1B Joints and Cartilage
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
skeletal system components
bones
cartilage
ligaments
skeletal system functions
support the framework of the body
protection - shields vital organs from injury
force translation - bones work with muscles and joints to produce movement
blood cell production - bone marrow is found inside certain bones and produces blood cells
mineral storage
types of cartilage
elastic cartilage
hyaline cartilage
fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
specialized tissue with many elastic fibers
both flexible and strong to maintain structure shape, able to bend and return back to its original shape
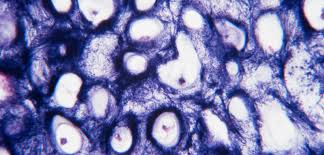
where is elastic cartilage found
epiglottis - small flap in your throat that returns to shape everytime you swallow
auricle (external ear) - visble part of your ear that makes it flexible
laryngeal cartilages - cartilage in your larynx (voice box) that move during speech and swallowing
hyaline cartilage
most abundant found in the body
weakest cartilage type
smooth surface for gliding, flexibility, support, friction reduction
viscoselastic connective tissue (behaves both as an solid and fluid depending on the force applied)
spreads body weight across more of the surface to stablize stress on certain joints
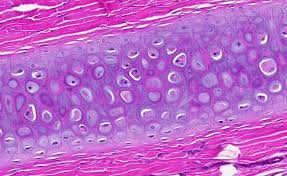
where is hyaline cartilage found
Articular cartilage - covers the ends of bones inside synovial joints to allow bones to slide smoothly over each other and reduces friction
Trachea/bronchi - windpipe made of c-shaped rings of cartilage to keep airways open
Epiphyseal plate - found near the ends of long bones in children/teens to allow bones to grow longer, hardens into bone once growth stops in adulthood
fibrocartilage
durable for joint support and cushioning
shock-absorber
high amount of collagen
found in symphysis joints, often need to withstand large forces
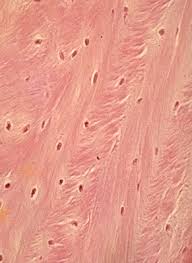
where is fibrocartilage found
intervertebral discs - soft, pad-like discs between the bones of your spine, prevents vertebrae from grinding together during movement
pubic symphysis - connects the left and right sides of the pelvis from the front, allows for a small amount of movement but mainly for stability
menisci (knee meniscus) - two crescent shape pads in each knee to protect the knee joint from wear and injury
Chondrocyte
found in all types of cartilage
mature cartilage cell that produces and maintains the cartilage matrix (collegen + elastic fibers)
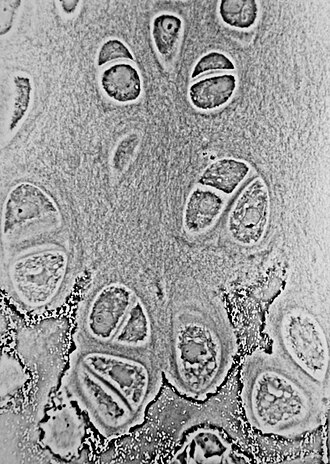
Why is hyaline cartilage also called articular cartilage?
