12 - Shoulder
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
what are some symptoms of lat tightness?
anterior pelvic tilt, spine extension
how to test for lat tightness?
if there is more shoulder elevation when knees are bent compared to straight, indicates tight lats
what attaches to the coracoid process?
pec minor, coracobrachialis, coracoacromial ligament, SH biceps
what muscle gets tight with poor posture?
pec minor
what muscles are often overused with shoulder pain?
upper trap and levator scap
what is resting position of the glenohumeral joint? CPP?
resting: 60º abd, 30º horizontal flex, 60º elbow flex with forearm 30º from horizontal plane (arm in sling position → allows for better blood flow)
CPP: 90º abd, full ER with elbow flexed 90º or in full extension, adduction, IR
what are the motions of the humeral head on the glenoid?
rotation: elevation, IR/ER, horizontal abd/add
translations: superior/inferior, medial/lateral, anterior/posterior
abduction elevation humeral rotation and glide (theory and evidence)
rotation: superior
glide theory: inferior
glide evidence: sup → inferior or centered
flexion elevation humeral rotation and glide (theory and evidence)
rotation: superior
glide theory: inferior posterior (to clear acromion)
glide evidence: inf/centered ant →post
IR/horizontal add humeral rotation and glide (theory and evidence)
rotation: anterior
glide theory: posterior
glide evidence: anterior
ER/horizontal abduction humeral rotation and glide (theory and evidence)
rotation: posterior
glide theory: anterior
glide evidence: posterior
what is the scapular plane?
30-45º of the frontal plane
what is the scapulohumeral rhythm?
ratio of motion between humerus and scapular during arm elevation
0-30º abd: has minimal scapular movement
≥30º: 2:1 ratio of humerus:scapula
where does motion in the clavicle occur?
SC and AC joint
what are the convex concave rules of the SC joint in the sagittal and frontal plane? what is CPP of SC joint?
sagittal: opposite rolls and glides
frontal: same rolls and glides
T/F the SC joint has an articular disc and shares a capsule with the 1st rib
T
clavicle glides inferiorly __º and retracts __º.
clavicle moves __º to every __º of humeral motion.
without the SC joint motion, you could only elevate approximately ___º
20, 20
4, 10
100
does the AC joint have strong capsule articulation? strong ligamentous support? when does the AC joint close?
no, yes
full elevation, horizontal shoulder adduction, shoulder IR
during elevation, the clavicle upwardly rotates through axis on acromion approximately __º.
30
what other joints should you assess besides the GH joint?
ST, AC, SC, cervical/thoracic spine and ribs
what are some shoulder self-report measures?
DASH, ASES (American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeon’s Shoulder Evaluation), SPADI (Shoulder Pain and Disability Index), Penn (University of Pennsylvania Shoulder Self-Report)
what are history questions to ask during evaluation?
MOI
athletic/rec activities
neck pain
sx in scapula or below elbow (pain above elbow or in neck often shoulder issue)
popping, clicking, catching
pain with overhead activities
shoulder pain after meals/recent trauma to abdomen
sx aggravated/alleviated by sleeping on shoulder (if pt feels relief sleeping on affected side, often a greater issue)
what does R shoulder pain after meals possibly indicate? what does L shoulder pain after accident/trauma possibly indicate?
