Paleo 202 Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 AM on 12/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
1
New cards
Homology
Similar characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry.
2
New cards
Traits
Features or structures
3
New cards
Synapomorphy
A shared (from a common ancestor), derived character
4
New cards
Convergent Evolution
Evolution in two unrelated lineages of a similar structure or analogue
5
New cards
Analogues Structures
Features with superficial resemblance, but have different origins
6
New cards
Vertebrata
A clade of animals containing agnathans and gnathostomes, including humans
7
New cards
Clade
A natural evolutionary group containing a single ancestor plus all of its descendants but no others
8
New cards
Chordata
A clade of animals containing vertebrates, tunicates, and cephalochordates
9
New cards
Cephalocordata
Lancelets- invertebrates with with chordate synapomorphies.
10
New cards
Tunicates
Sea Squirts- chordates with very different juvenile and adult forms
11
New cards
Myomeres
Muscle bundles that are visually differentiated into segments
12
New cards
Notochord
A hydrostatic organ found in Chordata that provides structural support for the organism; may be lost and functionally replaced in vertebrates. Fluid filled fibrous sheath.
13
New cards
Pharyngeal Slits
Openings in the lateral walls of the pharynx of chordates; may be modified or lost in different groups; associated with gills in adult fish
14
New cards
Endostyle
A groove on the ventral surface of the pharynx in tunicates and cephalochordates which produces mucous and aids in gathering food; believed to be homologous to the thyroid gland in vertebrates
15
New cards
Endoskeleton
The support structure of the body that lies internal to the skin
16
New cards
Pharynx
The region around the throat between the mouth and esophagus
17
New cards
Cambrian Explosion
The apparently sudden appearance of almost all modern major groups of animals in the fossil record, about 525 million years ago
18
New cards
Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord
The type of sensory cord found in vertebrates in which the nerve runs along the back of the animal, and forms through a rolling up of the sides to form a hollow tube. Above notochord, sends commands to muscles. Becomes vertebral column in vertebrates.
19
New cards
Post-anal Tail
The continuation of the muscles and skeleton of chordates beyond the end of the digestive tract (the anus)
20
New cards
Vertebrata Synapomorphies
Bone, neural crest cells, distinct head/brain, cartilage
21
New cards
Endochondrial bone
Starts as cartilage in the embryo
22
New cards
Ossification
Cartilage that becomes bone
23
New cards
Intramembranous Ossification
Bone that does not start as cartilage
24
New cards
Dermal Bone
Bone formed by dermis, ex. Body armour, stegosaurus plates, spikes, shells
25
New cards
Neural Crest cells
Formed along dorsal hollow nerve chord, anteriorly forms skull cartilage/bone, sensory nerves/organs and dorsally forms pigment cells, nervous system, hormone organs. It’s the most important evolutionary innovation. Differs from chordates
26
New cards
Clasts
Pieces of worn down rocks that form clastic rocks
27
New cards
Terrigenous
Derived from rocks on land
28
New cards
Brackish Water
Saltier than freshwater but not as salty as marine water
29
New cards
Delta
Sedimentary Body that builds outward over time at the end of a river. Has brackish water. Ex. Nile River Delta
30
New cards
Estuary
At the end of a river, with no outward building sediment. Forms scoured out channels. Mix of marine and continental sediments and plant roots, marine shelly fossils. Has brackish water. Ex. Gulf of Saint Lawrence
31
New cards
Coarsening Outward Succession
Transition from finer carbonate marine sediments to coarser, clastic, continental, fluvial sediments at the top of a water body. Found in deltas
32
New cards
Sedimentary Structures
Structure from where rock was deposited, from clasts
33
New cards
Clastic rocks
Are terrigenous. Sandstone, mudstone, bedrock, conglomerates.
