BIOL 1113 (General Biology 2) Exam 1 Mary Susan Potts Santone Study Set
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
Angiosperm
Any plant that has flowers and produces seeds enclosed within a carpel

Characteristics of Living Organisms
Cells and organization; energy use and metabolism; response to environmental change; regulation and homeostasis; growth, development and adaptation; biological evolution
Biological Organization
Cell (most basic unit of life) > tissue > organ > organ system > organism > population > community > ecosystem
Metabolism
- All chemical reactions in a cell
- Plants make energy via photosynthesis from sunlight into carbohydrates
- Humans then use these carbohydrates to go through cellular respiration and make ATP
- All life activities rely on ATP
Homeostasis
maintenance of internal conditions within certain boundaries
What is example of homeostatic imbalance?
A DISEASE
Growth, Development, Reproduction, DNA (characteristics of living organisms)
Growth produces more or larger cells; development produces organisms with defined set of characteristics; reproduction sustains species over generations; genetic material causes offspring to have traits like their parents
- Mitosis = creates cells that are carbon copies (identical)
- Meiosis = creates different cells because of crossing over events and independent assortment
(Biological) Evolution
Populations of organisms change over generations;
- heritable change in one or more characteristics of a population or species over generations that promote survival and reproductive success;
Descent with modification (represented in tree form)
all organisms come from a common organism that has adapted over time
- mutations over time
Horizontal gene transfer (non-offspring)
- represented by circle of life model
- genetic material transferred from one organism to another (not related)
- more common in prokaryotes, but very essential for determing how eukaryotes came about
Adaptation
Any modification that makes an organism better suited to its way of life/environment
- product of natural selection
Structure Determines Function (Complementary)
When a biological structure comes about as a species adapts to its environment