gall bladder
spleen
review C4, 5, 6, 7 dermatomes and facet referral patterns
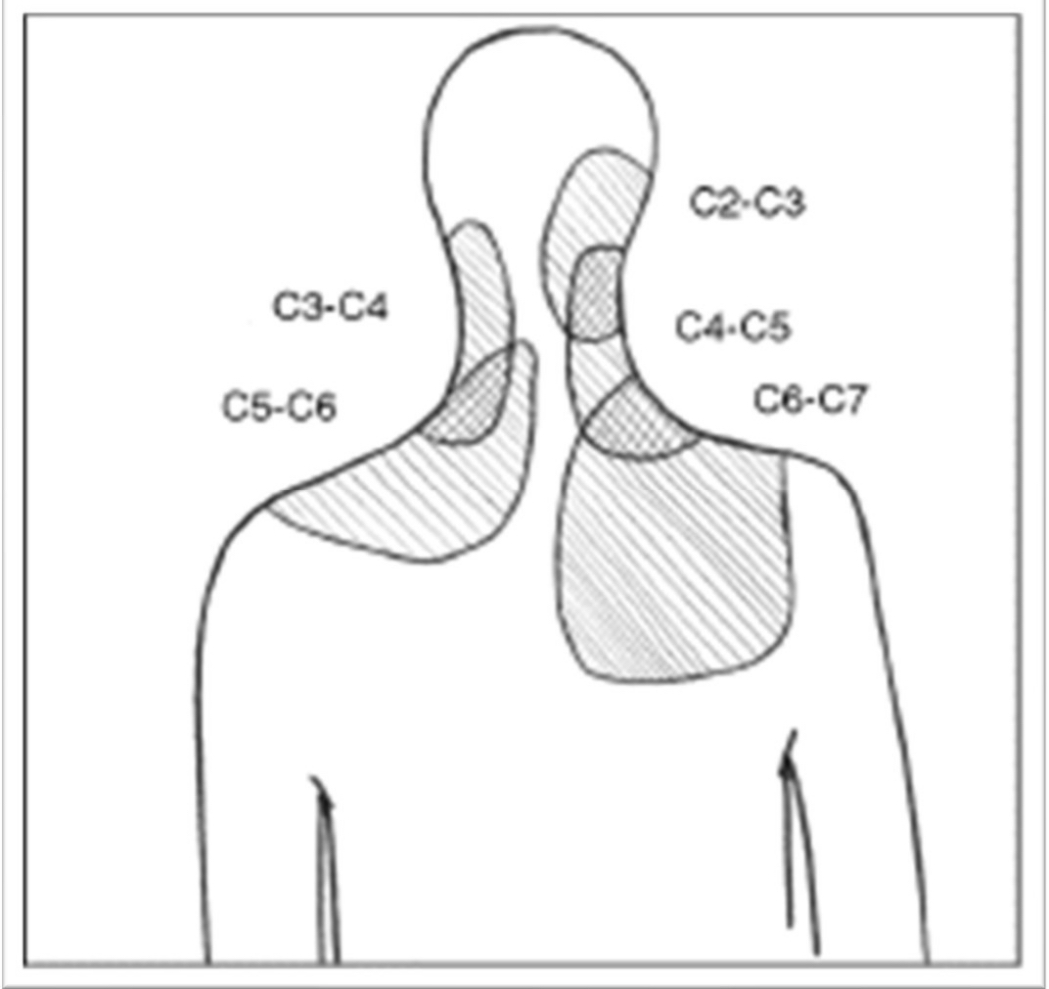
pain in scapula and posterior aspect of shoulder is more likely to be of ____ origin. symptoms of numbness and tingling especially extending to the hand are more likely to be of ____ origin. Referral of infraspinatus can be to _____ and supraspinatus to _____.
cervical, cervical, distal forearm, hand
ddx: pain referred to L shoulder/chest/clavicle region can be what problem?
heart
hx: HTN, heart disease, DM, HLD, smoking family hx
presentation: SOB, increased HR, sweating, chest tightness, arm pain/paresthesis
ddx: pain in left shoulder (Kehr’s sign: L shoulder p! with lying down and legs elevated) usually post trauma, hypotension
spleen
could also be liver and kidneys
ddx: pain in R scapular usually onset after eating
gallstones
risk factors: >40 yo, obese, females, fertile
ddx: pain in shoulder/lateral scapula, extending down medial aspect of arm, 4th and 5th digits, forearm/hand weakness, tingling/numbness, Horner’s syndrome
lung/diaphragm (Pancoast tumor)
ddx: shoulder/arm pain, tingling/numbness, most common along distribution of ulnar nerve, 3 main sites of compression (b/w anterior and medial scalene, clavicle and 1st rib, pec minor)
thoracic outlet syndrome
ddx: fever, weight loss, increased temp, fatigue
systemic signs, could be cancer
what are some yellow/red flags?
pain reduced with sleeping on shoulder - pulmonary pleural irritation
no difficulty sleeping (most pts have difficulty)
shoulder pain not alleviated by rest
insidious onset and pain can’t be reproduced
systemic signs/sx
what is upper cross syndrome? what muscles are tight?
tight: pec major and minor, suboccipital muscles
weak: deep neck muscles, scapular muscles (mid and lower trap, lev scap)
what is a sign of poor posture?
unable to elevate arms over head, may compensate with extended back
what are irregular scapulohumeral rhythms to watch out for?
tipping
winging - serratus anterior
dumping - lack of eccentric control, lev scap, serrative weakness
shrug - torn rotator cuff, can’t elevate shoulder
what causes scapular winging?
weak serratus anterior, weak middle/lower trap, tight pec major/pec minor, tight scapulohumeral muscles
what causes scapular anterior tilt?
