2 - 3: Overview of plant structures; Plant cell
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
development of 2ndary metabolites like tannins, alkaloids (nicotine)
protection from herbivory
schizogenous development
development of large intercellular spaces thru splitting
lysigenous development
development of large intercellular spaces thru cell breakdown
rhexigenous development
development of large intercellular spaces thru tearing; elongation/grown of plant so nasstretch

- storage of proteins in seeds
- temporary sugar storage during the day
- malic acid in CAM
vacuole storage: what is stored and in which part?
vacuole forms lytic compartments (tracheids, vessels)
breakdown of macromolecules, engulfing senescent organelles, programmed cell death through autolysis
produce toxic derivatives thru hydrolysis when vacuoles are damaged
how does vacuole detoxify cytoplasm + store defensive chemicals (nicotine, phenols, cyanide, mustard oils)
glyoxylate cycle
fats --> carbs
charophyte
- ancestral plants in aqua envi; green algae most closely related to modern plants
- submerged in water
- holdfast
- water mechanical support
- epidermis + cuticle for waterproofing
- stomata for water loss regulation
- separate sources of water + light, meristems
adaptive features of land plants
- parenchyma
- collenchyma, sclerenchyma (strengthening)
- 2ndary growth
mechanical support of of land plants
flavonoid compounds (anthocyanin)
protection from UV
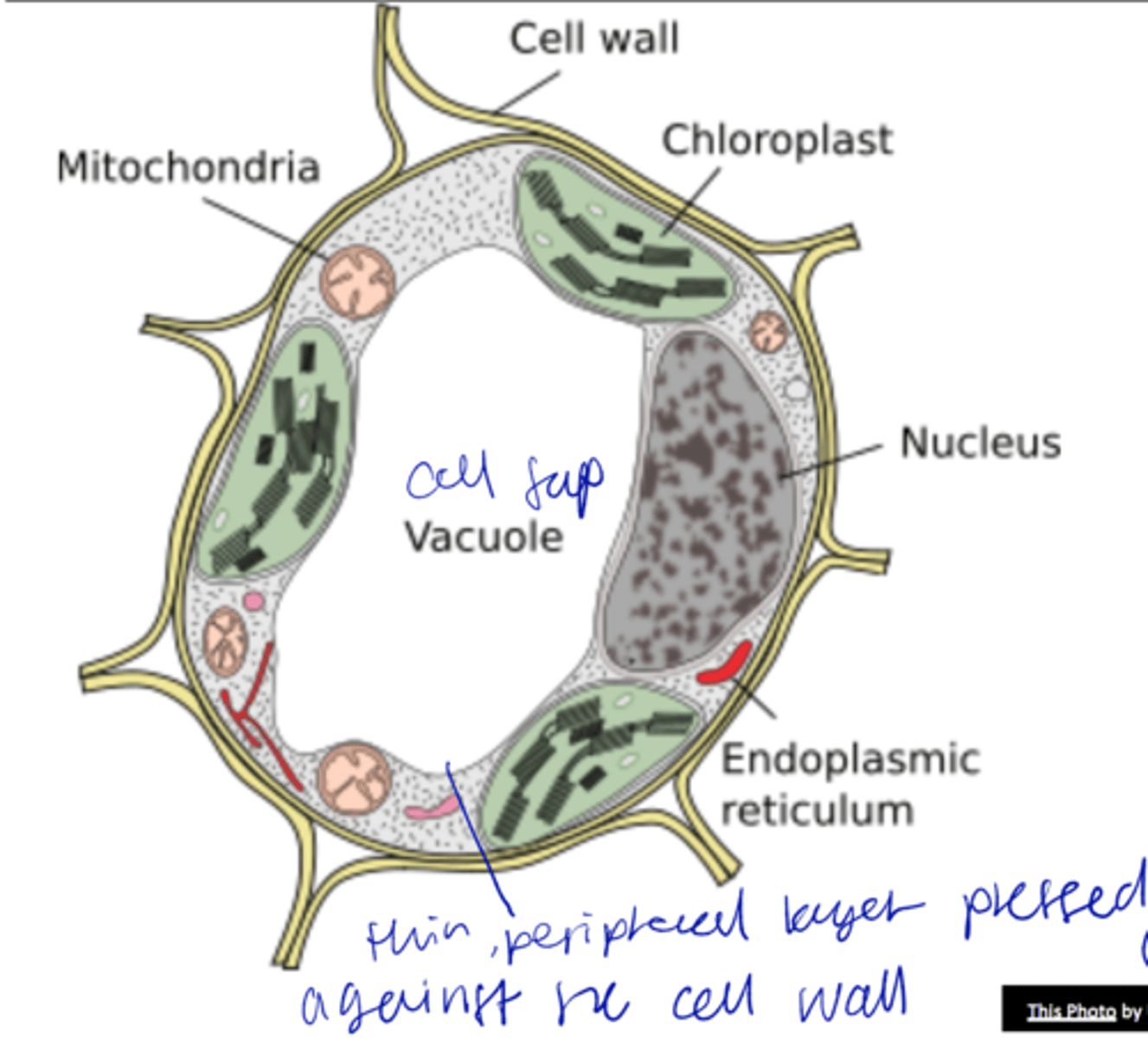
protoplast + cell wall
plant cell primarily consists of the
protoplast
The contents of a plant cell exclusive of the cell wall.
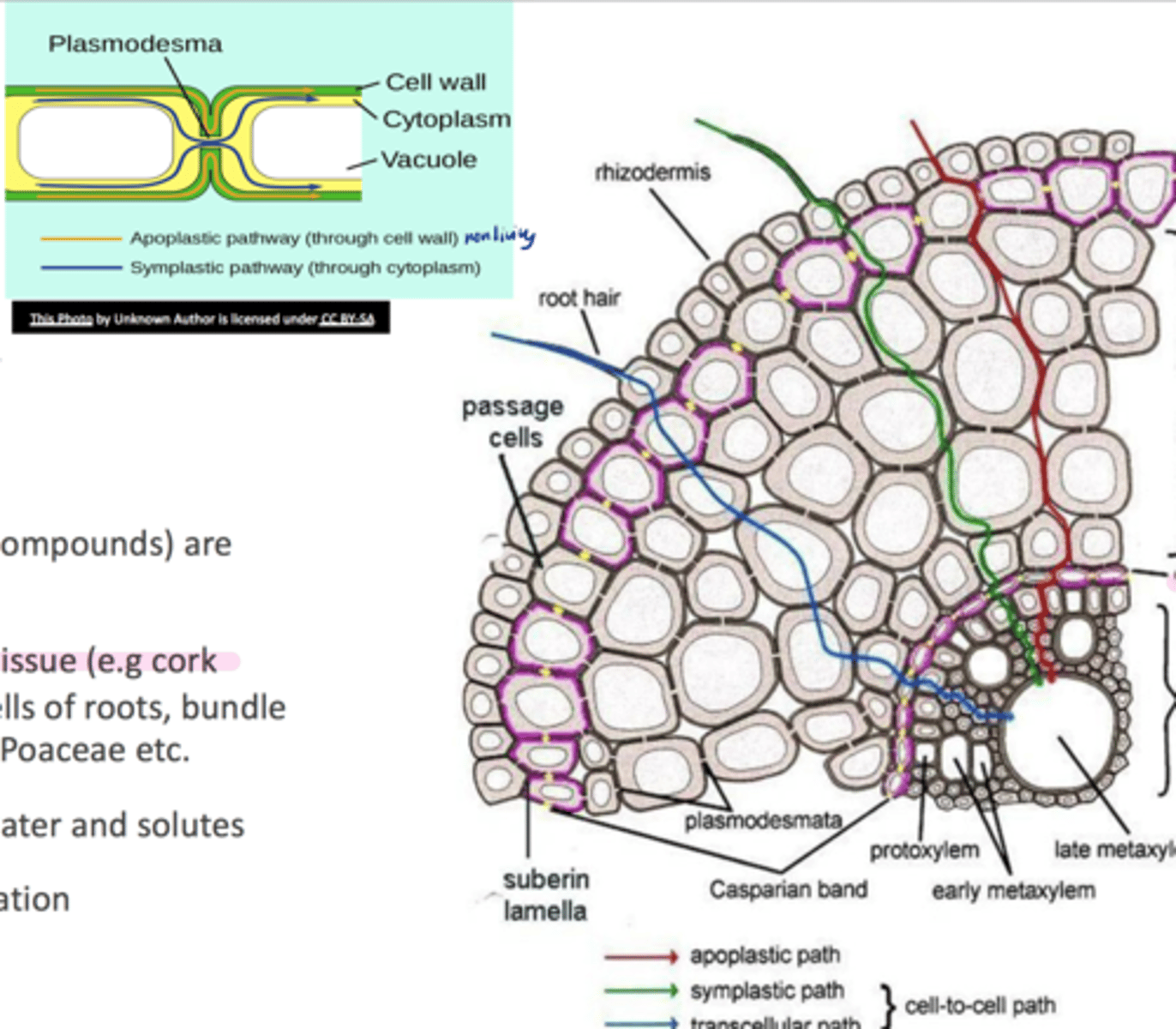
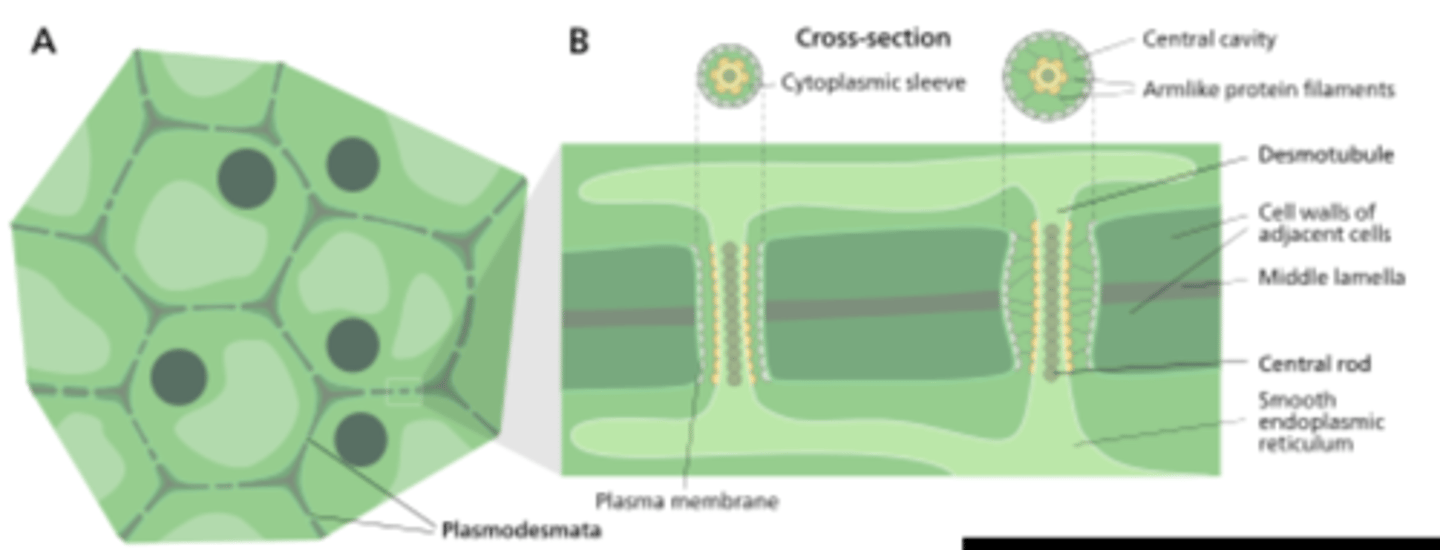
plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
14-faced polyhedron
cell wall faces
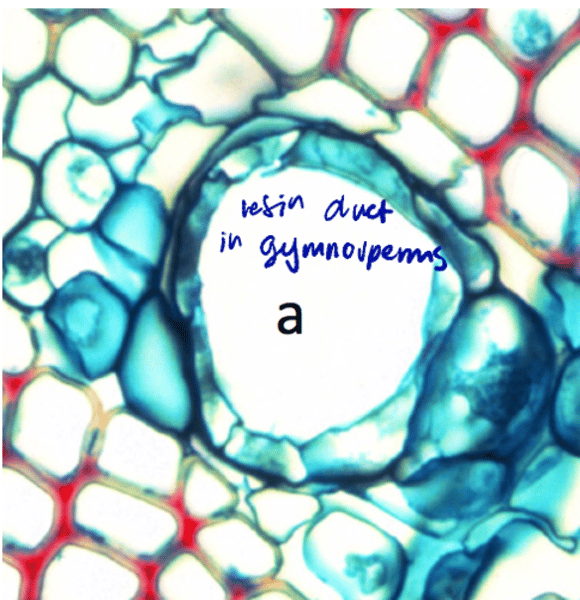
air spaces, ducts, lacuna
large intercellular spaces
1. Cell wall
2. Vacuoles
3. Plastids
4. Glyoxysome
meron sa plant cell wala sa animal cells
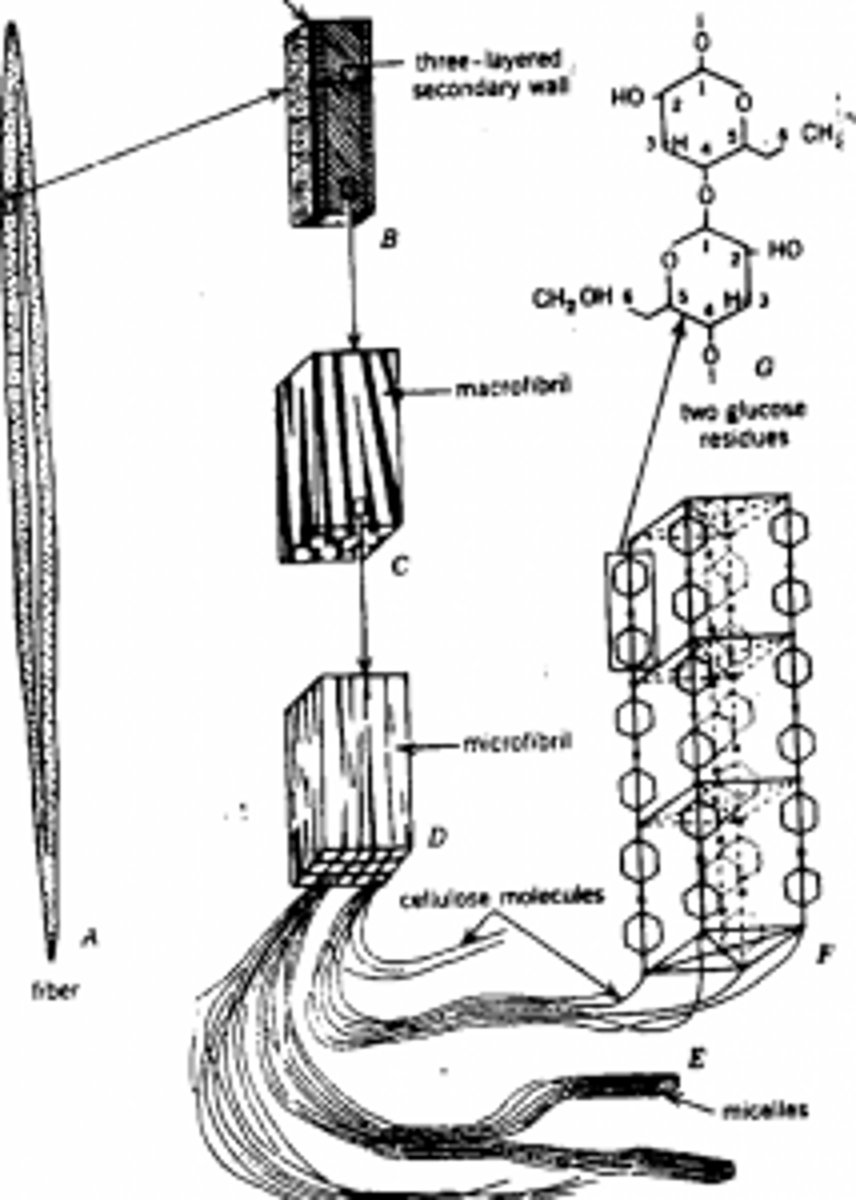
Cellulose (C6H10O5)n
comprise 20-60% of dry weight of cell wall
micelles
H bonds forming lattices