it covers the articular surfaces of bones (where they touch when forming a joint) in synovial joints
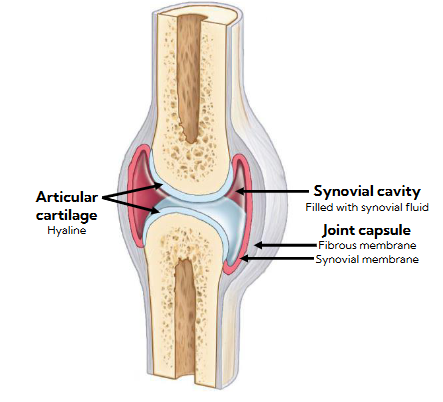
different of synovial and synchondrosis joints where hyaline cartilage is located
synovial:
bones are not directly connected
has a joint cavity (gap between the non-connecting bones)
joints used for moving freely
synchondrosis:
bones are directly connected
no joint cavity
little to no movement
joints used for growth or stability
avascular
all types of cartilage has no blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves
cartilage doesn’t get nutrients or oxygen from blood
Femoral condyles
rounded ends of the thigh bone at the knee
coated with a smooth layer of hyaline cartilage
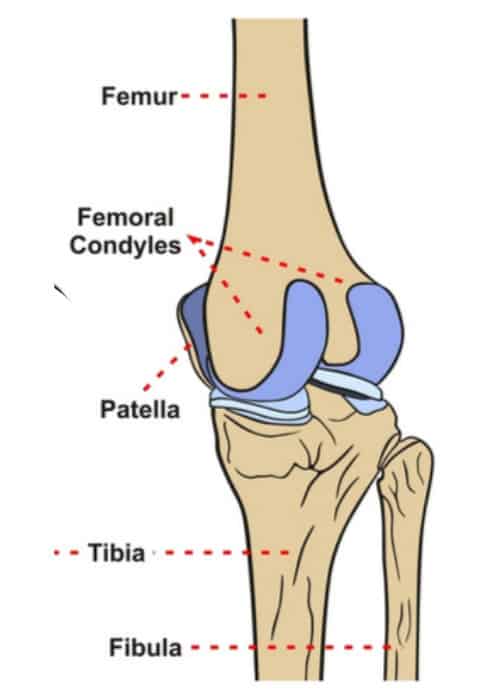
What happens to hyaline (articular) cartilage when a joint is loaded (force/weight is applied) and then unloaded (release of force/weight)?
When the joint is loaded, pressure pushes fluid out of the cartilage into the synovial cavity.
When the pressure is released, fresh synovial fluid containing nutrients flows back into the cartilage.
Nutrient and waste exchange happens via synovial fluid:
superfical zone spreads the load sideways
middle zone holds the fluid that gets unloaded and loaded
deep zone anchors cartilage to bone so it doesn’t slide off from pressure

interstitial fluid
60-80% of water contains lipids and electrolytes
found in all types of cartilage in all tissues
types of arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
what does a healthy joint look like (before arthritis)
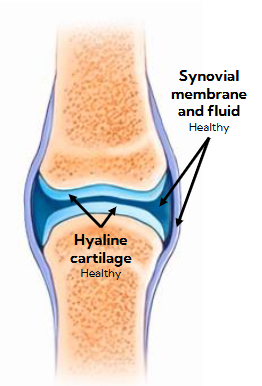
Osteoarthritis (OA)
most common type of arthritis
gradual loss of cartilage from “wear and tear”
common causes of hip and knee replacements
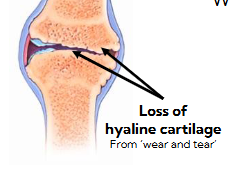
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
autoimmune disease
