Response Programming
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is an open loop?
The output has no influence on the control action (no time for feedback)
When is an open loop used?
During rapid movements
What is a closed loop?
An open loop system which contains feedback loops
When are closed loops used?
Slow, time consuming tasks
What does the open loop control involve?
Stimulus identification > Response selection > Response programming
The executive (brain) sends a signal to the effector (muscles) which carries out the movement
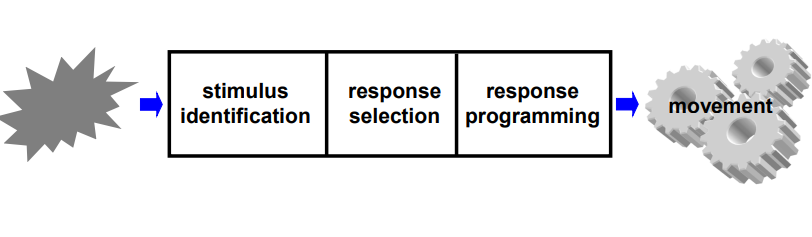
What is a motor programme?
An abstract that when initiated results in the production of a coordinated movement sequence
What is the order of a motor programme?
Motor programme > Motor neuron > Muscle
What are the 3 pieces of evidence for motor programmes?
Reaction times
Deafferentation studies
EMG studies
How does reaction times support the motor programme theory?
As a task gets more complex, reaction times are slower
More steps > More preparation > Slower reaction time
How does deafferentation studies support the motor programme theory?
When efferent nerves are removed, movement can still be produced
This proves that the motor programme is stored and feedback isn’t required
Explain the cat deafferentation study?
Cats had a mid-brain cut and they put it on a treadmill. The cats legs drag across the treadmill
However when the spine is electrically stimulated the cats legs start to walk, proving that the cats spine has pattern generators which once turned on will switch on and off different circuits to carry out the movement, e.g. walking
How does EMG studies support the motor programme theory (Elbow extension study)?
During an antagonistic muscle pair study, the antagonist will show electrical movement towards the end as it acts as a break
When the antagonist was blocked, the reading still had electrical movement. This shows it’s a pre-programmed movement sent in advance to the muscle
However these tests were done under rapid movement. When done under slow movement the athlete had time to override the motor programme
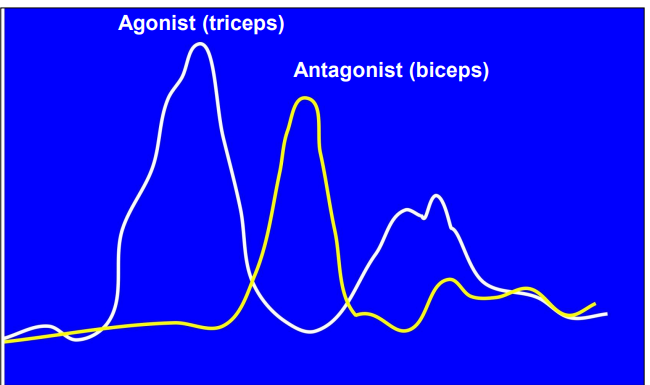
When must a stop signal be provided for a task?
The EMG elbow extension study found that the stop signal must be around 100m/s after the go signal for the whole motor programme to not be completed
What are problems with motor programmes?
Storage = the brain would need a seperate motor programme for every movement
Novelty = the brain doesn’t have a motor programme for new movements
Degrees of freedom = many muscles can move in multiple ways to achieve the same goal
What is a Generalised Motor Programme (GMP)?
A motor programme whose expressions can be varied depending on the choice of parameters
What are the 3 invariant features of a GMP?
Order of events
Relative timing
Relative force
Explain the order of events of a GMP
A modified programme will still have the same order of the sequence that the skill usually has
Explain the relative timing of a GMP
A study asked for a taekwondo kick as quick as possible and at 80%
When the timings were overlayed, the parts of the skill were sped up proportionately rather than certain parts of the skill
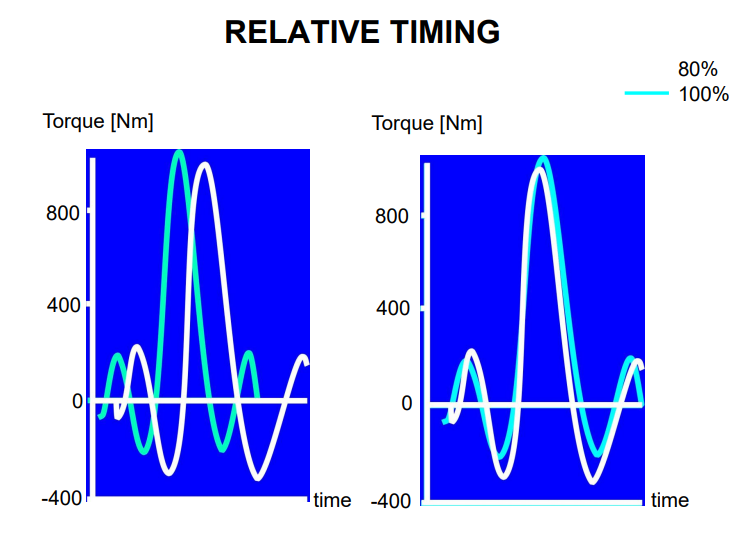
Explain the relative force of a GMP
When a force is needed to increase, all the muscles will increase at a proportionate level, not just certain muscles
What are the 3 changeable factors of a GMP?