34
New cards
Carbonate Rocks
Made of 50% calcium carbonate and shells of marine organisms, fossils are found here. Ex. Limestone
35
New cards
Miguasha
Devonian Fish fossil locality. Lake, lagoon or inland sea. Has terrestrial and marine features. An ancient estuary
36
New cards
Cross-Bed
Rocks deposited in tidal environments with alternating inclined layers
37
New cards
Cross Strata
Inclined rock layers
38
New cards
Cross Stratification
Layers of rocks
39
New cards
Herringbone Cross-Stratification
Water flow alternating in 2 different directions in a delta or estuary. Has fast sediments
40
New cards
Water Base
Depth where surface water affects deeper water
41
New cards
Fair Weather Wave Base
Usually around 5-15m
42
New cards
Storm Wave Base
Greater depth with high energy waves (20-200m)
43
New cards
Ripple Marks
Show how deep the water was when sediments were deposited. Currents are angled in current direction.
44
New cards
Wave Ripples
In shallow water above fair weather wave base. There are no ripple below storm weather wave base
45
New cards
Longshore Current
Waves breaking and releasing energy. Waves run parallel to coastline and deposit and reshape sediments. Sediments create barrier islands, spits and lagoons
46
New cards
Lagoons
Connected to the ocean, not affected by currents and tides because of barrier islands. Usually shallow with more dissolved sediments. Saltier than the ocean. Inhospitable to life because it is anoxic. Good for preserving fossils because there are few scavengers and there is mud and fine sediments
47
New cards
Evaporite
Formed in lagoons when sediments evaporate. No-clastic sedimentary rock. Imbedded in mud as lagoon rise and new seawater enters. Calcite, gypsum, anhydride, halite.
48
New cards
Black Mud
Black because of organic material
49
New cards
MOTH
Man on the Hill. Deep spot in a continental shelf with finely laminated carbonate and clays. Close to shore for fine clastic sediments but far enough for carbonate. Anoxic
50
New cards
Carbonate Platform
Shallow carbonate shelves. Good place to fine marine invertebrate fossils.
51
New cards
Plankton
Thrive in the photic zone, base of marine food chain, calcerous skeleton. From carbonate skeletons when dead
52
New cards
Bottom Dwelling Vertebrates
Eyes on top of head, mouths on underside. Ex. Osteostracans, Wobbegongs

53
New cards
Reefs
In shallow carbonate platforms. Full of corals
54
New cards
Coral
Eat plankton, in high energy environments with nutrient rich water. Form barrier ridges parallel to coastline. Protect lagoons. Sturdy at shallow water (Gogo formation in Australia with late Devonian fossils), delicate and branched in deep water (plate corals).
55
New cards
Bourma Sequence
Pattern of texture and sedimentary structures. Upward succession of upward sediments as flow loses energy.
56
New cards
Deep water
Lack of water shallow structures, slope between continental shelf is steep and unstable, affected by slumps and landslides.
57
New cards
Turbidities
Deep water deposits that are affected by turbidity currents. Less dense than marine flow when mixed with water.
