SKELETAL SYSTEM
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(konting awa lng)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Skeleton
Divided in 2 major parts
Axial Skeleton
the skull, It includes vertebral column (spine), and rib cage.
along with ligaments and muscles, allow the human body to maintain its upright posture.
Appendicular Skeleton forms
the appendages and their attachments to the axial skeleton.
It includes the bones of the arms and legs, hands and feet, and shoulder and pelvic girdles.
make possible locomotion and other movements of the appendages.
Function of the skeletal system
Support, shape and protection
Movement
Hematopoiesis
Mineral storage and Homeostasis
Hematopoiesis
is the process in which blood cells are produced. This process occurs in a tissue called red marrow, which is found inside some bones, including the pelvis, ribs, and vertebrae
Red marrow
synthesizes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Mineral Storage and Homeostasis
is storing minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus.
This storage function is related to the role of bones
the right levels of calcium and other minerals are needed in the blood for the normal functioning of the body
Type of bones
Flat bones
Long bones
Short bones
Irregular bones
Sesamoid bones
Long bones
function to support the weight of the body and facilitate movement
are mostly located in the appendicular skeleton and include bones in the lower limbs
Long bones examples:
(the tibia, fibula, femur, metatarsals, and phalanges) and bones in the upper limbs (the humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, and phalanges).
Short bones
are about as long as they are wide
provide stability and some movement
Short bones example
The carpals in the wrist (scaphoid, lunate, triquetral, hamate, pisiform, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium) and the tarsals in the ankles (calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid, lateral cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, and medial cuneiform) are examples of short bones.
Irregular bones
They often have a fairly complex shape, which helps protect internal organs
vary in shape and structure and therefore do not fit into any other category
irregular bones examples
the vertebrae, irregular bones of the vertebral column, protect the spinal cord, (pubis, ilium, and ischium)
Sesamoid bones
are bones embedded in tendons. These small, round bones are commonly found in the tendons of the hands, knees, and feet.
function to protect tendons from stress and wear
Sesamoid bones example
kneecap
Number of bones
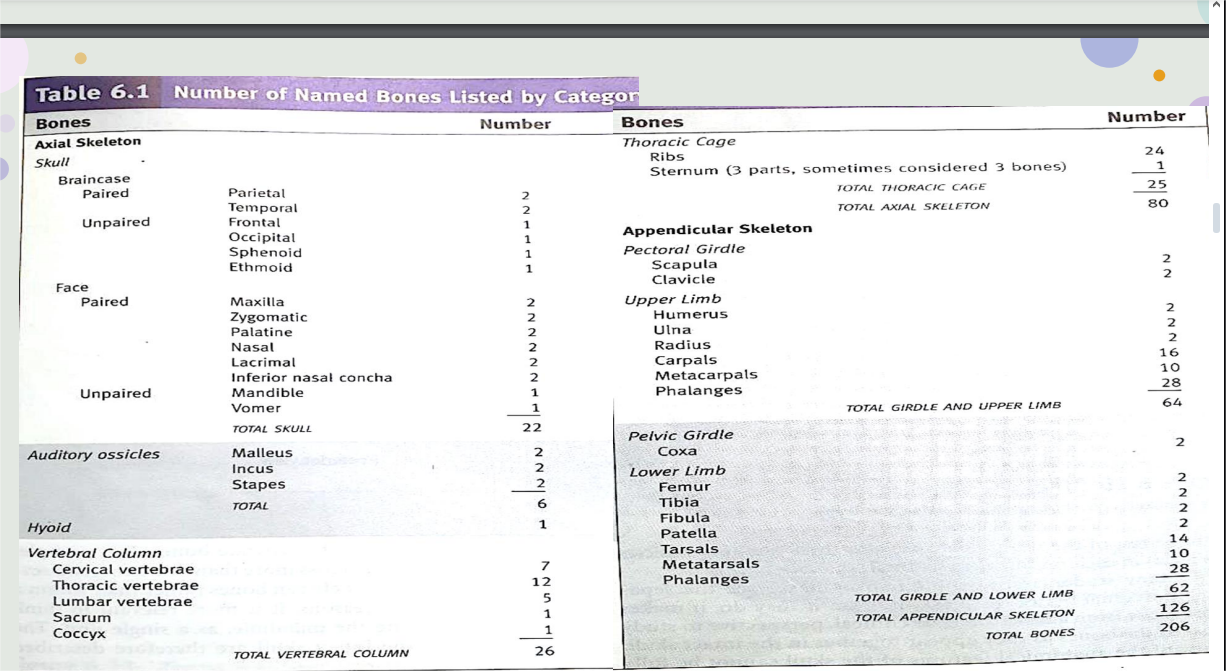
How many bones are there in skull?
