Lecture 12 - Confidence and Metacognition II
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is sense of confidence in decision making?
precision of readout
subjective sense that we’re correct about something
Why is confidence difficult to measure or build a model of?
because its subjective
Can we build a model to predict how the statistical confidence changes with task parameters?
yes
using a decision model allows us to test whether confidence reports correspond to the statistical computation of confidence
shape of confidence curve depends on task and environment
Why do we use a decision model for confidence? What is one issue?
allows us to test whether confidence reports correspond to the statistical computation of confidence
caveat: for each category of tasks, we might have to build a model of the decision process
What are 2 ways to measure confidence?
opt-out paradigms
measuring confidence-guided behaviour
What are opt-out paradigms?
option to decline the choice if low confidence on the outcome
the option to opt-out could be present on every trial or only a subset of trials
How can measure a confidence-guided behaviour explicitly or implicitly?
explicit report of confidence can be measured either binary (low/high) or on a graded scale
implicit report via a measure that is driven by confidence (time or money invested in a decision)
e.g. making wrong turn while driving and how long are you investing in that direction before turning around
e.g. how much money are you willing to bet on a decision
What are the results when asking ‘Which of Mexico and Canada has a higher
population?’
lots of evidence for Mexico’s population
distribution is skewed to Mexico and high confidence
What are the results for ‘Which of Mexico and Japan has a higher
population?’
populations are more similar so confidence is split up more
more low confidence votes
What are the results for ‘Which of Singapore and Mongolia has a higher
population?’
displays a small continuous distribution
even more low confidence votes
Describe the countries knowledge task to measure confidence? What is the difficulty metric?
Subjects are asked to determine which country has the high population
- They report their choice
- Then they report their confidence on a 1-5 scale (on 10% of the trial, there is an alternative task too)
difficulty metric = population log ratio
easier to decide when countries have larger log ratio/larger difference in population
For the countries task, how does confidence relate to accuracy?
confidence predicts accuracy
confidence measures follow the same pattern as the sensory discrimination task
psychometric curve is steeper on high confidence trials
What is perfect calibration for confidence?
for a given confidence level (e.g. 70%), the actual accuracy of the decisions matches the probability of being correct (70% correct)
What is bias for confidence?
over or under-confident
overconfident (positive confidence bias/shifted right): confidence predicts accuracy but the subjective confidence (probability of being correct) is higher than the actual accuracy
as confidence increases, accuracy increases
underconfident (negative confidence bias/shifted left): confidence predicts accuracy but the subjective confidence (probability of being correct) os lower than the actual accuracy
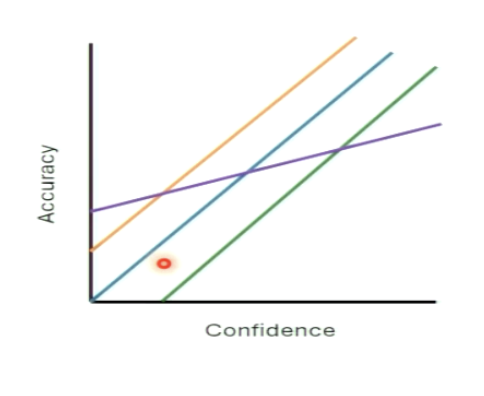
What is sensitivity for confidence?
metacognitive accuracy: how much does the confidence actually predict the accuracy
purple line: confidence behaviour doesn’t tell us much about the actual behaviour
less info in confidence report
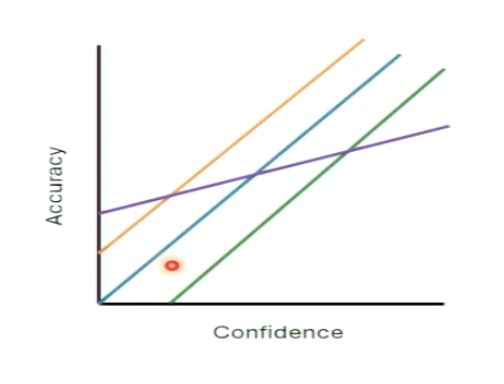
What is the difference between metacognitive bias and sensitivity?