- they are tied together
- structure determines function
ex: human hands and proteins
4 Overlapping Stages (for life to occur)
1. Nucleotides and amino acids produced prior to existence of cells
2. Nucleotides and aas become polymerized to from DNA, RNA, and proteins
3. Polymers became enclosed in membranes
4. Polymers enclosed in membranes evolved cellular properties
When did life emerge and what life came first?
4-3.5 bya and prokaryotic life came first
Abiotic synthesis (Reducing atmosphere hypothesis)
Theory of the origin of life;
- primitive atmosphere contained H20 vapor, N2, CO2 with small amounts of H2 and CO;
- little free oxygen resulted in reducing atmosphere; - spontaneous formation of organic molecules;
- monomers evolved and joined into polymers
- primordial soup = mineral rich broth
- life came from non-living molecules coming together to create life
Oparin-Haldane (Hypothesis)
Hypothesis: if the primitive atmosphere was reducing and if there was an appropriate supply of energy, then a wide range of organic compound might be synthesized
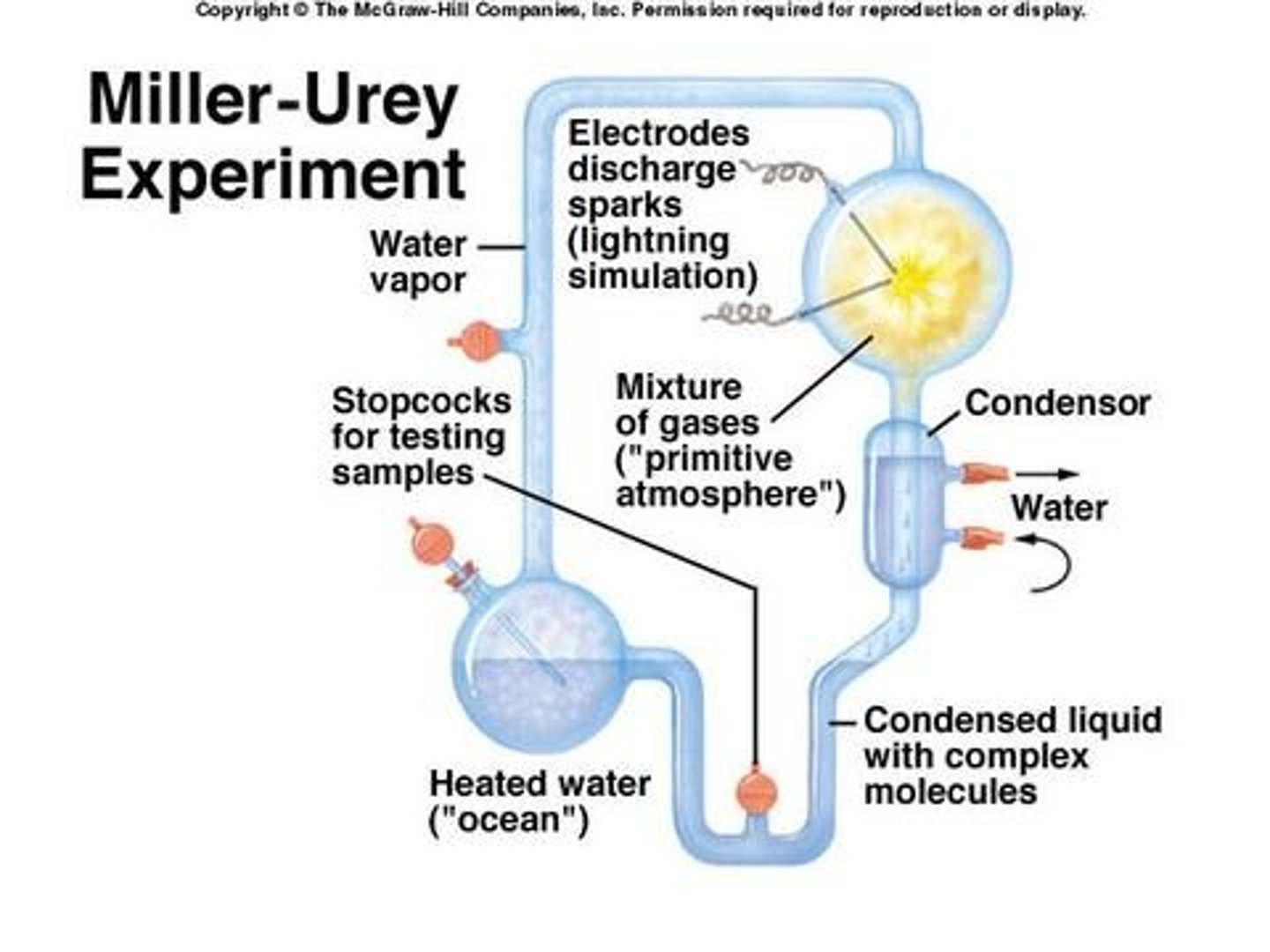
Miller and Urey's Experiment
*** Experiment that showed that biochemicals could be produced from simple non-biological sources through primitive atmospheric gas and strong energy sources (found sugar, carbs, amino acids, etc)
*** Does not matter if the environment was reducing or neutral
- tested abiotic synthesis theory
- apparatus involved gases present in reducing atmosphere = hydrogen, ammonium, methane, nitrogen
- ph=8.7 (alkaline)
- used glass to stimulate rocks
- applied electric sparks to stimulate the lighting, heat, volcanoes, uv light, etc that were pelting the earth because of no ozone layer
- boiling water = primordial soup
Extraterrestrial Hypothesis
Theory of the origin of life where organic carbon, amino acids, and nucleic acid bases from asteroids and comets of the carbonaceous chondrite family gave earth large amounts of organics
- very controversial, would carbon have died on impact
Deep sea vent hypothesis
Theory of the origin of life where key organics arose at deep-sea vents; superheated water rich in H2S and metal ions mixed with cold sea water and organics formed in temperature gradients around vents