22 bones of skull
How many bones are there in braincase?
8 Bones
How many bones are there in facial bone?
14 Bones
Axial Skeleton examples:
skull, laryngeal skeleton, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
Skull consist of what?
cranial bones and facial skeletal
Skeletal Bones pic:
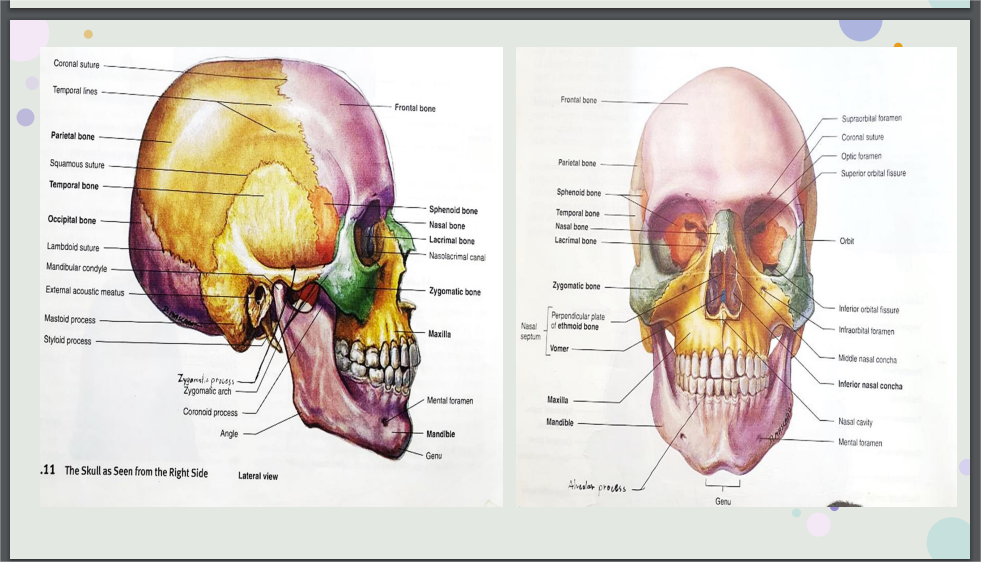
Facial skeleton examples
mandible, maxillae (r,l), zygomatics (r,l), and the bones that give shape to the nasal cavity: lacrimals (r,l), nasals (r,l), vomer, palatines (r,l), and the nasal conchae (r,l).
Cranial bones examples
occipital bone, parietal bone (r,l), temporal bone (r,l), frontal bone, sphenoid, and ethmoid
Skull Sutures
are immobile joints where cranial bones are connected with dense fibrous tissue
fontanelles
In fetuses and newborn infants, cranial bones are connected by flexible fibrous sutures, including large regions of fibrous membranes
The four major cranial sutures
lambdoid suture
coronal suture
sagittal suture
squamous sutures
lambdoid suture
between the occipital and parietal bones
coronal suture
between the frontal and parietal bones
sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
squamous sutures
between the temporal and parietal bones
What are the bones in inner ear?
malleus, incus, and stapes
Laryngeal Skeleton
It is located between the trachea and the root of the tongue
Hyoid Bone
bone provides an anchor point
The movements of the laryngeal skeleton both open and close the glottis and regulate the degree of tension of the vocal folds, which–when air is forced through them– produce vocal sounds
Vertebral Column
formed by a series of 24 vertebrae, plus the sacrum and coccyx
How many series are there in vertebrae?
series of 24 vertebrae
Cervical spine numbers
(C01-C07)
Thoracic spine
(T01-T12)
Lumbar spine
(L01-L05)
3 main bones in vertebral?