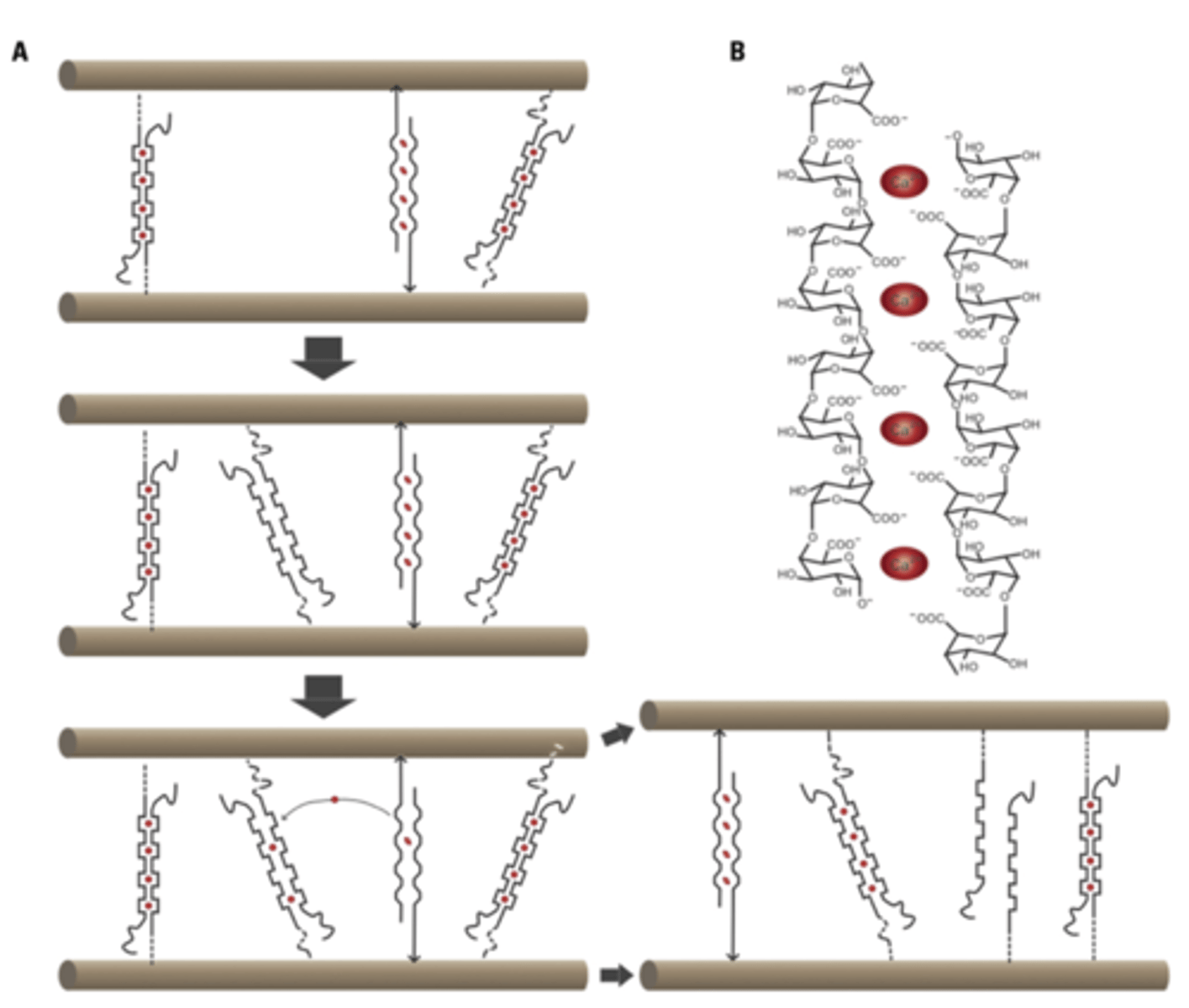
pectins
- non-cellulosic
- in the primary wall of eudicots
- lacking from secondary walls
- hydrophilic and forms gels
- plastic properties, stretch
- Meristems low in Ca2+
- During elongation and differentiation high in Ca2+
- Ca2+ increases, plasticity decreases, so elong stops bc cant be stretched anymore bc Ca2+ forms cross-links w pectin
effect of Ca2+ on pectin
Glycoproteins
structural proteins believed to strengthen cell walls (proline-rich proteins, glycine-rich proteins, extensins)
peroxidase
an enzyme that destroys hydrogen peroxide; defense
Cellulase and pectinase
enzymes in cell wall degradation (leaf abscission and formation of perforation plate in developing vessel element)
callose
o Principal cell wall polysaccharide in the developing cell plate
o Deposited between the plasma membrane and existing cell wall
o Deposited rapidly in response to mechanical wounding and stress (pathogen, environment)
lignin
o Phenolic polymers
o supporting (sclerenchyma) and conducting (xylem) tissues
o secondary walls wood
o Hydrophobic
o compressive strength and bending stiffness
o Resistant to microbial attack
- when water leaves, it pulls up the other water below (transpiration)
- strengthens xylem to endure negative pressure
- w/out lignin, it's like sucking on straw pag paubos na tubig
ginagawa ng lignin sa xylem
cutin
o Insoluble lipid; waterproof, hydrophobic
o Forms a matrix with wax to form cuticle
o Prevents water loss
o epidermis
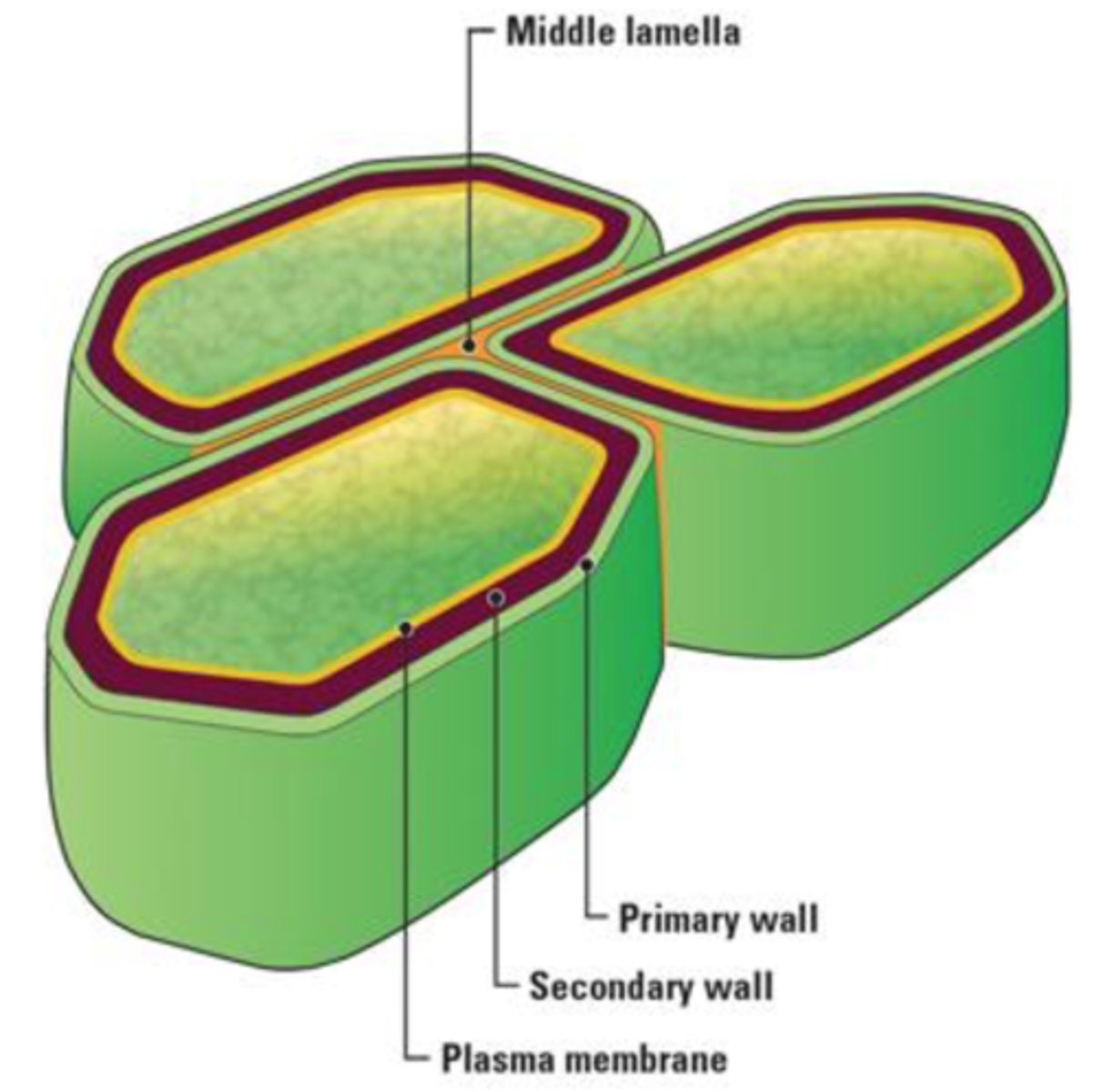
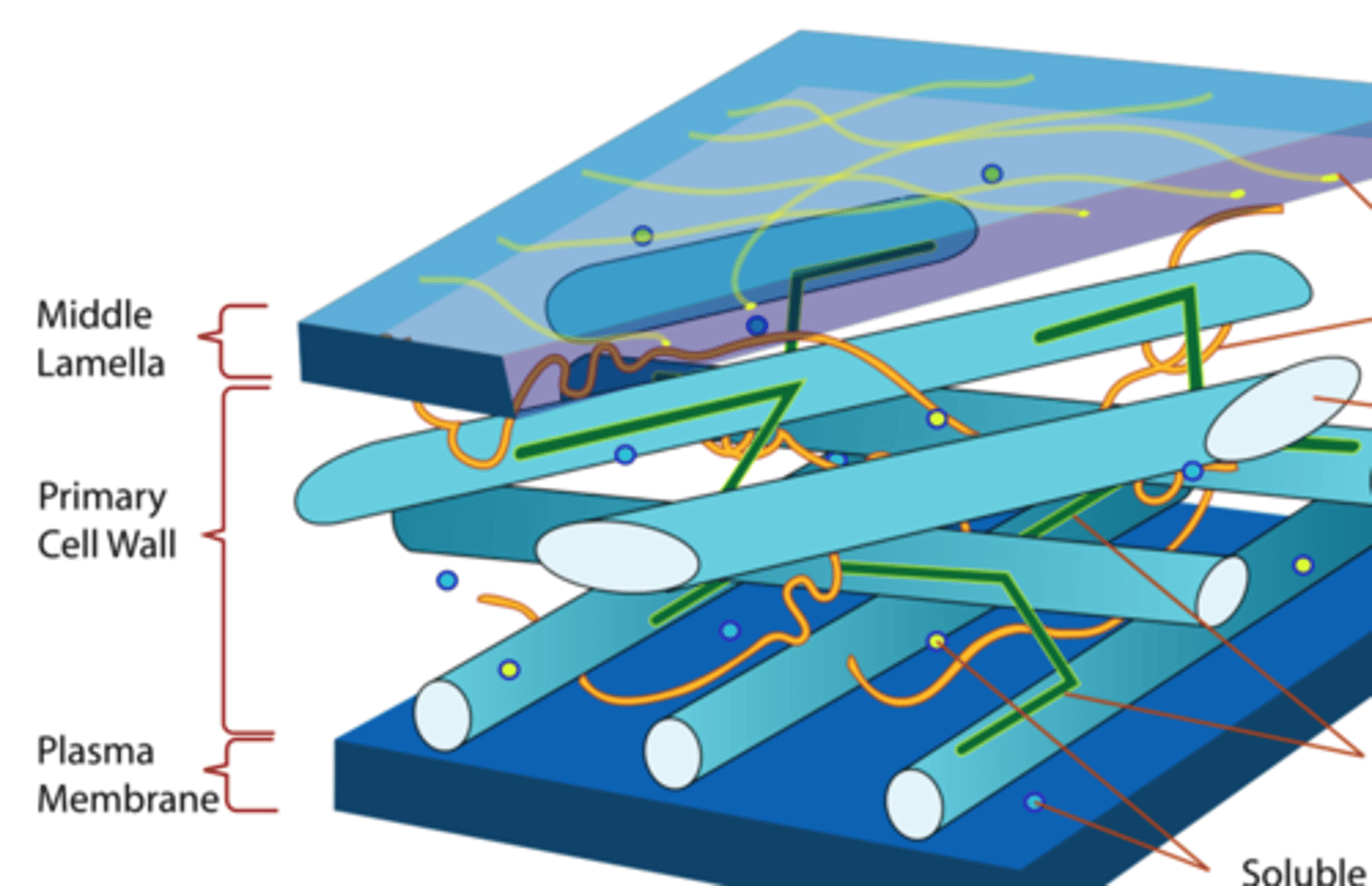
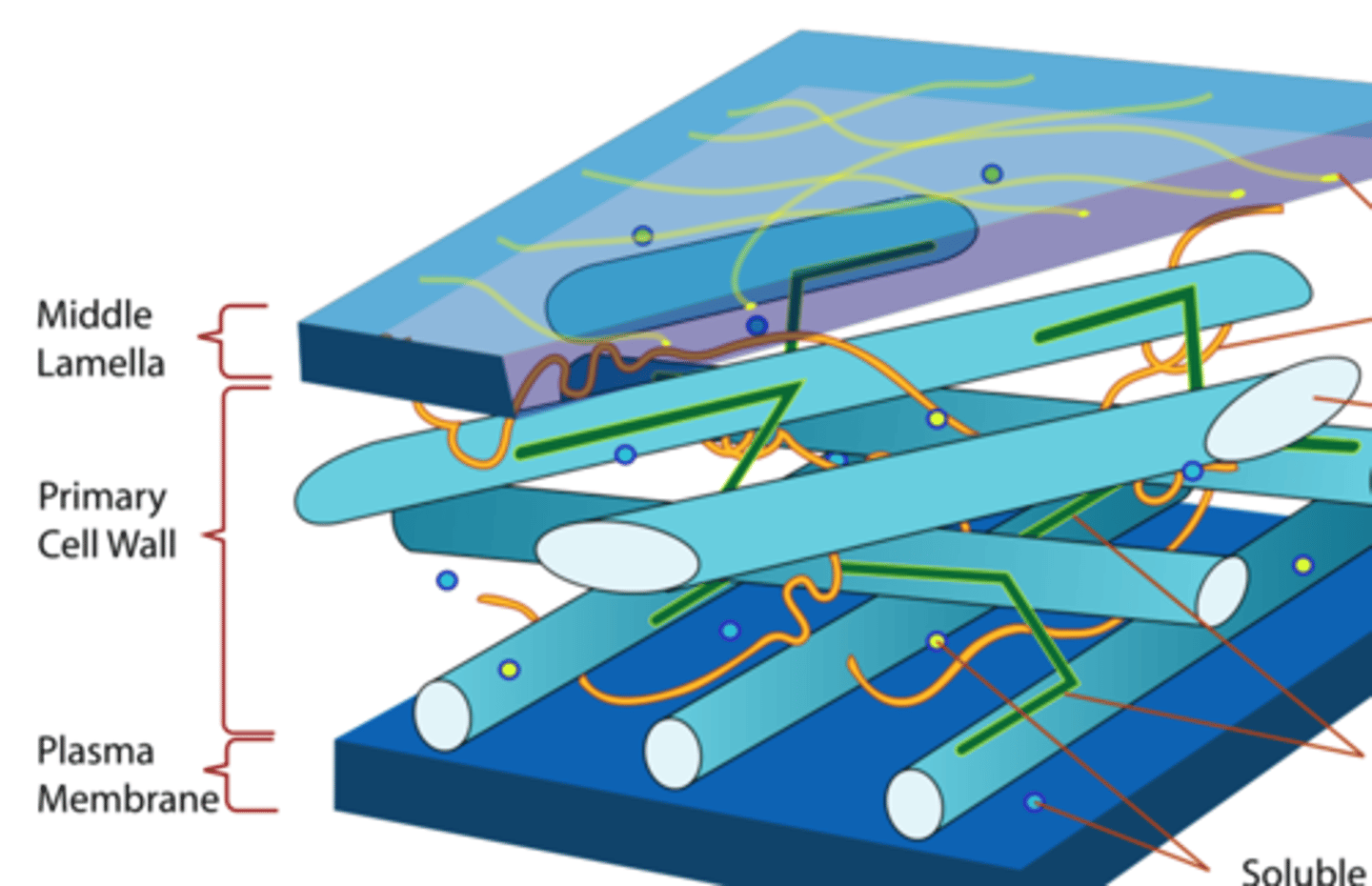
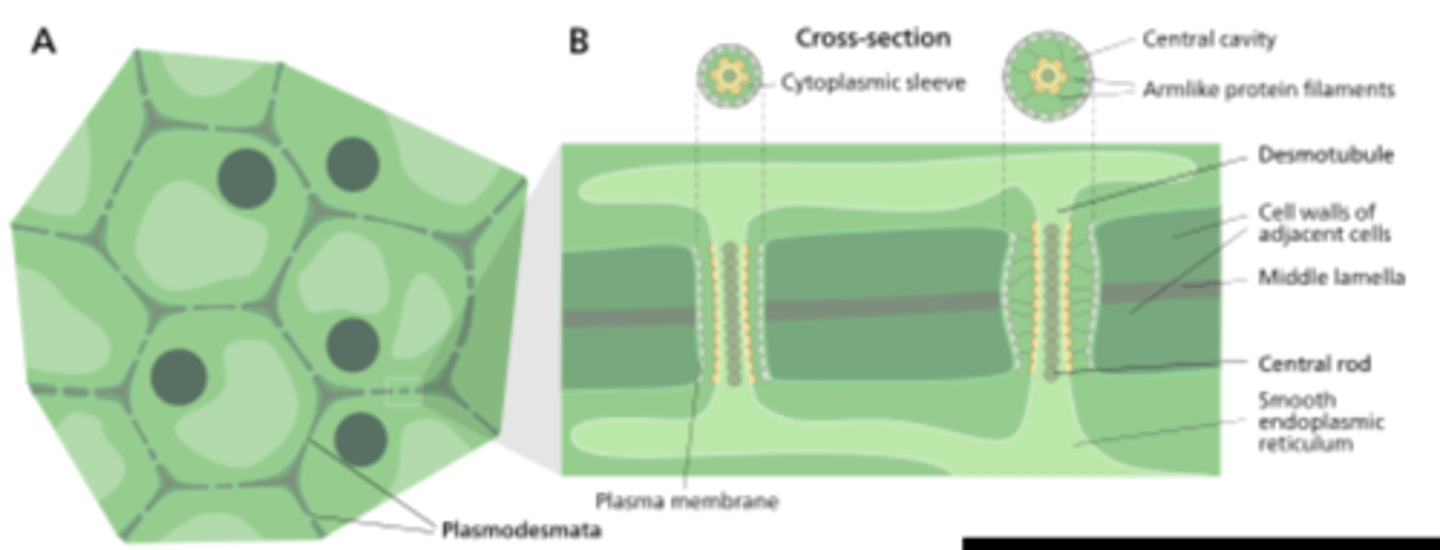
1. Middle lamella (intercellular substance)
2. Primary wall
3. Secondary wall
cell wall layers
middle lamella
o Cementing substance between plant cells
o Between two primary walls
o Contains calcium and magnesium pectate
break down the middle lamella (pectin-rich) for the cells to be separated by treating w enzymes or chemicals
What is the principle behind maceration, a microtechnique preparation that enables observation of individual plant cells?