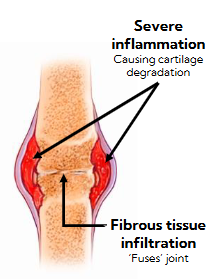
inflammation of synovial cavity and cartilage decreases your mobility over time
eventually cartilage degrades and leads to exposed bone ends
nutrient change issues
classifying synovial joints by how many directions they can move
More movement = less stability
Less movement = more stability
uniaxial (moves one direction), biaxial (moves in two directions), multiaxial (moves in many directions)
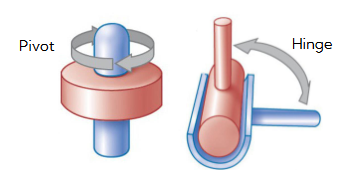
uniaxial
hinge - back and forth
pivot - rotation around one axis
very stable, limited movement
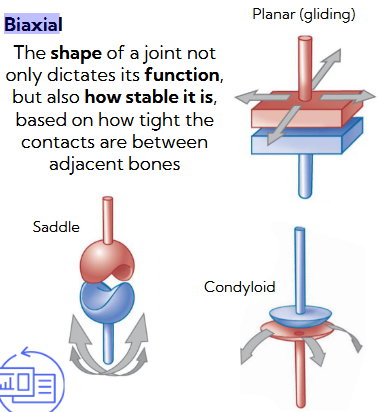
Biaxial
Planar (gliding) - sliding
saddle - back-forth, side-side
condyloid (ellipsoid) - two directions + cirsumduction
moderate stability, moderate range of movement
multiaxial
ball-and-socket - rotation, bending, straightening, abduction (moving away from the midline), adduction (moving toward the midline)
most movement, least stable
Factors contributing to range of motion
shape and arrangement of articulating surfaces - tight fit = less movement, loose fit = more movement
ligaments crossing the joint - ligaments are strong bands that limit how far a joint can move, more/tighter ligaments = less movements
surronding muscles - muscles around a joint hold it in place when they contract during movement
its a balancing act to maximize function when limiting chances of injury by increasing stability, you cannot have both extremes at the same time
ligament sprains
torn ligaments are called sprains
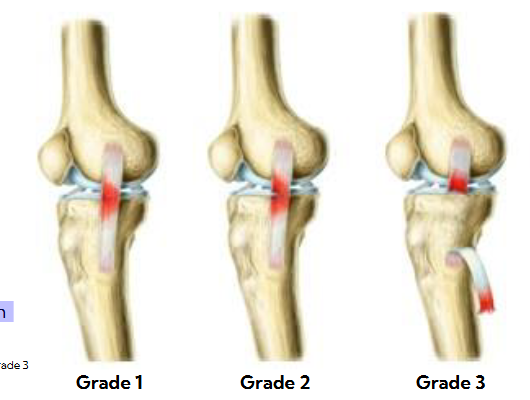
Grade 1:
• Stretching or slight tearing
Grade 2:
• Incomplete tear
Grade 3:
• Complete tear
needs immediate surgery
PRICE procedure for sprains
what to do when you get a grade 1 or 2 sprain:
Protection
Rest
Ice
Compression
Elevation
components of the muscular system
muscle
tendons/aponeuroses