Clay hypothesis
Theory of the origin of the first cell;
- simple organics polymerize on solid surfaces (clay, mud, inorganic crystals) and from into more complex organics
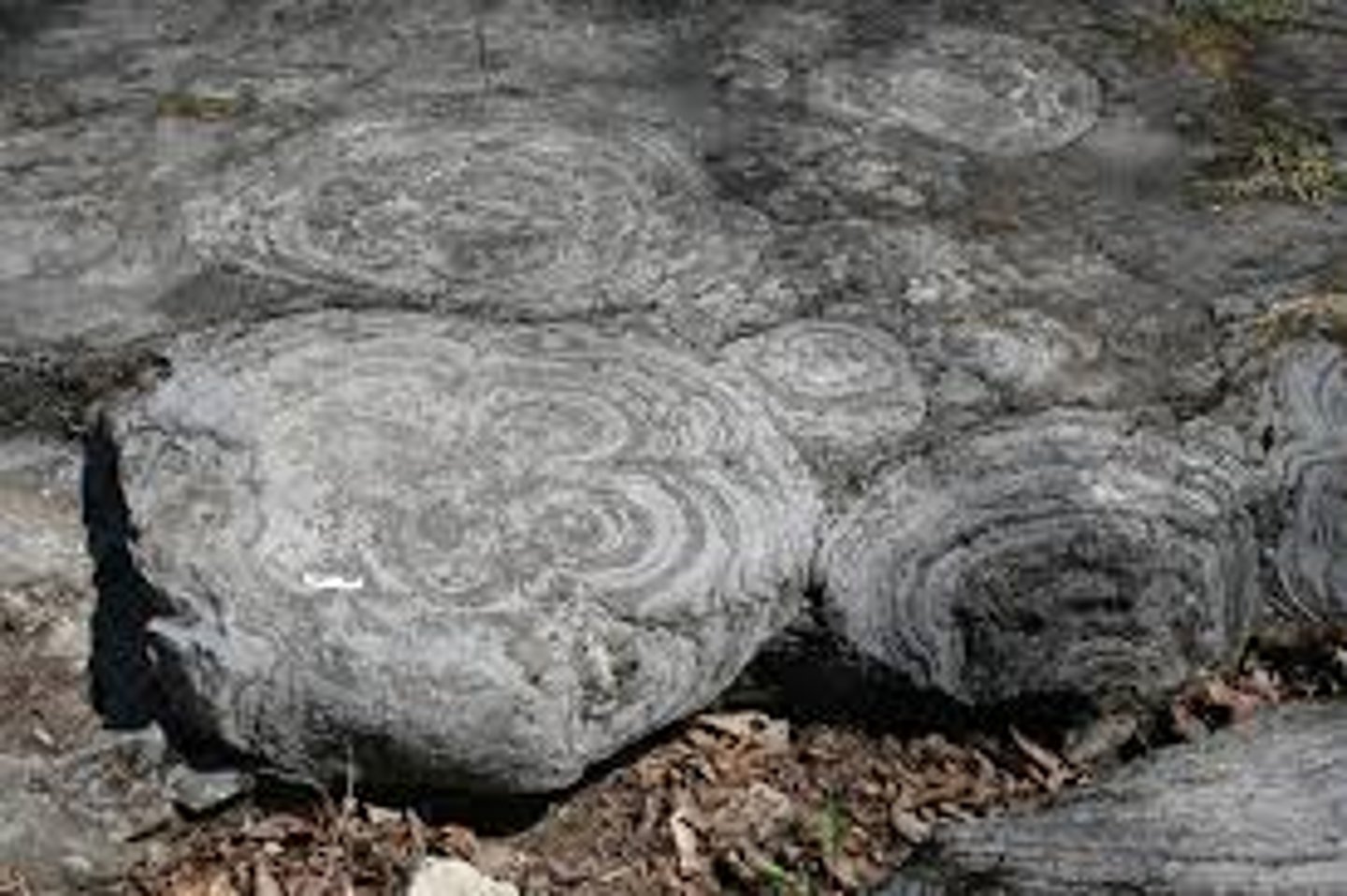
Stromatolite
Mats of mineralized cyanobacteria
- could be some of oldest forms of life

Protobiont
An collection of pre-biotically produced (macro)molecules that acquired a boundary, such as a lipid layer (liposomes) or coacervates, which allowed it to maintain an internal chemical environment
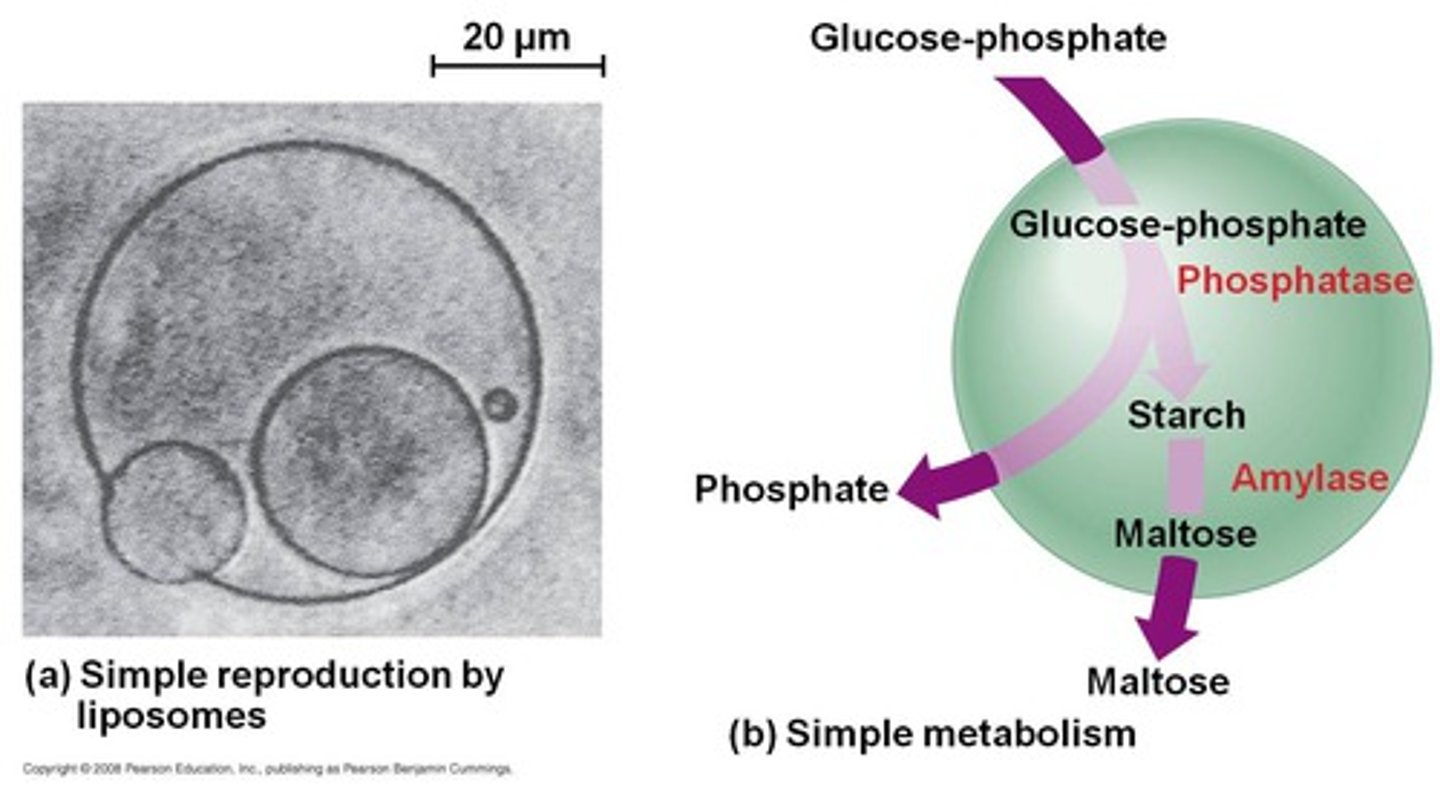
(Characteristics of) cell like structures
Boundary; polymers inside contain info; polymers inside w/ enzymatic function; self-replicating
RNA
This macromolecule:
1. Can store information in its nucleotide base sequence
2. Due to base pairing, has capacity for self-replication
3. Can perform a variety of catalytic functions
Chemical selection
When a chemical within a mixture has special properties or advantages that cause it to increase in number relative to other chemicals in the mixture
Chemical evolution
When a population of molecules changes over time to become a new population with a different chemical composition; Chemical selection results in this
RNA world
hypothetical period on early Earth when both the information for life and the catalytic activity of living cells were contained solely in RNA molecules
Advantages of RNA/DNA/Protein world
1. Better information storage: DNA relieve RNA of informational role and allowed for other functions, DNA less likely to mutate
2. Improved metabolism +: protein have a greater catalytic efficiency, proteins can perform other tasks
Fossil
Preserved remain of past life on Earth
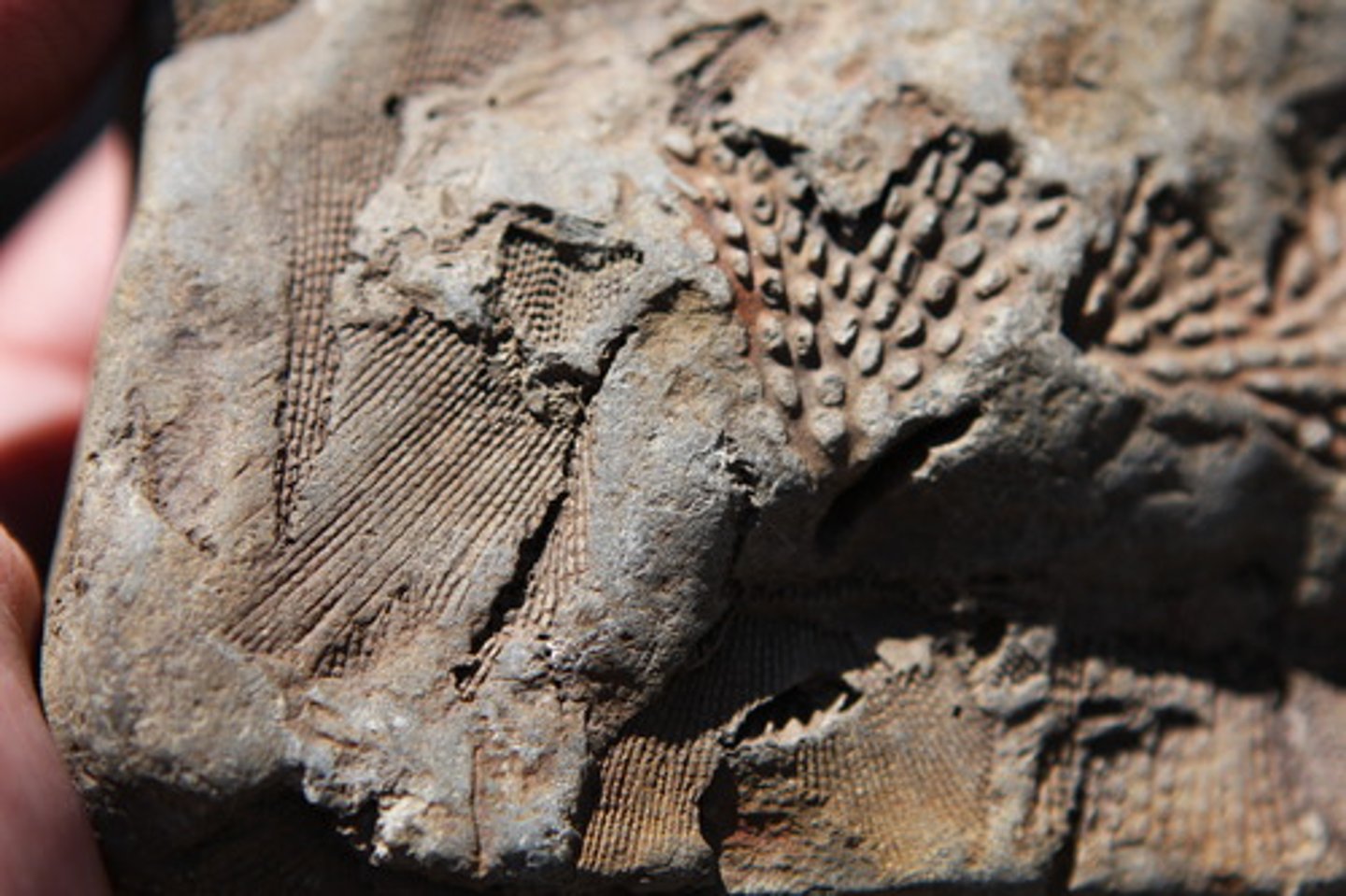

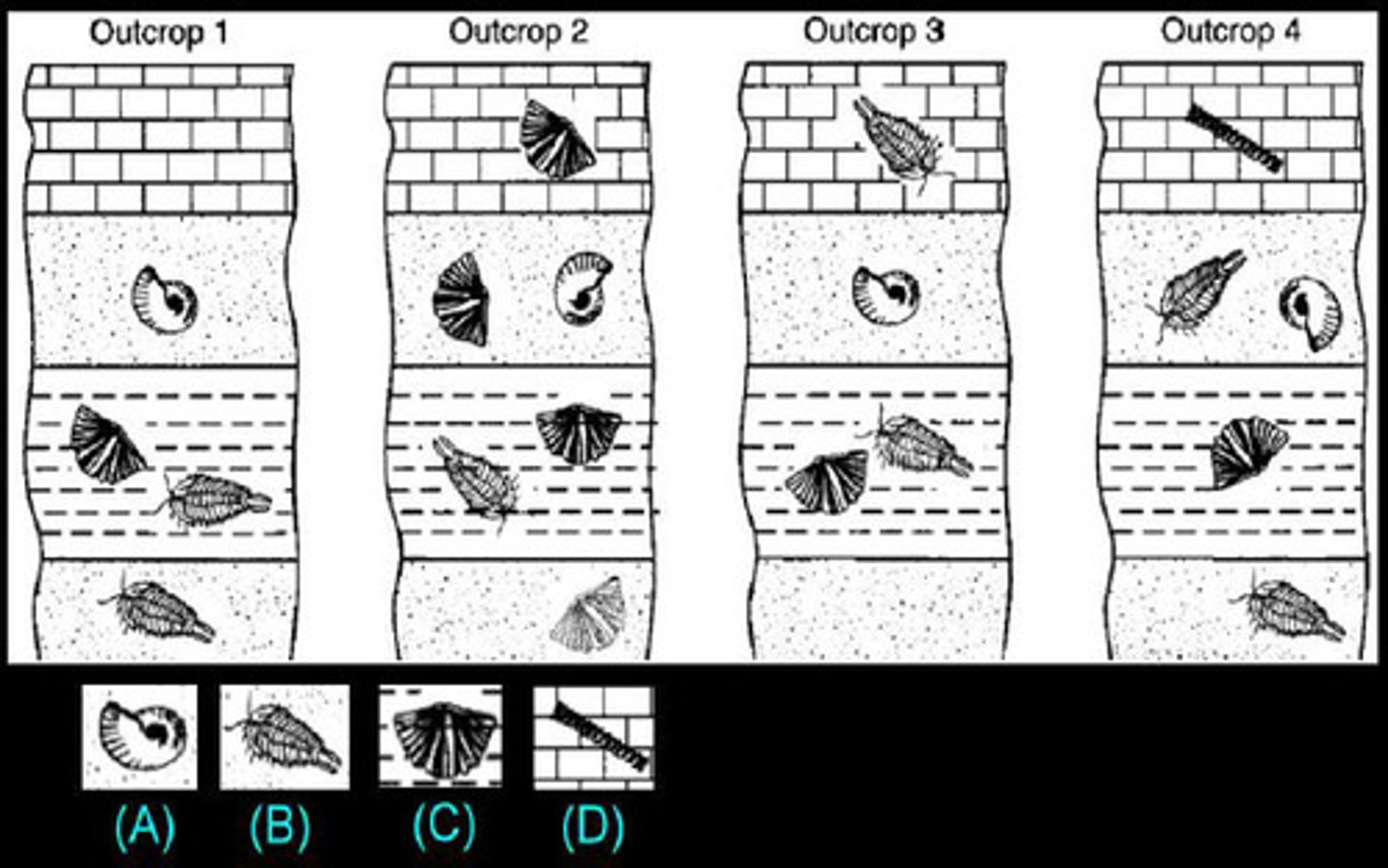
Relative fossil dating
Determining age of fossils by their position in layers of rock (older = towards bottom of the strata, newer closer to the top)
- index fossils = fossils that were widely available, lots of descendants, wide distribution, used to be able to approximate age of other fossils found around those fossils
Strata