primary wall
- First true wall
- Relatively thin (> 1 μm)
- young, growing cells
- simple, mature cells
- meristems, parenchyma
- Cellulose, pectic compounds, hemicellulose, non-cellulose polysaccharide
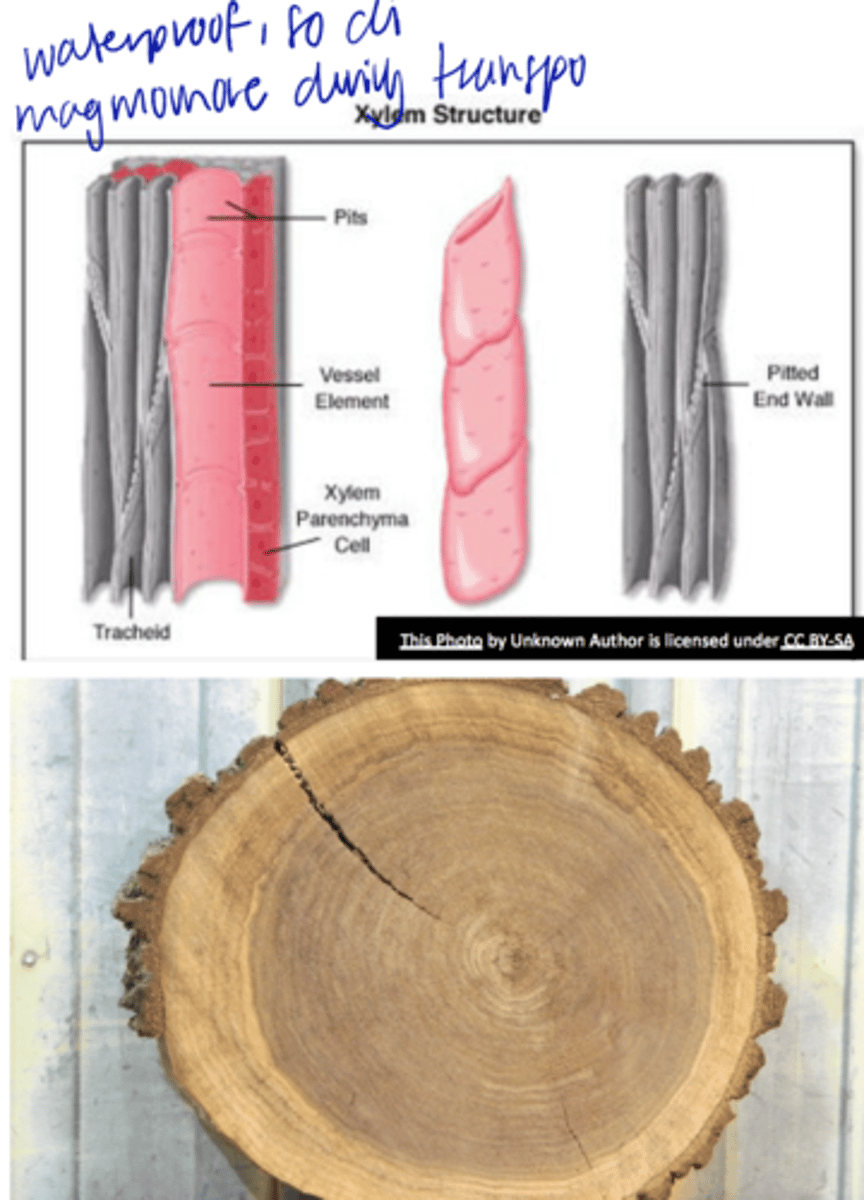
lumen
space in xylem vessel elements + tracheids
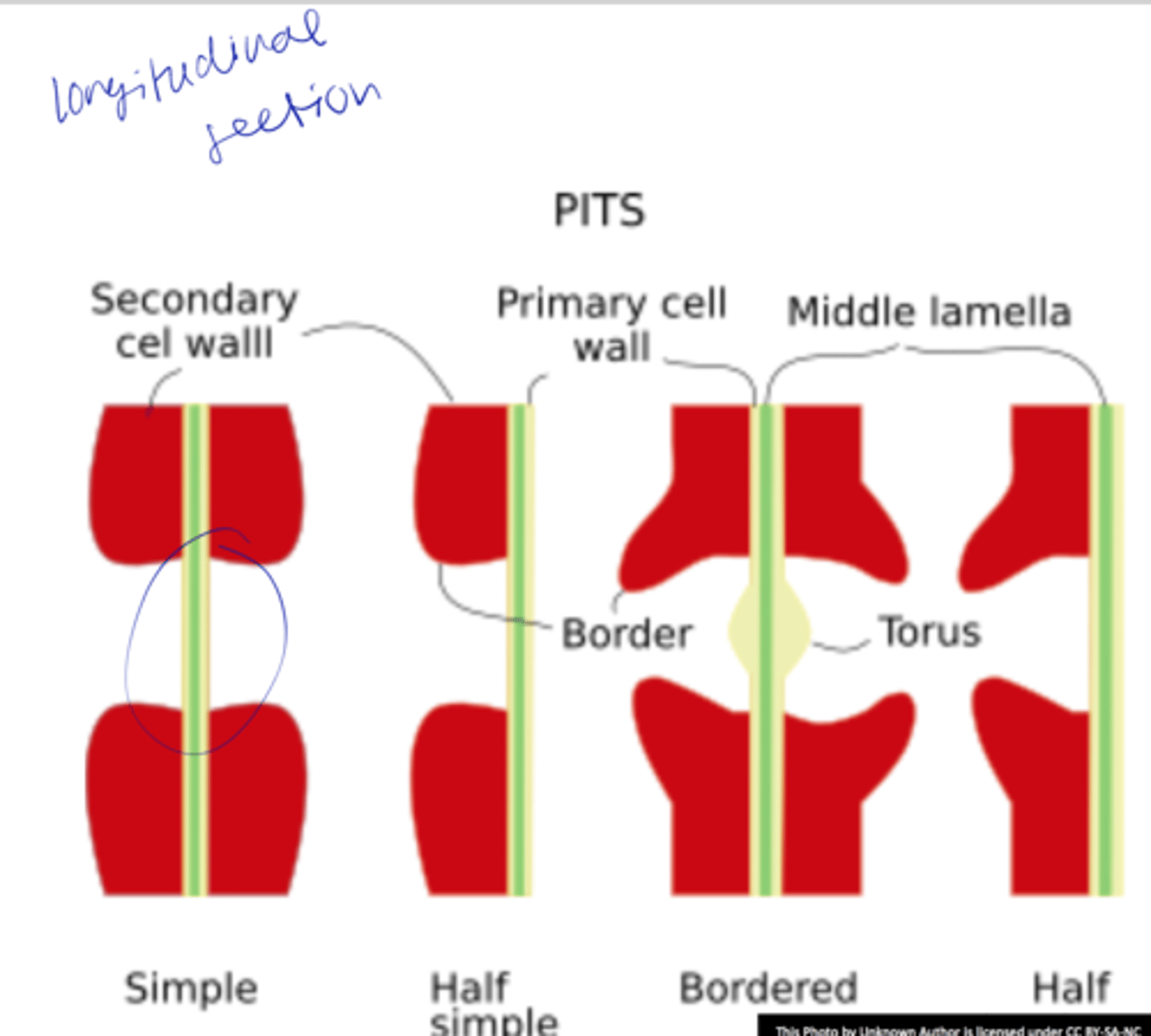
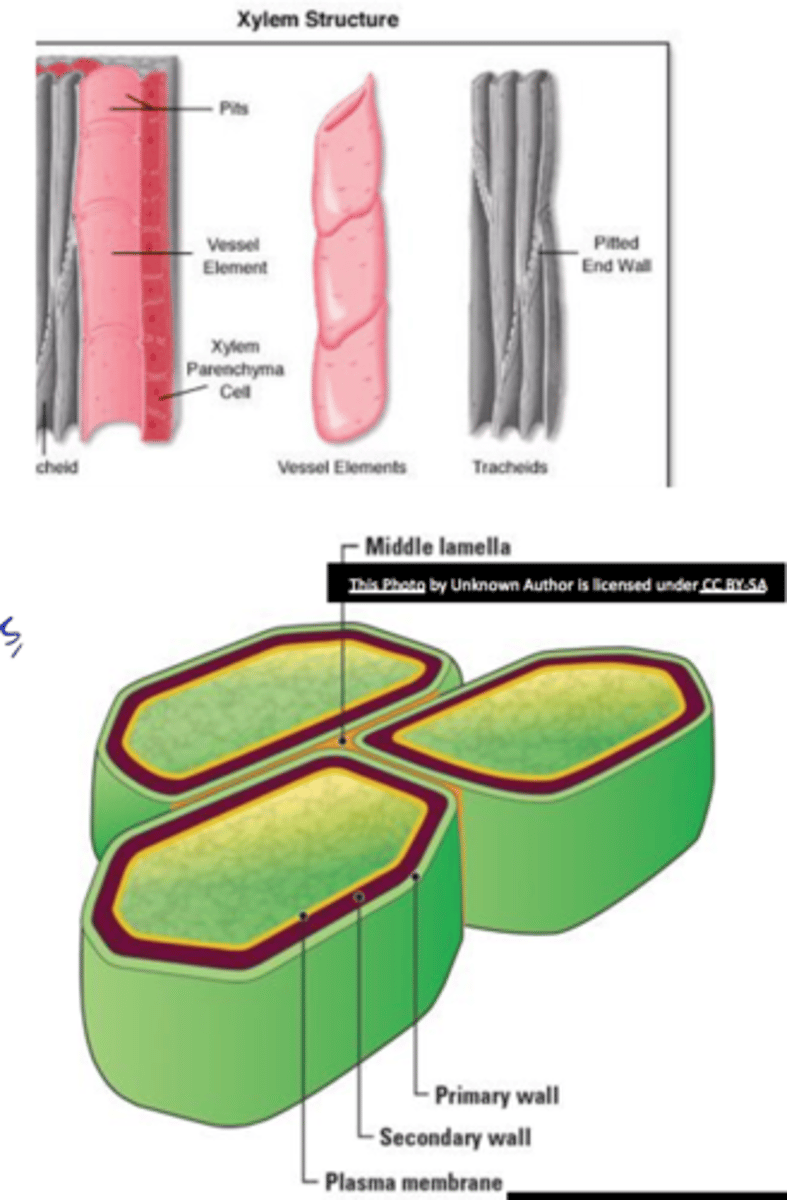
pits
o Cavities/discontinuities in thes econdary wall
o Secondary wall deposition, formed over the primary pit fields
o Usually occurs as pit-pairs
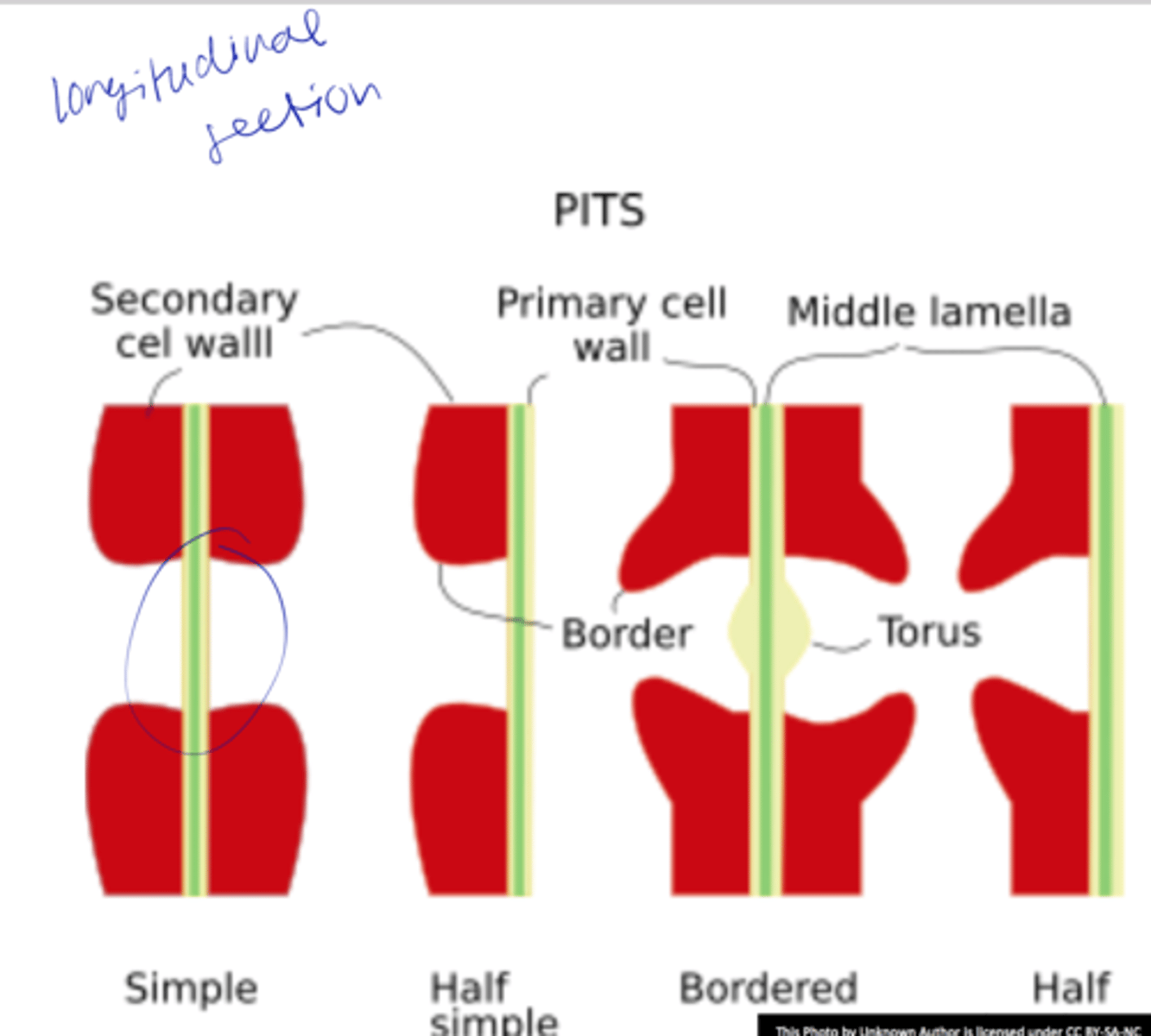
Pit membrane
middle lamella+ two primary walls between two pit cavities
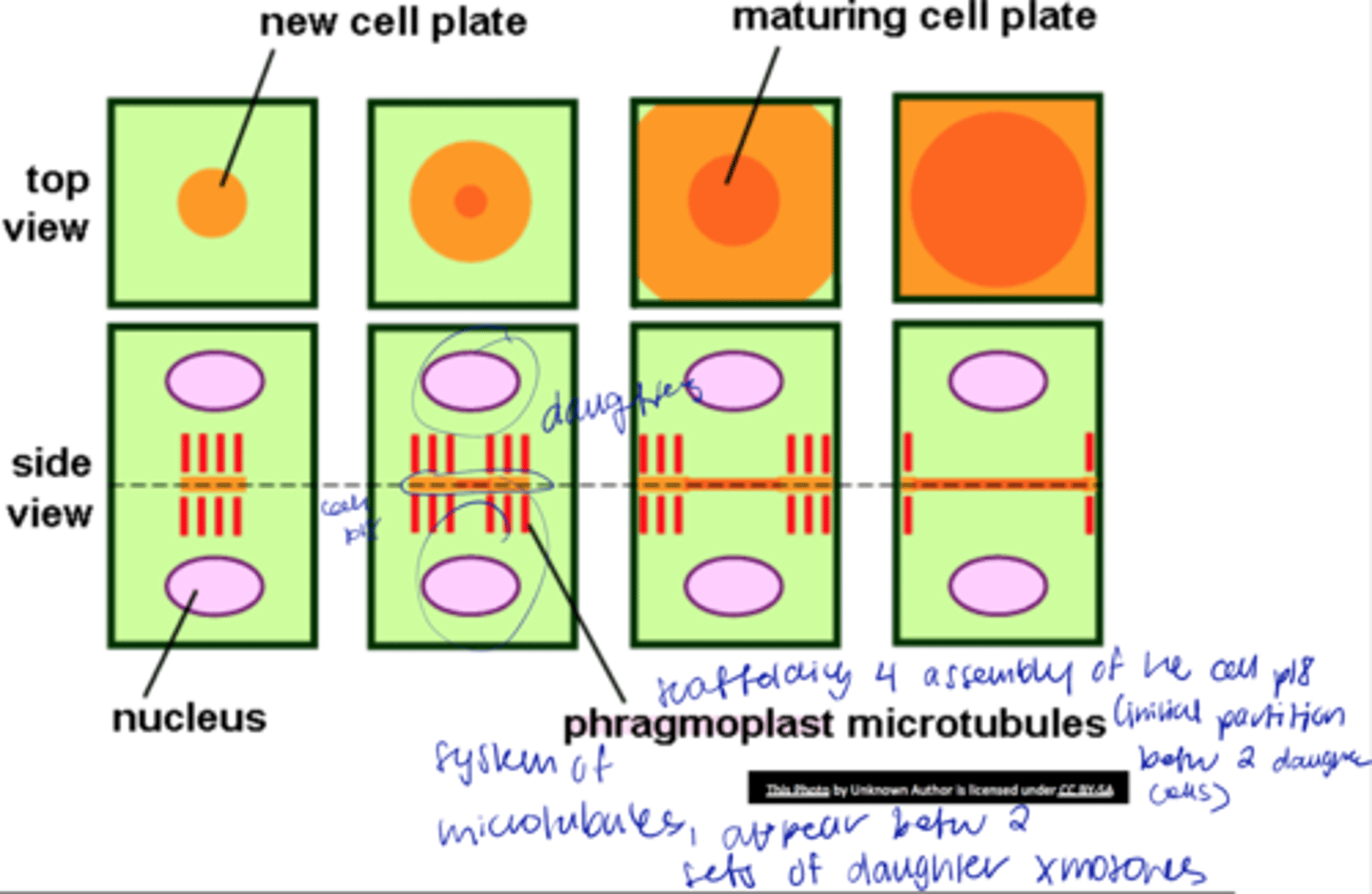
late anaphase
1. Cytokinesis initiated byphragmoplast
2. cell plate formed
3. expands centrifugally
4. growth reaches walls of dividing cells
origin of cell wall
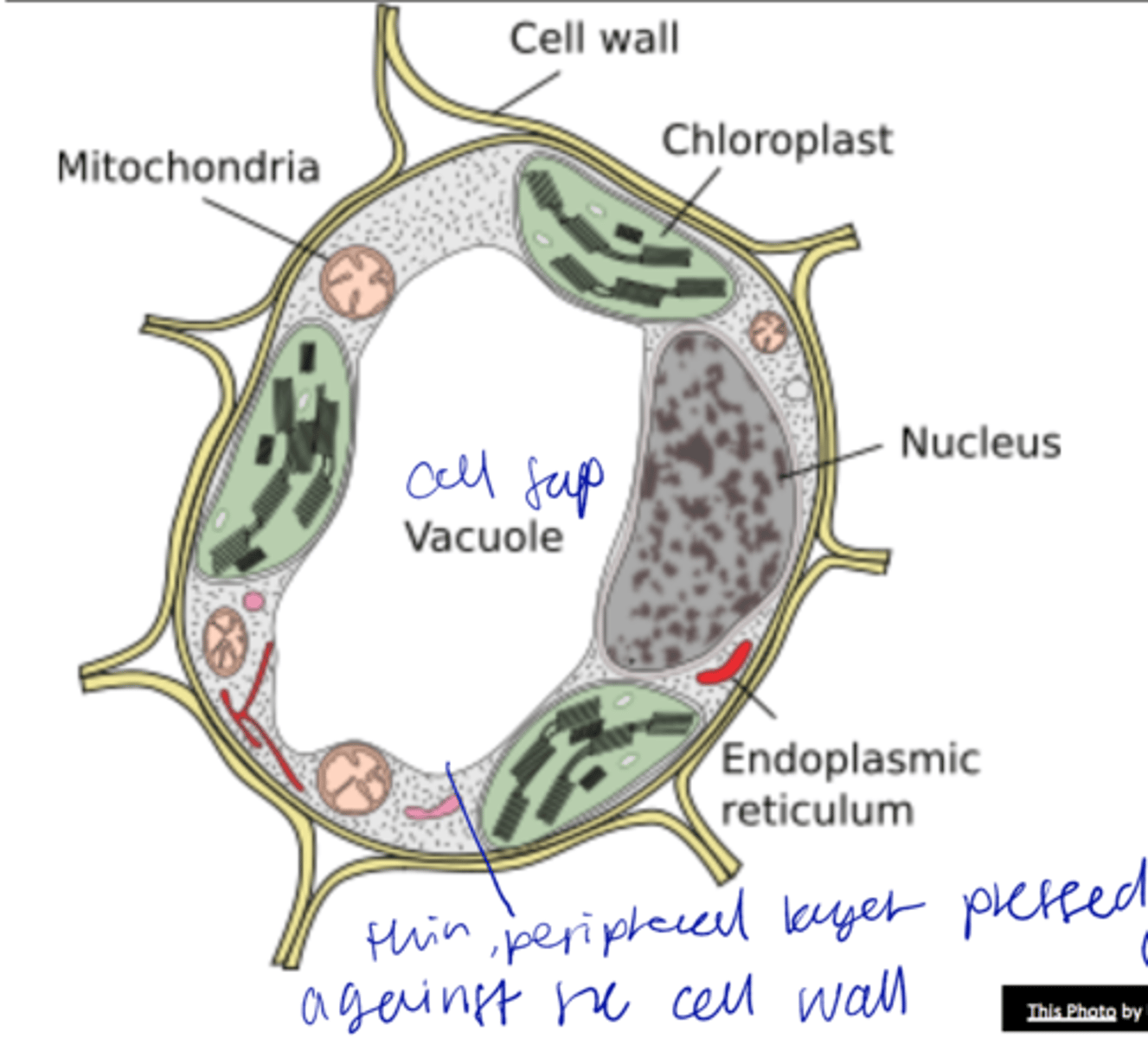
vacuoles
- 90% of space of cell, single membrane
- Increase in cell size involves vacuole enlargement