Vertebrae, Sacrum, Coccyx
how many bones are there in Cervical?
7 bones
how many bones are there in thoracic?
12 bones
how many bones are there in lumbar?
5 bones
how many bones are there in Sacral?
1 bone
how many bones are there in Coccygeal?
1 bone
What are the function of Vertebral Column
•Supports weight of the head & trunk
•Protects spinal cord
•Allows spinal nerves to exit the spinal cord
•Provides site for muscle attachment
•Permits movement of the head & trunk
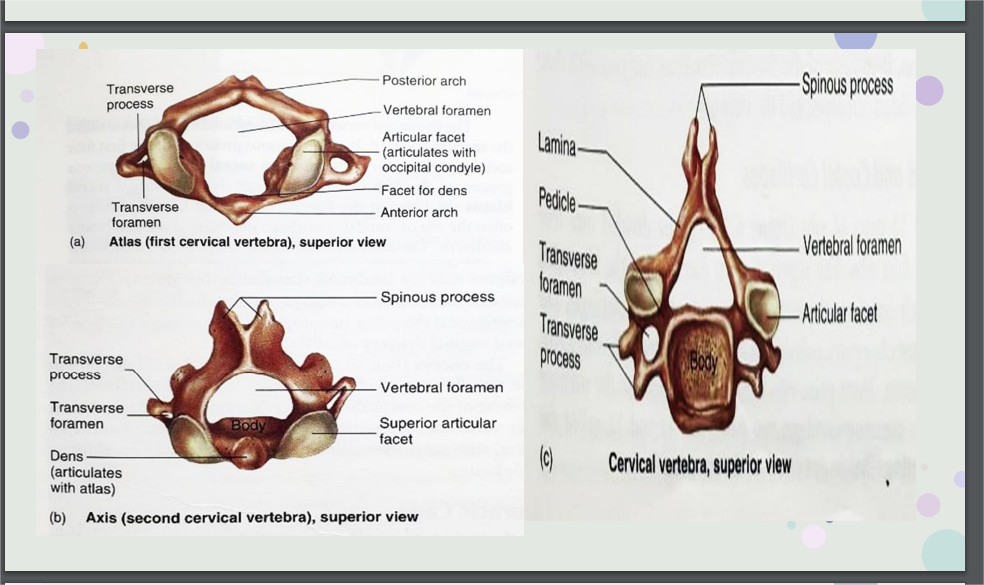
Cervical Vertebrae
Have very small bodies, except for atlas(which has no body)
Atlas
first cervical vertebrae; hold ups the head; Nodding movement, “yes” motion of head
Axis
tilting of the head; shaking of head, “no” motion of head
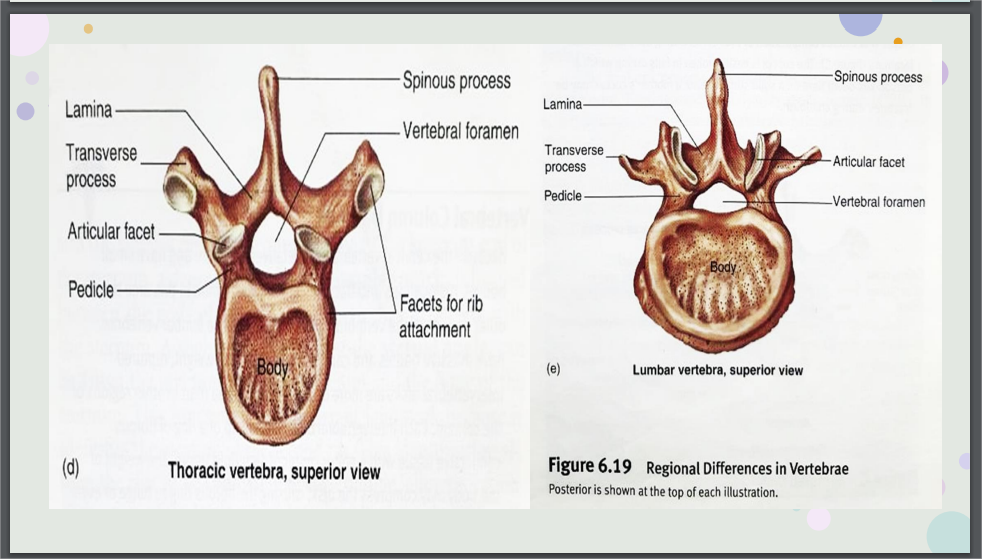
Thoracic Vertebrae
Possess long, thin spinous process that are directed inferiorly.