A layer of sedimentary rock whose composition is more or less the same throughout and that is visibly different from the rock layers above and below it
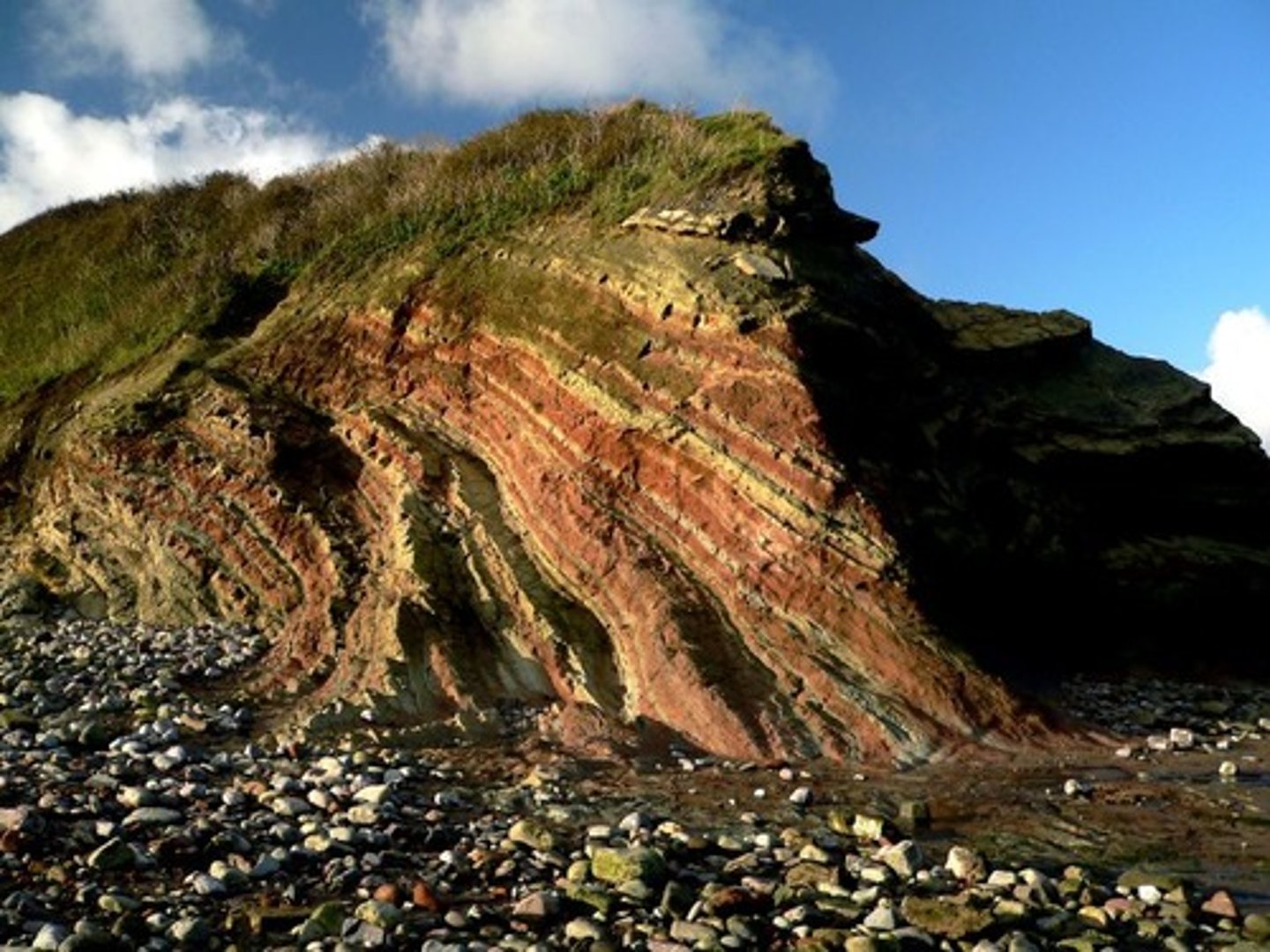

Sedimentary rock
Types of rock that are formed by the deposition and subsequent cementation of that material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water

Sedimentation
Collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle in place.
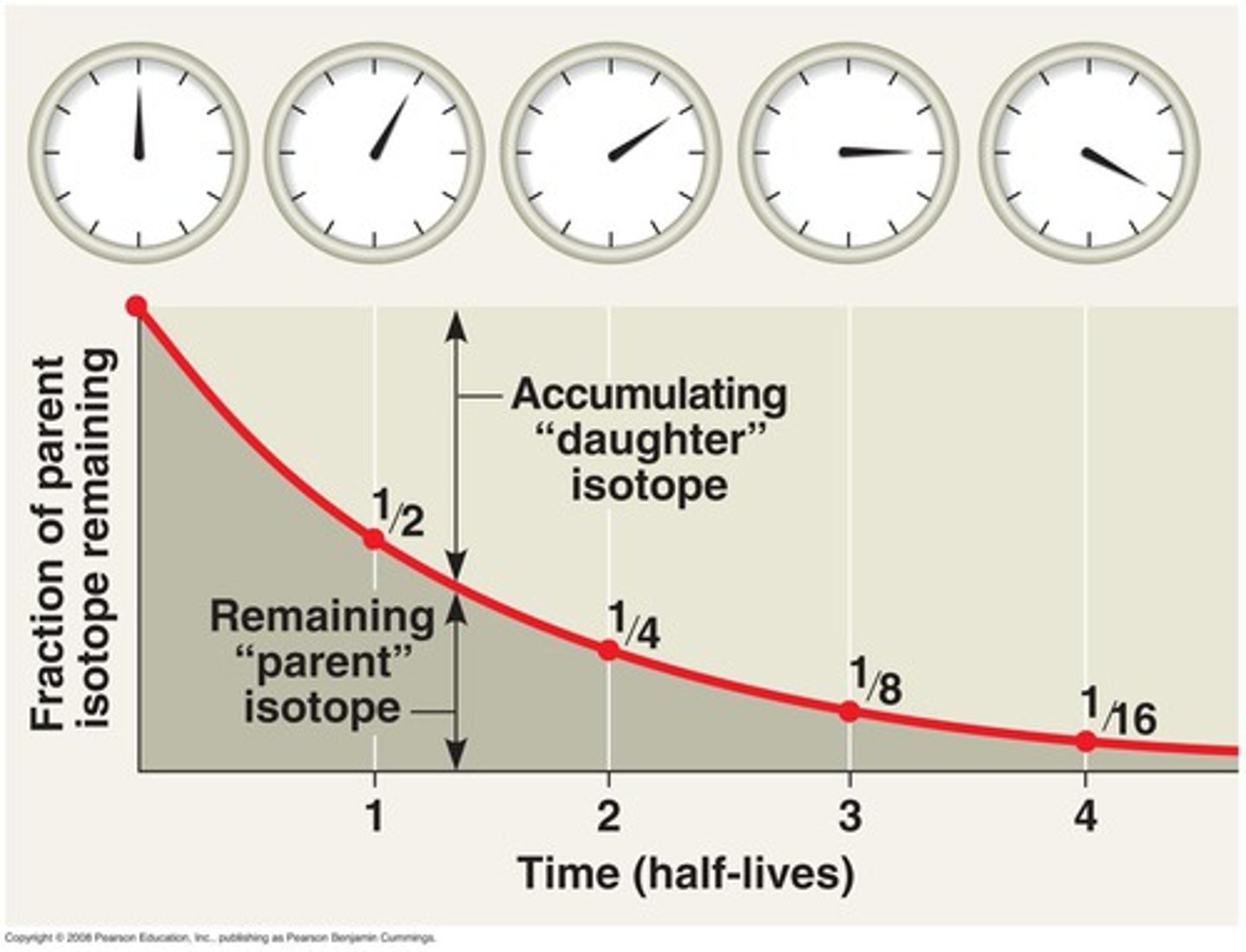
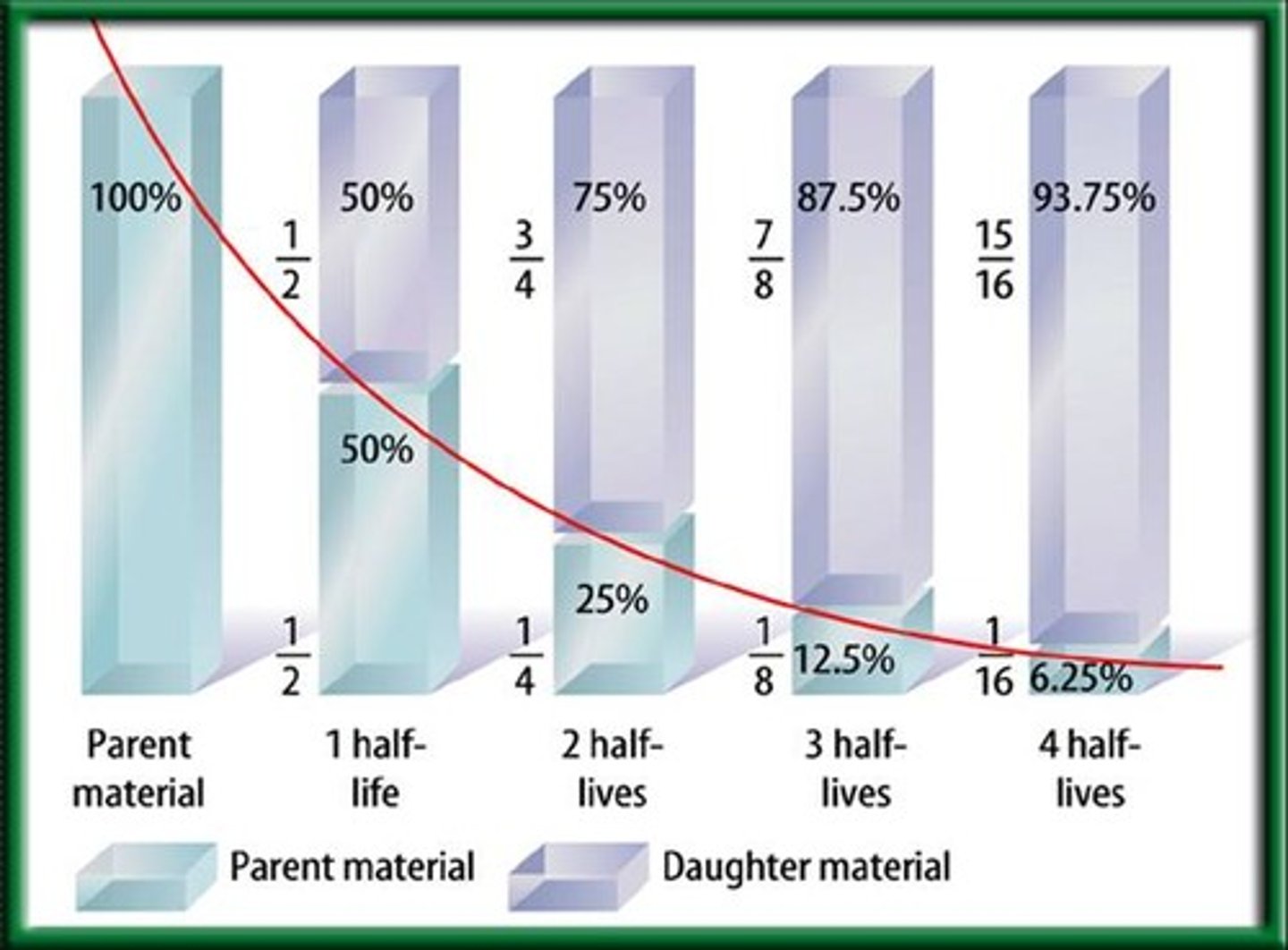
Radiometric dating (absolute dating)
A way to estimate the age of a fossil by analyzing the decay of radioisotopes within the accompanying rock (used in absolute dating)
Radioisotopes
Isotopes that have unstable nuclei and undergo radioactive decay
- they are unstable because they omit some type of particle
Half life
The length of time require for a radioisotope to decay to exactly half of its initial quantity (used in absolute dating)
- changed into something else by omitting particles
- after 1 half life there is a 1:1 ratio
- after 2 half life there is a 1:3 ratio
- after 3 half life there is 1:7 ratio
- after 4 half life there is 1:15 ratio
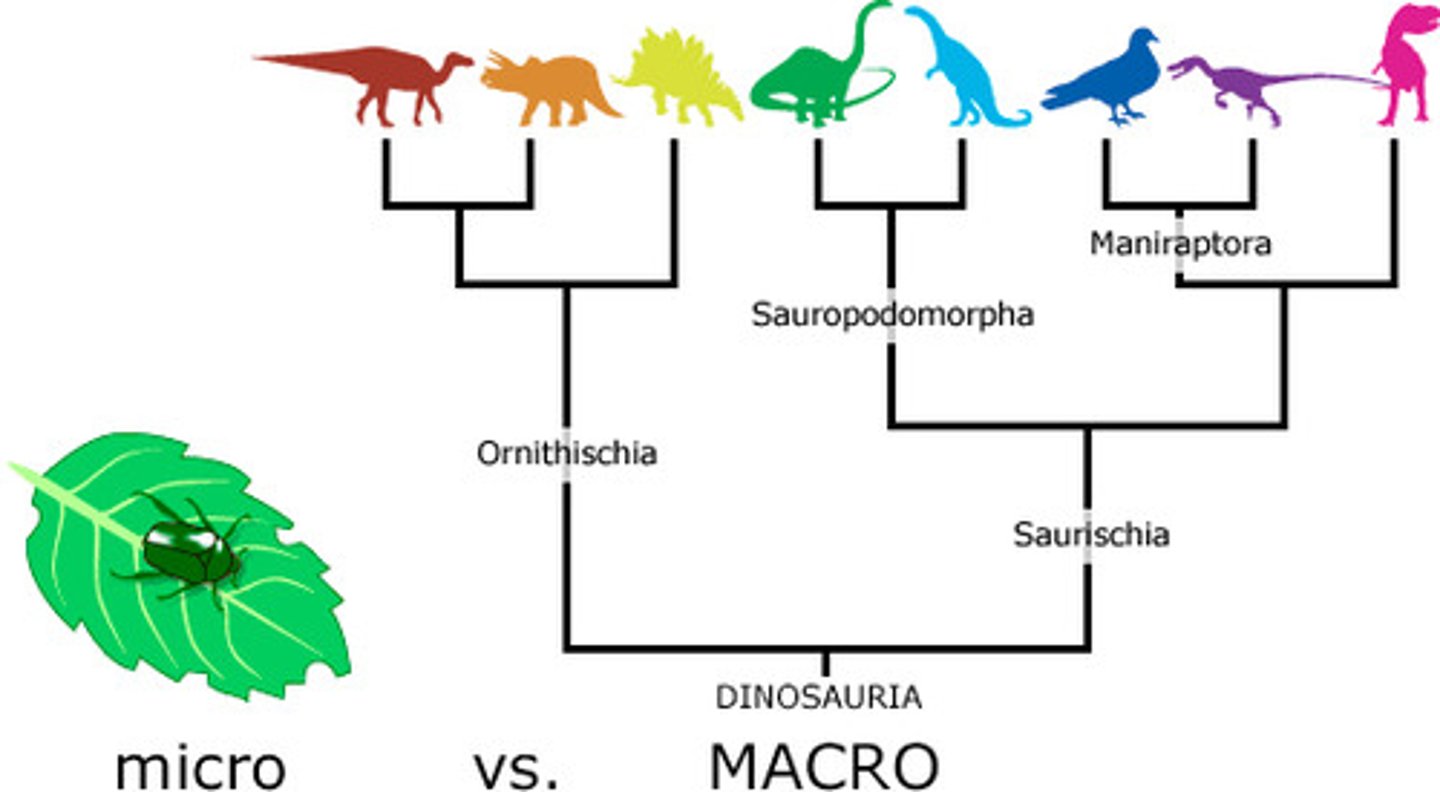
Macroevolution
Formation of new species or groups of species
Factors that affect the fossil record
1. Anatomy (hard body parts fossilize easier)
2. size (larger organisms are more likely to be found)
3. number (more in # = easier to find, best chance of fossilized)
4. environment (marine = more likely to be fossilized)
5. time (lived recently or existed for long period of time = more likely to be found)
6. geological processes (certain organisms are more likely to be fossilized because of their chemistry
7. interest of paleontologists (certain species are more interesting, hence will be found more)
Index species/fossils
Fossils that help define and identify geologic periods (used in relative dating)
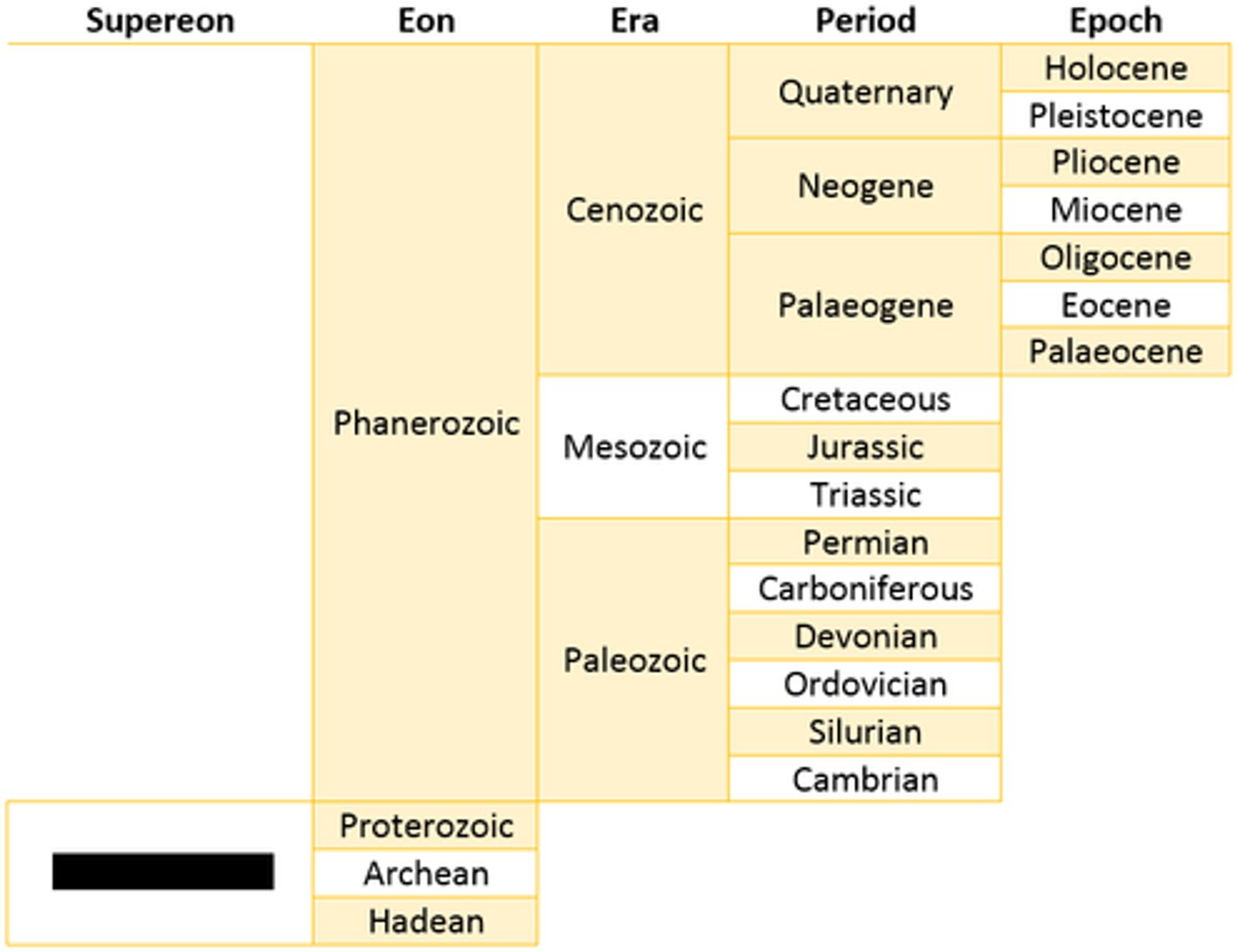
Geological timescale
Timeline of Earth's history and major events from its origin approximately 4.55 bya to the present (based on fossil evidence)
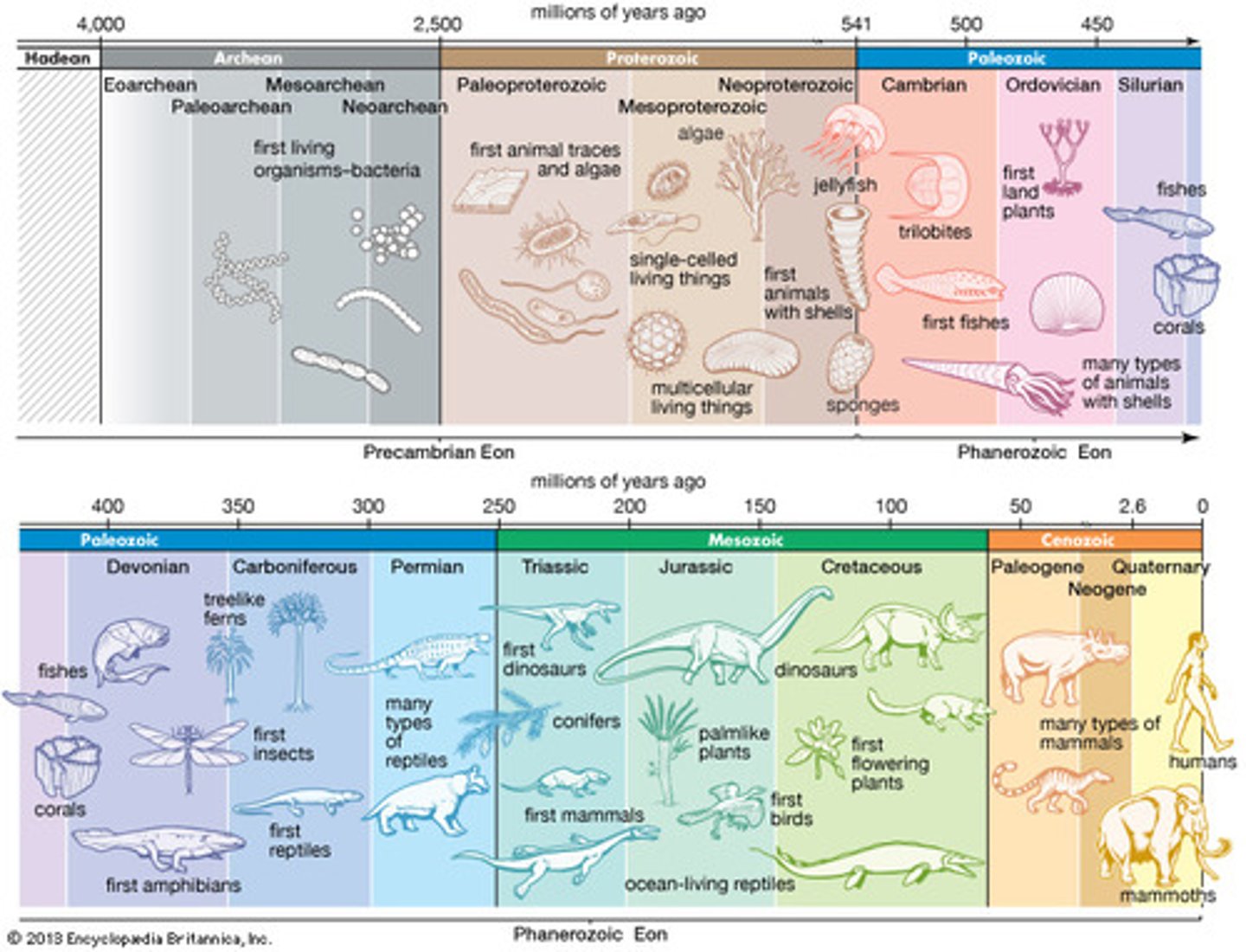
What patterns are associated with the geologic time scale?