motor unit (motor neuron + all the muscle fibers it controls)
muscular system functions
Skeletal movement
Maintaining posture and position
Opening and closing of orifices (openings in the body)
Maintaining homeostasis
types of muscle
skeletal, cardiac, smoth muscle
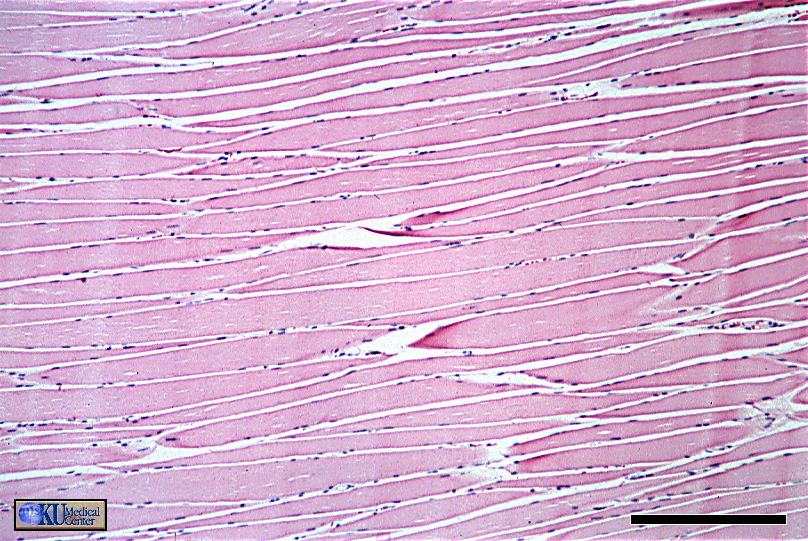
skeletal muscle features
Striated muscles with myosin and actin proteins
striped looking pattern because the two proteins are arranged in a repeating pattern that slide past each other to cause muscle contraction
Under voluntary control
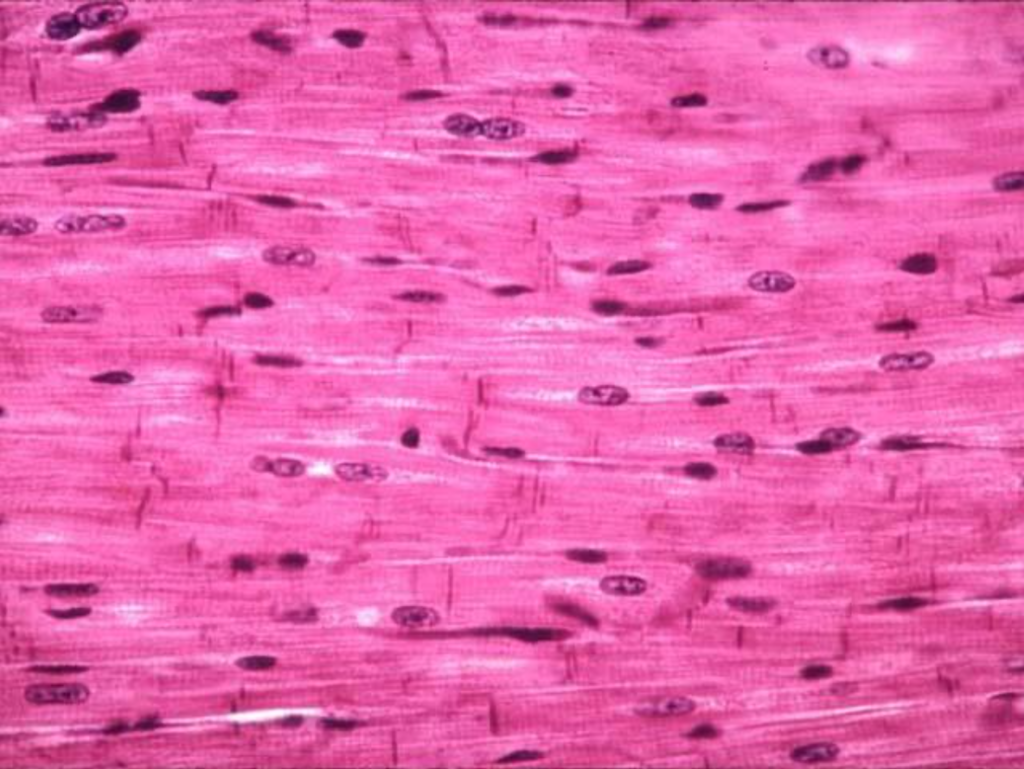
cardiac muscle features
Found in the heart
Striated muscle with actin and myosin, same as skeletal muscles
Involuntary control
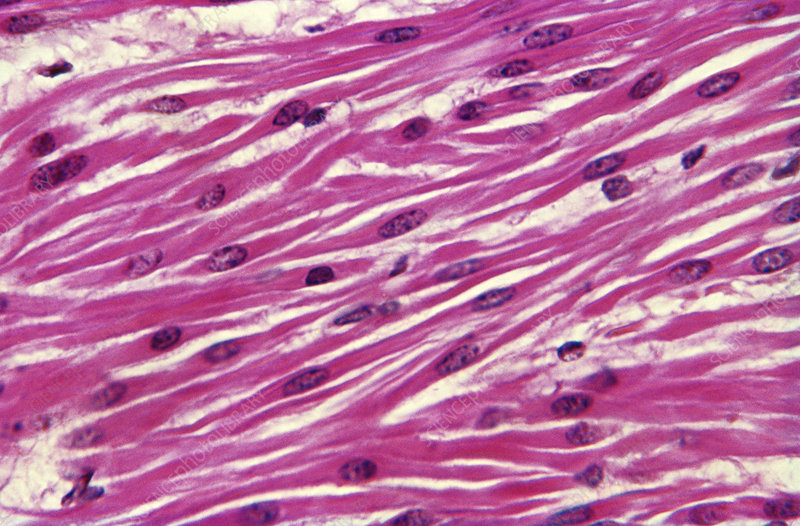
smooth muscle features
Found in viscera (internal organs inside your chest or abdomen), blood vessels, skin
Not striated because actin and myosin are arranged randomly, no repeating pattern
Under involuntary control
myocte
muscle cell
the three muscle types contains different myocytes that are different structures so they can carry out specific functions
basic muscle properties found in all muscle types
Electrical excitability - can respond to two kinds of signals
• Electrical signals used in the heart for heartbeats
• Chemical signals used in neuromuscular cleft (gap at the connection point between nerve and muscle) for muscle contraction
Contractility
• Muscle contraction/shortening produces force
• In skeletal muscles this force pulls on bones through tendons to create movement
Extensibility
• Can stretch/lengthen (to an extent) without damage
Elasticity
• Returns to its original length after contraction (shortening) or
extension (lengthening)
• Greatest elasticity in smooth muscle
Fascia
connective tissue that surrounds muscles
contains the blood vessels and nerves needed to supply the muscle for control and activation
