a stirrup is too long
If the mechanical joint axis is too proximal, what does that result in?
Foot being “pulled out of the shoe” and the calf band sliding down the leg
When would the mechanical joint axis be preferred to be too proximal?
In children when fast growth is expected
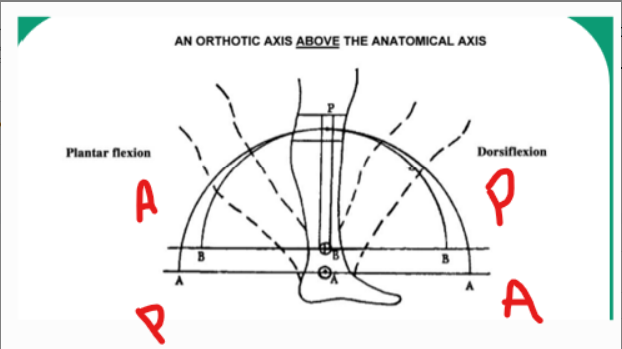
If the mechanical joint axis is proximal relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient dorsiflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will shift posteriorly and distally - pressure will be felt on the anterior portion of the leg
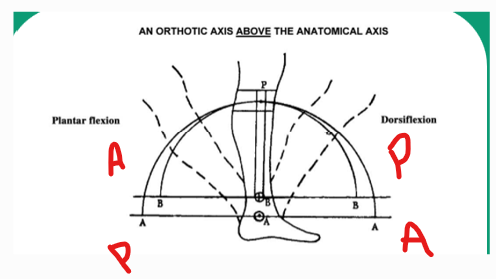
If the mechanical joint axis is proximal relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient plantarflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will move anterior and distal and pressure will be felt on the posterior portion of the leg
How does a mechanical joint axis move anterior relative to the ankle?
When the stirrup is placed too anterior in the shoe
Which plane are forces increased when the mechanical joint axis is too anterior relative to the ankle?
Increases transverse plane forces on the plantar surface of the foot
When the mechanical axis is too anterior OR posterior, it ___________ resistance to ankle joint motion and stiffness of the AFO
INCREASES
If the mechanical joint axis is anterior relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient dorsiflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will move posterior and proximal and pressure will occur on the anterior portion of the leg
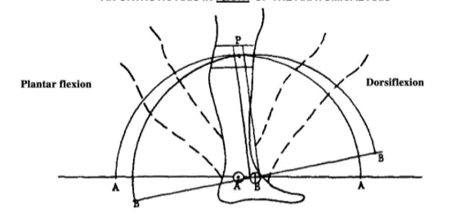
If the mechanical joint axis is anterior relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient plantarflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will move posterior and distal and pressure will be felt on the anterior portion of the leg
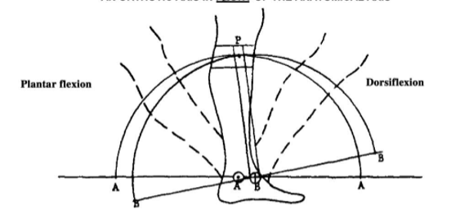
How would the mechanical joint axis end up too posterior relative to the ankle?
Occurs when the stirrup is attached too far posterior on the shoe
When the mechanical axis is too posterior, it _________ translational forces on the plantar surface of the foot
INCREASES
If the mechanical joint axis is posterior relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient dorsiflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will move anterior and distal and will feel pressure on the posterior portion of the leg
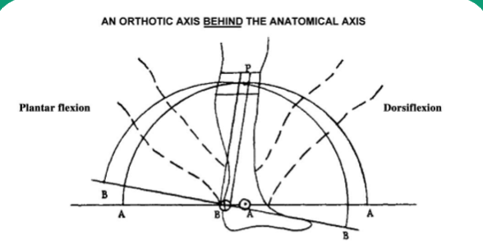
If the mechanical joint axis is posterior relative to the anatomical ankle center and the patient plantarflexes, where does the calf band move relative to the leg and what pressures occur on the leg?
Calf band will move anterior and proximal and will feel pressure on the posterior portion of the leg
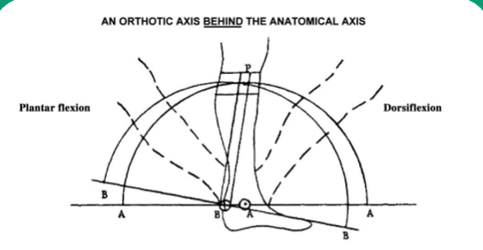
If the joints are not perpendicular, the weight is not transmitted vertically through the joints, resulting in _______ ________ and uneven wear of joint surfaces
sheer stresses
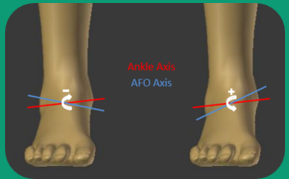
If the mechanical joint axis is not perpendicular to the mid-sagittal line, what can occur?
