PBS Biomed EOC
1/314
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Principles of Biomedical Science PLTW EOC study guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
315 Terms
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a medial imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to take pictures of the soft tissues of the body
Differential diagnosis
based on information like an individual's medical history, current symptoms, and the results of physical exams, routine testing, and blood work, a doctor develops this list of possible diseases/disorders
Eukaryote
organisms that have membrane-bound organelles
Somatic cell
any cell in the human body that is not a sex cell (egg or sperm)
DNA
a type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases; double-stranded and helical and functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses
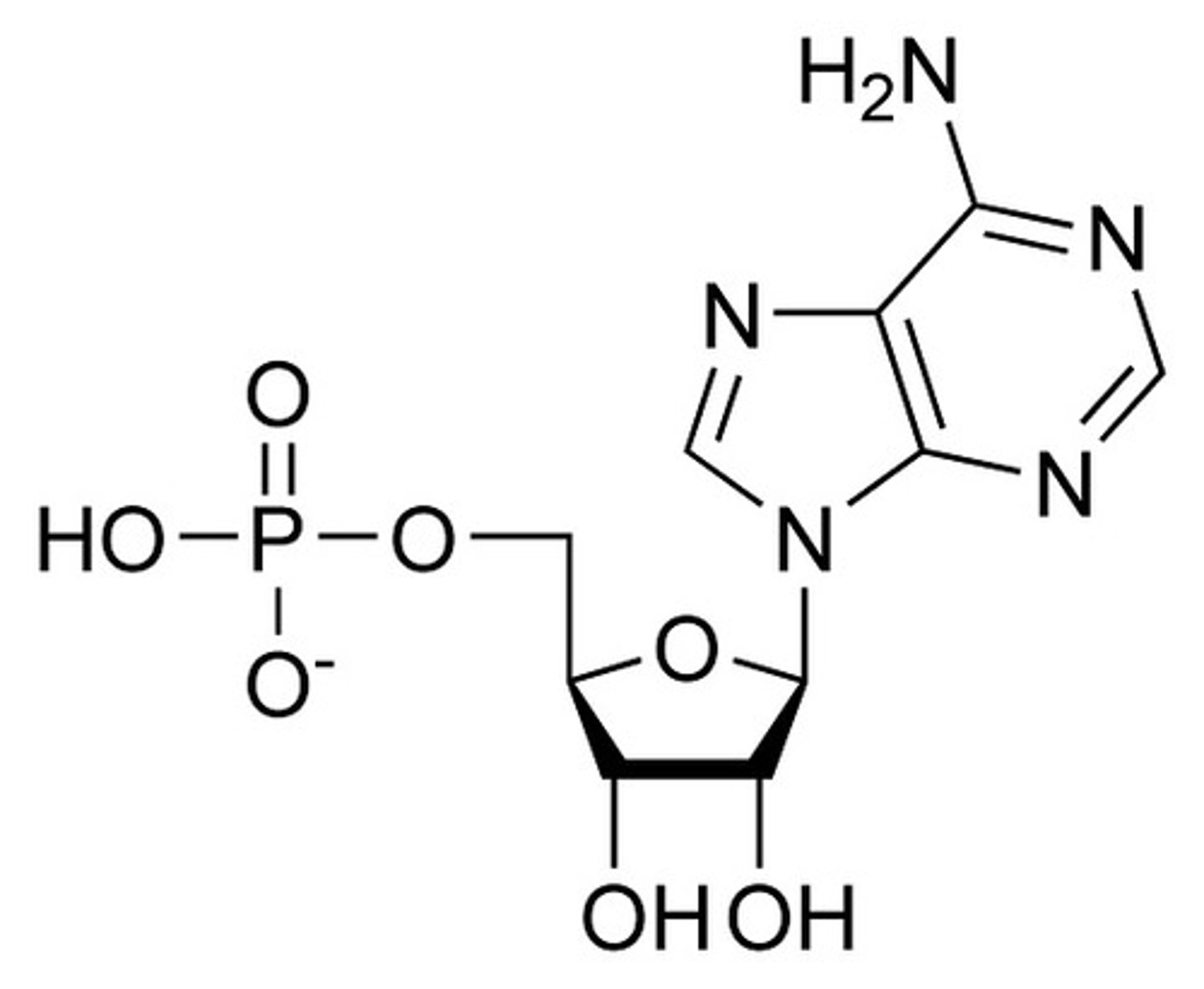
Nitrogenous base
adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine
Chromosome
tightly coiled DNA that is found in the nuclei of cells; humans have 46
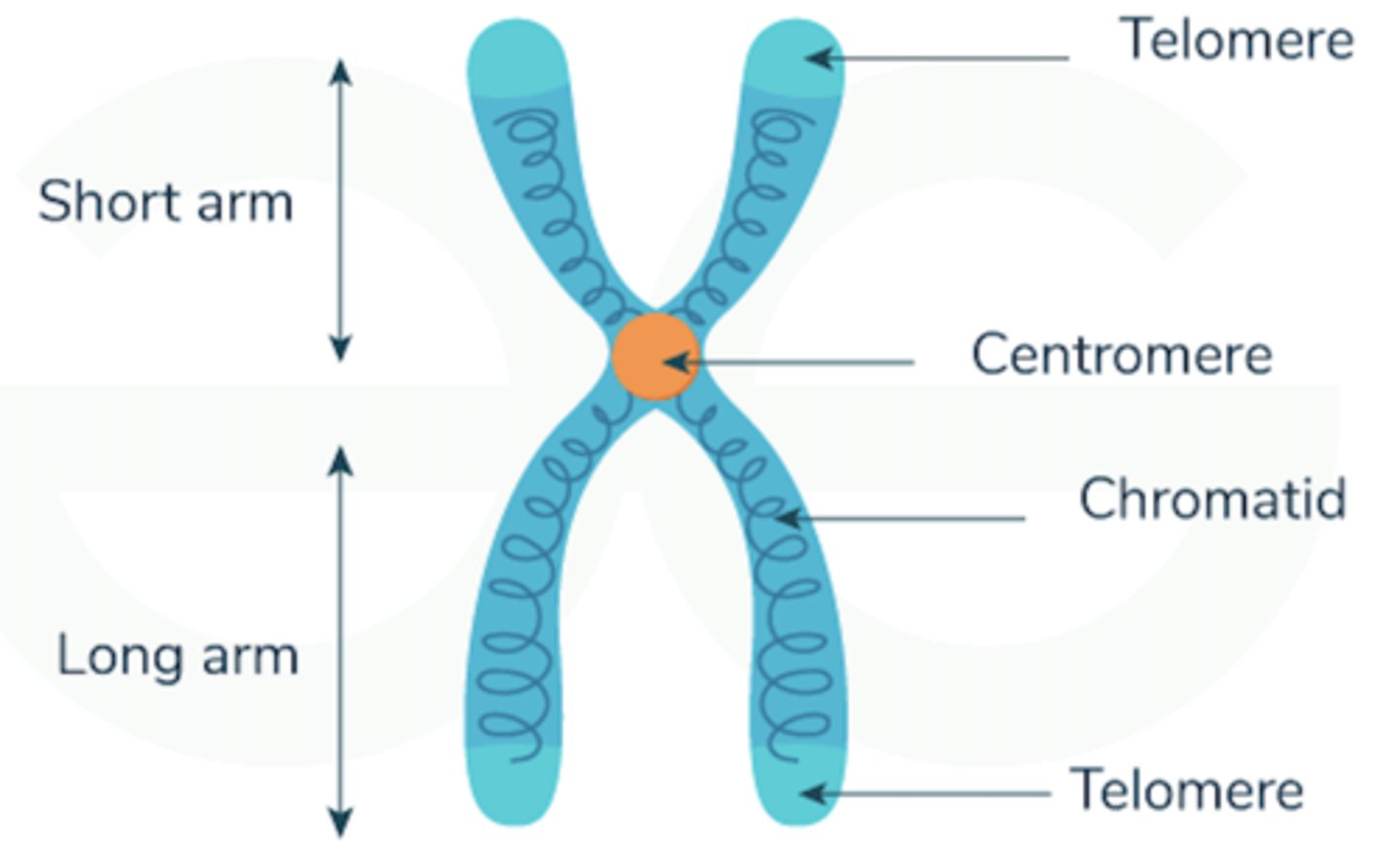
Chromatid
one half of the chromosome
Centromere
part of the chromosome where the two chromatids are connected
Telomeres
protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent the chromosome from getting damaged or sticking to other chromosomes