1. Climate/temp (hot, cold)
2. Atmosphere (was it neutral or reducing)
3. Land masses (plate tectonics & continental drift)
4. Floods/glaciation (sea level changes)
5. Volcanic eruptions (spewing molten lava and gas into the atmosphere)
6. meteorite impacts (local & widespread impacts)
Four eons
1. Hadean (probably no life)
2. Archaen (earliest life formed)
3. Proterozoic (recognizable tiny life, prokaryotes, before animal life)
4. Phanerozoic (animal life, larger organisms)
Precambrian time (87% of time)
- The Archaen and Proterozoic eons make up this time
- Life originating in primordial soul
- Little or no atmospheric oxygen (reducing or neutral atmosphere)
- No ozone shield (let UV light bombard Earth)
- First cells came into existence in marine environments (Prokaryotes -- similar to modern day cyanobacteria)
- Dominated by microbial life (would need microscope to see it)
- Added first oxygen to atmosphere to lead to aerobic processes like glycolysis
- First organisms Heterotrophs, then giving rise to Autotrophs
Endosymbitoic Hypothesis
eukaryotes cells evolved roughly 2 billion years ago
- discovered this by looking at where DNA was located in eukaryotes
multicellularity came about about 1.5 bya
Edicaran/Vendian Period
- End of Proterozoic eon
- Named for edicaran hills where fossilized organisms have been found
- First fossil evidence of multicellular life
- found in shallow, marine mud flats
- animals very unusual forms (no bones, no organs)
- Evidence of collagen protein which is most abundant protein in animal world
- New evidence suggests possibly that life may have began even earlier than this
How many eras in the Phanerozoic (well displayed life) era?
3
Paleozoic Era (ancient animal life)
- 1st Part of Phanerozoic eon
- 3 major mass extinctions
Cambrian period (explosion)
- The first period in the Phanerozoic eon and Paleozoic era;
-Cambrian explosion
- farthest we can go back to this explosion for every type of animal we have today
- Climate = warm, wet, oxygen present, no ice at the poles
- No major reorganizations of body plans since the Cambrian explosion
- Many shells, first vertebrates
- Rise in O2 (change ocean chemistry), uses oxygen with other ocean chemicals to generate calcium carbonate (can make shells)
- Hox genes = determine specific body plans
- Predator/Prey arms race
Burgess Shale
- Body of fossils found in British Columbia
- Great set of fossils from organisms that lived during Cambrian Explosion
- Radioants recently found there which is a new animal discovery
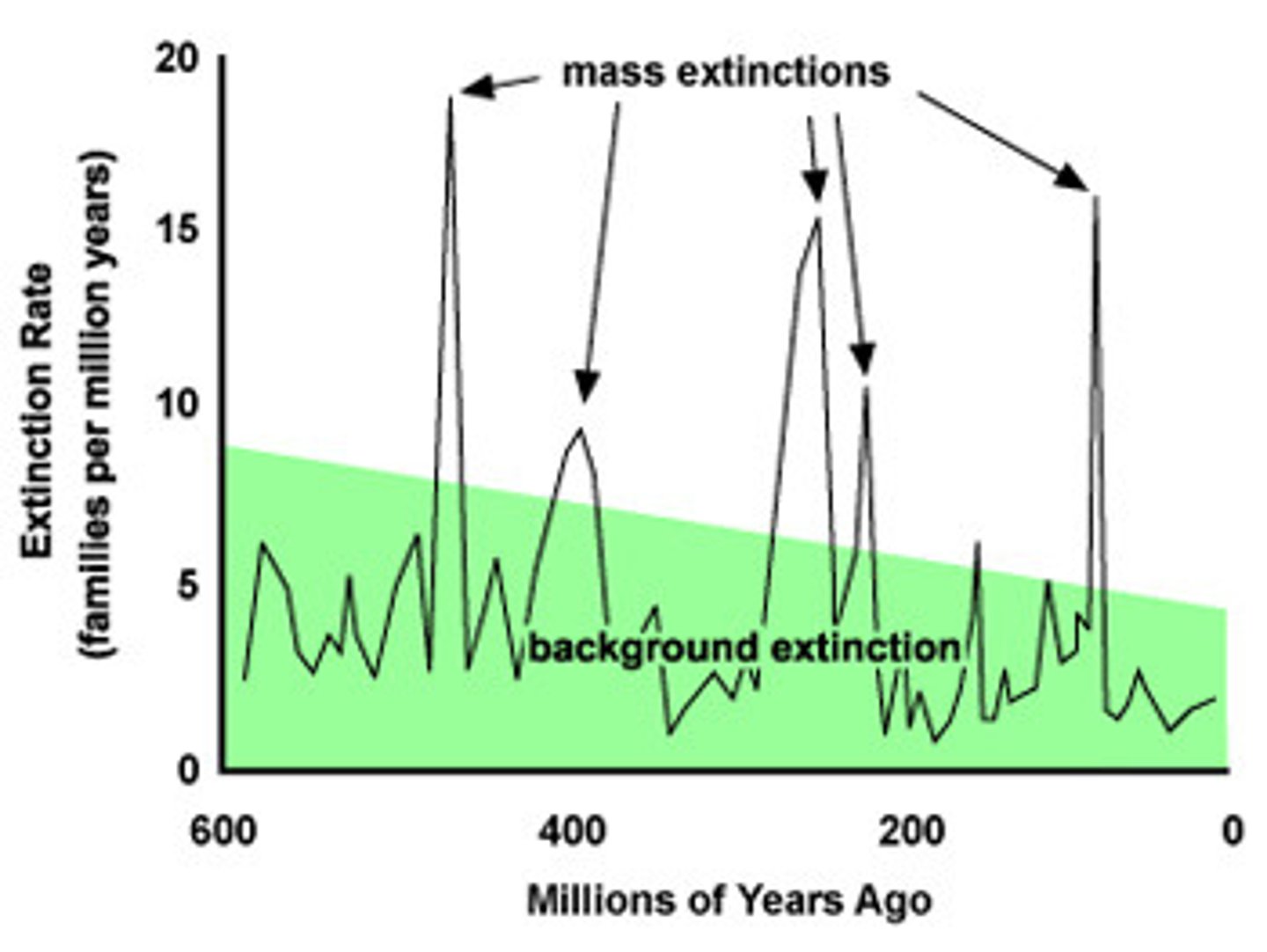
Extinction
The complete loss of a species or group of species
5(+) mass extinctions
1. ends of the Ordovician (sea level changes)
2. Devonian (global cooling, loss of oxygen in water)
3. Permian (biggest extinction, marks beginning of new era, dramatic climate and sea level fluctuations)
4. Triassic (
5. Cretaceous KT (marks transition from 3rd eon to now, the great dying, volcanic activity from meteorite hitting the earth)
6. We are living in one now
Changes in the atmosphere
Prior to 2.4 bya there was little oxygen in the atmosphere, but the emergence of photosynthetic organisms caused the increase of O2 to become 21% of the atmosphere today. This describes what?
Archaean Eon
When did the first prokaryotic cells develop?
Heterotroph
Organisms that must obtain organic food from other organisms

Autotroph
Organisms that produce their own organic molecules from inorganics and/or light
Phanerozoic eon
The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras are a part of which eon?
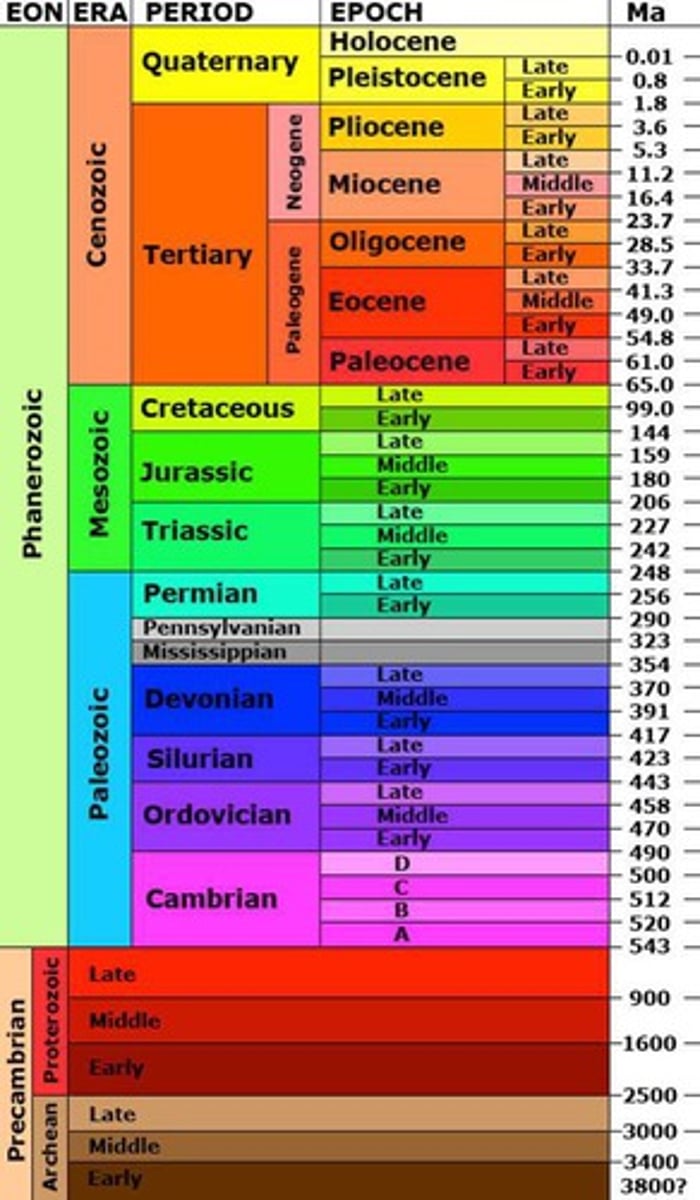
Paleozoic era
The Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian periods are a part of which era?