Unequal pressure distribution on the foot, causing callus formation
Increased wear of joints
Lateral instability from reduced shoe area contacting floor
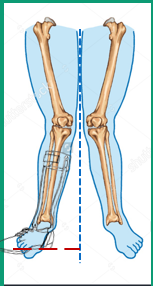
If the AFO is not aligned to accommodate genu valgum deformity, what can occur?
Excessive pressure on the medial surface of the foot
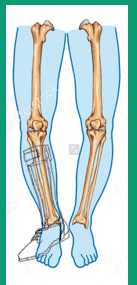
If the AFO is not aligned to accommodate a genu varum deformity, what can occur?
Excessive pressure on the lateral surface of the foot
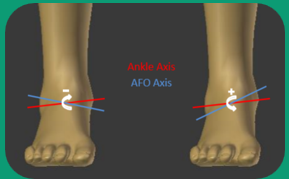
What occurs when internal rotation of the mechanical joint happens?
Pressure concentration on the lateral surface of the foot during gait
May cause a valgus or a forefoot pronation deformity
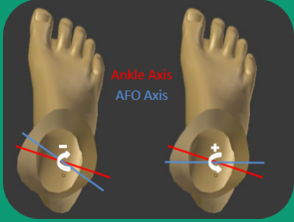
What occurs when the mechanical joints are externally rotated?
Pressure concentration on the medial surface of the foot during gait
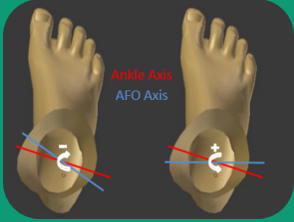
When there is rotation in the transverse plane from an AFO, what is it usually because of?
Incorrect tibial torsion alignment
Which plane can cause the most issues when there is misalignment?
Transverse plane
_______-__________ misalignments were found to have a much larger effect on the amount of calf band travel than proximal-distal misalignments
Anterior-posterior
Ankle joint is normally ____-____ degrees externally rotated
10-20 degrees
Toe out
Angle between long axis of the foot and line of progression - officially long axis of the second two, occasionally using the medial border but will be a smaller number
What factors influence toe out?
Hip rotation, tibial torsion, subtalar alignment, forefoot ABduction
What type of alignment is the most important?
Transverse alignment, as misalignment in this plane has the worst effects
Adults prefer to error toward….
The mechanical joint being too distal
Children prefer to error toward…..
the ankle joint being too proximal (for longitudinal growth
When determining what length of stirrup to order you must consider
Sole thickness X2
Height of ankle axis X2
Number of 90 degree bends
Heel width
T/F: When creating a schema, the mid-sagittal line represents a vertical line so that the heel line will be parallel with the ground even if the patient has a genu varum or valgum presentation at the knee
TRUE
What will the patient experience if the mechanical ankle joints are aligned distal to the anatomical joint?
Pulling the foot down into the shoe
Calf band sliding up the leg
T/F: When contouring the head of the stirrup, you should not bend the head within 1" of the ankle joint hole.
TRUE
T/F: The midpoint of a stirrup is always centered on the shoes heel width, even when a significant rigid hindfoot valgus deformity is present.
FALSE
T/F: The distance between a patients feet is assumed to be somewhere between 5cm - 10cm depending on the source.
TRUE
If the mechanical ankle joint is placed distal with respect to the patient anatomical ankle joint, the calf band will move more _________________ when the patient dorsiflexes.
Anterior and proximal
T/F: Tibial Torsion and Toe-Out are the same thing and can be used interchangeably.
FALSE
When placing mechanical ankle joints for a pediatric patient which mal-alignment is preferable?
Slightly proximal
Which alignment between the anatomical ankle axis and mechanical AFO ankle axis is the most important in a Metal and Leather AFO?
Transverse alignment
If the schema only considered the long axis of the tibia (did not extend to the perineum to establish a mid sagittal line) and the patient presented with Genu Varum. The resulting, un-corrected Metal AFO, would result with excessive pressure on the
Lateral surface of the foot