Visual computing part 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:24 PM on 1/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
What’s the location of pixel (x,y) in memory using rgb?
3 x (y x w + x)
2
New cards
What’s the location of pixel (x,y) in memory using greyscale?
(y x w + x)
3
New cards
What do HSL and HSV stand for?
Hue, saturation, lightness/value.
4
New cards
Fourier transform linearity
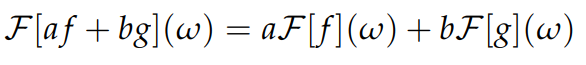
5
New cards
Fourier transform shifting
g(x) = f(x-a)
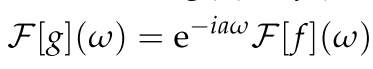
6
New cards
Fourier transform modulation
g(x) = e^{iax} f(x)
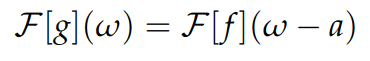
7
New cards
Fourier transform scaling
g(x) = f(ax)
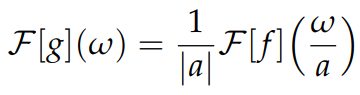
8
New cards
Fourier transform differentiation
do (iw)^n for higher order derivatives
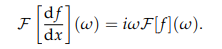
9
New cards
Fourier transform convolution
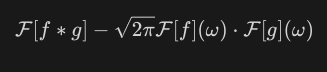
10
New cards
What is the relation between focus(f), object distance(u), and image distance(v)
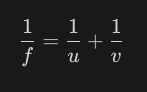
11
New cards
What are the two types of image sensor?
CCD and CMOS
12
New cards
How do LCD displays work?
Twist polarisation, max energy = 90 degress, min light
13
New cards
How do we workout total number of colour for an 8-bit image?
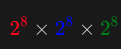
14
New cards
How do we distribute quantisation error over multiple pixels?
Error diffusion!
15
New cards
What is a horizontal gradient sobel filter?
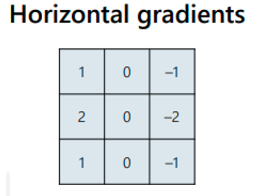
16
New cards
What is a vertical gradient sobel filter?
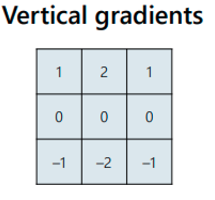
17
New cards
What is a diagonal gradient sobel filter?
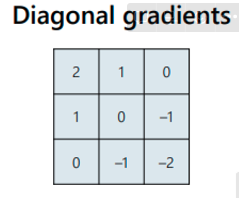
18
New cards
How does erosion work?
Only keep a pixel white if all surrounding pixels are white.
19
New cards
What is opening?
erosion then dilation
20
New cards
What is closing?
dilation then erosion
21
New cards
What is euler’s formula?
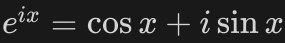
22
New cards
What is the Fourier transform useful for?
* Low and high pass filtering
* Linear filtering
* Removing structured noise
* Compression
* Linear filtering
* Removing structured noise
* Compression
23
New cards
What is the complexity of the fourier transform?
naive O(n^2), can split into two inputs of size n/2 which gives us O(n \\log n)
24
New cards
What is uniform scaling?
Scalar is the same for each component (axis)
25
New cards
Formula for anti-clockwise rotation?
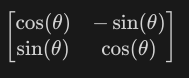
26
New cards
Formula for clockwise rotation?
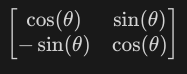
27
New cards
Formula for shear/skew
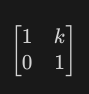
28
New cards
What are projective transformations? How do we do them?
1. Parralel lines are not preserved
2. Fill in the bottom row of transformation matrix
29
New cards
What is the formula for a 3d rotation about x axis?
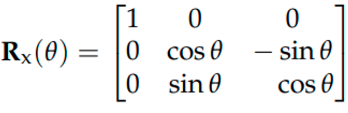
30
New cards
What is the formula for a 3d rotation about y axis?
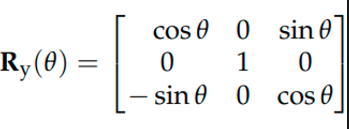
31
New cards
What is the formula for a 3d rotation about z axis?
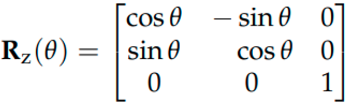
32
New cards
How do we project a 3d transformation through a pinhole onto the image plane?
1. Apply the transformation based of the focal length, and then transform so the result is in the top right, this is called the **intrinsic camera matrix**.
2. We then add a 3d transform from world to camera-co-ordinates.
33
New cards
What is the difference between perspective and orthographic projection?
Perspective parralel lines don’t stay parallel, orthographic they do
34
New cards
What are the different ways we can represent 3d projections?
* 3x3 matrix, not a minimal representation
* Euler angles, minimal parametisation, has gimbal lock
* Axis- angle, no gimbal lock minimal representation
* Euler angles, minimal parametisation, has gimbal lock
* Axis- angle, no gimbal lock minimal representation
35
New cards
What is openGL?
is cross-language/platform and is most widely used and supported
36
New cards
What is webGL?
is a JavaScript API this is based on OpenGL but can run in browser and dosen’t need to be compiled
37
New cards
What is three.js?
is an easier to use wrapper for webGL.
38
New cards