58
New cards
Burgess Shale
Cambrian locality deposited by turbidity currents
59
New cards
Hallucigeania
Chordate worm with paired spines and appendages. Related to extant velvet worms
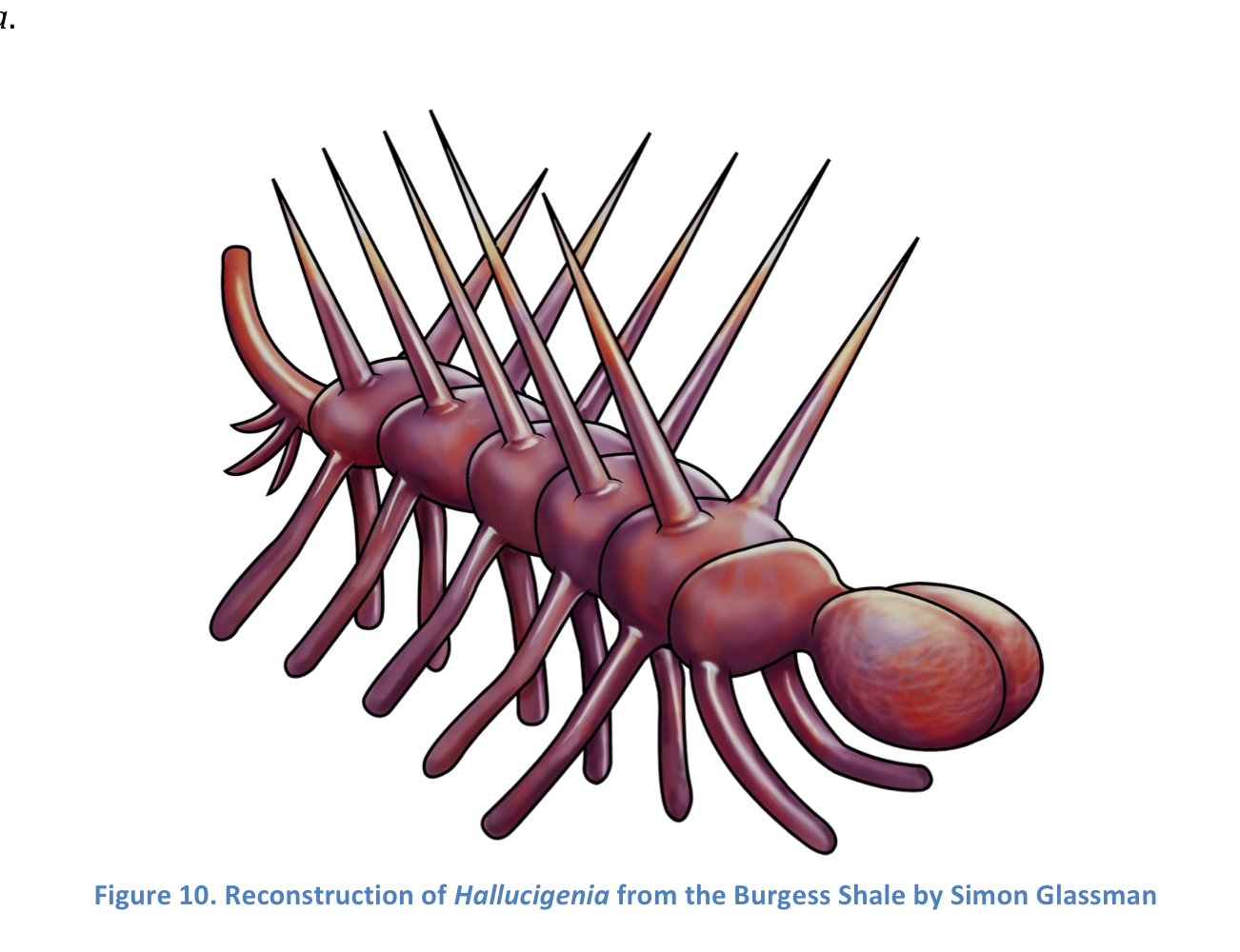
60
New cards
Odontogriphus
Chordate like a sandal. Early mollusk
61
New cards
Pikia
Early chordate with tentacles. Has post anal tail, myomeres, rod-like notochord. Related to cephalochordates