these ideas can be decoupled
bias: shift of the scale used to report confidence (over/under confident)
accuracy: measures the info contained in the confidence reports, how distinguishable are the reports for correct and error trial given the accuracy
Examples of value-based choice in confidence task.
subjects choose between chips or candy bar, rate confidence in your choice
subjects presented with an item and asked to submit a bid for each item (what is monetary value of item), rate confidence
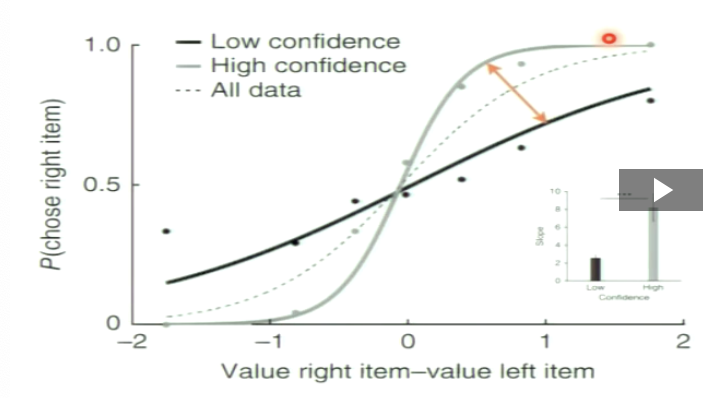
What happens if we plot the decision variable to make psychometric curve based on value-based task?
the change in slope in the psychometric curve as a function of the confidence report can be used as a measure of metacognitive accuracy
with no metacognitive accuracy, the choices would be the same whether there was high or low confidence
positive values mean the item is valued more
negative values mean the item is valued less
What is confidence in the domain general way?
one single monitoring process to compute confidence irrespective of the source of the information
one confidence area that just computes confidence about everything (sensory, episodic, general, etc.)
What is confidence in the domain specific way?
distinct computations for each modality (confidence about visual info, confidence about auditory info, etc.)
How can we compare confidence behaviour across domains? What are two contrasting tasks to do this?
perceptual decision task
two stimuli with different number of dots
report choice (left or right) - which has more dots?
report confidence of choice
memory-based decision task
remember a list of words
old vs. new classification - was this word there before?
report confidence of choice
similar structure tasks
lesion an area and see if the metacognitive accuracy changes for one or both tasks
What did they find from patient population with overlapping lesions? What brain regions were lesioned?
anterior PFC group → implicated in confidence computations
temporal lobe group
lesions are localized but not precise to one area
Why is it important to have control tasks?
test other cognitive domains
e.g. inability to have working memory will impair the task
e.g. attentional defiticits could impair the task
What was found about performance and mean confidence across healthy patients, aPFC and TL for 2 tasks?
performance is similar across the 2 tasks
mean reported confidence is similar across the 2 tasks
metacognitive bias is not affected
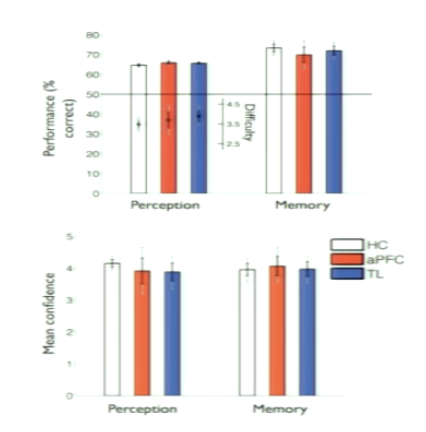
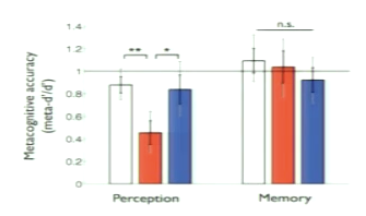
What was observed about metacognitive accuracy during two tasks? What does suggest about domain computations?
metacognitive accuracy is degraded in the perceptual task for the aPFC lesion group
when they tell you their level of confidence, doesn’t give us any info on if decision is correct or not
specific to perceptual task
suggests that part of our confidence estimation is domain-specific
but also we could have a domain-general system that integrates modalities
How can we measure confidence?
e.g. perceptual task with confidence rating
or
questionnaires
measuring more subjective/specific cognitive domains (OCD, anxiety, etc.)
