Shock/MODS
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
shock
A condition in which the circulatory system fails to provide sufficient circulation to enable every body part to perform its function; also called hypoperfusion.
types of shock
Hypovolemic
Distributive: septic, neurogenic, anaphylactic
Cardiogenic
distributive shock
+fluid leaks from the vascular/intracellular space into interstitial space; usually takes longer than other types
stages of shock
Initial/Compensatory
Progressive
Refractory/Irreversible
changes during shock (to monitor during all stages)
BP, HR, RR, lungs, GI, kidneys, pH, liver, LOC, glucose, temp, O2, coagulation studies
compensatory stage
+CO increases/O2 decreases, tachycardia first
+Lactic Acid increases: pulling oxygen from smooth muscle
+RR increase
+Fluid retention & shift: reabsorption of water and sodium
+GI changes: decrease of peristalsis
+Mental status: lethargy, mild confusion
+Cold, clammy skin
+Glucose increases: problem for diabetic pts
+Temperature changes: can go up or down
+Significance of changes depends on the timing/severity of issue
progressive stage
+Deterioration worsens dramatically
+Hypotension
+Tachycardia increases
+Systemic hypoxia
+Lungs fail; atelectasis
+Kidneys fail
+GI tract; one of the first ones; constipation/issues with metabolism
+Lactic Acid increases, acidosis ensues (both; metabolic/respiratory usually first)
+pH drops, PaCO2 up, Bicarb down
+Liver failure: rapid decreases chance of survival
+Coagulation problems
+(DIC) possible
+Know Coagulation Studies (PTT, PT/INR, Fibrinogen); increases and raises hemorrhage risk
+Thrombocytopenia
coagulation studies
PTT: 25-30 sec
PT: 10-13.5 seconds
INR: 0.8-1.1
fibrinogen: 200-400mg/dL
thrombocytopenia
low platelet count
PT/INR
prothrombin time/international normalized ratio
irreversible stage
+Severe organ damage
+Hypotension worsens
+Acidosis worsens
+MODS progresses (multiorgan disfunction syndrome)
+Death
monitoring needed for shock treatment
central venous: may need multiple; also for CVP
dialysis catheter or CRRT
peripheral access: 16/18G IV or IO
arterial line
swan-ganz
TPN
urinary catheter
continuous ekg
treatment of shock
fluids
vasopressors
vasodilators: initially, esp for cardiogenic
inotropic
monitoring
nutrition
positioning
oxygen
blood cultures; esp for septic
fluids for shock tx
crystalloids: LR (first), or NS
colloids: albumin; pulls water into intravascular
blood products:
-plasma: decreases hemorrhage risk
-RBC: tx anemia
-platelets: tx thrombocytopenia
vasopressors
drugs used to increase blood pressure
norepinephrine (levophed): first line for septic
epinephrine: good for anaphylactic shock
vasopressin: adjunct for septic
phenylephrine
dopamine: good for cardiogenic; mixed effects
assessments for vasopressors
extremities because of peripheral vasoconstriction
check for extravasation: can lead to tissue necrosis
vasodilators
can be used in initial phases; esp in cardiogenic shock
Isorbid dinitrate (Iso-Bid, Isotrate, Sorbitrate)
Isorbid mononitrate (IMDUR)
Hydralazine (Apresoline)
inotropic agents
drugs that stimulate the heart to increase the force of contractions
ex: dobutamine
CRRT
continuous renal replacement therapy
aka very slow dialysis
sequence of pressors
for sepsis, no benefit to starting in a particular sequence, though
NE VASO EPI PHENYL DA is common.
CVP normal
2-6 mmHg
usually low; tx with crystalloids, albumin, vasodilators
nutrition and shock
+Increased protein & calories
+Enteral vs IV: may need TPN; but leads to hyperglycemia and needs IV insulin drip
+GI motility: risk of obstruction or paralytic ileus
+GI prophylaxis: decrease risk of gastritis
hypovolemic shock
shock resulting from blood or fluid loss; Most common type of shock; can coincide with other forms
+Intracellular vs Interstitial fluid vs Intravascular fluid
+Can be internal &/or external
+Careful with your cardiac patients; fluid overload
cardiogenic shock
Shock caused by inadequate function of the heart, or pump failure.