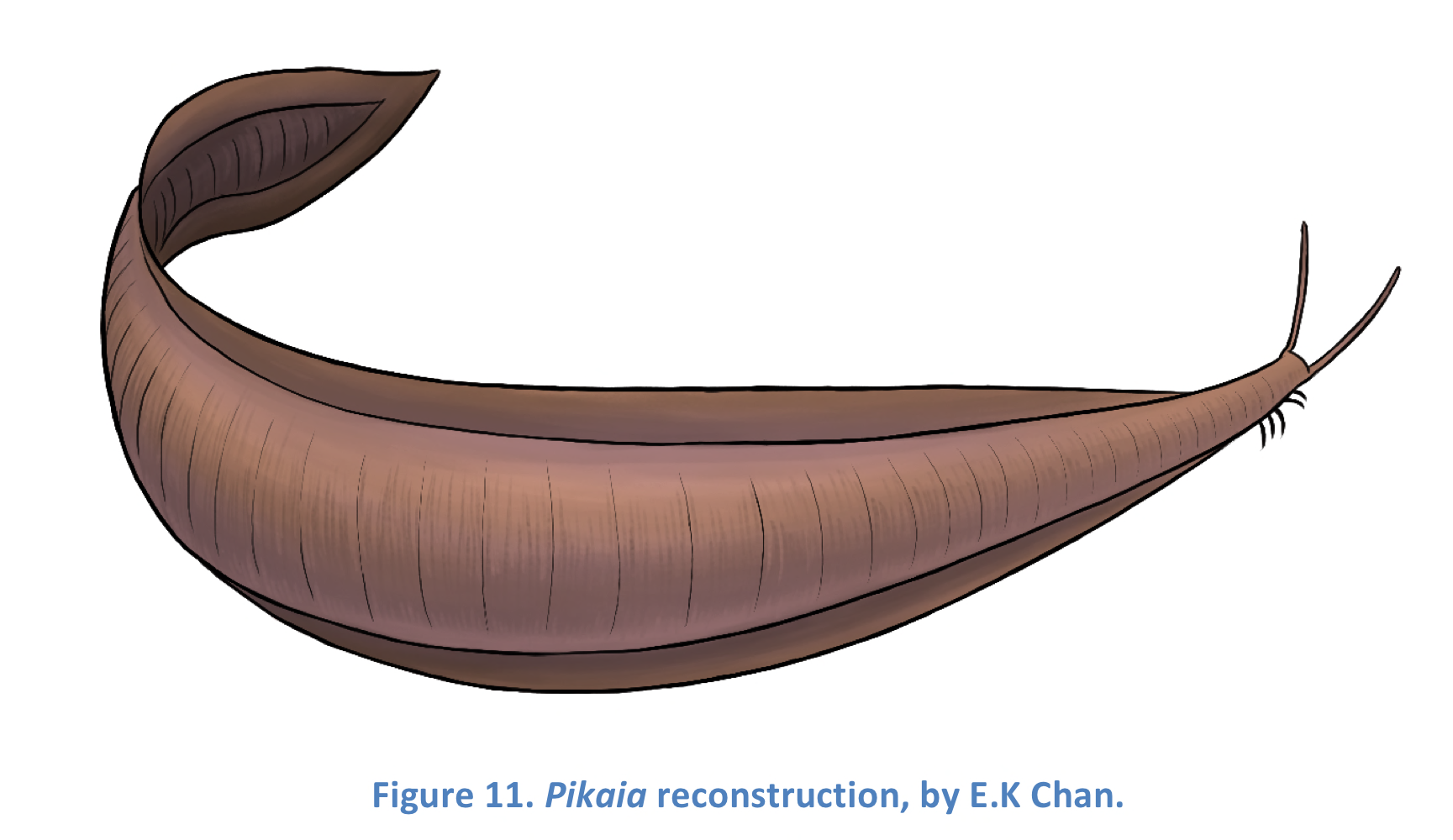
62
New cards
Metaspriggina
Early vertebrate with a edicaran form. Has notochord, eyes, brain, myomeres, cartilage and gills. Related to arthropods and annelid worms
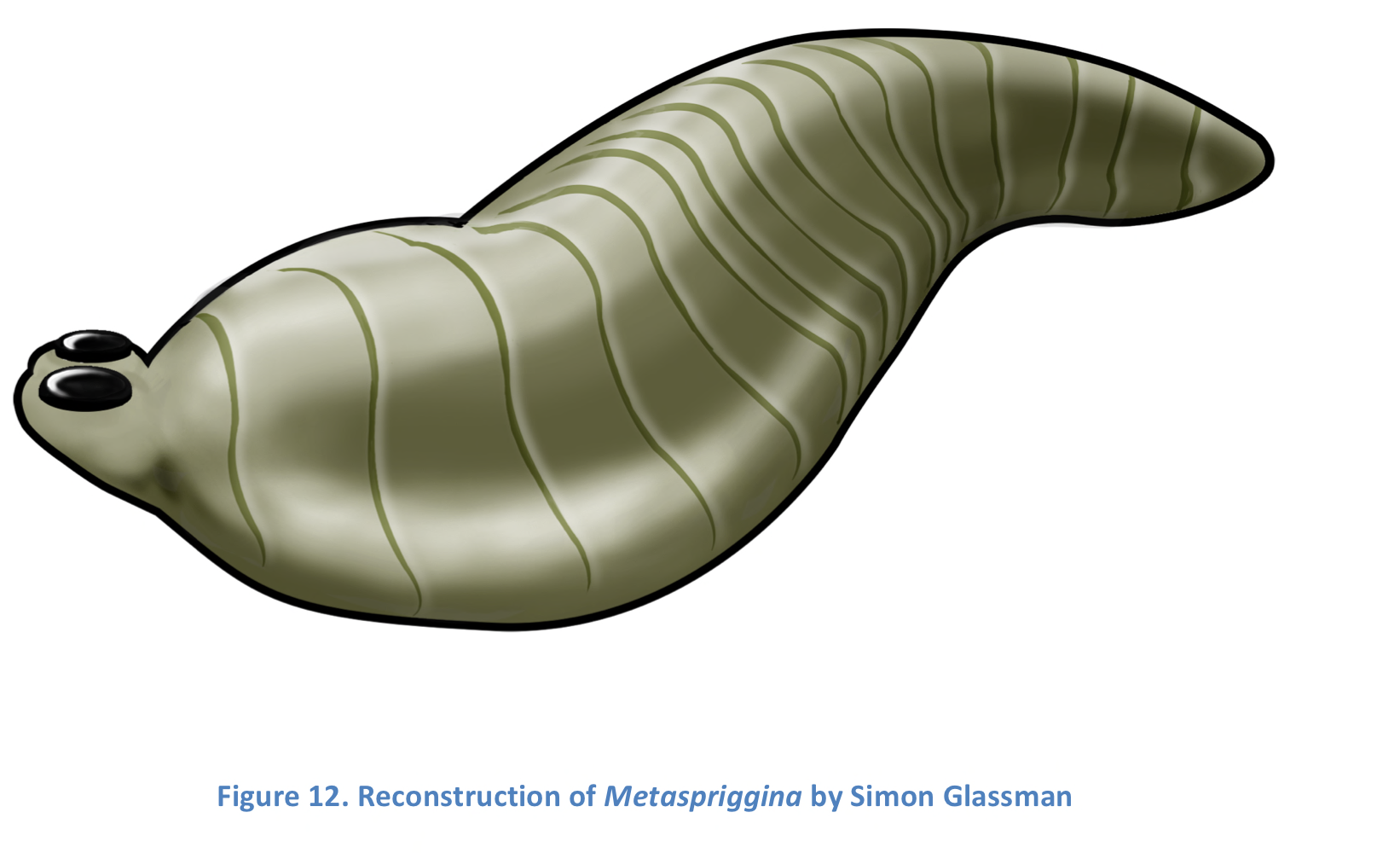
63
New cards
Biota
Collection of organisms. Ex. Mistaken Point in Newfoundland, Ediacara Hill in Australia
64
New cards
Cloudina
Tube dwelling chordate. First to produce calcium carbonate shells. Fossils had holes in the shell to indicate competition
65
New cards
Kimbrella
Early bilateral chordate
66
New cards
Chordata Synapomorphies
Myomeres, notochord, dorsal hollow nerve chord, endostyle, pharangeal slits, post anal tail.