Lumbar Vertebrae
have large, thick bodies & heavy, rectangular transverse & spinous process.
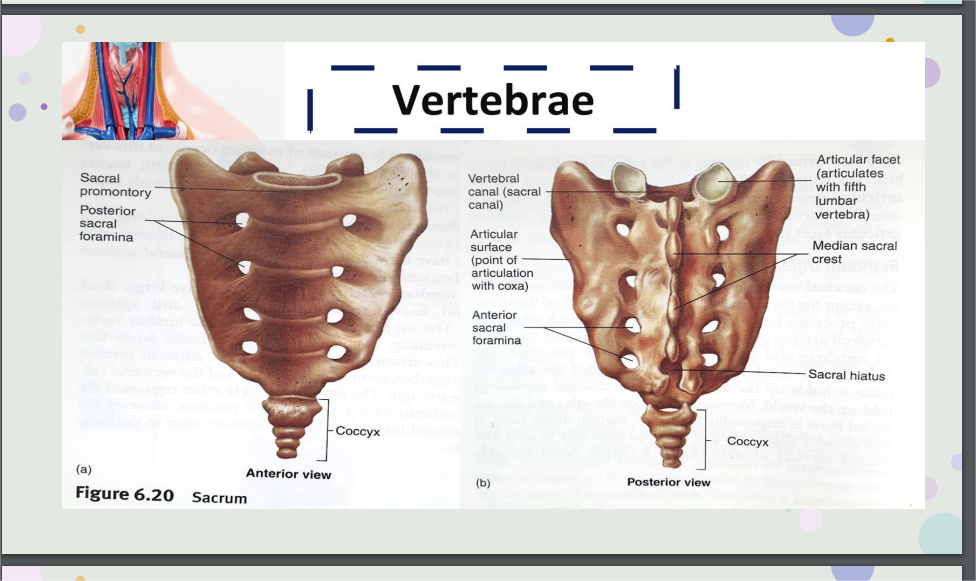
Sacrum
5 sacral vertebrae are fused into single bone.
Coccyx
tail bone, consist of 4 more-or-less fused vetebrae
Axis and Cervical vertebrae picture":
Thoracic vertebra and Lumbar vertebra
Anterior and Posterior view of Vertebrae
Thoracic cage
formed by the ribs and sternum, protects internal organs and gives attachment to muscles involved in respiration and upper limb movement. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body of the sternum, and xiphoid process.
What are the true ribs?
Ribs 1-7
What are the false ribs?
Ribs 8-12
RIbs 11-12 is also known as?
Floating ribs
Appendicular Skeleton
make up the rest of the skeleton, and are so called because they are appendages of the axial skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton examples:
Shoulder Girdle, Upper Limbs, Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs,
shoulder girdle consists of??
scapulae and clavicles
upper limbs includes??
bones of the arm (humerus), forearm (radius and ulna), wrist, and hand. The only bone of the arm is the humerus, which articulates with the forearm bones–the radius and ulna– at the elbow joint
Ulna
is the larger of the two forearm bones.
Wrist Bones
carpus, consists of eight carpal bones
also called carpals
What are the 8 carpal bones?
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetral, Pisiform, Trapezoid, Trapezium, Capitate, Hamate
Hand Bones
includes 8 bones in the wrist, 5 bones that form the palm, and 14 bones that form the fingers and thumb
Metacarpals
bones that form the palm of the hand are called?