tight pec minor, tight biceps, weak middle/lower traps, weak serratus anterior
what are the muscles involved in scapular upward rotation
upper trap, lower trap, serratus ant
what causes scapular downward rotation?
weak upper trap, weak lower trap, weak serratus ant, tight levator scap, tight rhomboid, tight pec minor
ULTT: how to test for median nerve?
shoulder depression/abduction, elbow extension, forearm supination, wrist extension, finger extension, contralateral cervical SB
ULTT: how to test for ulnar nerve?
shoulder depression/abduction, elbow flexion, forearm pronation, wrist extension/radial deviation, finger extension, shoulder ER, contralateral SB
ULTT: how to test for radial nerve?
shoulder depression/abduction, elbow extension, forearm pronation, wrist flexion/ulnar deviation, finger flexion, shoulder IR, contralateral cervical SB
what is impingement syndrome (SAIS)?
theory is mechanical compression of structures in the SA space
could also be due to degeneration of tendon/bursae secondary to overuse and aging
what is the roof, floor and contents of the subacromial space?
roof: inferior acromion surface, CA ligament, coracoid process, AC joint
floor: greater tub, humeral head
contents: supraspinatus, subacromial bursa, long head of biceps, capsule
what are the types of classification of the etiology of SAIS?
Neer’s classification - age and tissue related
primary vs secondary - cause of SAIS
intrinsic vs extrinsic - cause defined by location: contents in the SA space or outside the SA space
what are the stages in Neer's Classification of SAIS?
stage I: edema/hemorrhage of bursa and cuff, <25 yo
stage II: fibrosis and tendinitis of cuff/bursa, 25-40 yo
stage III: partial/full tears of the rotator cuff, bone spurs, >40 yo
what are the primary vs secondary causes of SAIS?
primary: direct compression of RTC, biceps, bursa. cause is an intrinsic or extrinsic factor, ex: “hooked” acromion, RCT
secondary: caused by another pathology such as GH instability or glenoid labral tear
how to identify primary impingement?
>50 yo, degenerative changes, DJD of AC joint, bursitis, tendinitis/tendinosis - atrophy/weakness, biceps tendinitis, scap dyskinesias
how to identify secondary impingement?
<30 yo, anterior/anterolateral pain, repetitive OH use, issue with static stabilizers (capsule/labrum) and dynamic stabilizers (cuff) is fatigued/weakened
what are intrinsic causes of SAIS?
degeneration/inflammation within tendon/bursa. this can be due to overuse or age related vascular and metabolic changes
rotator cuff weakness or motor control issues. decreased strength or muscle imbalance of ER, IR, or both due to overuse, aging, faulty ST kinematics and possibly poor posture. result in disruption of force couple of deltoid (humeral head translates superiorly causing impingement). ER/IR with RC weakness, deltoid
what is the vicious cycle of impingement?
RC weakness causing impingement causing pain causing more weakness
what are some extrinsic causes of SAIS?
scapular muscle weakness, muscle imbalance, motor control issues. caused by instability or faulty control of ST articulation, faulty GH kinematics, poor posture, inhibition secondary to cervical/thoracic pathology
how does C-spine and T-spine affect SAIS?
forward head changes L-T relationship of muscles → scapular muscle issues
T-spine flexion is associated with altered scap kinematics and decreased GH abduction force → scapular muscle issues
how does poor posture affect GH motion?
GH joint has decreased motion
what is posterior capsule tightness? causes?
humeral head has increased superior and anterior translation
cause: altered GH kinematics affecting scap kinematics, increased tone in infraspin
is it possible to isolate PCT in a test? what are some tests you could use?
no, tests measures shoulder complex
GH IR in supine, horizontal add w/scap retraction, post shoulder tightness test
what is posterior shoulder tightness test?
pt is in supine, passively IR and measure before anterior shoulder lifts from table. need to compare bilaterally
what is normal horizontal add with scap retraction (both supine and SL)?
94º horizontal adduction
what scapular dyskinesias are related to reduced SA space? what are humeral dyskinesias are related to reduced SA space?
reduced posterior tilt, ER, upward rotation during GH elevation
increased anterior and superior humeral head translation during elevation
what are the types of acromial morphologies? do they predict RC disease?