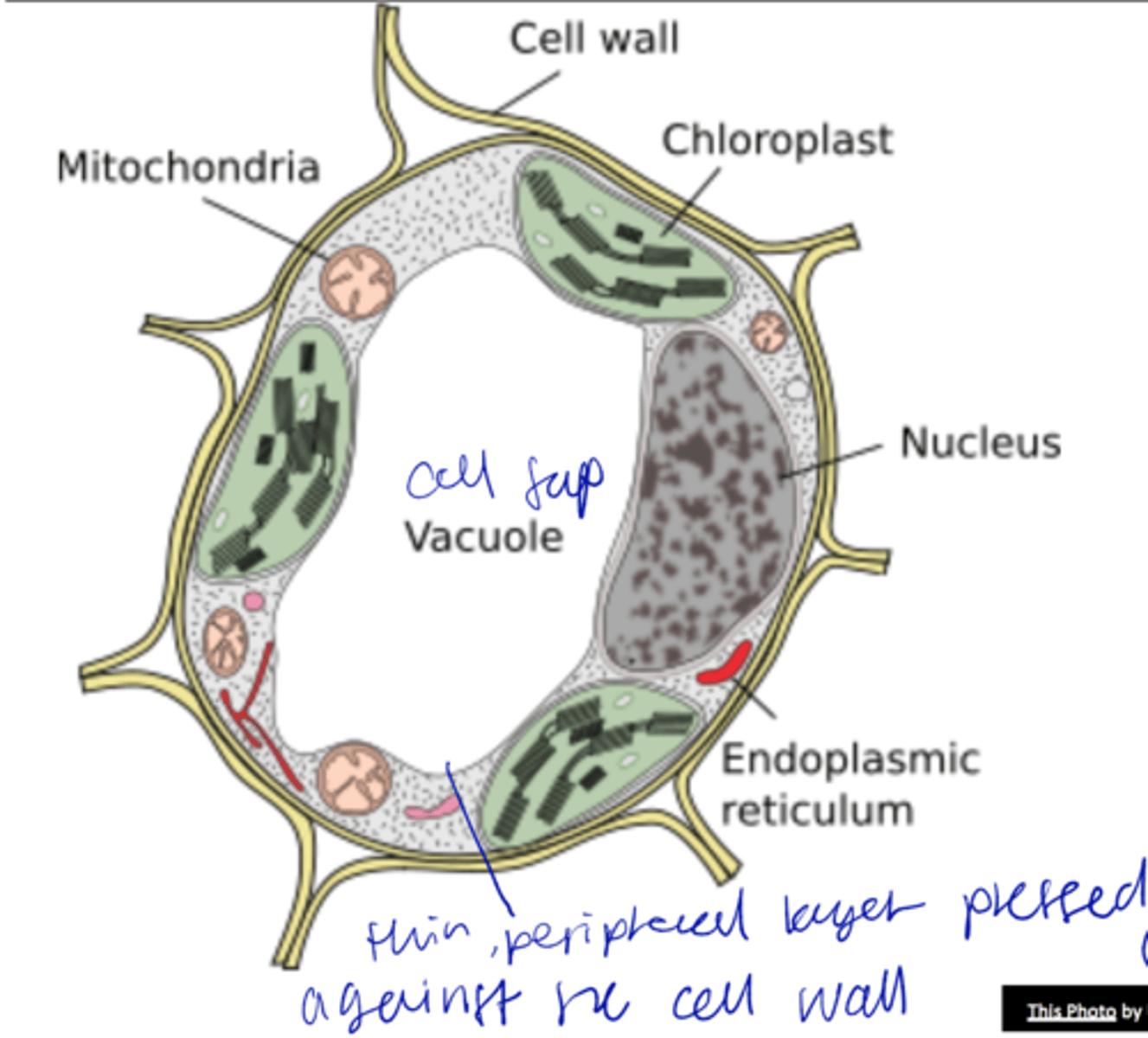
Tonoplast
vacuolar membrane
cell sap
inorganic ions (Ca2+, Cl-, K+, NO3-), sugars, organic acids, and amino acids in vacuole
hypertonic vacuole
more water inside the cell than outside, water will flow out of the cell, and the plant will wilt and possibly die
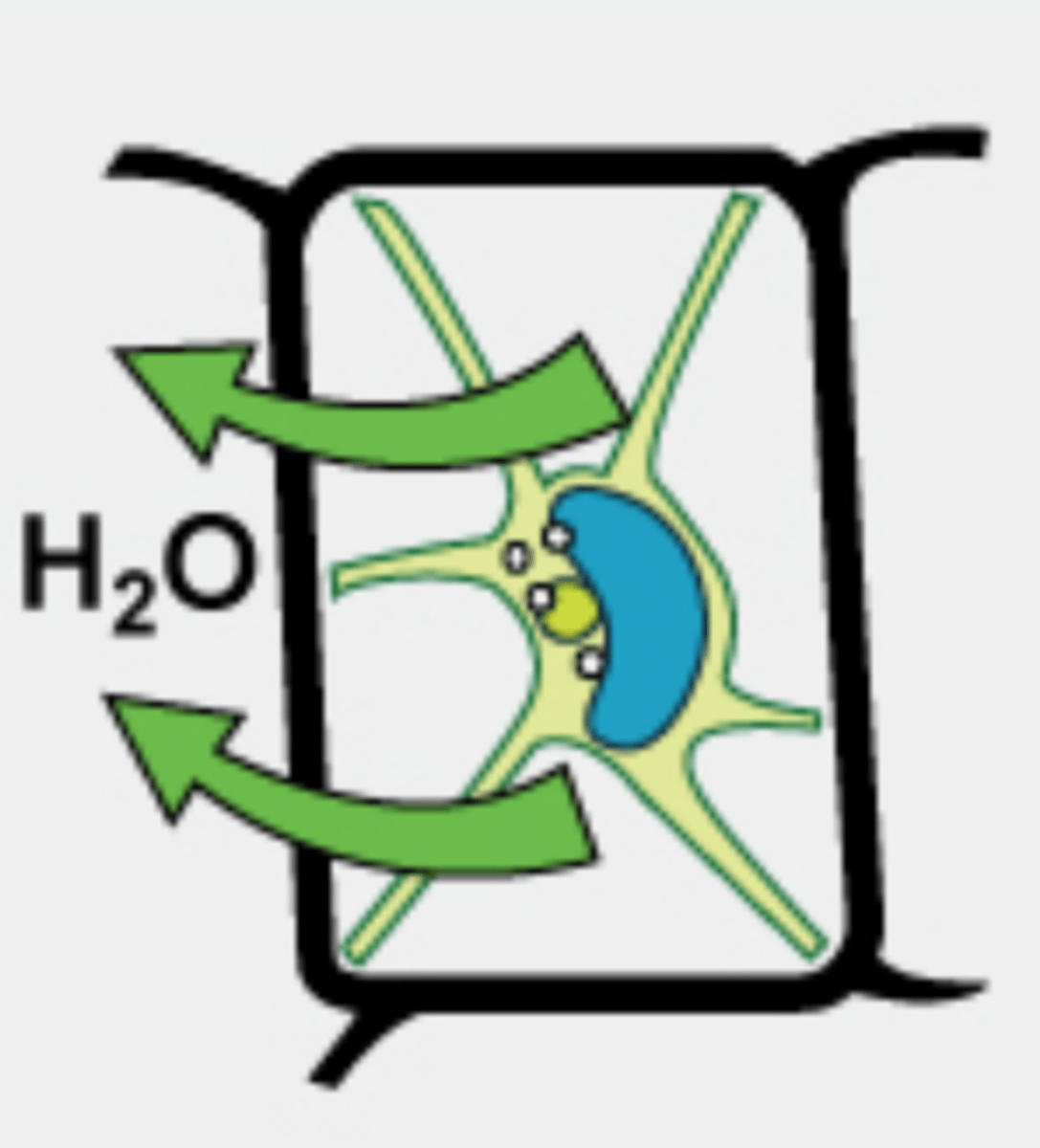
turgid in hypotonic solution, H2O conc high outside the cell, H2O enters towards the cell
explain the osmotic phenomenon in vacuole
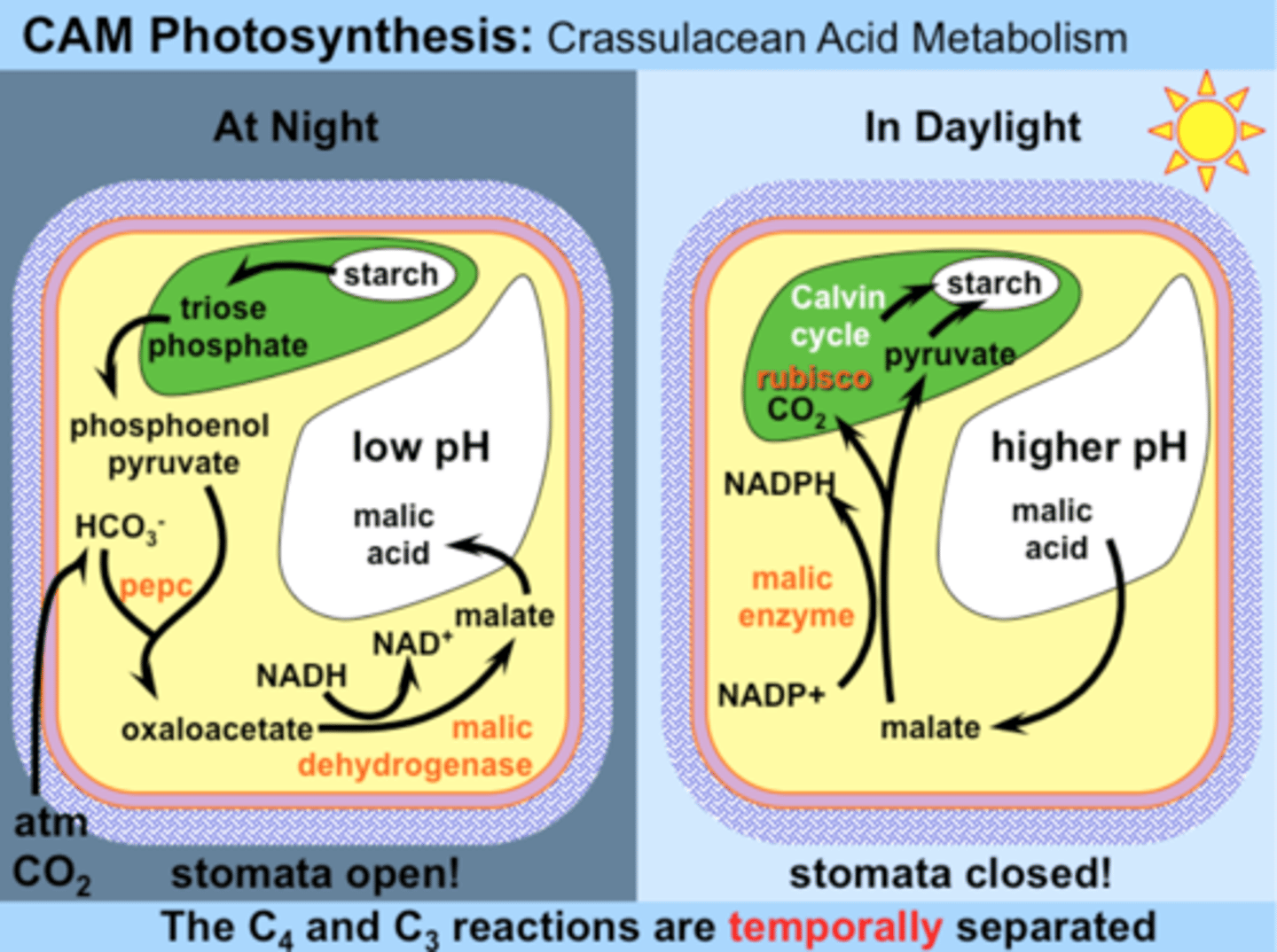
- CAM plants in arid, dry conditions close stomata during the day, so no CO2 during the day
-stomata opens during the night to acquire CO2
- CO2 is stored in vacuole in the form of malic acid
-in the next day, malic acid is converted back into CO2 for photosynthesis
explain malic acid and CAM
- when Ca2+ high in cell, it binds to oxalate, forming crystals
- crystals deter herbivory by irritating gut
- gabi family
how does vacuole regulate calcium levels and removal of oxalate? what are its functions?