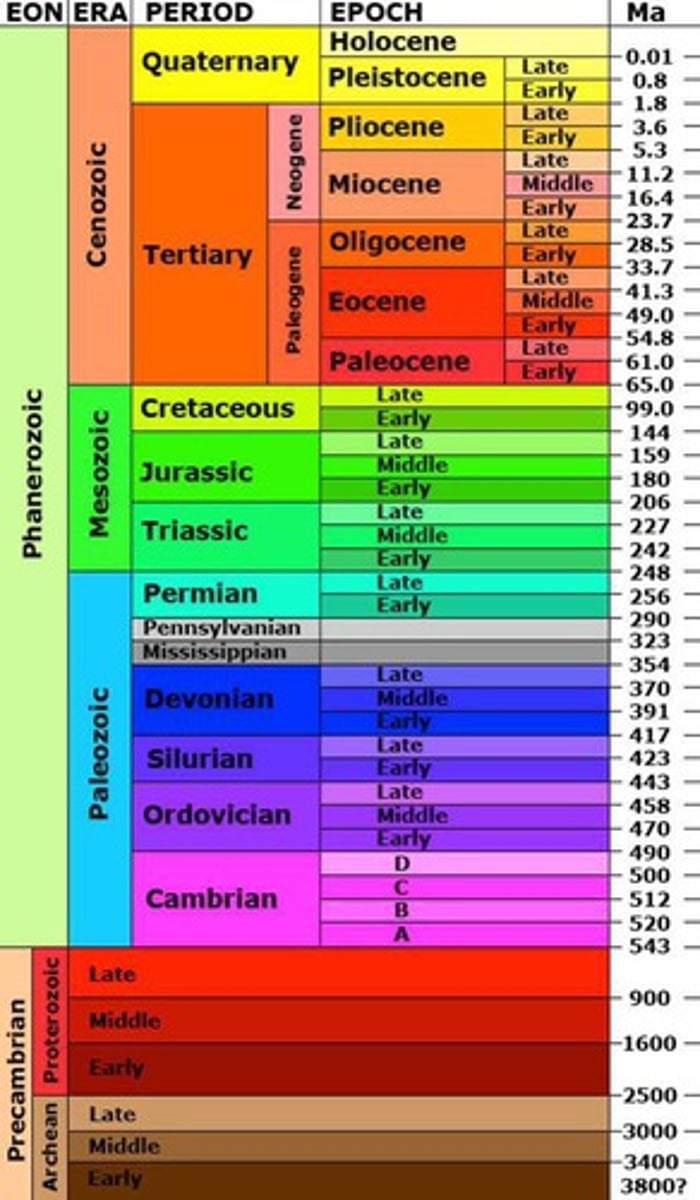
Mesozoic era
- The Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods were a part of this era, that saw the rise and fall of the dinosaurs
- long period of recovery in the beginning from permian extinction
- hot, dry climate, little ice at poles,
- age of reptiles
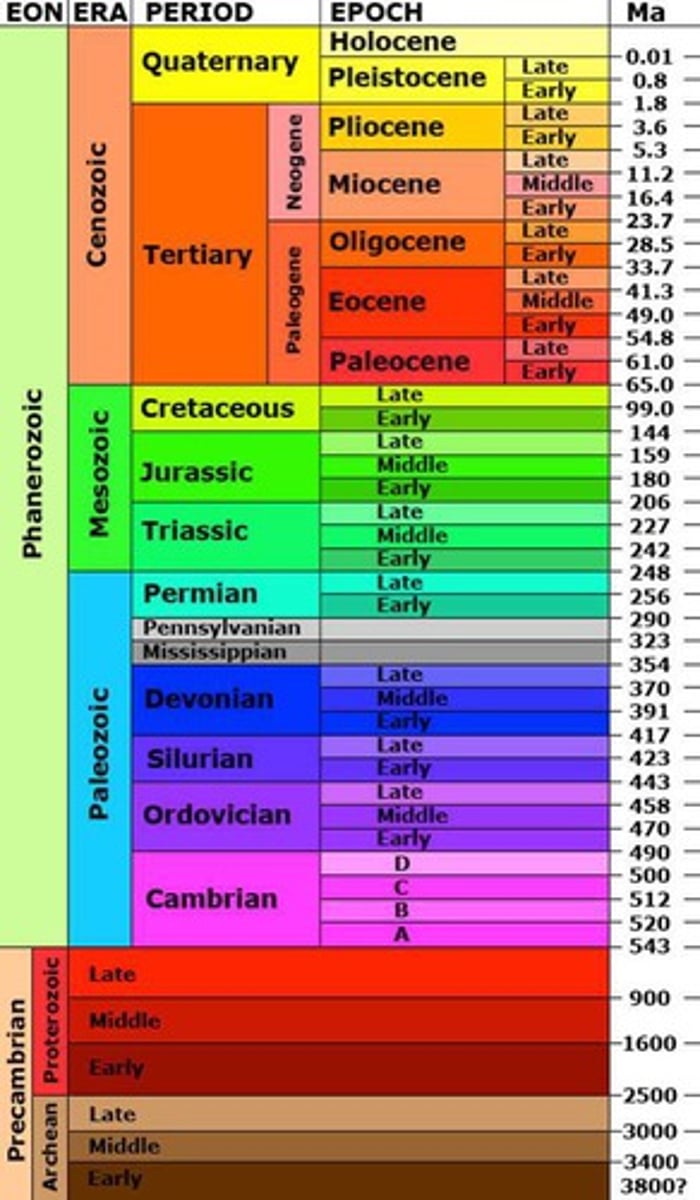
Cenozoic Era
- The Tertiary and Quaternary periods make up this, most recent/current era ;
- Age of Mammals (modern/new animal life)
- 65 mya - today
- colder, drier climate
- flowering plants became important as reproductive successes
- 4 glaciation events (GOT type animals)
- Primate evolution
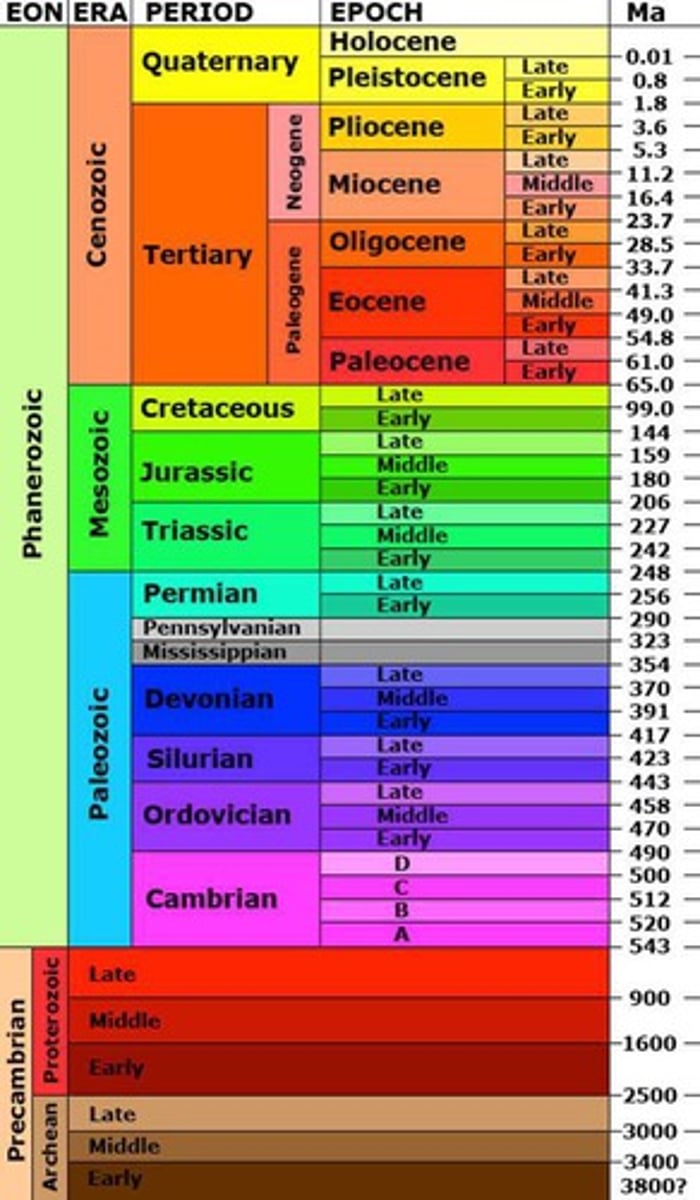
Ordovician Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
- warm temperatures, moist atmosphere, lots of CO2 in atmosphere
- diverse marine invertebrates (shells) -- trilobites and brachipods
- land was in supercontinent (one giant continent)
- primitive plants and arthropods made their way onto land!
- ended with abrupt climate change to mass extinction
Silurian Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
- Stable climate, glaciers melting, rise in sea levels
- Vertebrate species evolving, plants, coral reefs appeared,
- Seedless vascular plants created first forests
- Spiders and centipedes like animals, arthropods
Devonian Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
- age of the fishes
- rapidly diversifying fish life in marine environments
- gymnosperms evolved (allow dispersal)
- flying insects emerged
- tetrapods and amphibians started to emerge from bony fishes
- first forests were forming
Carboniferous Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
- Goal and natural gas deposits laid down
- Diversifying plants and animals
- Flying insects emerge
- Age of amphibians (earliest tetrapods) - huge back then
When did amniotic egg emerge?
Carboniferous Period
- Reptiles produce this egg which gave them an advantage because the offspring were protected by the shell
- Eggs could be laid on land, does not need to be in sea
Permian Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
- Supercontinent Pangea formed from continental drift
- Forests shift to gymnosperms
- Reptiles became dominant because of their egg, amphibians still prevalent
- First mammal life reptiles appear
- At the end largest mass extinction occurs (Permian extinction)
Triassic (transitional) Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Mesozoic Era
- gymnosperms dominant
- first true mammals came into being (1st dinos)
- reptiles present
Jurassic Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Mesozoic Era
- Dinosaurs grew to huge size
- Huge diversity
Cretaceous Period
- Part of Phanerozoic Eon, Mesozoic Era
- Dinosaurs began decline
- Eventually led to extinction of all dinosaurs besides flying ones
- Mammals begin to fill in the gaps the dinosaurs left open (adaptive radiation)
- Ends with KT extinction
When did hominoids appear?
- Quaternary period of the cenozoic era
- Hominids are -- a member of a group of primates that includes humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and gibbons, plus all of their recent ancestors
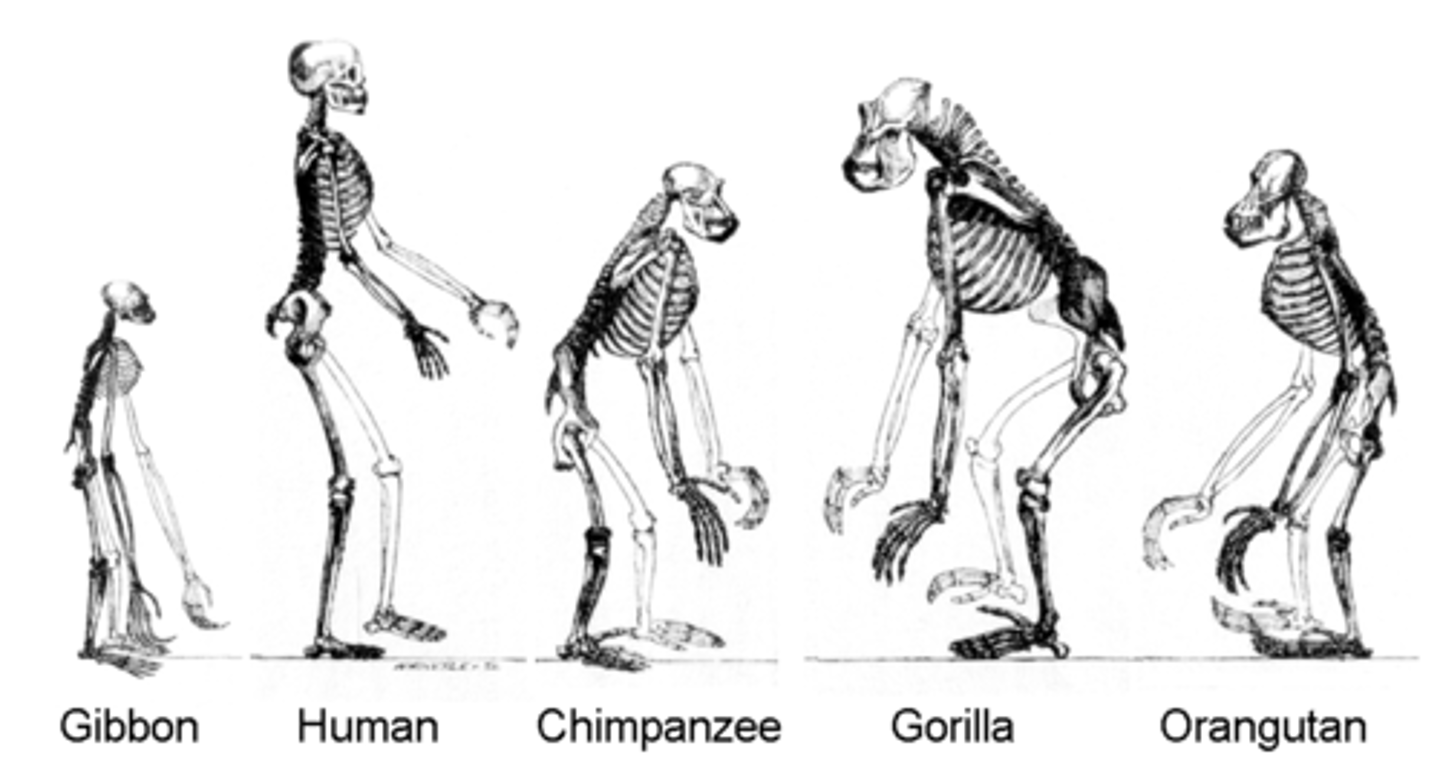
Quaternary Period & primate evolution
- Part of cenozoic era
- Primate evolve (descendent from tree dwellers or arboreal)
- Homo sapiens evolve
- Adapted for climbing trees
1. Rotating shoulder joint
2. Big toe and thumb widely separated from other digits
3. Stereoscopic vision (depth perception, gauge distances)
- 1 offspring per pregnancy, fingernails, upright body form, bipedalism (for homo species),
6th mass extinction
- Holocene or Anthropocene extinction
- worst species die off since KT extinction
- caused by human overpopulation and humans misusing environment
Species
Group of related organisms that share a distinctive form; in species that produce sexually, they are capable of interbreeding (viable, fertile offspring)
Population
Members of a species that live in the same area at the same time and have the opportunity to interbreed.