67
New cards
Pelagic
Sediments that floated before settling
68
New cards
Silica
Plankton skeleton remains. Forms quartz, becomes chert. Ex. Pelagic limestone. Formed below silica
69
New cards
Chert
Laminated rock in deep water
70
New cards
CDD (Calcium Compensation Depth)
Lower depth where calcium dissolves due to higher pressures (4000-5000m).
71
New cards
Arrectionary Prism
Pile of oceanic crust sediments are scraped off of sinking plates and attaches of leading edge of overriding plates
72
New cards
Obducted
Oceanic crust pushed on top of continental plate at convergent plate boundary
73
New cards
2 ways Paleozoic fossil can be created
On continental shelves: Accretionary prism, obducted plates
74
New cards
Ophiolite
Preserved oceanic crust in obducted plates
75
New cards
Lagerstatten
“Storage place,” areas of exceptional fossil preservation
76
New cards
2 Lagerstatten types
Konzentrat/concentration-lagerstatten, konservat/conservation lagetstatten
77
New cards
Konzentrat/concentration lagerstatten
Deposits with high concentration of disarticulated fossil parts. Deposited over a long time with poor preservation quality. Cannot assume animals are from same time period.
78
New cards
How Konzentrat/concentration lagerstatten is formed
slow sedimentation, flowing water moves fossil parts together (river and beach deposits), caves or pitfalls
79
New cards
Exception to Konzentrat/concentration lagerstatten
Bone beds and mass death layers
80
New cards
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
Well preserved fossils, 3 categories: conservation deposits, stagnation deposits, obtrutions deposits
81
New cards
Conservation deposits
Mummification, freezing of ice age mammals in permafrost, insects in amber,
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
82
New cards
Stagnation Deposits
Anoxic and low rate of decay, fine sediments, produce impressions, moulds, casts,
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
83
New cards
Obtrution Deposits
Organisms buried so fast, there is no time for decay, steep cliff, caused by turbidity currents from a storm, produce impressions, moulds, casts, ex. Burgess Shale,
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
Konservat/Conservation Lagerstatten
84
New cards
Agnathans
Jawless fishes, a grade (non-monophyletic) of fishes
85
New cards
Age of Fishes
The Devonian Period; a time when most of the main groups of fossil fishes had evolved and were thriving globally
86
New cards
Paraphyletic Assemblage (Grade)
A group of organisms that is not united by synapomorphies; a group that excludes some descendants of the common ancestor
87
New cards
Haikouichthys
A Cambrian fossil vertebrate found in deposits about 525 million years old in China- swam by flexing myomeres.
88
New cards
Pectoral Fins
The anterior paired fins of fishes
89
New cards
Pelvic Fins
The posterior paired fins of fishes
90
New cards
Gills
Membranous structures supported on cartilage or bone that allow gas exchange between the blood and water; found in fishes and some amphibians
91
New cards
Anal Fin
The median fin on the ventral surface of the body; may vary from none to two fins depending on species
92
New cards
Dorsal Fin
A fin found on the back of a fish; there may be zero to three, depending on the species of fish
93
New cards
Caudal Fin
The median fin at the posterior end of an aquatic vertebrate
94
New cards
Cartilage
A firm, flexible connective tissue that forms skeletal elements in vertebrates; cartilage is replaced by bone in endochondral bone formation
95
New cards
Bone
A mineralized tissue incorporating calcium hydroxyapatite and collagen, support and muscles attachment, storage for phosphates, protection
96
New cards
Endochondral Bone
Embryonic elements are pre-formed in cartilage and later replaced by bone during ossification in the vertebrate skeleton
97
New cards
Odontoblasts
Specialized cells that produce dentine
98
New cards
Osteoblasts
Bone forming cells
99
New cards
Dentine
Calcareous material that is harder than bone but softer than ganoine/enamel; found in teeth and scales of certain vertebrates
100
New cards
Gnathostomata
The group of jawed vertebrates; see phylogenetic tree