helps increase force by limiting how much the muscle expands outwards during contraction, allowing more force to be transferred to bone movement
sacromere
smallest unit of muscle contraction where actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to create force
muscle is always trying to shorten but sometimes it does not succeed due to the force not being able to overcome the load
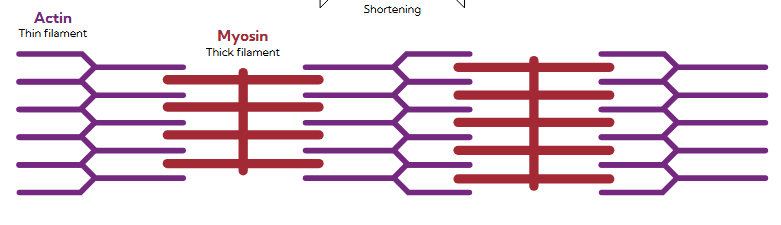
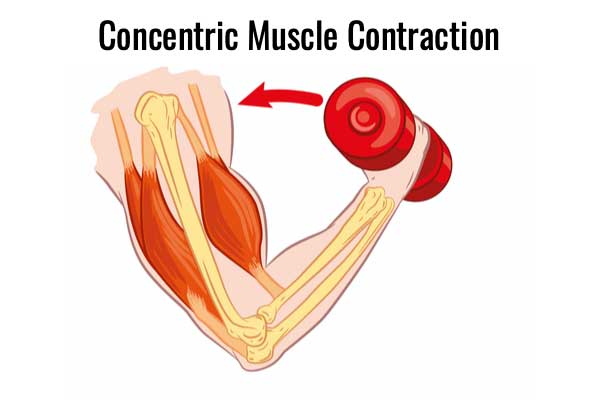
concentric contraction
muscle shorten when actin and myosin come together
lighter load, muscle wins
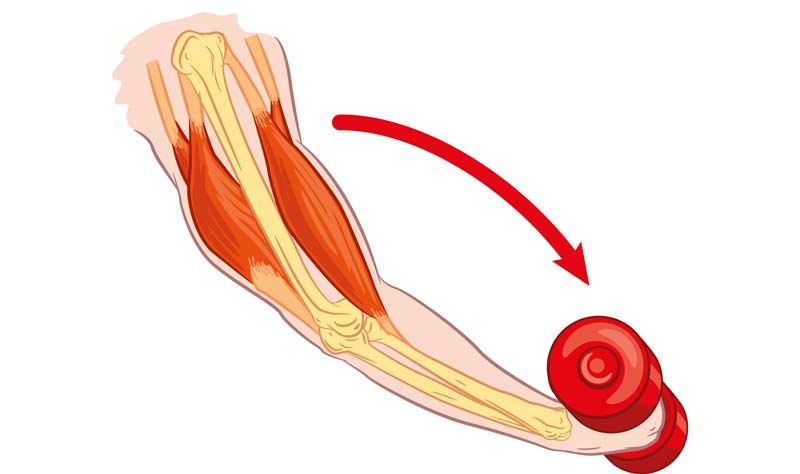
eccentric contraction
muscle lengthen when actin and myosin move apart
heavy load or gravity wins, muscle loses and is forced to lengthen even though it’s active in function
single motor unit
one neuron and all its muscle fibers that it innervates (connects and controls)
several motor units are required to innervate an entire muscle
contralateral control
when the left side of your brain controls the right side of your body and vise versa
origin used for skeletal muscles
the attachment that has minimal movement or doesn’t move at all, acting as an anchor
usually closer to the body’s center, proximal
insertion used for skeletal muscles
the attachment that does move
usually father from the body’s center, distal
gets pulled toward the origin during muscle contraction, muscles cannot push
the farther a muslce attaches from a joint, it is easier for that muscle to move the joint and produce more force
phasic contractions
short, temporary muscle contractions that are on and off
used for movement and typical in skeletal muscles
can be isometric or isotonic contractions
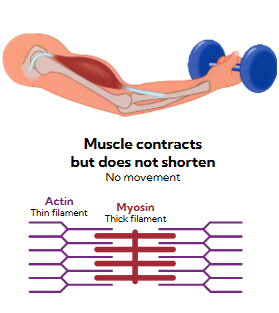
isometric contractions
muscle contraction produces force to support the load but doesn’t shorten
no movement