Molecular evolution
Changes at the level of genes and proteins that underlie the phenotypic changes associate with evolution
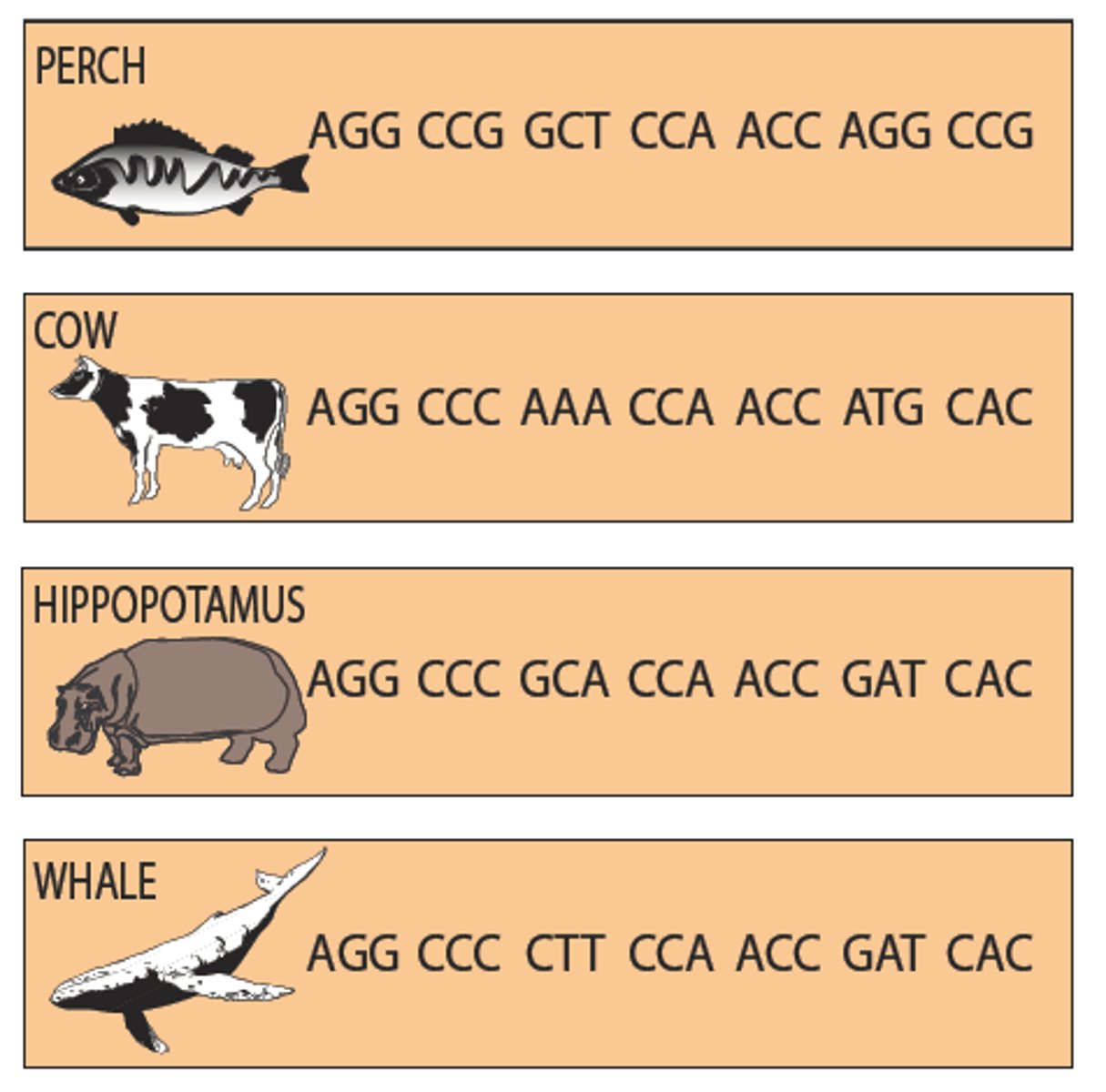
Microevolution
Changes in a single gene in a population over time
- Caused by mutations, environment decides if they are good/bad/neutral
- Natural Selection is a large cause of microevolution
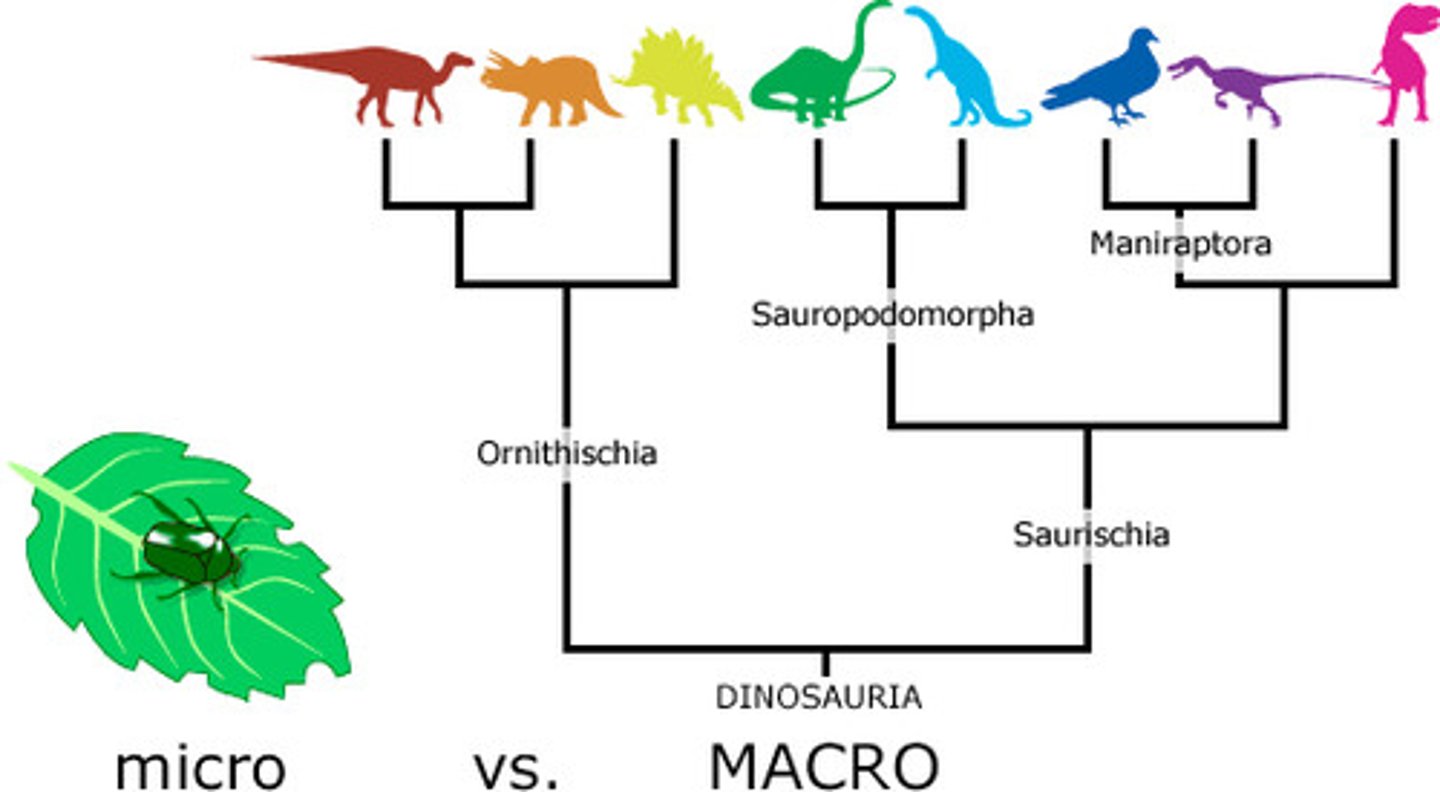
Evidence of biological evolution
Studies of natural selection, fossil record, biogeography, convergent evolution, selective breeding, homologies (anatomical, developmental, molecular) are used as what?
Transitional form
An organism that provides a link between earlier and later forms in evolution
- sits in between two different organisms
Biogeography
- Study of the geographic distribution of extinct and living species
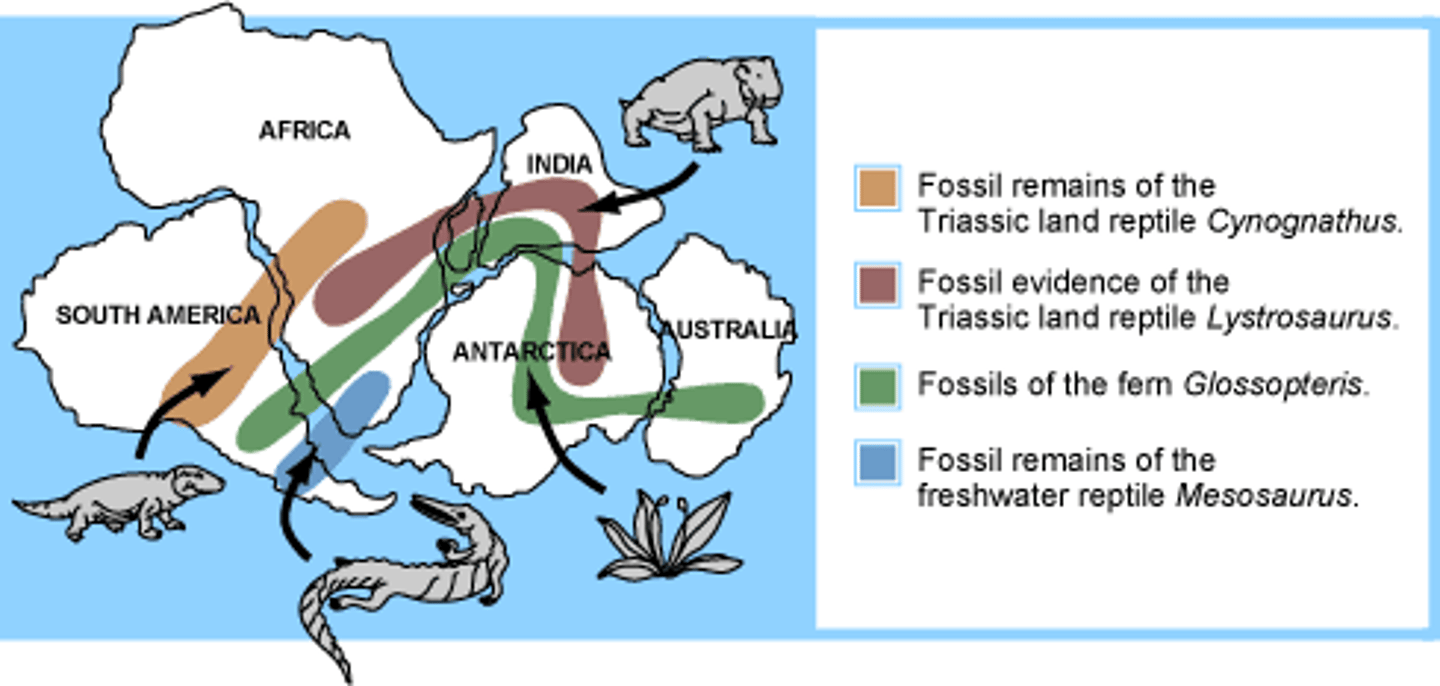
Endemic
Species that are naturally found only in a particular location (islands commonly have this)
Pepper Moth Example
During the industrial revolution, birch trees were dyed black and the already black pepper moths thrived resulting in their expansion. Random mutations caused the speckled form to appear.
