lesson 3- water and life & ph and buffers
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
cohesion
linking together of like molecules
adhesion
clinging of one substance to another
in a water molecule, the oxygen atom
carries a partial negative charge
in a water molecule, the hydrogen atom
carries a partial positive charge
hydrogen bond
slightly positive hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the slightly negative oxygen of a different water molecule
emergent properties of water that are critical for life
cohesion/adhesion of water molecules
moderation of temperature by water
floating of ice on liquid water
water is an excellent solvent
what does adhesion do?
adhesion of water to cell walls helps counter the downward pull of gravity
what does cohesion do?
contributes to the transport of water and dissolved nutrients against gravity
surface tension
measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
heat
measure of the matter’s total kinetic energy due to the motion of its molecules. depends on the matter’s volume
temperature
measure of heat intensity. represents the average kinetic energy of the molecules
1 calorie equals
amount of heat to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1 °C
1 kilocalorie equals
amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1kg of water by 1 °C
specific heat
amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1h of a substance to change its temperature by 1°C
why does water have a high specific heat?
hydrogen bonding releases energy when hydrogen bonds are formed
evaporative cooling
keeps organisms cool. when water molecules evaporate, the remaining liquid is cooler as the molecules with the most kinetic energy leave the liquid phase
why is water unusual?
the solid phase of water is less dense than the liquid phase. hydrogen bonds cannot be broken
solution
liquid that is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances
solvent
the dissolving agent of a solution
solute
substance that is dissolved in a solution
solvent explanation
a solute dissolved in a solvent to make a solution
what do water molecules do (solvent)?
form a hydrogen shell as oxygen atoms are attracted to cations and hydrogen atoms are attracted to anions
amino acids
building blocks for proteins
hydration shell
when water interacts with the charged surface of a protein. water is polar
hydrophilic
water loving: salts, charged molecules, and polar molecules that will dissolve in water
hydrophobic
water fearing: oils, non-polar amino acids, and molecules that will not dissolved in water/create hydrogen bonds
creating ions
hydrogen atom participating in a hydrogen bond between 2
water molecules can shift from one molecule to the other
hydroxide ion
ion that shifted in a hydrogen bond and lost one of its proteins
acid
a substance that increases the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution
base
a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion (H+)
concentration of a solution
log scale
way of compresses the range of H+ and OH- concentrations
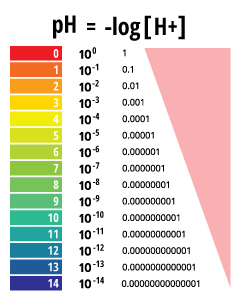
difference in log scale
1 unit represents a tenfold different in H+ and OH- concentrations
ph of a solution
negative logarithm= -log[10^-x]
acids…
have a higher [H+]
bases…
have a lower [H+]
buffers
prevent rapid changes in pH when an acid or case is added to a solution/compounds that readily accept or donate H+ ions