Mitosis
a process that takes place in the nucleus of a dividing cell, it involves the doubling and separation of genetic material and results in the formation of two new nuclei, which each have the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
Interphase
DNA replicates so that there are two copies of each chromosome
Prophase
chromosomes condense and become visible under a light microscope and they pair up with their sister chromatids, the mitotic spindle forms, and the nuclear envelope disappears
Metaphase
chromosomes line up at the center of the cell, fibers attach to each of the sister chromatids and will pull each chromatid to opposite pulls of the cell
Anaphase
each chromosome separates and the sister chromatids are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell
Telophase + Cytokinesis
the cells split into two, each new daughter cell looks identical to the original cell
DNA replication
process of copying DNA during mitosis, happens during interphase, ends with two complete sets of DNA, each with an original and new strand
Helicase
enzyme that unzips DNA for DNA replication
DNA Polymerase
the enzyme that builds a new DNA strand
Tumors
lumps or masses of tissue caused by uncontrolled cell division that are characterized as benign or malignant
Benign
cancerous tumors that are generally considered harmless, they will not spread to other parts of the body or invade other tissues
Malignant
also known as cancerous tumors, harmful and can invade other tissues or spread to other parts of the body if not treated
Metastasis
the spread of cancerous cells to other tissues or parts of the body
Basal Cell Carcinoma
type of skin cancer that originates in the basal cell layer of the epidermis, basal cells are mutated and replicate uncontrollably, they form tumors within the skin and on the surface
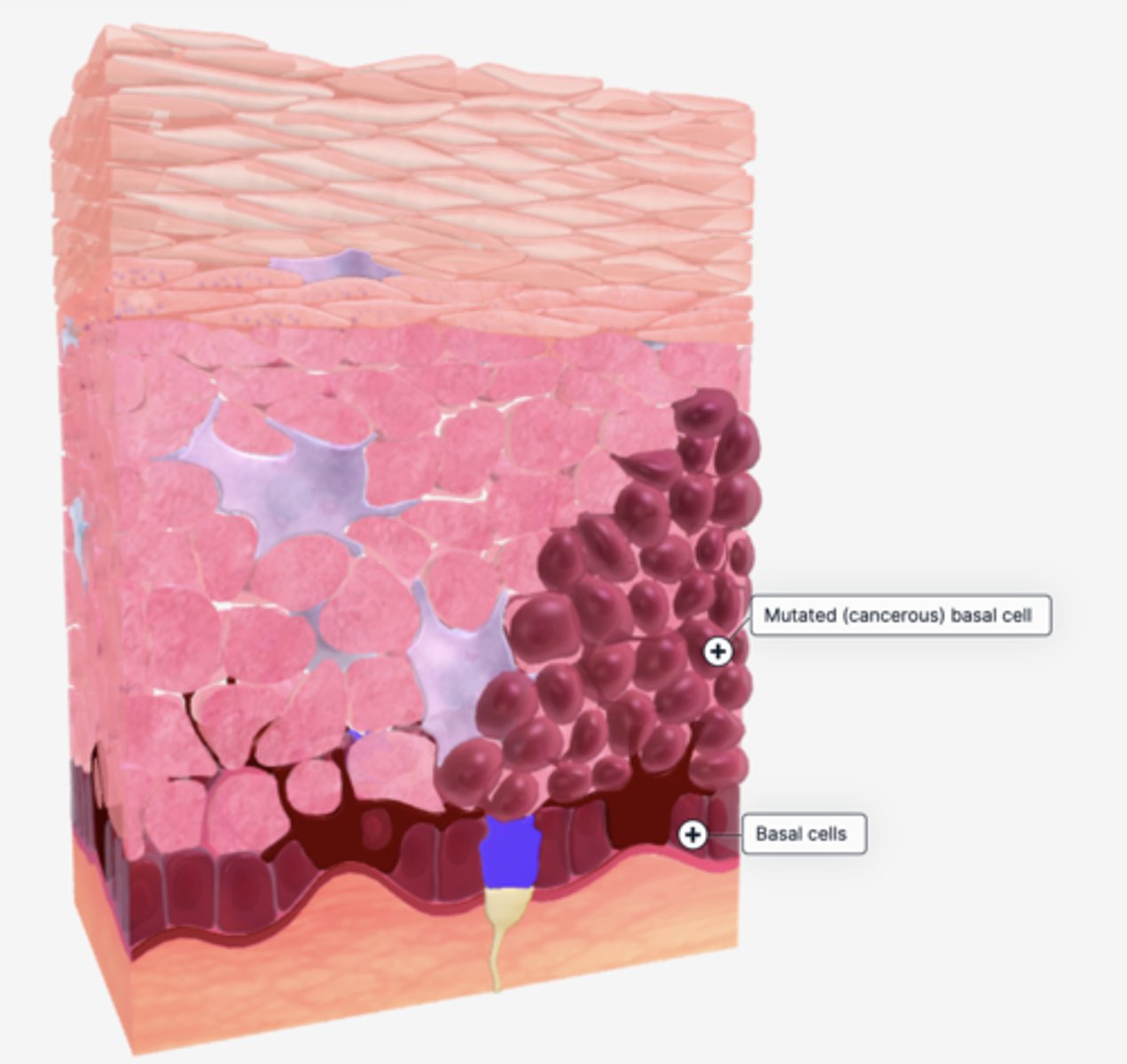
Epidermis
outermost layer of skin that makes cells to replace about 40,000 old skin cells, and has melanin
Genes
a sequence of nucleotides that codes for a protein, resulting in a specific phenotype
Mutation
a rare change in genetic material, which ultimately creates genetic diversity within a species
Protein synthesis
the creation of a protein from a DNA template
mRNA (messenger RNA)
what DNA is transcribed to (egg)
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
what mRNA sits on to transcribe (pan)
tRNA (transfer RNA)
brings amino acid and anticodon (ends up being the same as DNA but with U's instead of T's, is NOT translation)
AUG (met)
start codon
UAA, UGA, UAG