- white moths used to thrive then black moths thrived because of the new tree color leading to evolution of the moths to be darker
Convergent evolution
Process in which two species from different lineages have independently evolved similar characteristics because they occupy similar environments
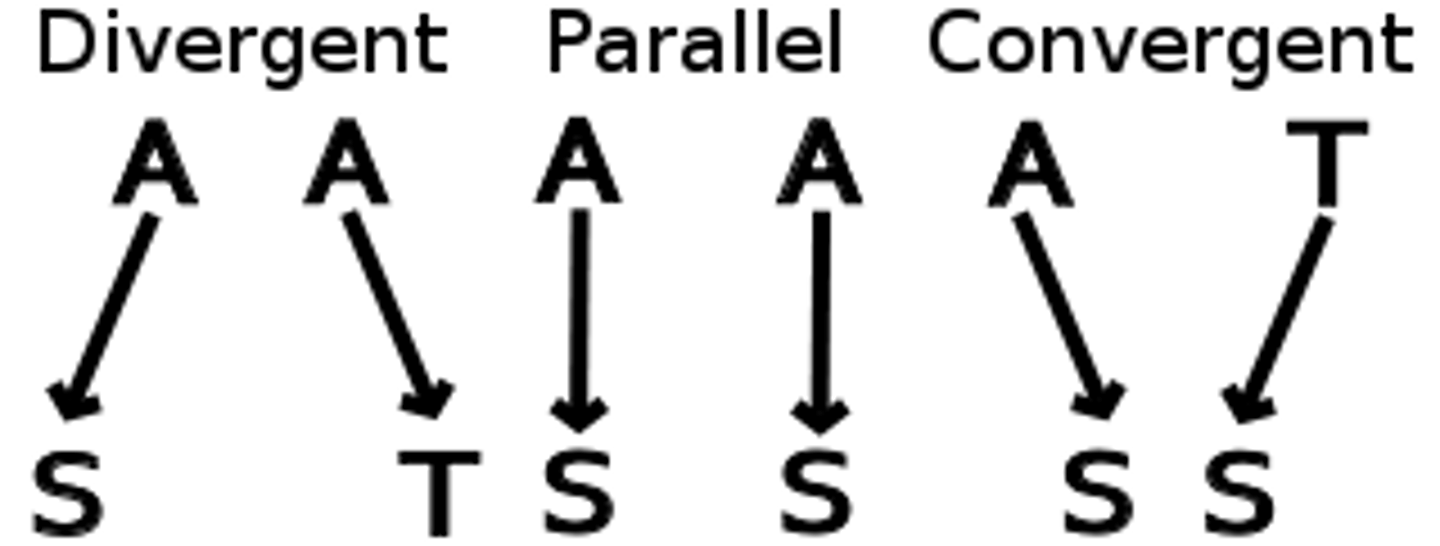
Homologous genes
Two or more genes derived from the same ancestral gene
Paralogs
Two or more homologous genes within a single speices
Gene family
Set of paralogs (related genes) within the genome of a single species; ie globin genes
Vertical evolution
Process in which species evolve from pre-existing species by the accumulation of mutations
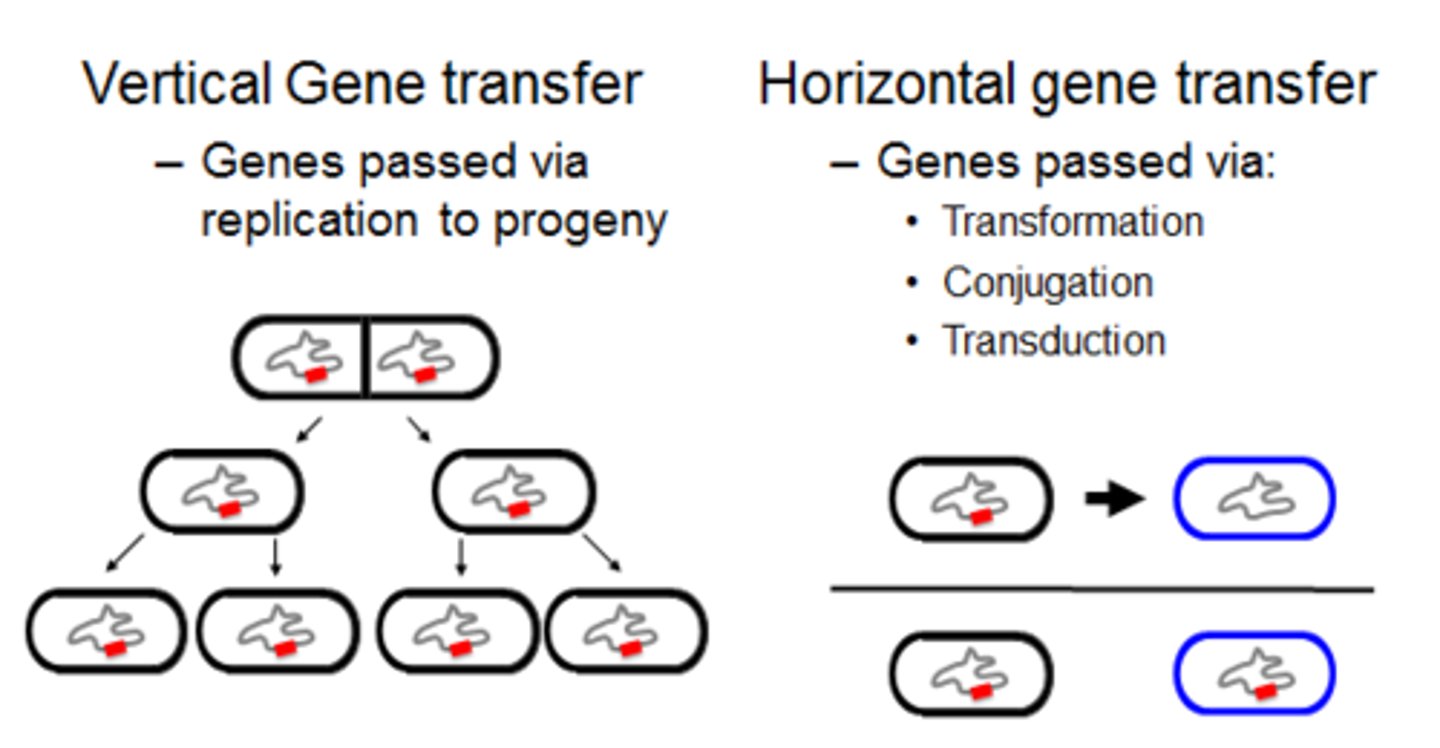
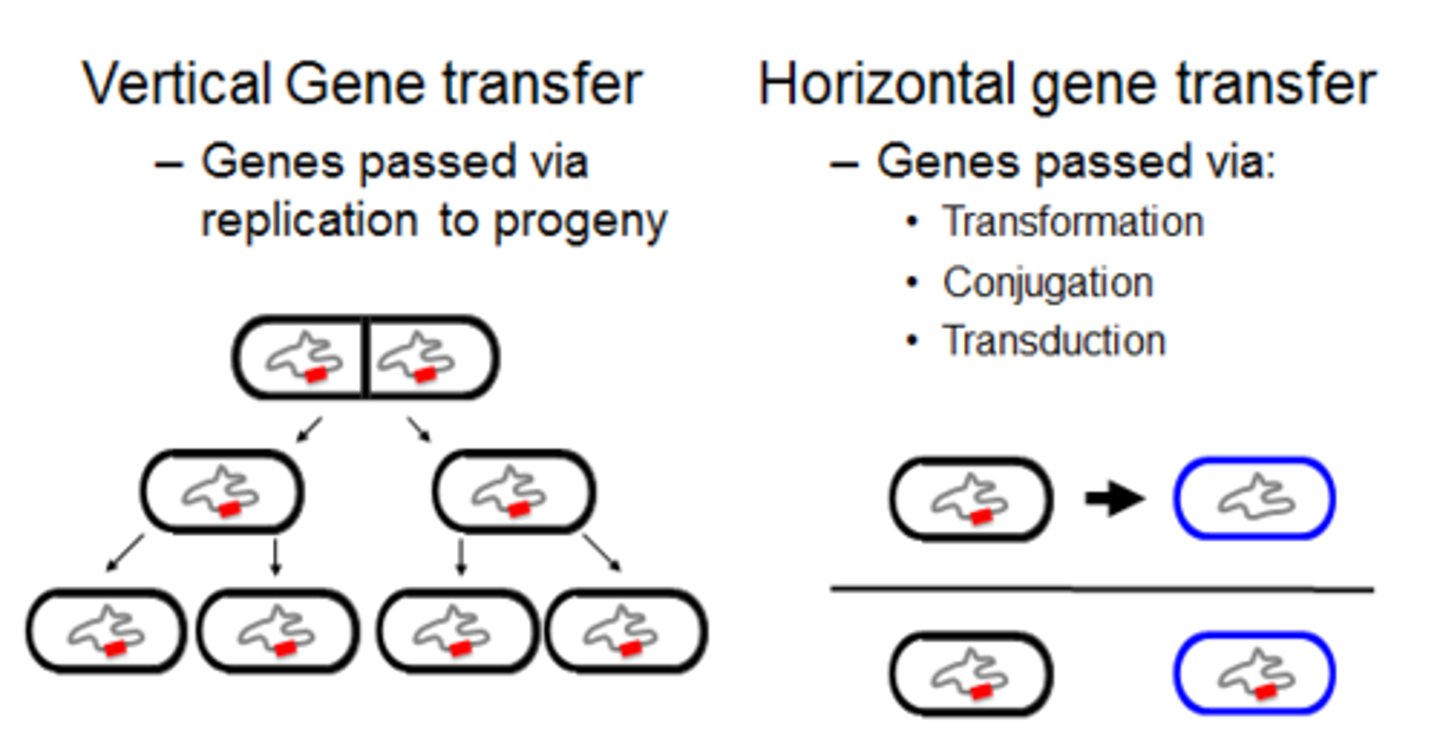
Horizontal gene transfer
Process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism
Empirical thought
Thought that relies on observation to form an idea or hypothesis rather than trying to understand life from a nonphysical or spiritual point of view
Anaximander
Ancient greek philosopher who first suggested organisms evolve over time
Plato
Ancient greek philosopher that supported "essentialism:" objects are temporary reflection of ideal forms
Essentialism = theory of form (some ideal form does exist)
Aristotle
Ancient greek philosopher who believed all living things can be arranged in linear hierarchy;
- Scala Naturae (scale of life) = put inanimate matter at the bottom, then intermediate forms, then vertebrates at the top, with humans at the top (above nature)
- Father of classic taxonomy
Creationism
Belief that all life on Earth was created out of nothing by a devine being as an act of freewill
Spontaneous generation
- sweaty rags turns into mice after 21 days
- saying inanimate matter becomes transformed into living organisms
(John) Ray
- 17th century English naturalist;
- 1st study of natural world with structure and function
- introduced modern concept of species; developed an early classification system of plants and animals in the first published study of the natural world

(Carolus) Linnaeus
18th century Swedish naturalist who
- supported the idea of fixed species,
- each species has ideal structure and function and a place in the scale naturaea
- came up with system of binomial nomenclature (way we name things today)

(Georges) Buffon
18th century French zoologist proposed that populations of living things change through time;
- 44 volume catalog of all know plants and animals

Erasmus Darwin
18th century English physician
- suggested common descent from evidence in developmental patterns, artificial selection, and vestigial organs;
- grandfather of Charles Darwin

(Georges) Cuvier
Early 19th century French zoologist and paleontologist who was first to use comparative anatomy to develop a system of classification;
- founded scientific field of paleontology;
- recognized that fossils were animals that once lived that had gone extinct
- proposed catastrophism - events in past had case later strata to have new mixes of fossils

(Jean-Baptiste) Lamarck
18th century naturalist;
- first biologist to propose evolution and to link diversity with environmental adaptation;
- more complex organisms descendants from less complex
- proposed Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics

Inheritance of acquired characteristics
Idea that organisms altered their behavior in response to environmental change and these modifications were inherited by offspring
- believed that organisms went through changes to meet their needs (ex: giraffes got longer necks because they all tried to stretch their necks)
(Charles) Lyell
Early 19th century Scottish geologist;
- suggested changes in the Earth are directly cause by recurring events;
- earth is subject to slow and continuous cycles of erosion and uplift
- proposed uniformitarianism - rates and process of change were constant
- Principles of Geology book -- extended age of the Earth