LOTS OF VARIABILITY IN THESE (in accuracy and confidence)
How can we identify trends across questionnaires?
analyze how responses co-vary across questionnaires
fall into 3 dimensions that characterize variability
given that variability can that predict behaviour on perceptual task
How much can we predict behaviour and confidence from the questionnaire factors?
e.g. if this person has anxious-depression, do they perform better/worse on task
accuracy in the task is not predicted by any of the factors
variability in confidence level and metacognitive accuracy can be predicted by the questionnaire factors
e.g. compulsive behaviour predicts confidence bias positively but metacognitive efficiency negatively
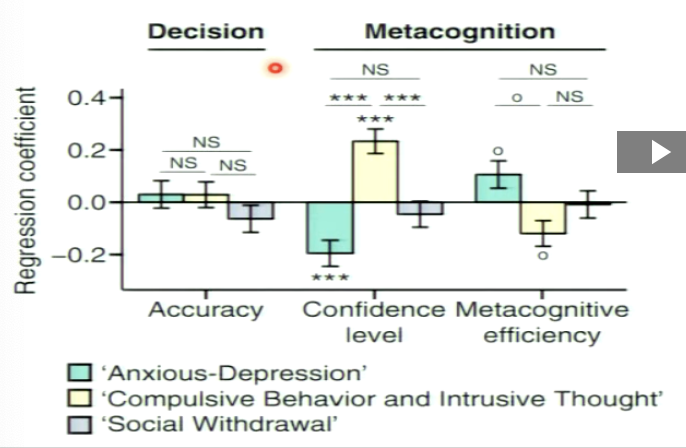
What does the relationship between questionnaire predicting confidence levels show?
shows that although there is domain specific confidence, there is a shared meta-level priors on confidence since these two unrelated tasks are correlated
What type of confidence measure do we have to use on animals?
implicit measure
time or money investment
What was the olfactory task for rats and confidence?
we use an odour mixture as the sensory stimulus
the rat must choose which odour is dominant
the mixture ratio controls the difficulty
time investment in the study
before getting reward, they have to wait
the time to wait to varied
rats have to decide whether to wait for potential reward or restart the trial
on some trials we do not give a reward even if the rat was correct (to measure how long the rat would have waited)
how long are you willing to commit to that decision
Can we link time investment to confidence?
time investment has the properties we would expect of statistical confidence in this task
this task allows us to link the rats’ behavioural accuracy (psychometric curve) with the expected time investment (WT - waiting time) if the investment was driven by confidence
time investment has all properties of what confidence would look like

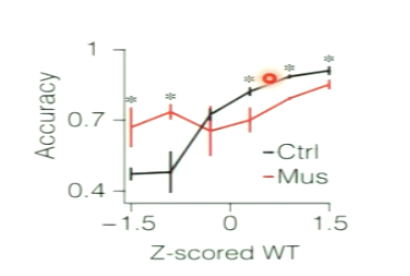
What does this graph show?
time investment predicts accuracy
if we take trails where the rat waited, they are more likely to be correct choice
and psychometric curve is steeper (more accurate) for long time investments (longer WT)
What occurs when we lesion the OFC with GABA agonist ability to do task and metacognitive bias?
temporary!
psychometric curve is not affected by muscimol injection in OFC
no change in ability to do task
average time investment (WT) is also unchanged
confidence bias is not affected by the inhibition of OFC
What occurs when we lesion the OFC with GABA agonist and metacognitive accuracy?
time investment no longer carries much information about the accuracy of the decision
deficit in metacognitive accuracy
how long they wait is unrelated to how accurate they were on that trial
What is the confidence index?
a measure of metacognitive accuracy
it is degraded in muscimol sessions
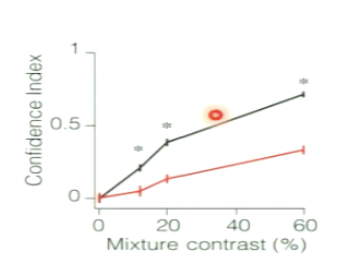
What does OFC inactivation cause?
impairs metacognitive accuracy but not decision accuracy or metacognitive bias