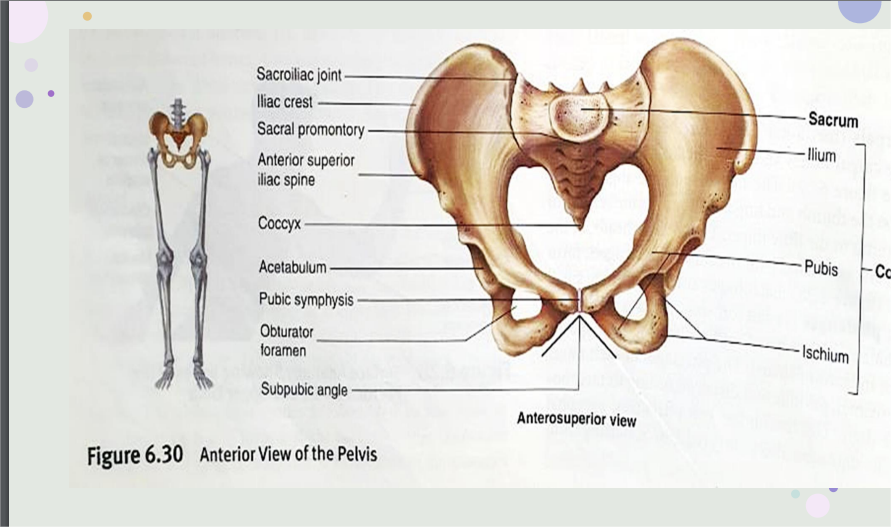
Pelvic girdle
is a ring of bones attached to the vertebral column that connects the bones of the lower limbs to the axial skeleton
What are the 3 irregular bones om the pelvic girdle?
ilium, ischium, and pubis
What is the difference of Female and Male Pelvis ?
The female pelvic brim is larger and wider than the male’s. female pelvis (over 90 degrees)
the male pelvis (less than 90 degrees). The male pelvis is deeper and has a narrower pelvic outlet than the female’s.
Anterosuperior part of the pelvis
Lower limbs
include the bones of the thigh, leg, and foot
Femur
is the only bone of the thigh
Bones in the lower limbs
Femur, Patella, Tibia and Fibula, Tarsus, Metatarsals, Phalanges
Foot bones
consist of the tarsal bones of the ankle, the phalanges that form the toes, and the metatarsals that give the foot its arch
Foot bones has?
five metatarsals, five proximal phalanges, five distal phalanges, but only four middle phalanges (as the foot’s “big toe” has only two phalanges).
Ankle bones
tarsus, consists of seven tarsal bones
Ankle bones examples
the calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, and three cuneiforms.
Foot Arches
They serve as shock-asborbing structures that support body weight and distribute stress evenly during walking.
How many arches are there in Foot arches?
3 Arches, Transverse arch, Longitudinal arch, Longitudinal arch
Joint
hold the skeleton together and support movement
what are the 2 categorize joints?
Range of motion and Organization of joints by structure
Synarthroses
include skull sutures, the articulations between the teeth and the mandible, and the joint found between the first pair of ribs and the sternum
Amphiarthrosis
include the distal joint between the tibia and the fibula and the pubic symphysis of the pelvic girdle
Diarthrosis
include many bone articulations in the upper and lower limbs. Examples of these include the elbow, shoulder, and ankle.
Fibrous Joints
is thick connective tissue, which is why most (but not all) fibrous joints are immovable (synarthroses)
3 types of Fibrous joints
Sutures, Gomphoses, Syndesmosis
Sutures
are nonmoving joints that connect bones of the skull. These joints have serrated edges that lock together with fibers of connective tissue.
Gomphoses
The fibrous articulations between the teeth and the mandible or maxilla
Syndesmosis
is a joint in which a ligament connects two bones, allowing for a little movement (amphiarthroses). The distal joint between the tibia and fibula
Cartilaginous Joints
Joints that unite bones with cartilage
2 types of cartilaginous
Synchrondosis and symphysis
Synchrondosis
is an immovable cartilaginous joint. One example is the joint between the first pair of ribs and the sternum.
symphysis
consists of a compressable fibrocartilaginous pad that connects two bones
Synovial Joints
are characterized by the presence of an articular capsule between the two joined bones. are protected by a coating of articular cartilage.