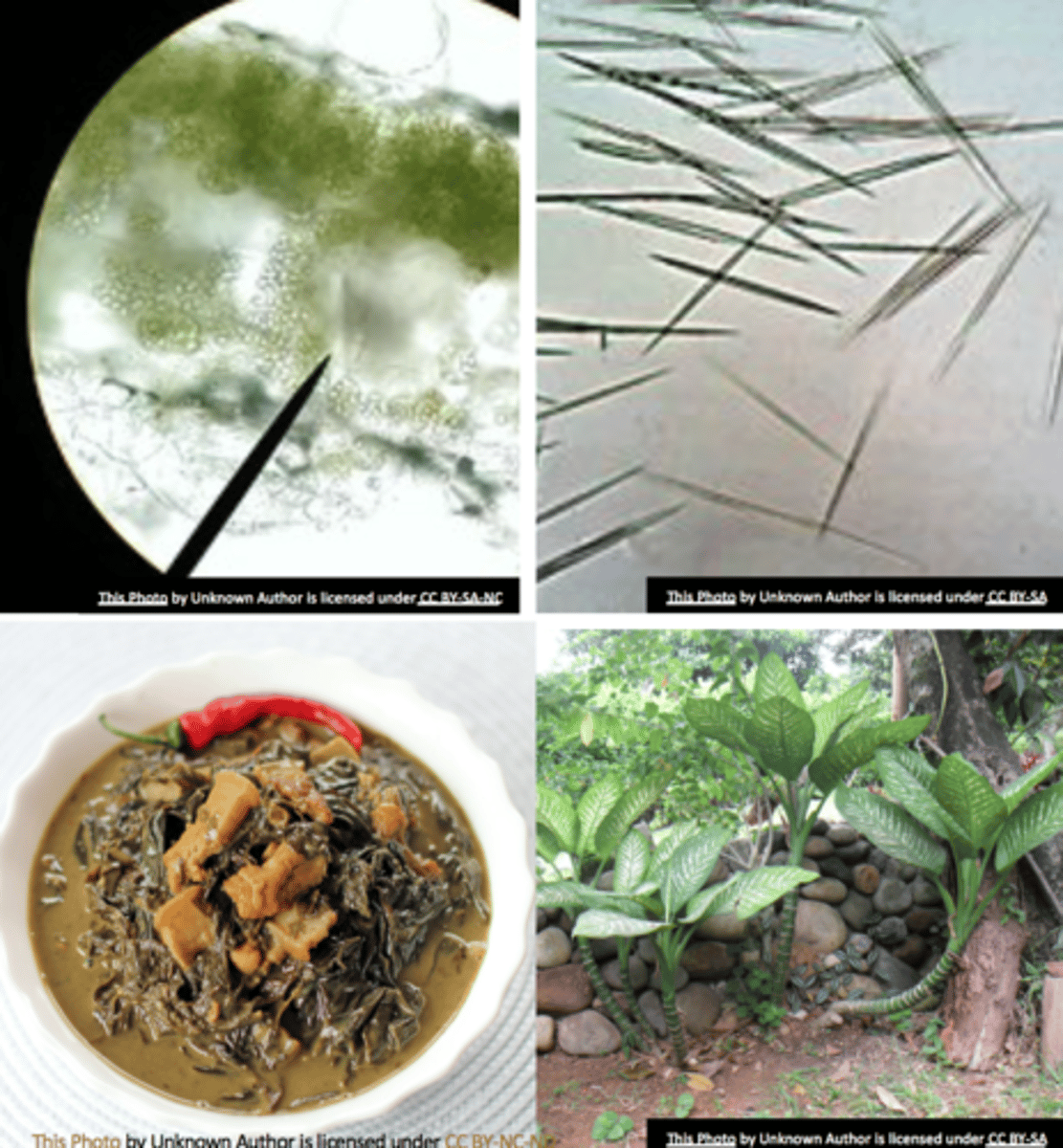

anthocyanin
- pigment deposition vacuole
- blue, violet, dark red, scarlet colors
- attracts pollinators and seed dispersers
- photo-oxidative damage protection to the leaves as they senesce during fall
- protects against photoinhibition (common in understory plants)

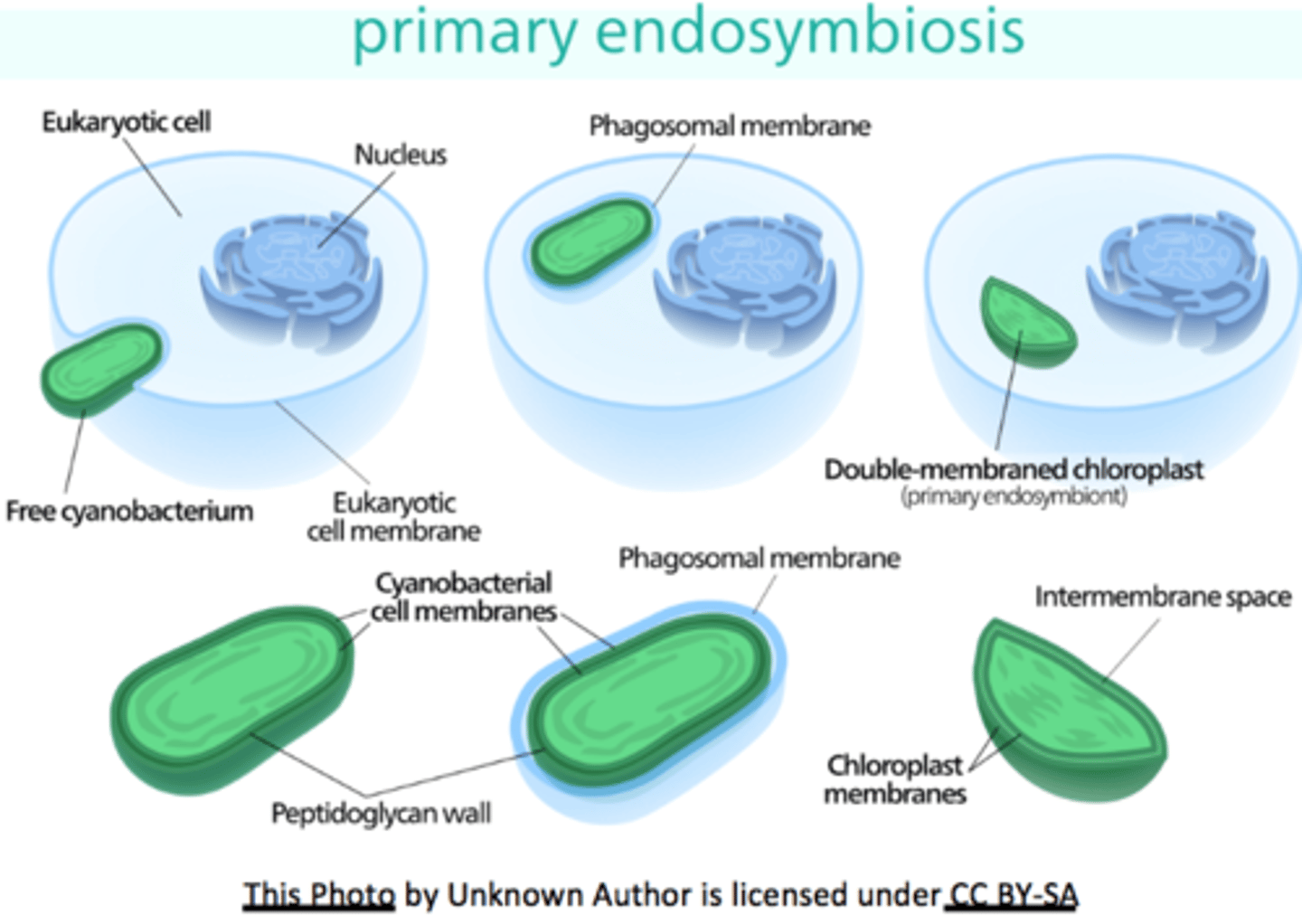
formerly photosynthetic bacteria engulfed by a eukaryotic cell
primary endosymbiosis
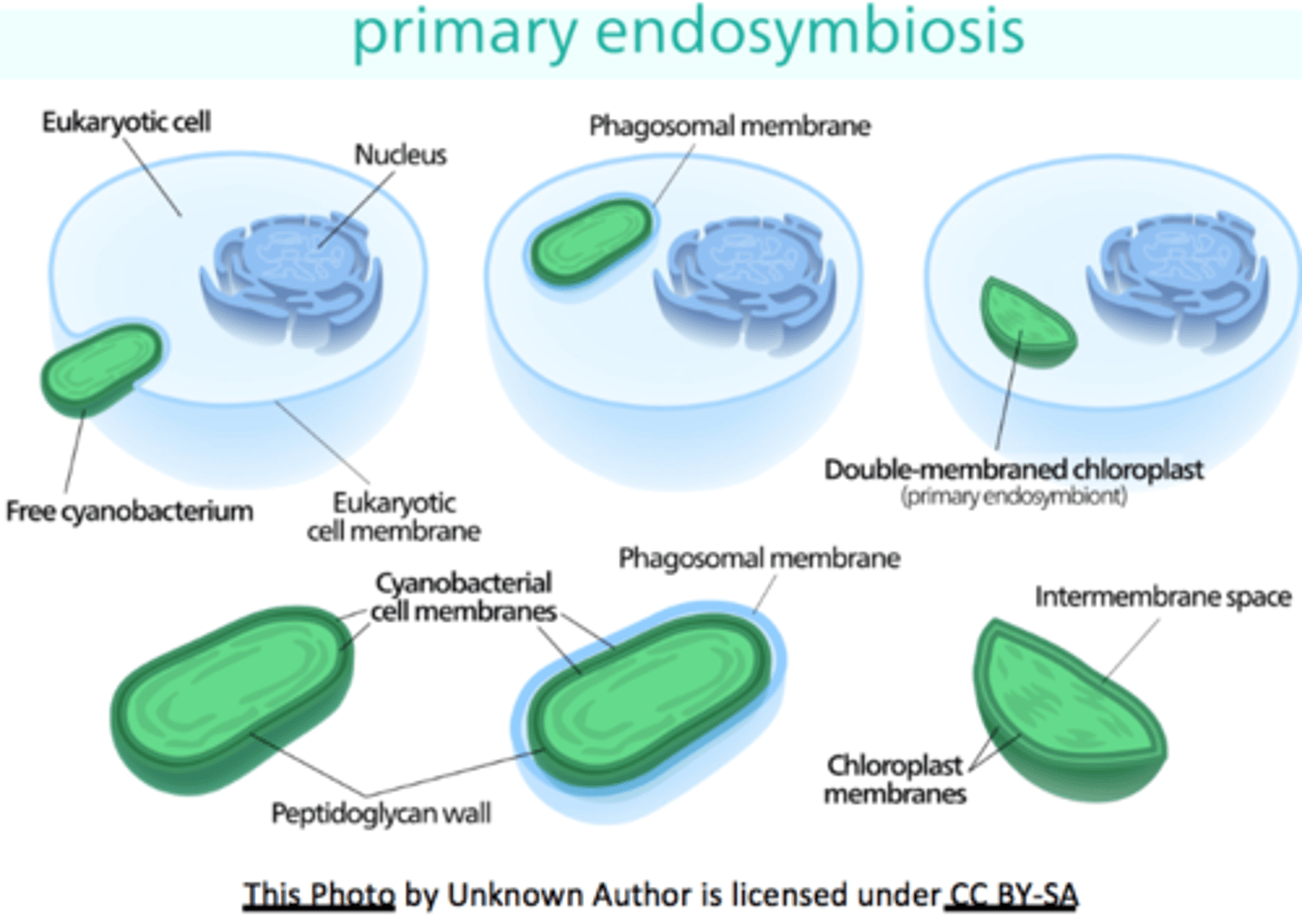
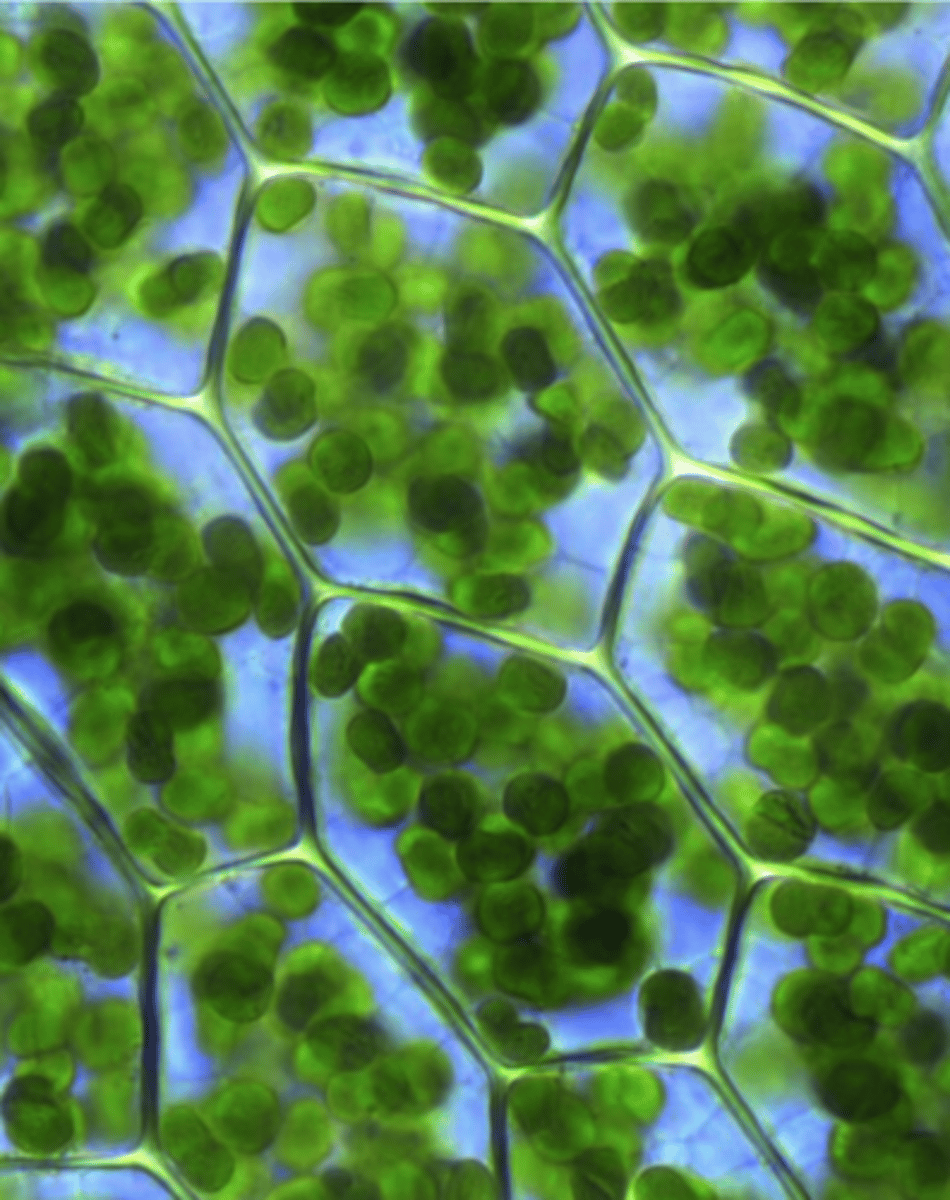
chloroplast
o Sites of photosynthesis
o assimilation starch
o Contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments
o Disk-shaped; 3-300 in mesophyll cell
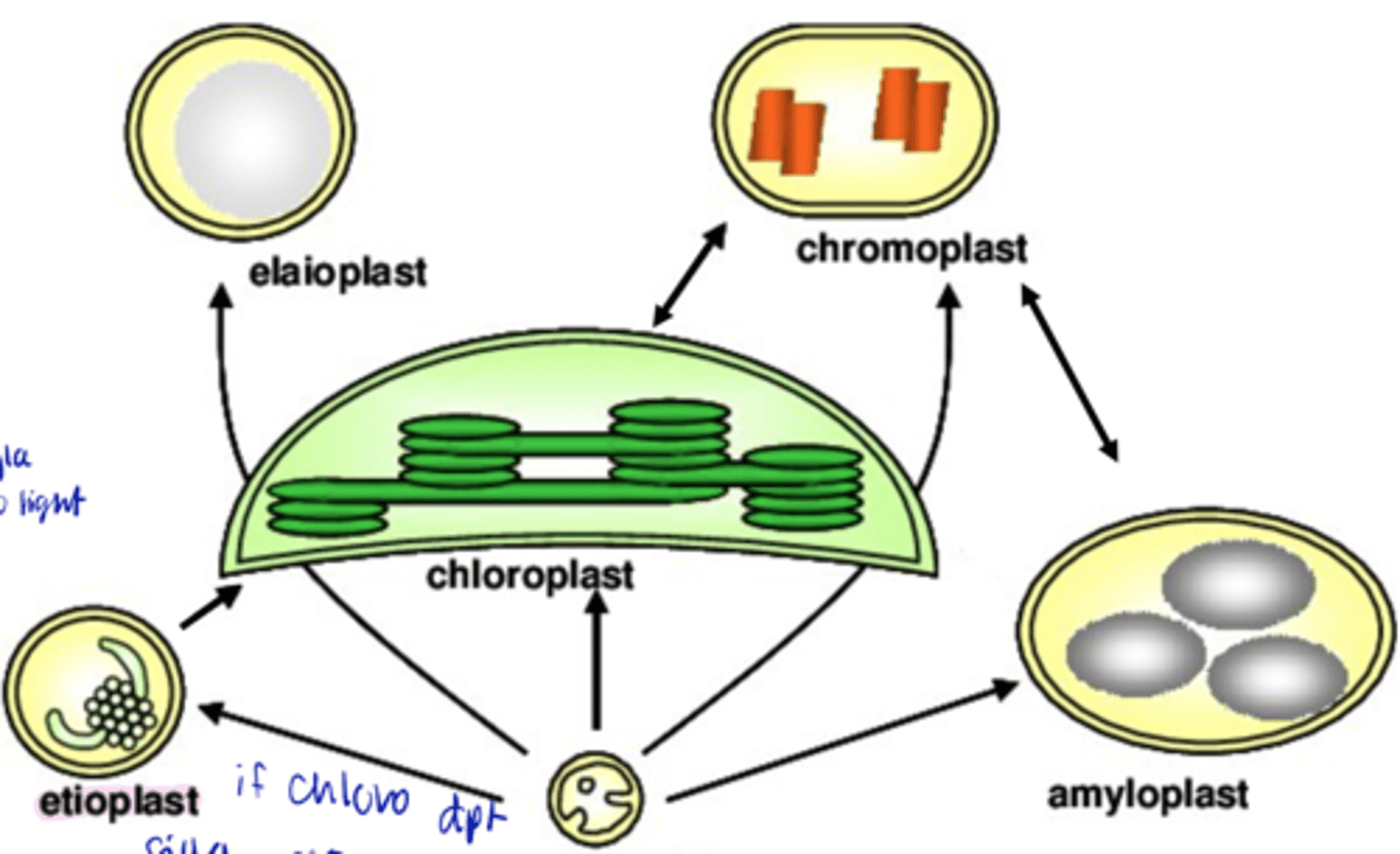
chromoplast
- ONLY carotenoid
- May develop from previously existing green chloroplasts (e.g. ripening of fruits)
- Chlorophyll and thylakoids disappear
- attractants to pollinators and seed dispersers
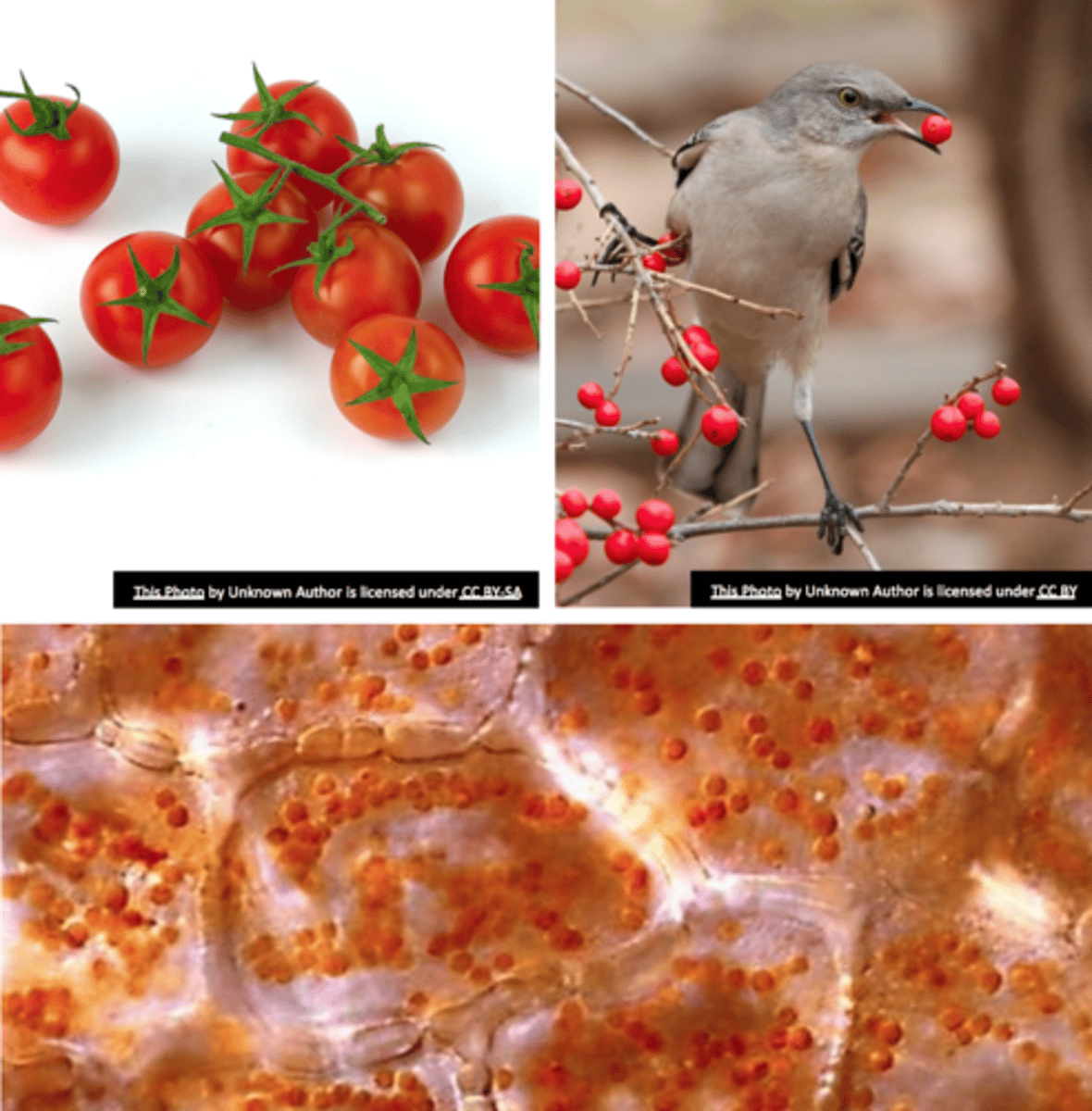

elaioplasts
fats storage leucoplast
proplastids
- Precursor of all plastids within an adult plant
- Small, colorless plastids in undifferentiated regions of the plant body
- Various kinds of plastids can change from one type to another