stop codons
Substitution mutation
one DNA base is switched for another (ex: A to G)
Insertion mutation
one DNA base is inserted into a gene sequence
Deletion mutation
one DNA base is deleted from a gene sequence (the worst mutation)
Genome
complete set of the genes in one organism
Allele
any of the alternative forms of a gene that may occur at the same place on a chromosome (ex: genes responsible for blood type are on chromosome 9)
Prognosis
the likely course a disease will take over an individual's lifetime
FH (familia hypercholesterolemia)
autosomal dominant genetic condition in chromosome 19 that causes LDL, making you more likely to have atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries)
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) gene testing
testing done through a healthcare provider to determine the predisposition (increased likelihood) to certain diseases
Cytogenetics
laboratory technicians who harvest cells from biological samples
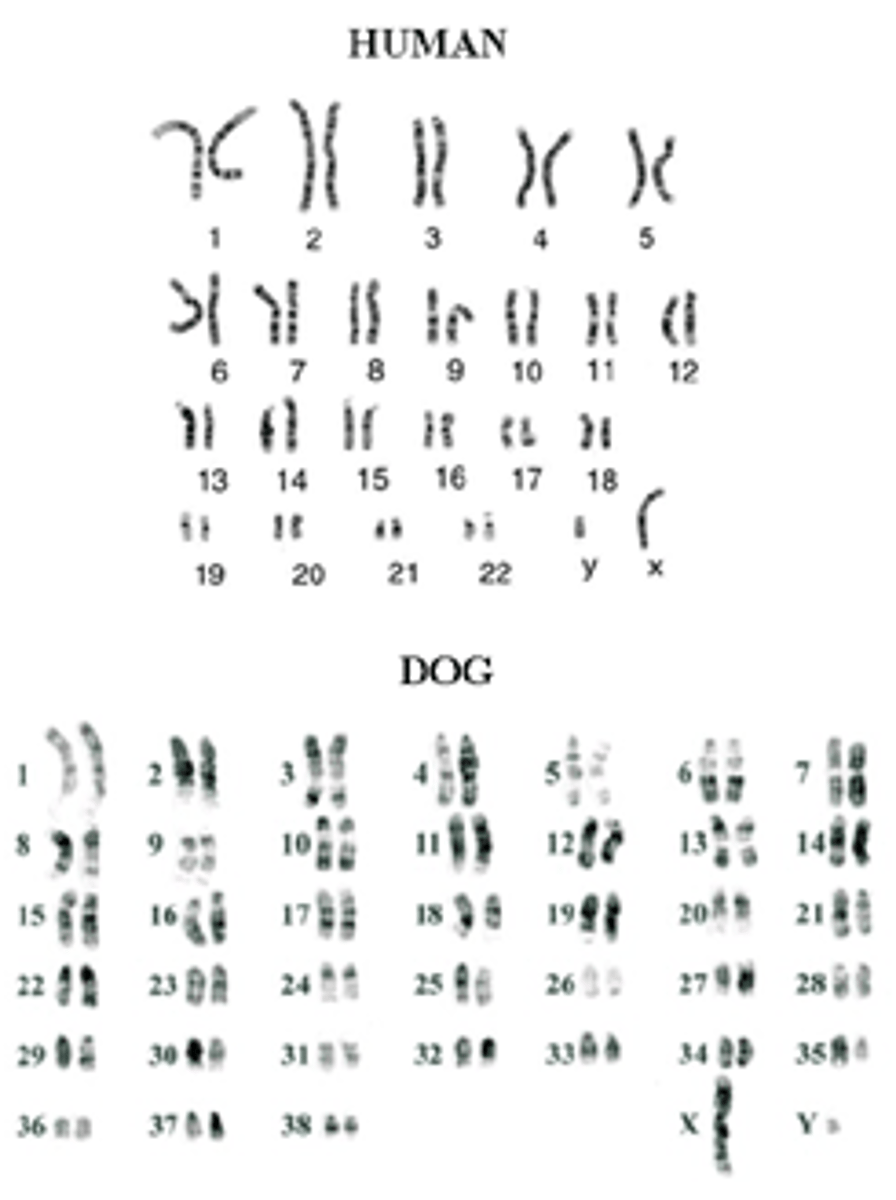
Karyotype
an image of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape
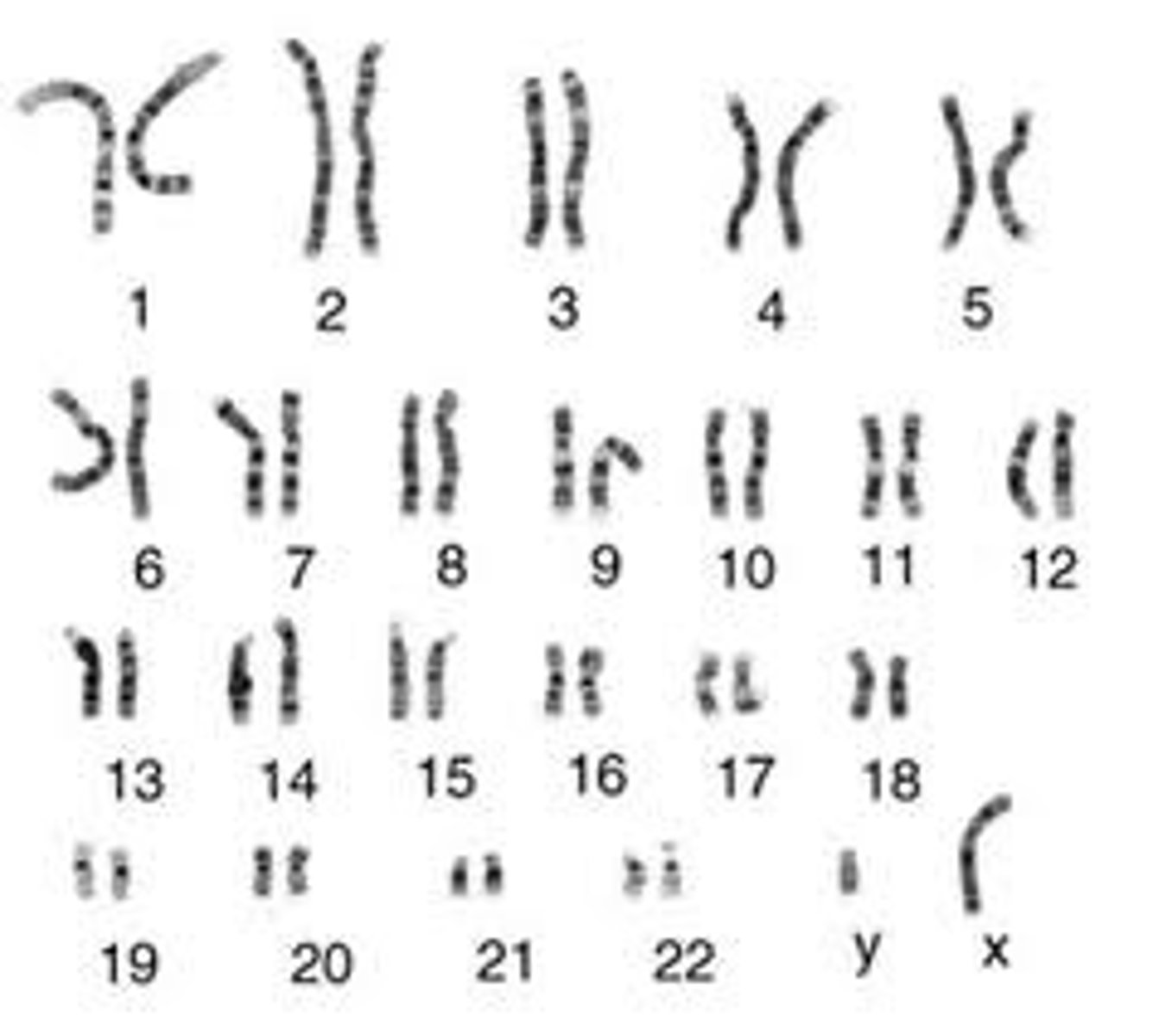
Nondisjunction
an accident during mitosis or meiosis, in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to move apart properly
p arm
short arm chromosome structure