actin and myosin still try to slide, but they do not manage to actually move past each other and sacromere length stays the same
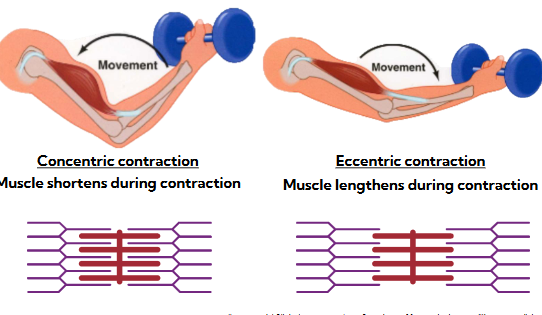
isotonic contractions
includes concentric (shortening) and eccentric (lengthening) contractions
concentric: actin and myosin slide past each other, sarcomere shortens
eccentric: actin and myosin try to interact but external force is stronger and pulled away despite resistance
agonist muscle
the main muscle that produces a movement by contracting concentrically
antagonist muscle
the muscle that opposes and controls the agonist by contracting eccentrically
helps control the movement being produced by the agonist to prevent uncontrolled or rapid movement
synergist muscle
muscle that assists the agonist muscle by adding additional force or stabilizing the movement
usually contracting concentrically
muscle atrophy
progressive muscle loss that happens to everyone starting from ~age 30 and onward, less power and strength
gradual, but will acclerate if you don’t constantly use your muscle
muscle mass is replaced with fibrous connective tissue that’s non-contractile and adipose (fat)
caused by loss of motor neurons that activate muscle fibers, slower conduction speeds where nerve signals travel more slowly, and a loss of muscle fibers
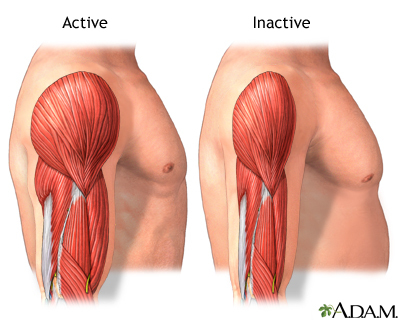
benefits of excerise
increases neuron firing rate of how often it sends electrical signals, muscle mass which slows down muscle atrophy, and bone density
cardiovascular, pulmonary and neuron benefits
makes the musculoskeletal system more effective and resilent to injury
muscle strains grades
Grade 1:
• Stretching or slight tearing
Grade 2:
• Incomplete tear
Grade 3:
• Complete tear
Doesn’t always require surgery
aggressive physiotherapy can have equal or better outcomes than surgery
recovery process for muscle strains
Protection
Rest
Ice
Compression
Elevation