Overall duration
Overall force
Muscle selection
Explain the overall duration of a GMP
The GMP will have constant order of events and relative timing, but the duration of the skill can be sped up or slowed down
Explain the overall force of a GMP
The relative force of a GMP is constant, but the overall force will adjust to the demands of the task
E.g. throwing a 5kg ball will require a larger overall force than a normal basketball
Explain muscle selection for a GMP
The athlete must decide the appropriate muscles to use for a motor programme
E.g. using a different muscle for different bowls in cricket
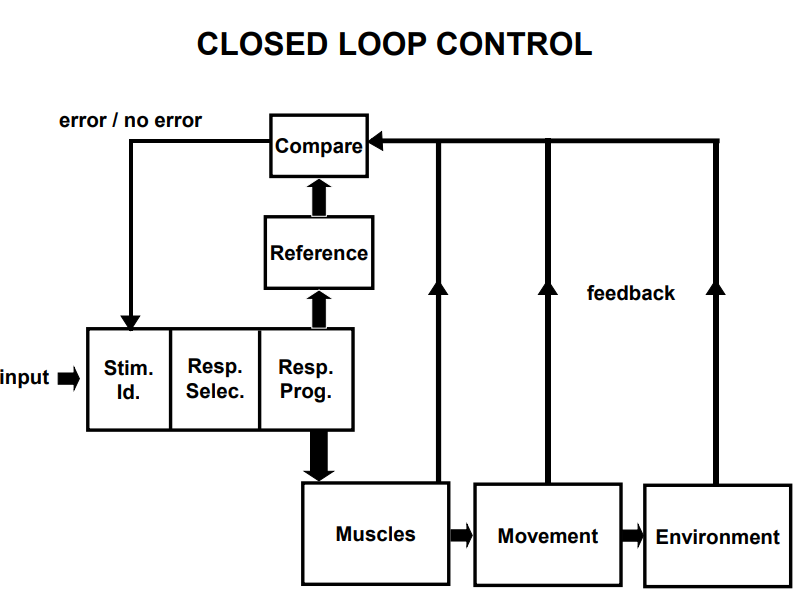
Explain the closed loop control diagram
Reference of correctness = predicting what the movement should feel like
Feedback = this is received from the motor programme. this will be compared to the reference of correctness
What is feedforward?
Athlete predicts the movement and selects the correct GMP before acting.
Executes the action without waiting for feedback.
Compares expected feeling of the movement to the actual sensory feedback afterwards to evaluate performance.
What is the reflexive closed loop control study?
A study on keeping elbow flexion at 90 degrees
A person will only produce a certain force level for this.
However when an unexpected increase in weight occurs the person will drop their arm because the force produced was insufficient.
Then the participant will return their arm to 90 degrees by increasing their force output
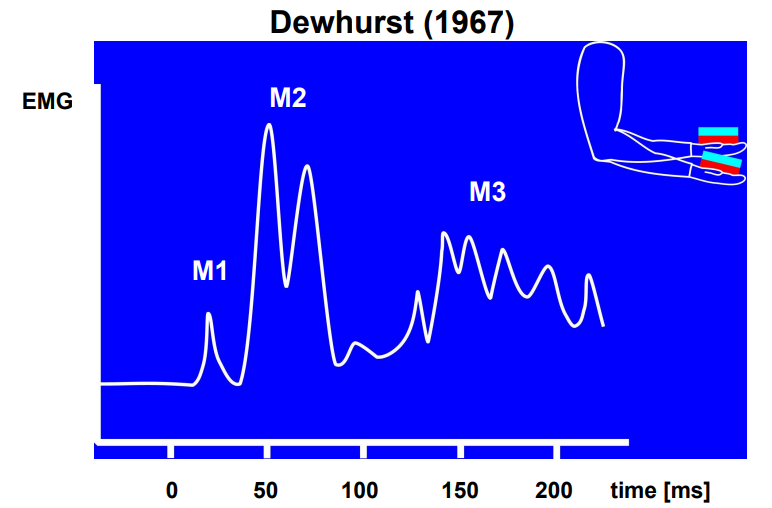
Explain the monosynaptic stretch reflex 1 (M1)
After 30 ms of the weight being added there is a small muscular activity
This is due to muscle fibres in the bicep stretching
Muscle spindles then send signals to the spinal cord which activates the bicep motor neurons
This causes the muscle to contract automatically
Explain the triggered/long loop response reflex (M2)
After 50-80 ms of the weight being added, the muscle spindles send information up the spine into the brain
This triggers a pre-programmed response
This is still an unconscious process
Explain the voluntary reflex (M3)
After 120 ms of the weight being added
Information has entered the stages of information processing