type I: flat
type II: smooth
type III: hooked
poor reliability
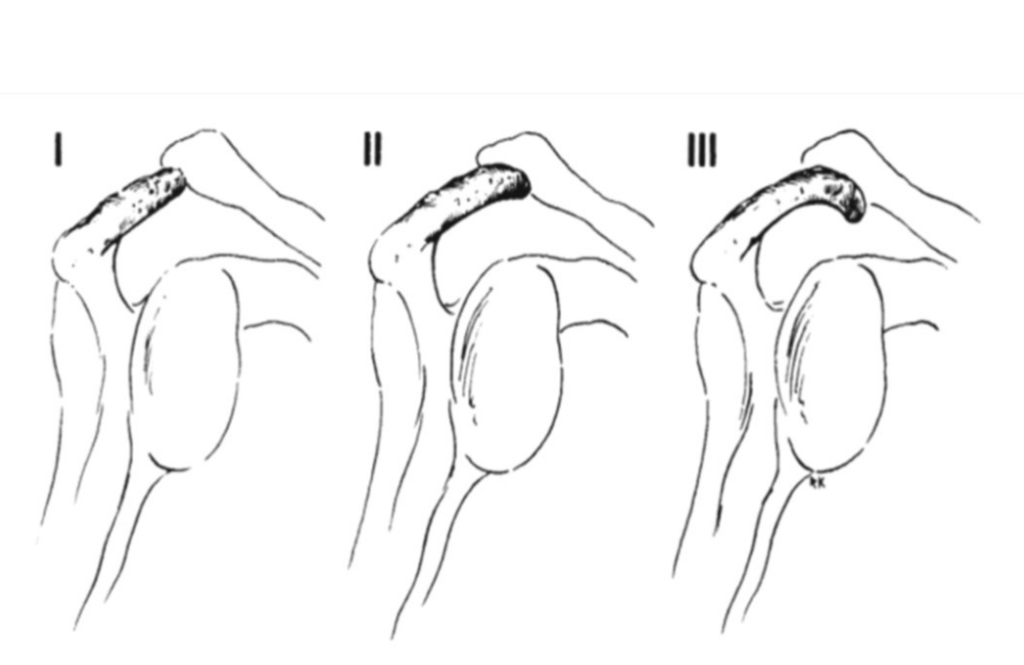
what is the acromial angle? what is its significance?
angle between the spine of scapula and acromion process
associated with RC tears and SAIS
OS acromiale is a condition where distal epiphysis is unfused
how does aging affect SAIS?
tendons degenerate and cumulative trauma can occur from overuse. increased incidence of RC tears
AC joint degenerates and osteophytes in inferior surface of acromion and SA space
bursa thickens, associated with chronic inflammation
how might your SAIS dx change depending on the age of a pt?
older with SAIS may likely also have degenerative changes
younger with SAIS more likely has GH instability and labral tear
mx history of IS?
predisposing factors like sports/work with repeated overhead activities
often insidious onset of sx, but also sx with onset with activity
slow onset of sx
pain w/activity and provocative positions
pain distribution is typically local but can be referred in C5,6
examining IS - what should your typical findings be for SAIS in pain, type of pain, palpation, A/PROM, painful arc, strength, posture? what special tests should you use?
pain location: local, C5,6 dermatome (assess C-spine)
pain type: sharp w/provocative movements (overhead, cross body, behind back)
palpation: pain of RC tendons
A/PROM: limitation dependent upon pain w/ROM, edema, length of sx
painful arc: pain with elevation from 60-120º, best position of supraspinatus impingement is 60º flex, 60º abd, IR
strength: pain with resisted abduction and ER
special tests: Hawkin’s, Neer, painful arc, horizontal adduction, posterior impingement
painful arc:
pain/sx with 60-120º of abd often associated with? pain/sx with 160/70-180º of abd?
SAIS and RCT (SAIS most common in mid ROM)
AC joint, SAIS, RCT tears
what is the Hawkin’s test?
tests for SAIS
stabilize scap, place elbow at 90º flex and max IR
+ is pain/sx in superior/lateral arm at end ROM
what is the horizontal adduction test?
tests for RC, SAIS, AC
horizontal adduct arm
+ pain at anterior/superior shoulder
ddx: pain at AC joint is AC joint dysfunction
what 3 tests point to SAIS? what is LR?