q arm
long arm chromosome structure
Deletion
segment of a chromosome is removed or lost
Duplication
occurs when a segment of the chromosome is replicated and inserted next to the original copy
Inversion
occurs when part of a chromosome is placed in the wrong orientation compared to the rest of the chromosomes
Insertion
occurs when a part of one chromosome is removed and aded to another chromosome
Translocation
occurs when two chromosomes swap
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
laboratory technique to amplify DNA
Gel electrophoresis
separation of nucleic acids or proteins on the basis of their size and electrical charge for analytical purposes
Restriction enzymes / restriction endonuclease
a degradative enzyme that recognizes specific nucleotide sequences and cuts DNA at these sequences
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)
variations in DNA fragment sizes produced when DNA is cut with restriction enzymes and the variation is due to differences in each organism's DNA sequence
Meiosis
cellular process that results in the number of chromosomes in gamete-producing cells being reduced by half, also involves a reduction division, in which one pair of each pair of paired chromosomes passes to each daughter cell
Prophase I
chromosomes pair up with their matching chromosomes called homologous chromosomes & crossing over
Metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up at center of the cell, fibers attach
Anaphase I
each chromosome separates and the sister chromatids are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell
Telophase + Cytokinesis I
cell splits into 2, each new daughter cell look identical but are genetically different from the original cell
Prophase II
chromosomes pair up with their matching chromosomes called sister chromatids
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up at center of both cells and fibers attach to each of the sister chromatids
Anaphase II
each chromosome separates and the sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase + Cytokinesis II
nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes, 4 daughter cells are produced with half the number of chromosomes from the original
Medical history
a record of information about a patient's past and current health, includes information about patient's habits, lifestyle, and even the health of their family
Chief complaint
the patient's description of what they feel is their main health problem
Physical signs
pieces of evidence that indicate an illness that can be observed externally, such as a rash, coughing, or elevated temp.