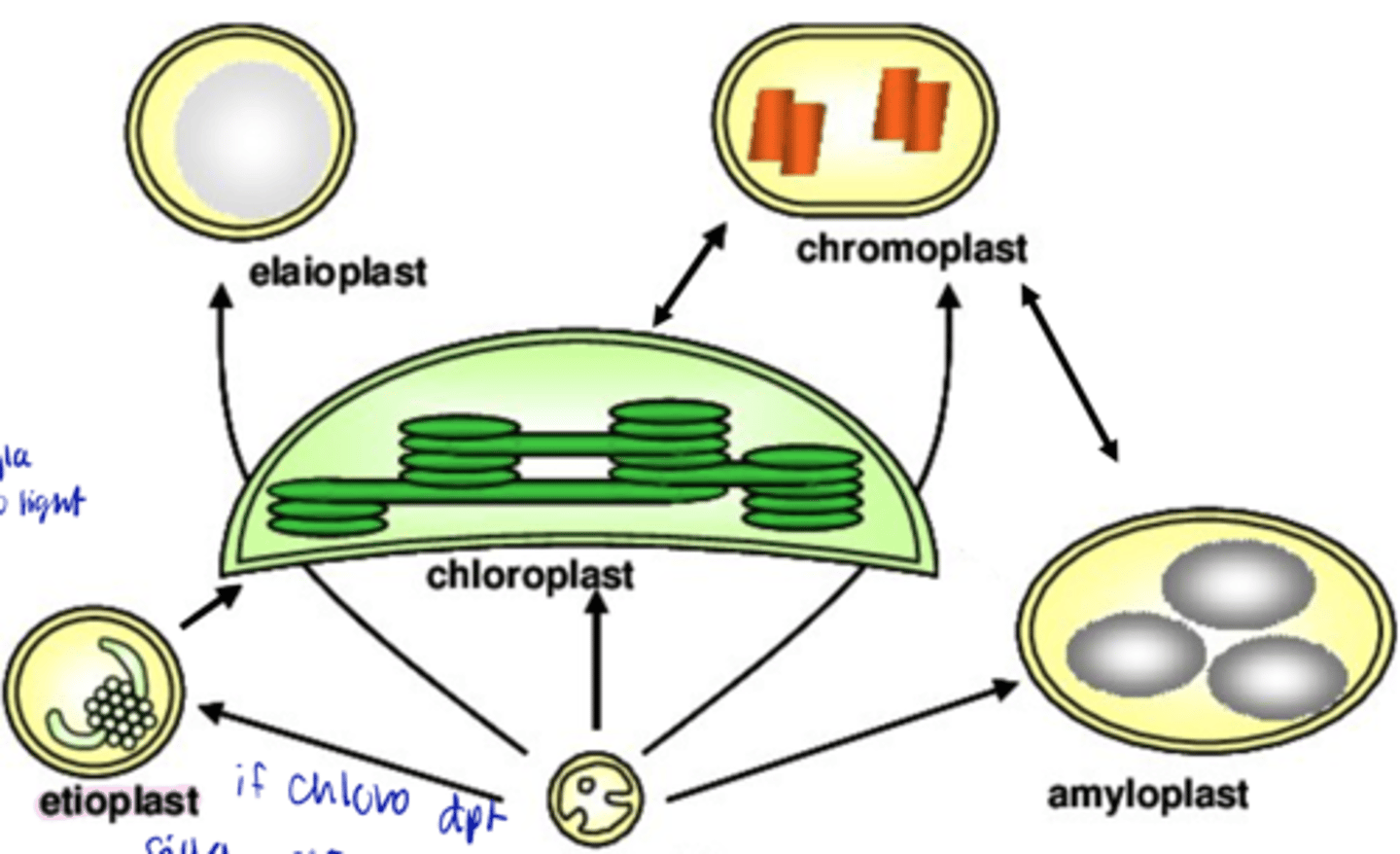
etioplasts
contain prolamellar bodies, which are the precursor of thylakoids (turns into thyla when exposed to light)
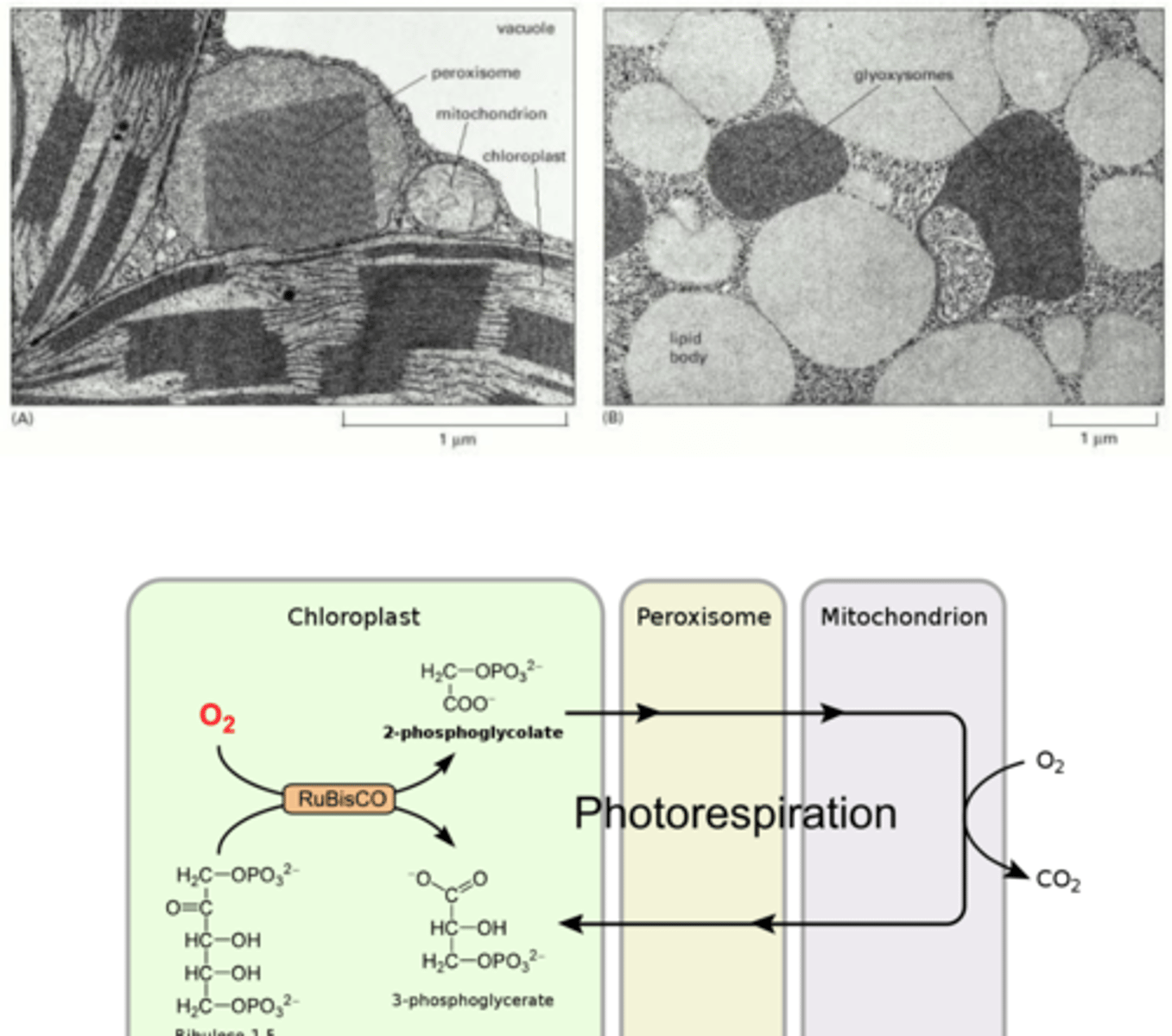
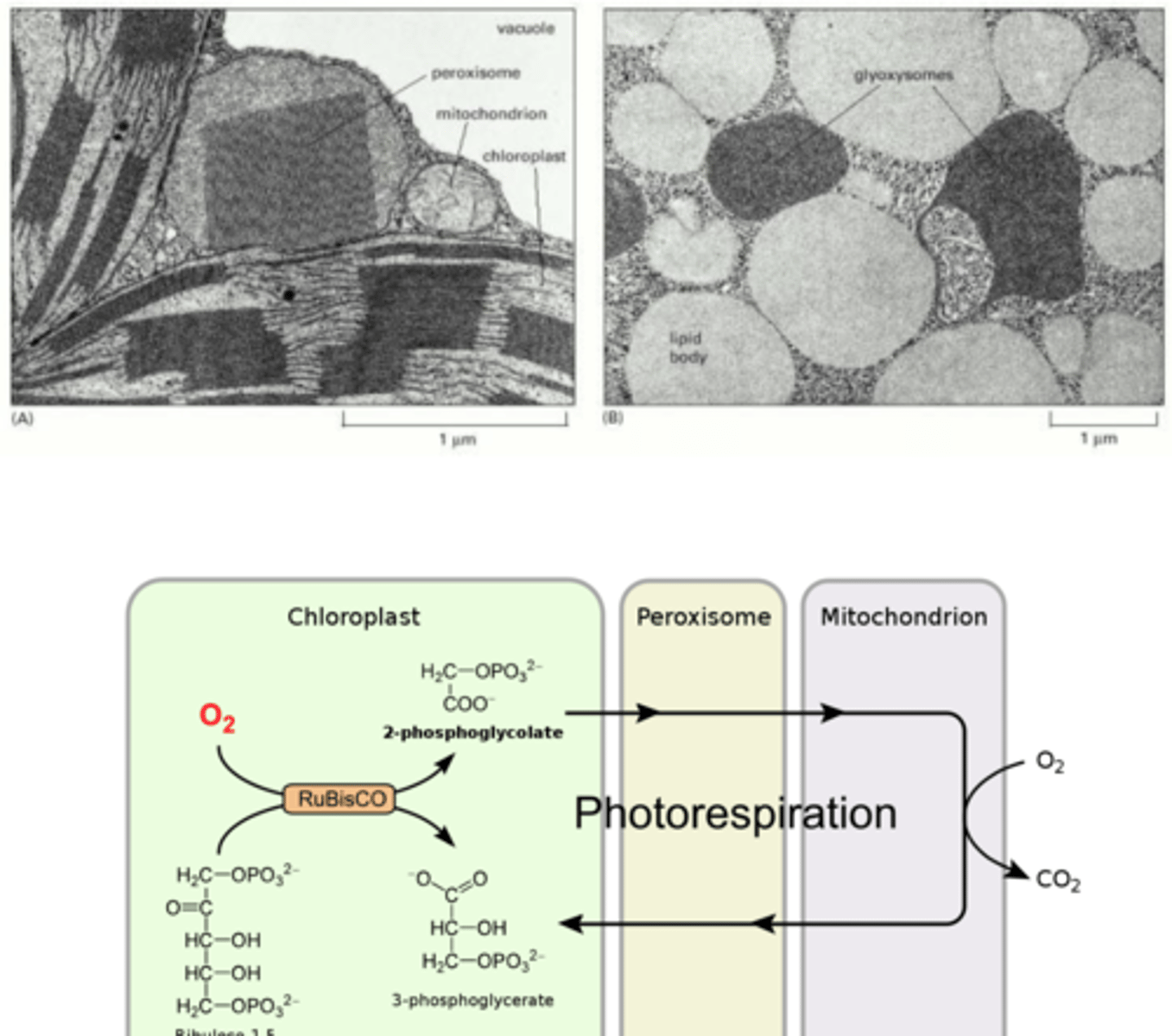
peroxisomes
- Single-membrane bound organelle
- Lacks DNA and ribosomes
- No internal membranes
- Contains catalase + oxidase
catalase
splits H2O2 to water and oxygen, turns into non-harmful components
catalyses reduction of oxygen to water or hydrogen peroxide
oxidase
interconvertible
trait of peroxisomes depending on presence of fats and appearance of chloroplast
Leaf-type peroxisomes
involved in glycolic acid metabolism in leaves (associated with photorespiration)
glyoxysomes
- unique to plants
- glyoxylate cycle in endosperm or cotyledons of germinating seeds
- stored energy --> smn usable
scle even thickening, collen uneven
sclerenchyma vs collenchyma
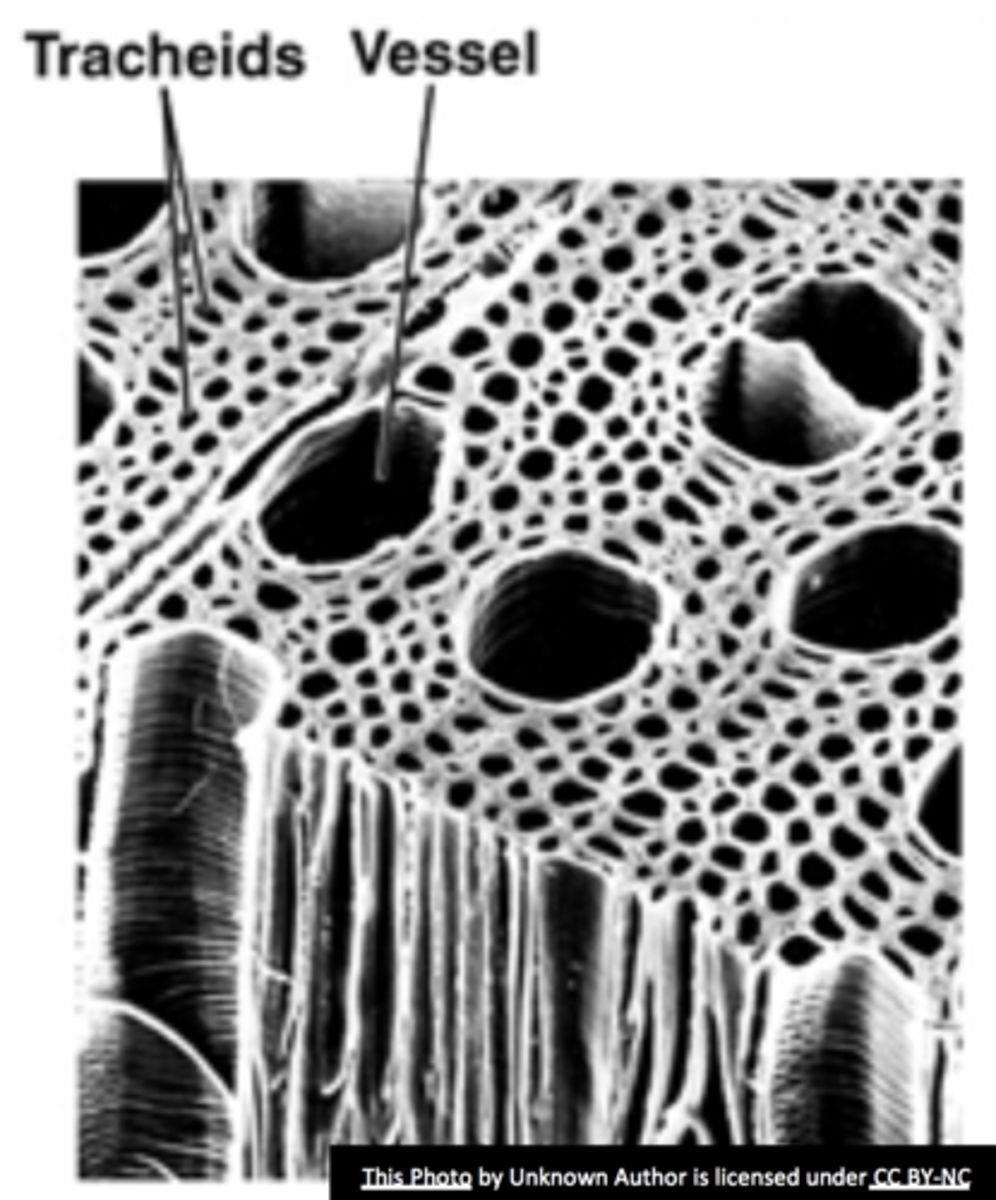
conducts water and materials from roots pataas
xylem
conducts photosynthesis products pababa from leaves
phloem
efficient hollow tube network, unobstructed flow, structural support, durability
Why are xylem cells like tracheids and vessel elements dead?
