MRI Exam 4
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What causes aliasing?
under sampling
What does the eye use to detect light?
Rods and Cones
How does the phase-encoding gradient work in MRI?
Both B and C -It is energized as a pulse before signal reception & its amplitude is varied while its duration is fixed
What is the primary difference between regular visual images and medical images?
Medical images are of the interior body, while visual images are of the surface
What is the purpose of the 180 degree RF pulse in a spin echo sequence?
To refocus the spins
Bandwidth _____ as RF pulse duration _____.
narrows; increases
Which of the following is not a parameter that affects the pixel character in MRI?
Imaging time
Which of the following modalities typically has the best spatial resolution?
X-ray
Multislice imaging techniques help to _____.
decrease imaging time
What is the purpose of quantization or resolution in digital imaging?
All of the above- to improve the precision and dynamic range of pixel values & to reduce the effects of false contouring
Which MRI pulse sequence is best for producing T2-weighted images?
Spin echo with long TE
How does receiver bandwidth affect signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and field of view (FOV) in MRI?
Narrower bandwidth improves SNR but reduces FOV
Which of the following is the most widely used type of pulse sequence in MRI?
Spin echo
Which of the following is used during night vision or scotopic vision?
Rods
What does the term dynamic range refer to?
The number of gray scales a system can display
How do partial saturation and inversion recovery pulse sequences differ in their effects on the spins?
Partial saturation uses a 90 degree pulse, while inversion recovery uses a 180 degree pulse
What will help improve contrast resolution the most?
An increase in SNR
What do we call the diagram that lays out the schematic of an MRI acquisition procedure?
pulse sequence
What is the purpose of the gradient coils in an MRI system?
All of the above
Which of the following is implemented before signal reception and not during the RF transmit pulse?
Phase-encoding gradient
What is the relationship between the matrix of k-space and the resulting image?
Both A and C
A radiograph is primarily what type of image?
Electron density
If the field of view (FOV) of an MRI scan is increased, what will happen to the pixel size if the matrix size stays the same?
It will increase
What is the RF pulse sequence for an inversion recovery MRI technique?
180…90…/…180…90…/…180…90…/….
What is the purpose of high-amplitude phase encoding gradients in k-space?
Both A and C
Which is not a state that MRI proton spins can exist in?
Partial equilibrium
Which of the following localizes the MRI signal?
Gradient coil
Which of the following determines slice thickness?
Slice-encoding gradient amplitude
Which of the following has the highest proton density?
CSF
Which MRI pulse sequence is best for producing proton density weighted images?
Partial saturation
What is the purpose of the sinc function in MRI?
All of the above
What is the typical resolution of an MR image?
1 lp/mm
How are the different k-space sampling methods (spiral, square spiral, interleaved spiral) processed?
Both B and C
What type of artifact appears as a “wrap around”?
Aliasing
In what units do we typically measure spatial frequency in MRI?
lp/cm
What is the purpose of the spatial frequency domain (k-space) in MRI?
To provide information about the spatial frequency content of the image
What is the definition of digital imaging?
All of the above
Which of the following will improve the SNR?
Narrowing the receive bandwidth
The transmit bandwidth primarily affects what?
Slice width
In an inversion recovery sequence, the null point is where _____.
the signal is lowest
What is the purpose of using gradient magnetic fields in MRI?
Both A and B
Information in k-space is
in the spatial frequency domain
How many shades of gray can the human eye detect?
24
What is the minimum number of bits required to represent the 26 uppercase and 26 lowercase letters of the alphabet?
6 bits
What does the Fourier transform relate in imaging?
All of the above
How does the computer convert the spatial frequency domain (k-space) information into the spatial domain of the MR image?
All of the above
What is the definition of the spatial frequency domain?
Both A and C
How do we obtain the modulation transfer function (MTF)?
by taking the FT of the edge
What is the primary determinant of pixel character in an MRI image?
Radiofrequency pulse sequence
How many bits are required to have reasonable precision when detecting and storing an MRI signal?
12 bits
The FT of a square wave gives what?
Sinc function
If the matrix size of an MRI scan is decreased, what will happen to the pixel size if the matrix size stays the same?
It will decrease
What is the difference between phase encoding and frequency encoding in MRI?
Phase encoding encodes the phase, frequency encoding encodes the frequency
What is the primary determining factor of contrast character in MRI?
Pulse sequence
What is the relationship between spatial resolution and pixel size in MRI?
Spatial resolution improves as pixel size decreases
In a spin echo pulse sequence, which of the following would result in a T2-weighted image?
TR= 2000 ms and TE= 100 ms
A ‘spark artifact’ will usually appear in the final MR image as what?
Alternating light and dark lines
Which of the following is implemented during MRI signal acquisition?
Frequency-encoding gradient
What are the two primary ways we evaluate the quality of a diagnostic image?
Contrast resolution and spatial resolution
What is the main cause of aliasing in MRI?
Undersampling of the MR signal
Which of the following structures detects color?
Cones
How does the slice thickness depend on the gradient magnetic field and RF pulse bandwidth?
Steeper gradient and narrower bandwidth result in thinner slices
What is the purpose of the 90 degree RF pulse in a spin echo sequence?
To excite the spins
What are the two main properties of each pixel in an MRI image?
Character and location
What is the key feature of the spin echo pulse sequence in MRI?
All of the above
What is the purpose of the inverse Fourier transform in MRI?
To reconstruct an MR image from spatial frequency information
What is the main advantage of 3D Fourier Transform MRI over 2D Fourier Transform MRI?
All of the above
The pixels that make up an MRI image are stored _____.
in an image matrix
What do we use to convert spatial frequency information into spatial location in MRI?
Inverse Fourier transform
What is the primary advantage of MRI over CT?
Soft tissue contrast
What is the relationship between contrast and spatial frequency in an image?
Low spatial frequencies represent high contrast
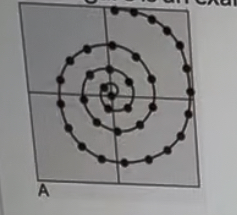
This figure is an example of what?
Spiral image space sampling
What is the purpose of the pulse sequence in MRI?
All of the above
What are the two most common 2DFT artifacts in MRI?
Undersampling and motion
How do multiple acquisitions improve MRI scanning?
Increase SNR
What type of artifact is caused by a spike of noise in k-space?
Spark artifact
What are the key features of a partial saturation pulse sequence?
Short TR, minimal TE, and only a portion of longitudinal magnetization is flipped
Recording occasional values from a set of information is referred to as
sampling
What is the primary limitation of spatial resolution in MRI?
Pixel size
In MRI, the phase-encoding gradients with _____ fill the periphery of the k-space.
high amplitude
What is the purpose of the frequency-encoding gradient in MRI?
To determine one axis in the xy-plane of the slice
Which MRI pulse sequence is best for producing T1-weighted images?
Inversion recovery with short TI
What are the three principal magnetic resonance imaging parameters?
Proton density (PD), spin-lattice relaxation time (T1), and spin-spin relaxation time (T2)
If all else remains the same, what will decrease slice thickness?
Higher slice-encoding gradient amplitude