Symptoms
any subjective evidence of disease a patient perceives, such as aches, nausea, or fatigue, allow the health care provider to narrow down the possible conditions that may be affecting the patient and then run tests to make a diagnosis
Diagnosis
the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs
Components of a Medical History - Current History
the patient's chief complaint and any other current health issues, symptoms, and any treatments or tests the patient has recently had or is scheduled to have related to these conditions
Components of a Medical History - Previous History
includes info about any past health issues, procedures, medications, vaccinations, and previous hospital stays
Components of a Medical History - Social History
addresses aspects of the patient's life, such as living situation, occupation, school, travel, and other activities that could have a direct or indirect impact on health
Components of a Medical History - Family History
includes medical info about the patient's close relatives
Patient liaison
medical professionals who connects patients with healthcare providers for their needs; key point of contact between patients and healthcare providers (ADDED BY LEAH)
Demeanor
outward behavior or bearing; a doctor might have a cheerful, peaceful, or friendly demeanor and put the patient at ease
Tact
discretion and sensitivity in dealing with others; a doctor might choose their words carefully to not upset a patient when they deliver bad news
Empathy
ability to understand and share the feelings of another person
Vital signs
measurements - specifically pulse rate, temperature, respiration rate, and blood pressure, that indicate the state of a patient's essential body functions
Homeostasis
the maintenance of stable internal physiological conditions which enables the optimal functioning of an organism
Pulse
the rhythmic expansion and recoil of arteries resulting from heart contraction
Respiratory rate
the number of breaths an organism takes per minute
Blood pressure
the pressure that blood exerts upon the walls of blood vessels, especially arteries, usually measured with a sphygmomanometer and expressed in millimeters of mercury
Body Mass index
a measure of body fat that is the ratio of weight of the body to its height
Formula to calculate Body Mass Index
Weight / Height (in inches)^2 x 703
Lung/Breathing Sounds
the sound and clarity of breaths using a stethoscope and measured as a description of sound (wheezing, clear, crackles)
Oxygen saturation
amount of oxygen in blood measured in percentage using a pulse oximeter
Systolic pressure
measures the pressure generated in the arteries by the heart's left ventricle during systole
Systole
heart contracts to push blood throughout the body
Diastolic pressure / diastole
measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats, when the heart is relaxed
Hypertension
an abnormally high blood pressure
Cornea
outermost layer of eye that helps shield from germs and dust
Cancer
disease caused when the cells divide uncontrollably
Melanoma
most serious form of skin cancer that develops when you're frequently exposed to sun in the face, limbs and back
ABCDE System
evaluating whether a mole is normal or abnormal
A (Asymmetry)
one half of the mole does not match the shape of the other half
B (Border)
the edges of the mole are irregular or jagged
C (Color)
the mole is not one uniform color, but shows different colors or shades throughout
D (Diameter)
the diameter of the mole is larger than a pencil eraser
E (Evolving)
the mole appears to be changing shape, color, size, overtime
Clear lung sound
clear whoosh of air with each inhalation and exhalation