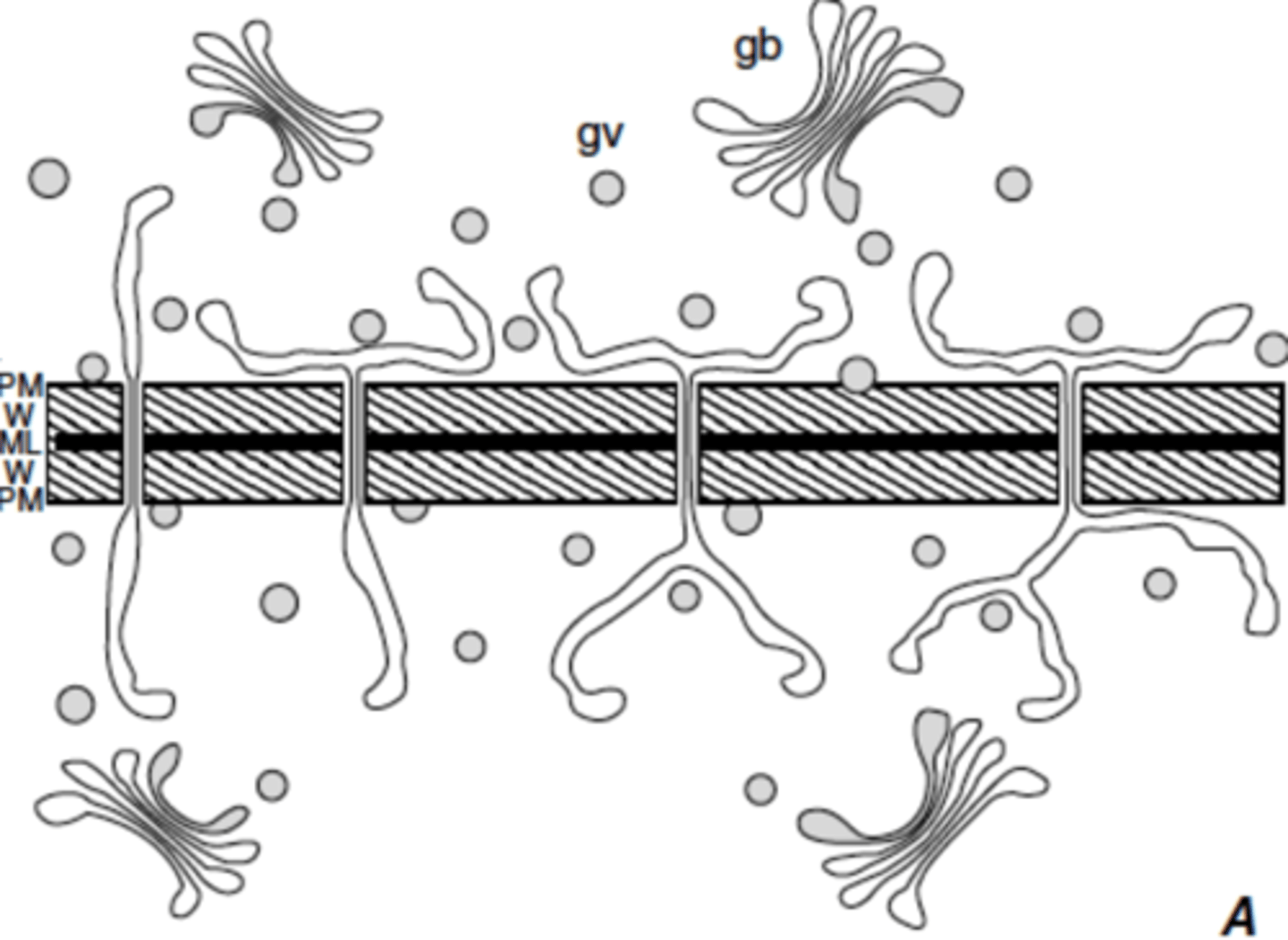
Intercellular spaces
non-contact between some sides of the cell wall faces due to increase in number as cell volume increases (lose contact w adjacent cells); characteristic of mature cells
- limits size
- prevents rupture when turgid
- physical barrier
- size + shape, final form, texture
- cell-to-cell signaling
cell wall functions
glucose units forming hbonds —> crystal lattice —> micelles --> microfibrils (bundle) --> macrofibrils (when they wrap around each other)
cellulose molecule strands
cellulose comp
non crystalline form?
hemicellulose, pectins, glycoproteins
other components of the cell wall (non-cellulosic matrix)
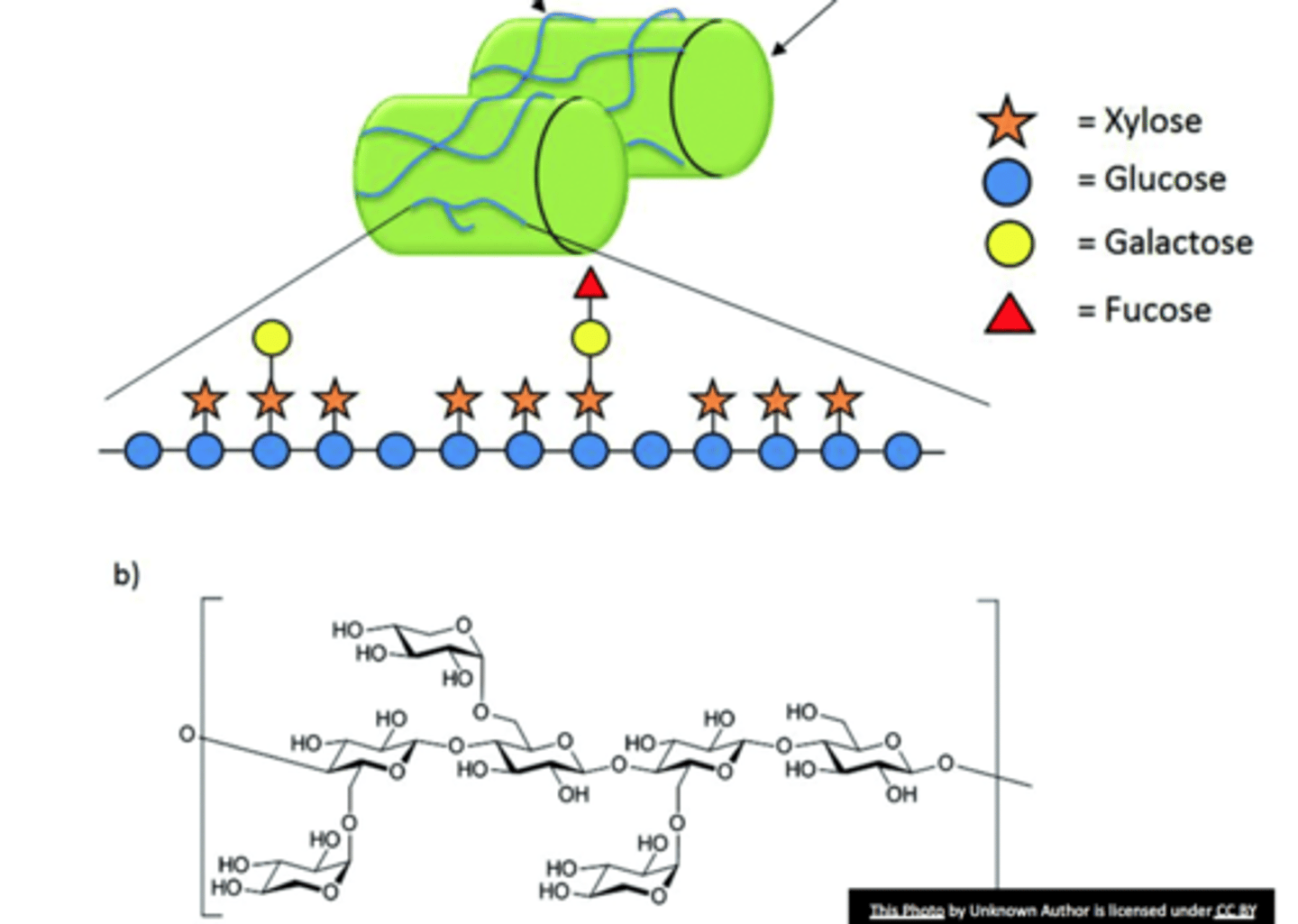
hemicellulose
non-crystalline glycans attached to cellulose microfibrils
Xyloglucan
- eudicots and half of the monocots
- hemicellulose tightly bound with cellulose microfibrils
- limits the extensibility
- regulates cell enlargement
suberin
o Insoluble lipid
o secondary protective tissue (e.g cork cells), endodermal and exodermal cells of roots, bundle sheath surrounding the leaf veins
o Restricts apoplastic movement of water and solutes
o barrier to microbial penetration
secondary wall
- Deposited when cell growth has ended
- some protoplasts die leaving a lumen
- Found in cells that have strengthening and water conduction functions
-Contains lignin
- Contains more cellulose than primary wall and pectic substances are lacking (therefore rigid)
primary pits
o Thin areas in the primary walls
o Plasmodesmata aggregates
Primary pit fields
clusters of primary pits
phragmoplast microtubules
- system of microtubules appearing betw 2 sets of daughter xmosomes
