Congenital and Hereditary Diseases of the Thoracic and Cardiovascular Systems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is cystic fibrosis
Hereditary disease caused by defective gene of chromosome 7 - secretion fo excessive viscous mucous by exocrine glands - thick mucus secreted by trachea and bronchi block airways (can lead to atelectasis)
What are significant signs and symptoms of Cystic fibrosis
poor growth or weight gain, greasy bulky stools. children sweat excessively, newborn obstruction
What is the radiographic appearance of cystic fibrosis
irregular thickening of lung markings - hyperinflation (large lung) - reticular pattern
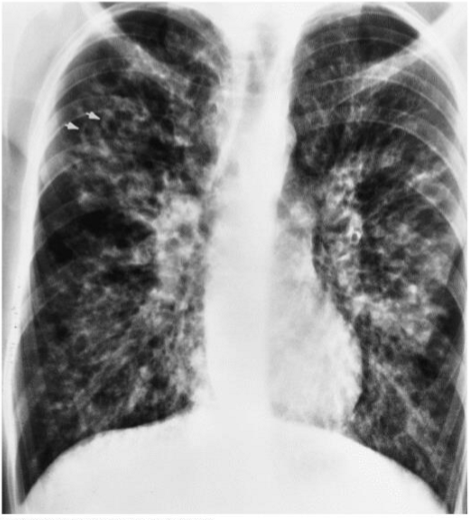
What is this
Cystic Fibrosis
What is hyaline Membrane Disease (IRDS)
occurs in infants who are premature, have a diabetic mother, or are born c-section - evident within 6 hours after delivery - lack of surfactant and immature lungs
What is a main sign and symptom of hyaline membrane disease
cyanosis - grunting sounds when breathing
What is the radiographic appearance of hyaline membrane disease
under aeration - finely granular appearance of pulmonary parenchyma - air bronchogram required
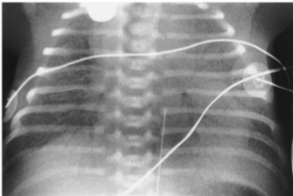
What is this
Hyaline Membrane Disease
What are the 4 abnormalities of Tetralogy of Fallot
High ventricular septal defect - pulmonary stenosis - overriding of aortic orifice above ventricular defect - right ventricular hypertrophy
What are the main signs and symptoms of tetralogy of fallot
blueish colour skin, lack of alertness
What is the radiographic appearance of tetralogy of fallot
enlargement of right ventricle causing upward and lateral displacement of the apex of the heart - wooden shoe
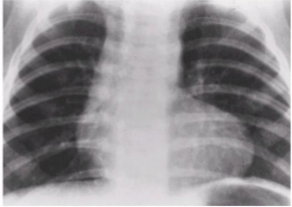
What is this
tetralogy of fallot
What are septal defects? What are the 3 kinds?
left-to-right shunt most common - Atrial Septal, Ventricular Septal, and Patent Ductus Arteriosus
What is Atrial Septal
communication between the atria as result of patent foramen ovule - increased pulmonary blood flow and overloading of RV
What is ventricular septal
communication between the ventricles. Causes increased pulmonary venous return which overloads LA & LV
What is Patent Ductus Arteriosus
shunts blood from pulmonary artery into systemic circulation during uterine life. Closes after birth normally. Blood from higher pressure aorta goes to pulmonary artery and overloads LA & LV
What are the signs and symptoms of septal defects
frequent respiratory infections, difficulty breathing, tiring when feeding, SOB, Skipped heartbeat
What is the radiographic appearance of Atrial septal defects
Because the left atrial pressure is higher that the RA, the blood shunts L to R causing enlargement RV, RA, pulmonary outflow tract - cardiomegaly and enlarged pulmonary outflow tract
WHat is the radiographic appearance of ventricular septal defect
Left ventricular pressure is higher that the pressure in the right ventricle > L to R shunt > ^pulmonary flow > ^ pulmonary venous return> overloading and enlargement of LA and LV - any blood directed to the RV immediately goes to the pulmonary artery therefore no overloading of RV so no enlargement on CXR - heart and pulmonary trunk enlarged
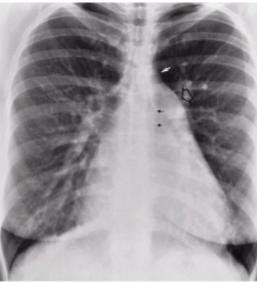
What is this
Atrial Septal Defect
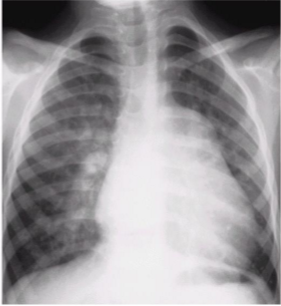
What is this
Ventricular septal defect
What is dextrocardia
heart is on the right
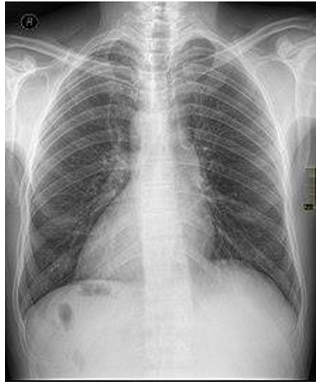
What is this?
Dextrocardia