can be coronary or non-coronary
•BP falls, CO & venous return decrease
coronary cardiogenic shock
Most common in those with an acute MI, resulting in damage to the left ventricular myocardium
non coronary cardiogenic shock
Caused by factors that stress the myocardium
Severe hypoxemia, acidosis, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, tension pneumothorax, cardiomyopathies, valvular damage, cardiac tamponade, and dysrhythmias
tx specific to cardiogenic shock
•Cardiac Enzymes
•Emphasis on ^ output (inotropic agents, vasopressors)
•Antiarrhythmics
•Cardizem (CCB/atrial issue), Amiodarone (ventricular issue)
•Intra-Aortic balloon pumps
IABP
intra-aortic balloon pump; used to support patients in cardiogenic shock
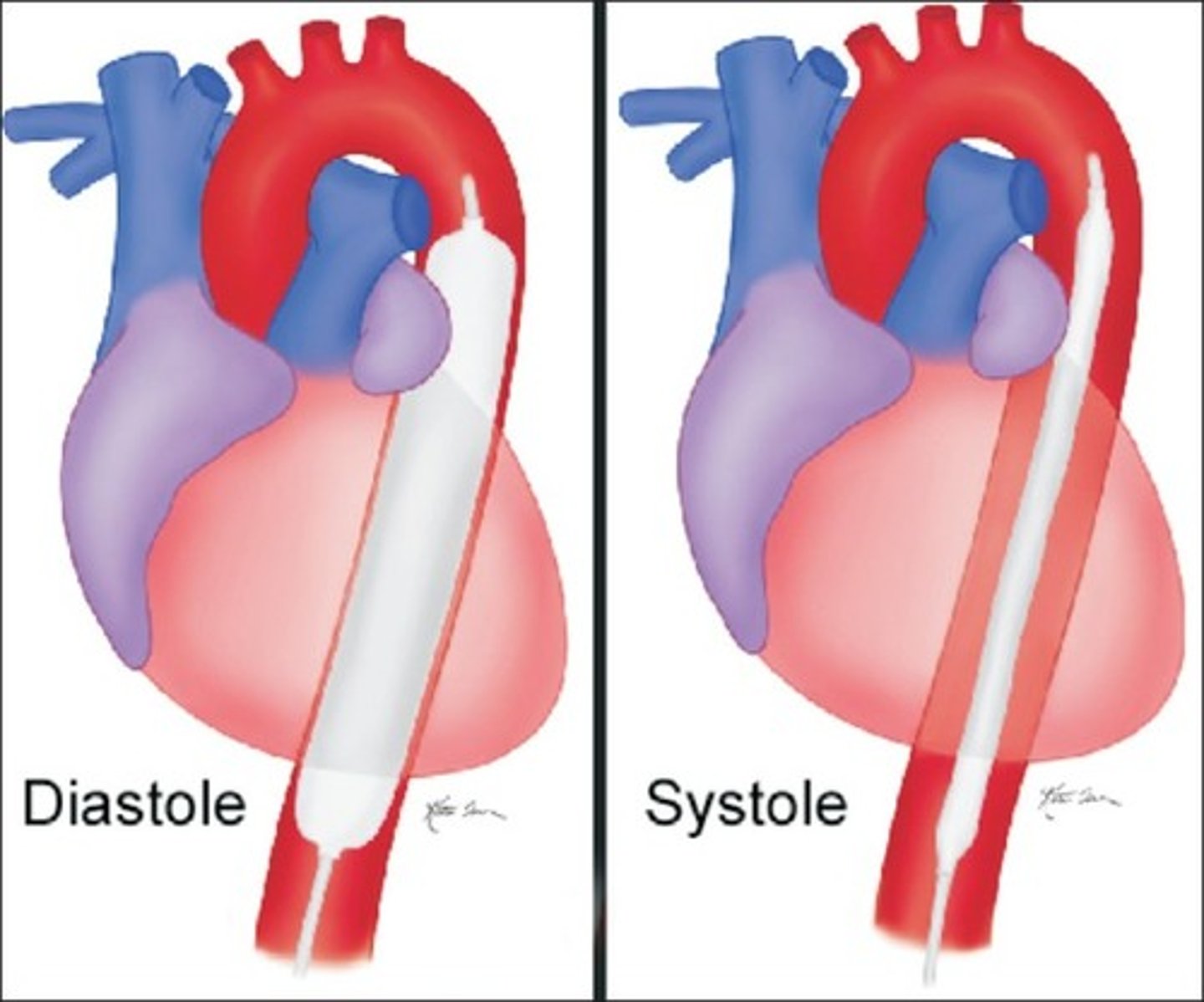
septic shock
+Caused by infection, or response to infection
+Most common distributive form of shock
+Highest level of death from shocks
causes of septic shock
+MRSA
+C-Diff
+Inflammatory Response Syndrome
+Pneumonia
+UTI: urosepsis
+Immunosuppression
inflammatory response syndrome
•Sepsis dx must have 2 of the 4 s/s of Inflammatory Response Syndrome:
1. Fever (>100.4 F) or Hypothermia (<96.8 F)
2. Tachycardia
3. Tachypnea (CO2 < 32 or mechanical ventilation)
4. Leukocytosis (WBC > 12000) or Leukopenia (WBC < 4000)
tx specific to septic shock
+Same as others, to a degree: vasopressors, crystalloids
+Blood cultures
+Antibiotics: esp gram neg ones that are very strong
+CRRT (as with other shocks)
neurogenic shock
+Vasodilation due to imbalances / miscommunication of PNS & SNS
As a results:
+Bradycardia, not tachycardia; BP varies
+Dry / warm skin
+Poikilothermia: poor thermoregulation
anaphylactic shock
+Severe allergic reaction due to antigen-antibody reaction
+IgE; histamine response
+Mass vasodilation occurs due to excessive histamine release
S/S of anaphylactic shock
hives, itching, bronchoconstriction, angioedema, stridor, wheezing, and hypotension
Tx of anaphylactic shock
Epinephrine
diphenhydramine
prednisone
albuterol