- scaffolding 4 assembly of the cell plate
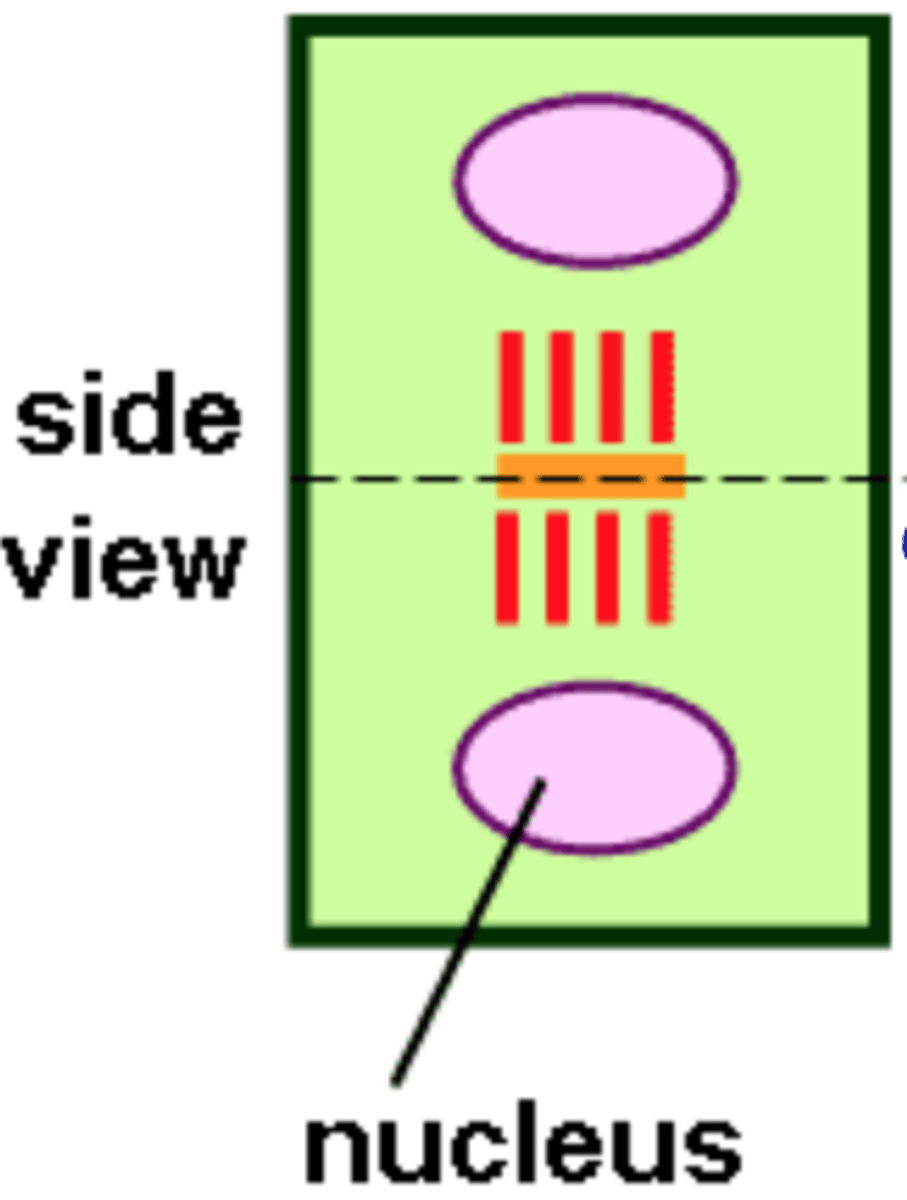
As cell wall formation is completed, some parts of he ER are entrapped within the developing wall, leading to the formation of plasmodesmata
plasmodesma formation
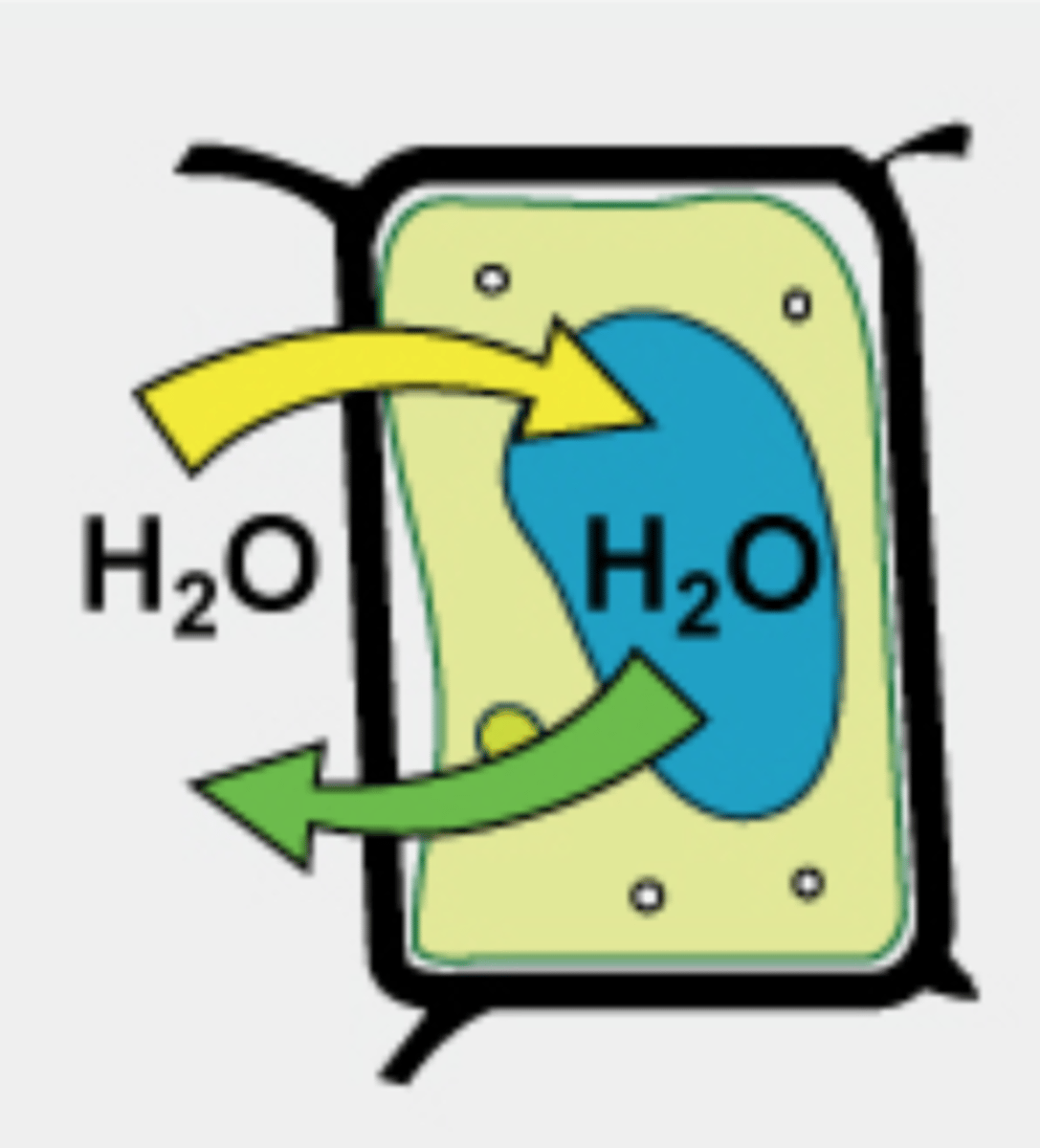
isotonic vacuole
does not result in any net movement of water in/out of the cell, however, a plant cell may become flaccid (soft, drooping or inelastic)
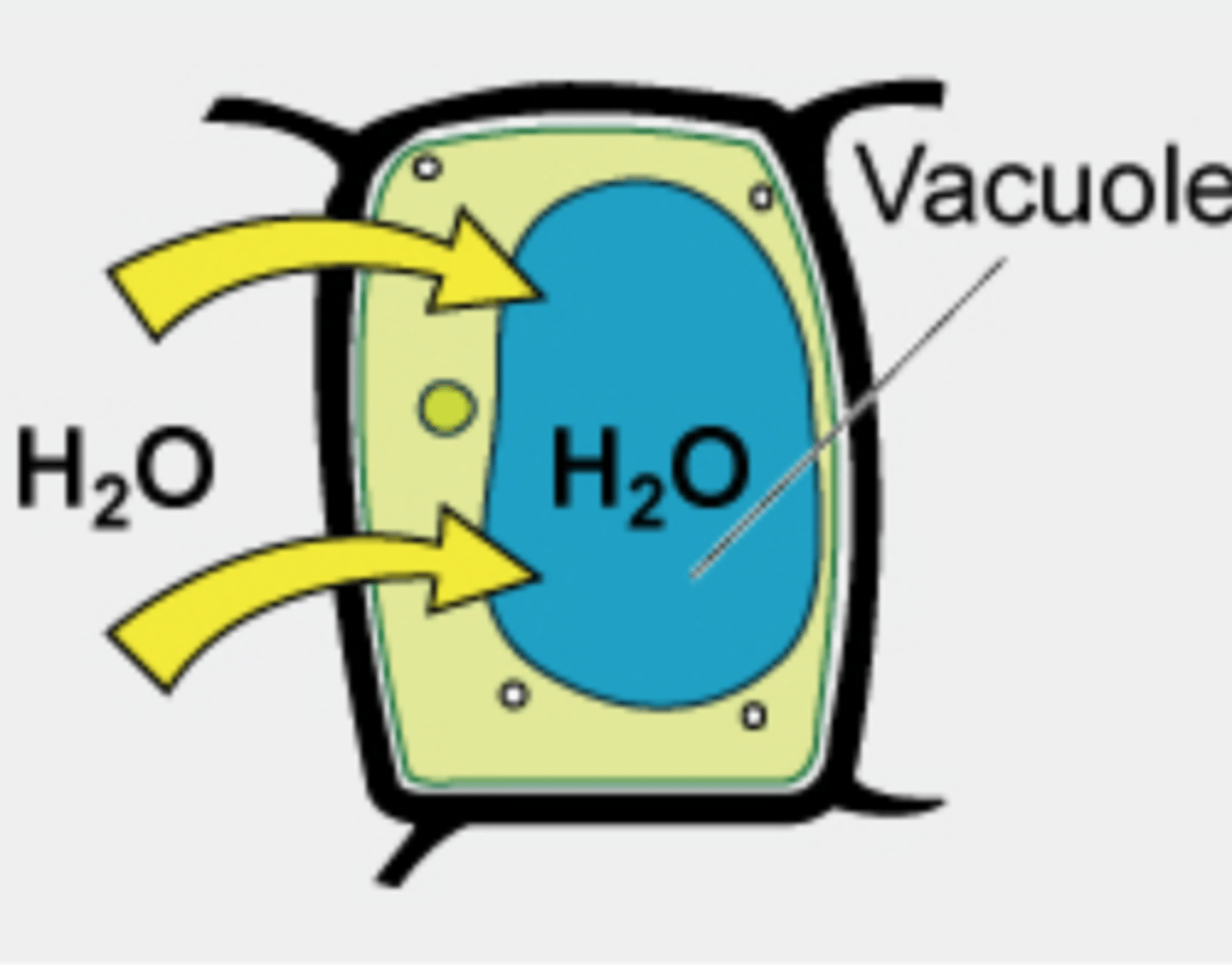
hypotonic vacuole
higher concentration of water molecules outside the cell than inside, and water will flow into the cell; high turgidity; optimal condition for plant cells
Photoinhibition
refers to a decline in photosynthesis efficiency resulting from excess excitation by light
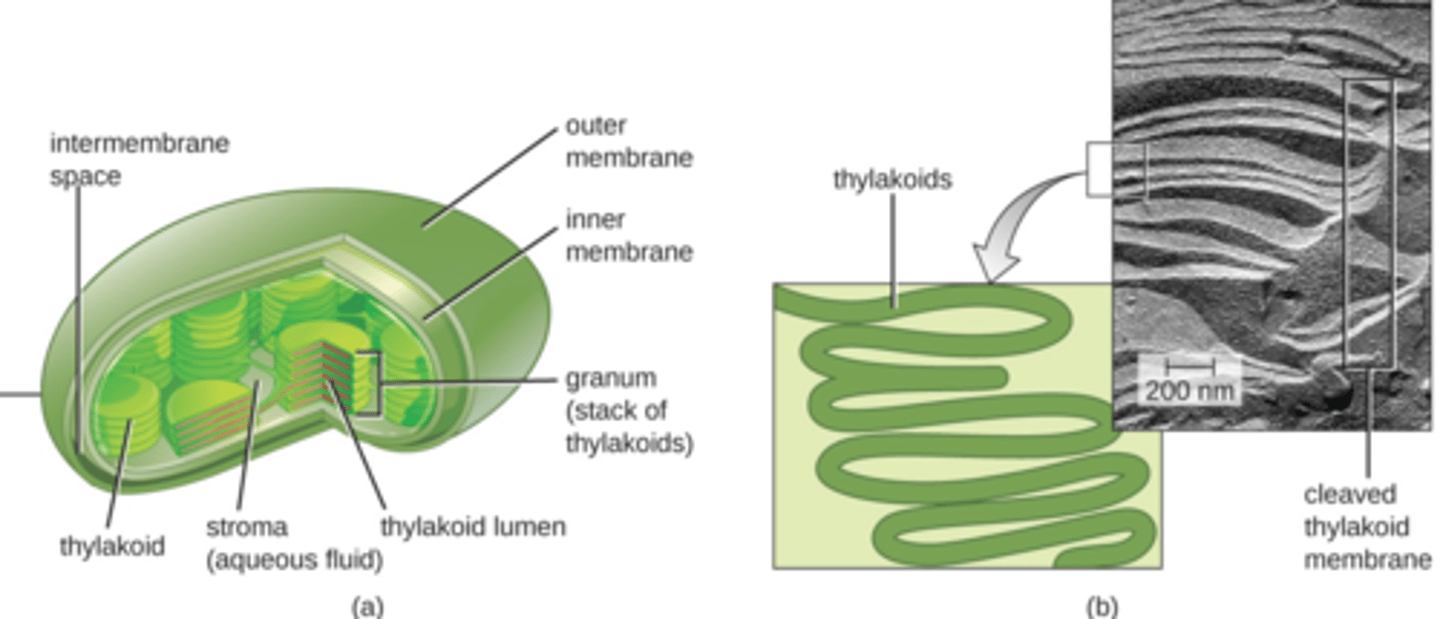
plastids
- Double-membrane
- Stroma, thylakoids, granum, stroma
- Reproduce by binary fission
- Semi-autonomous (endosymbiosis)
have DNA, can synthesize own proteins
what does it mean that plastids are semi-autonomous
like cyanobacteria, plastids have circ DNA + repro by binary fission
Name a few similarities between a bacterium and the plastid
assimilation starch
Temporary storage of starch
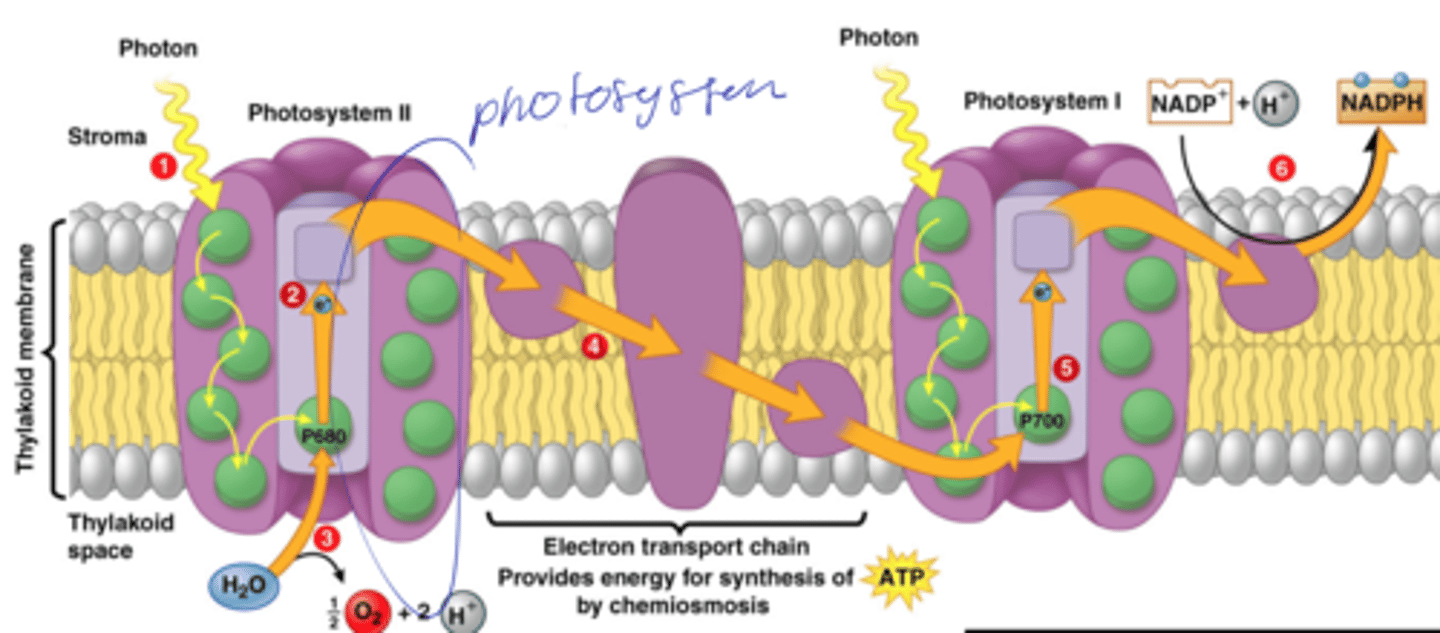
embedded in the thylakoid membranes (photosystems)
saan ang chlorophyll and carotenoids
antioxidant (prevent photooxidative damage); to attract seed dispersers and pollinators due to its color
purpose of carotenoids
leucoplast
- Non-pigmented plastids
- Least differentiated
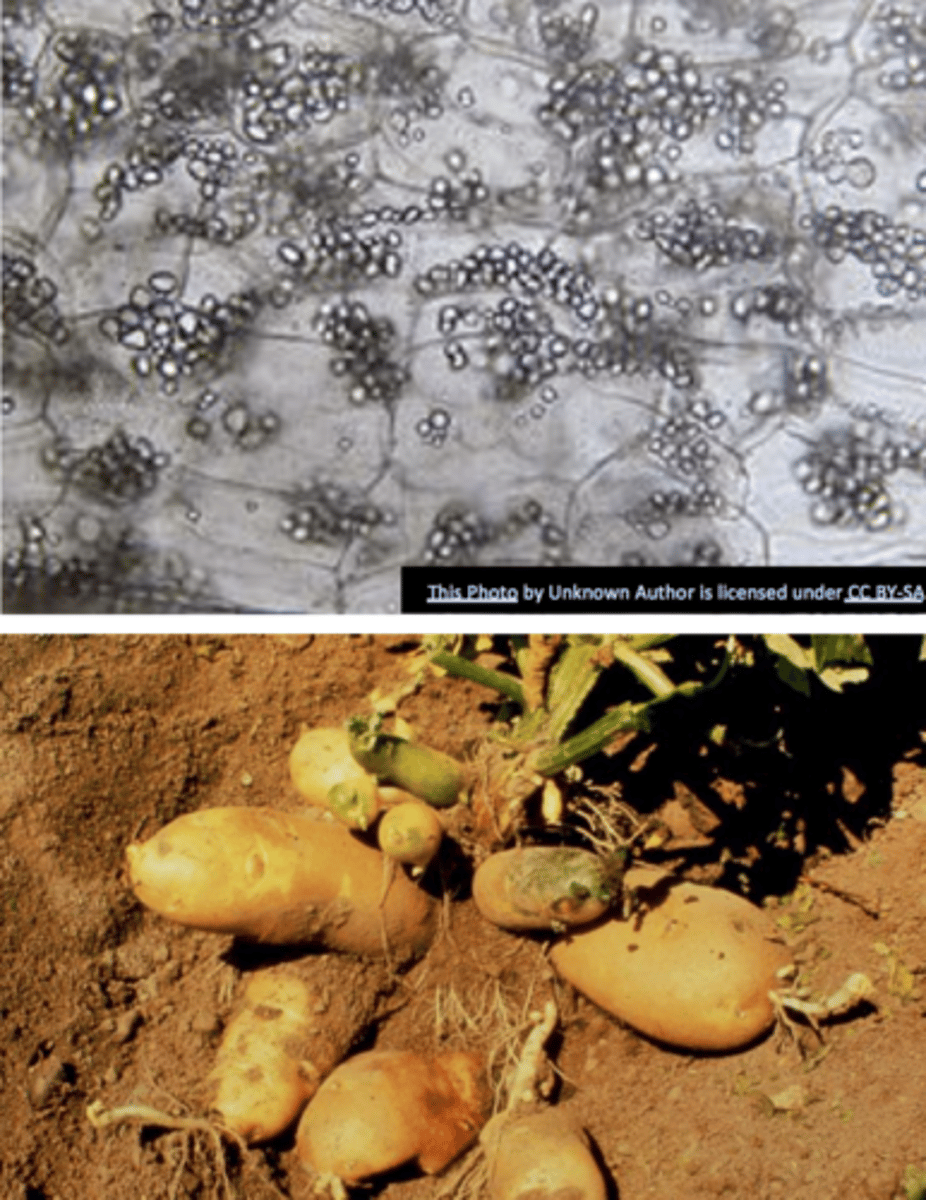

amyloplast
starch storage leucoplast
proteinoplast
protein storage leucoplast