Solid Waste, Mining, and Plate Tectonics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is leachate
“garbage soup water”
forms when rainwater filters through wastes placed in a landfill
what is liner
layers of plastic and clay to prevent groundwater contamination
landfills are a major source of what
CH4 (methane)
what are 2 ways of reducing methane gas emissions
flaring and capturing landfill
what is flaring
combustion
what can be made with captured CH4
create electricity
what is e-waste
electronic waste
what is a landfill alternative
incineration/burning trash
what are pros and cons of incineration
get electricity from it
Wastewater/ash needs specially treated and the cost of cleaning up the air
what are ores
concentrated accumulations of minerals
where are ores localized
earth’s crust
small areas of high concentration of ores are called what
veins
how does an active mine’s age influence its environmental impact
the longer the mine is open the more chemicals that need to be used
so, the older the mine, the better environmental impact
what is a reserve
the publicly known estimate of how much of a particular resource is available
what is strip mining
removal of overlying vegetation and strips of soil and rock

what is open-pit mining
creation of a large pit in the ground for extraction of ores close to the surface

what is mountaintop removal
removing mountaintop with explosives

what is placer mining
looking for minerals, metals, and precious stones in river sediments

what are environmental impacts of surface mining
loss of tress, air pollution (dust from the mining), alteration of downstream river flows, waste called tailings
what is subsurface mining
below the surface mining
risks: black lung disease, mine collapses
environmental issues: acid drainage from water in the water table needing to be drained
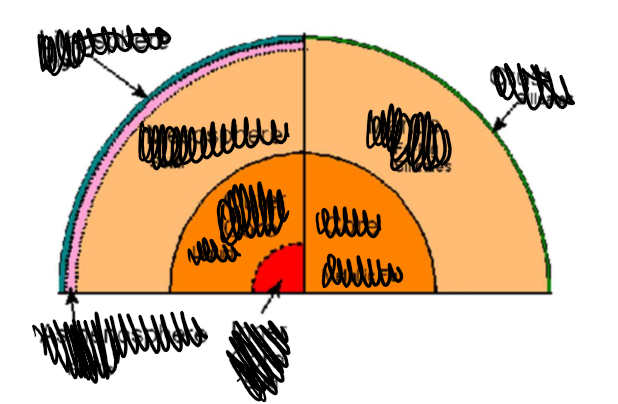
what are each of the layers of the earth
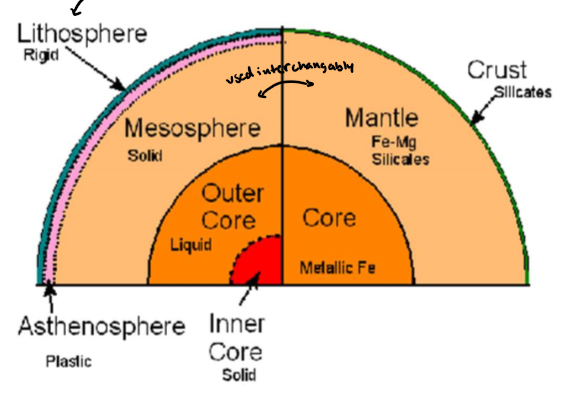
what is the crust
make sup less than 1% of earth’s mass
contains top of lithosphere
what is the lithosphere
cool layer broken into tectonic plates
what is the mantle
top layer (asthenosphere) and the inner layer (mesosphere)
what is the core
composed of nickel and iron
outer: liquid
inner: solid (due to pressure)
what is the evidence for the internal structure of the earth
seismic waves
what are seismic waves
waves that travel through the Earth’s interior during an earthquake which changes speed and direction when traveling through different densities
p waves vs s waves
P: primary, travels through solids, liquids, and gases, coiled
S: secondary, travels throug solids only, not coiled (up and down)
what measures the seismic waves
a seismometer
how do natural disasters occur
when two plates move together/apart
how do tectonic plates move
because convection currents that flow up from earths core and circulate under the asthenosphere
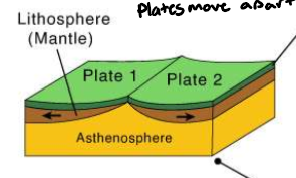
divergent plate boundary
plates moving apart
convergent plate boundary
plates moving together
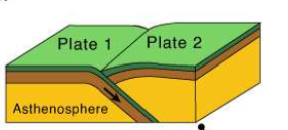
transform plate boundary
plates moving past each other
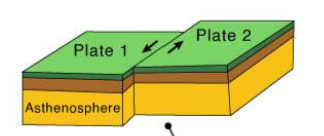
what do divergent plate boundaries form
mid-ocean ridge formations
what do convergent plate boundaries form
volcanoes, earthquakes, trenches, subduction zones
what do transform plate boundaries form
volcanoes and earthquakes
what are subduction zones
occurs at convergent plate boundaries
denser plates subduct beneath less dense plates
oceanic vs continental crust
oceanic: more dense
continential: less dense
what is a fault
a fracture or crack in the earth’s crust where rocks have moved or slipped past each other