Hawkins, Painful arc, pain/weakness with ER resistance
+LR of 10.56 if all 3 tests are +
-LR of 0.17 if all 3 tests are –
does SAIS often occur in isolation?
no, your examination should rule out other shoulder disorders like GH instability, GH tightness, labral tears, FT-RCT
what are the types of RCT?
partial thickness - impingement syndrome category
full thickness - all the way through top to bottom
small: <1cm, medium: 1-3 cm, large: 3-5 cm, massive: >5cm
what is more common, FT or PT RCT?
partial thickness 2x more common
what is hx of RC-FT tear?
age, patients >60/65 yo have increased chance
night pain
previous hx of shoulder pain
same complaints as SAIS - lateral/superior shoulder pain, pain with overhead activities
what tests should you do to check for RC-FT tear?
strength tests: weak abd w/full or empty can tests (supraspinatus), weak ER
special tests: Neer may be +, drop arm test, painful arc, lift off test, ER lag sign, full can/empty can
what is the drop arm test?
tests RTC, supraspinatus
ask pt to abduct to 90º and lower arm slowly, no need to do if pt already demonstrates ability to abduct
+ is pain and difficulty lowering arm slowly
tests for FT tears, SAIS (very painful)
what is the lift off test?
tests subscapularis FT-tear or joint capsule tightness
hand at sacrum/LB, ask pt to lift hand away from the back
+ is inability to lift off from back
what is the belly press test?
tests for subscap tear
max IR - press hand into belly
+ is weakness, inability to maintain IR (wrist flexes, elbow drops back, shoulder extends)
what is the ER lag sign?
tests for RTC tear
at 0º abd, 90º elbow flex, passive ER shoulder as far as possible then have pt hold position
+ if unable to maintain full ER, “lags” back to less than full ER
what is the full can/empty can test?
humeral ER and IR resistance
empty can tests for supraspinatus tear
full can tests for RTC
what are 3 s/sx that have a high LR for RCT?
age >65
weakness in ER
night pain
what are 4 s/sx that have high LR of FT-RCT?
age ≥60
+ painful arc test
+ drop arm test
+ infraspinatus test
what are tissues involved in GH instability?
capsule, GH ligament, CH ligament, RC, deltoid, neural
sublux vs dislocation?
sublux: partial popping then going back in
disloc: head pops out fully
what is common MOI for instability?
anterior and inferior displacement
FOOSH (posterior), overhead pressure (ant/inf), arm out to side
*the longer the joint is dislocated, the harder is to put back in socket
what are signs of GH instability?
sulcus sign, visible/popping acromion, sublux of humeral head
TUBS vs AMBRII classification of GH instability?
TUBS: traumatic, unilateral/unidirectional, Bankart lesion, Surgery required to stabilize (most common is anterior dislocation)
AMBRII: atraumatic, multidirectional instability, bilateral involvement, rehab is first option then surgery, inferior capsule and rotator interval (insignificant trauma)
what is a Bankart tear?
anterior-inferior labral tear associated with anterior instability and dislocation
what is Hill-Sach lesion?
humeral head defect of the posterior-lateral aspect with anterior dis/instability, typically occurs over time
reverse Hill-Sachs is anterior-medial defect with posterior dis/instability
anterior GH instability is usually due to?
apprehension position (abd/ER), cocking and acceleration phase of throw, overheads and serves (tennis, volleyball)
posterior GH instability is usually due to?
positions of flex, add, IR, FOOSH injuries
multidirectional instability is usually due to?
inferior traction of humerus and generalized laxity
instability - what to observe in mx hx?
patient <40 yo
history of repetitive overhead activity, primarily associated with anterior instability
traumatic or insidious
direction: MOI, sx with activity or position of feeling of instability
recurrent sublux: w/activity, “dead arm syndrome”, paresthesia
what to look for in examination for GH instability?
does it sublux or dislocate with exam?
determine direction of instability in mx hx to determine which test to use
does it dislocate voluntarily
assess labral tear
Hill-Sachs or reverse
nerve damage
what happens with impingement of axillary nerve?
atrophy and weakness of deltoid
what are special tests for GH instability?
anterior instability - load and shift, apprehension, anterior release, relocation
posterior instability - load and shift, posterior apprehension
inferior/multidirectional instability - sulcus, accessory joint testing (ant, post, inf), rule in/out additional dx like labral tears, SAIS, lift-off test with ant/inf instability
what is the sulcus test?
tests for multidirectional instability
pt sitting, place traction on humerus at elbow
+ is space between acromion and HH as compared bilaterally (graded 1+ to 3)
what is the load and shift test?
tests capsule and labrum, anterior/posterior instability and glenoid labral tears
load the humerus into the glenoid then ant/post translate
+ is amount of translation and click for labral tear
what is the apprehension test?
tests for anterior instability
pt is supine or standing, first abd 90º then gradually ER the shoulder maximally
+ is apprehension or sx reproduction
what is anterior release test?
apply posterior force with arm in 90/90 position
+ is apprehension/pain with released force
what is posterior internal impingement test?
tests for impingement usually of infraspinatus/supraspinatus at posterior superior edge of glenoid
may be associated with anterior instability more common with overhead athletes